In the world of motorcycle maintenance and restoration, understanding the layout and structure of individual mechanical elements is crucial. Each part plays a significant role in the overall performance and longevity of the vehicle. By examining how various elements fit together, you can better appreciate the complexity and precision required in assembling a well-functioning machine.
A well-detailed illustration of mechanical components can offer invaluable insights for both professionals and hobbyists. Such layouts provide a clear roadmap for repairs, upgrades, and regular upkeep, ensuring that every aspect of the system operates as it should. Without a clear understanding of the assembly, even the smallest issue can lead to larger mechanical failures.
In this guide, we’ll explore how these essential elements are organized within the system, giving you the knowledge needed to approach maintenance tasks with confidence. Whether you’re restoring an older model or simply performing routine checks, understanding the inner
Overview of the CB750 Parts Diagram
This section provides a detailed guide to understanding the various elements and components that make up the internal and external structure of a classic motorcycle model. By exploring this overview, you’ll gain insights into how different sections work together to ensure optimal functionality and performance.
Below is a simplified table showcasing key areas of the vehicle’s mechanical structure, categorized for easy navigation:
| Component Group | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine System | This includes the power-generating unit and related parts that drive the entire machine. Proper maintenance ensures the machine runs efficiently. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical Network | The electrical setup governs everything from ignition to lighting, ensuring the vehicle’s systems operate smoothly and reliably. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Frame and Suspension |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | The storage unit that holds fuel before it is distributed to the engine. |
| Fuel Pump | Responsible for pumping fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. |
| Fuel Filter | Filters out impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Carburetor or Fuel Injector | Mixes fuel with air in the appropriate ratio for combustion. |
| Fuel Lines | Hoses that transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and engine. |
Suspension Parts and Diagram
The suspension system of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride. It is designed to absorb shocks from the road and maintain stability while cornering, providing comfort to the rider. Understanding the various components involved can help in maintenance and performance optimization.
Key Components
This system comprises several essential elements that work together to enhance handling and comfort. The primary components include springs, dampers, and linkages, each contributing to the overall functionality of the setup.
Component Overview
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Forks | These are the front suspension elements that support the front wheel and absorb bumps. |
| Shock Absorbers | Located at the rear, they help manage the bike’s bounce and improve traction. |
| Springs | They provide the necessary tension to keep the motorcycle stable during rides. |
| Linkage | A system of arms that connects various components, allowing for coordinated movement. |
Braking System Configuration
The braking mechanism of a motorcycle is crucial for ensuring safety and control during operation. This system typically comprises several key components that work together to achieve effective deceleration and stopping power. Understanding the arrangement and interaction of these elements is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
At the heart of the braking system are the brake calipers, which house the brake pads that press against the discs. The hydraulic system plays a significant role, as it transfers force from the lever to the calipers, enabling smooth engagement. Additionally, various lines and hoses connect these components, ensuring the proper flow of brake fluid while minimizing the risk of leakage.
Incorporating advanced technologies, modern setups may feature anti-lock braking systems (ABS) that prevent wheel lock-up during sudden stops, enhancing stability and control. Adjustments to the brake lever and pedal can also influence the overall feel and responsiveness of the system, allowing riders to customize their experience based on preference and riding conditions.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the braking elements are vital to prevent wear and ensure reliability. Replacing worn pads, checking fluid levels, and inspecting the condition of lines contribute to a safe and efficient braking experience.
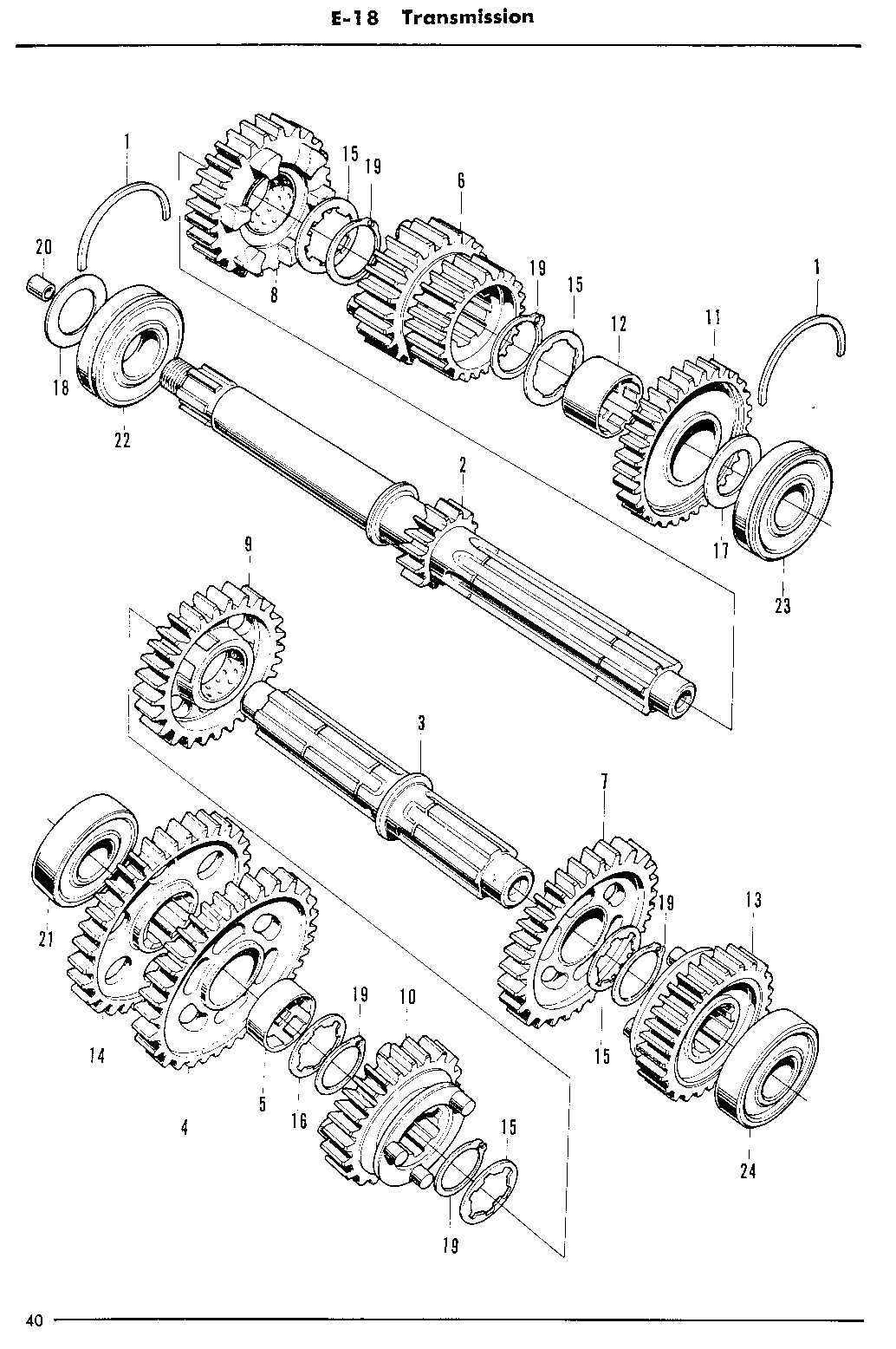
Transmission and Gear Mechanism
The transmission system is a crucial component in any motorcycle, enabling the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. This intricate mechanism allows for the adjustment of speed and torque, ensuring optimal performance across various driving conditions. Understanding the functionality and configuration of the gear system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
At the heart of the transmission lies the gear assembly, which consists of multiple gears that engage and disengage to regulate power output. This mechanism is designed to facilitate smooth transitions between different speed ranges while minimizing energy loss.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Gear Selector | Allows the rider to choose the desired gear ratio, affecting acceleration and speed. |
| Drive Shaft | Transmits power from the engine to the rear wheel, crucial for propulsion. |
| Clutch Assembly | Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, enabling smooth gear changes. |
| Final Drive | Converts the rotational motion of the transmission into the linear motion of the wheels. |
Maintaining the transmission system is vital for ensuring reliable operation. Regular inspection of the components can prevent issues such as slipping gears or difficult shifting, enhancing the overall riding experience.
Cooling System Parts and Function
The cooling system of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperatures and ensuring efficient performance. This system is designed to dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing overheating and potential damage. Understanding the various components and their functions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Radiator: This component is responsible for cooling the engine coolant. As the heated liquid flows through the radiator, air passing over the fins helps to dissipate heat.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates the coolant throughout the system, ensuring consistent flow and preventing hotspots within the engine.
- Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the temperature of the coolant. It opens and closes based on the coolant temperature, allowing for efficient heat management.
- Coolant Reservoir: This tank stores excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction as temperatures fluctuate.
- Hoses: These flexible tubes connect various components of the cooling system, transporting coolant between the engine, radiator, and reservoir.
- Fan: Often located near the radiator, the fan assists in drawing air through the radiator when additional cooling is required, especially during low-speed conditions.
Each element of the cooling system works in harmony to ensure the engine remains within the optimal temperature range. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance performance and extend the lifespan of the engine.
Steering and Handlebar Assembly

The steering and handlebar assembly is a crucial component that ensures smooth maneuverability and control of the vehicle. This section will explore the key elements involved in this assembly, highlighting their functions and importance for overall performance.
Key Components
- Handlebars
- Stem
- Throttle control
- Brake lever
- Clutch lever
- Wiring harness
Assembly Process
- Begin by attaching the stem securely to the fork.
- Position the handlebars onto the stem, ensuring they are aligned properly.
- Install the throttle and brake levers on the handlebars.
- Connect the wiring harness to the necessary components.
- Double-check all connections and ensure the assembly is tight and secure.
Proper installation and maintenance of the steering and handlebar assembly are vital for safety and functionality, allowing for precise navigation and enhanced rider experience.
Commonly Replaced CB750 Parts
For motorcycle enthusiasts, maintaining optimal performance often involves replacing certain components over time. Understanding which elements are frequently updated can enhance the riding experience and prolong the lifespan of the machine.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Essential for ensuring effective stopping power, worn pads can significantly impact safety. |
| Chain | A crucial part of the drivetrain, a worn chain can lead to poor performance and should be monitored regularly. |
| Oil Filter | This helps keep the engine lubricated by removing contaminants from the oil, making it vital for engine health. |
| Battery | Reliable starting and electrical performance depend on a well-maintained battery, often requiring replacement after a few years. |
| Spark Plugs | These are critical for ignition efficiency, and replacing them regularly can improve fuel economy and engine performance. |