Understanding the structure and organization of individual elements within a vehicle can be a crucial aspect for those involved in maintenance or repairs. By examining detailed illustrations of essential elements, one can gain insights into how various systems function and how they interconnect to create a smooth driving experience.
In this guide, we delve into the essential sections of a popular compact car. Each section showcases critical mechanical and electronic components, providing a clear overview of how different systems collaborate. This knowledge is valuable for ensuring proper maintenance, replacing worn-out elements, and enhancing the overall performance of your vehicle.
Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a vehicle enthusiast, having access to comprehensive illustrations can simplify the process of identifying key elements. This detailed breakdown will help you navigate through various sections and better understand the layout of essential systems in your vehicle.
Understanding the Key Components of a 2008 Mazda 3

Every vehicle is composed of multiple crucial systems that work in harmony to ensure smooth operation and performance. These systems include mechanical elements responsible for movement, electrical setups for powering various functions, and safety features designed to protect both the driver and passengers. Understanding how these essential units interact provides a clearer picture of the vehicle’s overall functionality.
| Component | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | The power source that converts fuel into energy to propel the car forward. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transmission | Responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move at different speeds. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
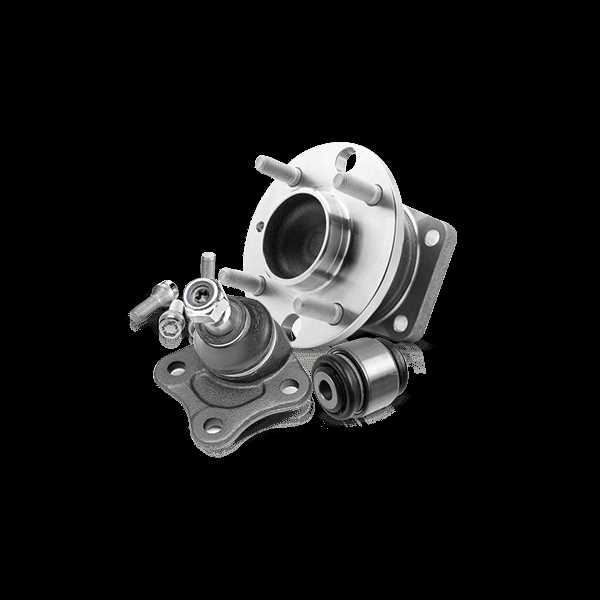
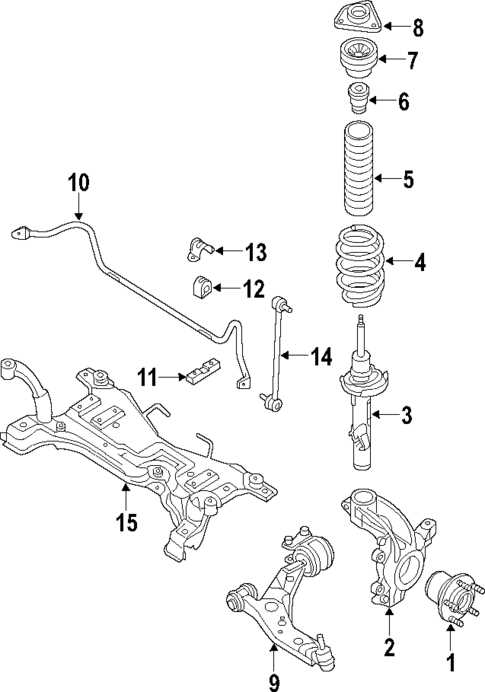
| Suspension System |
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strut | Supports the weight and acts as a shock absorber to soften road impacts. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Control Arm |
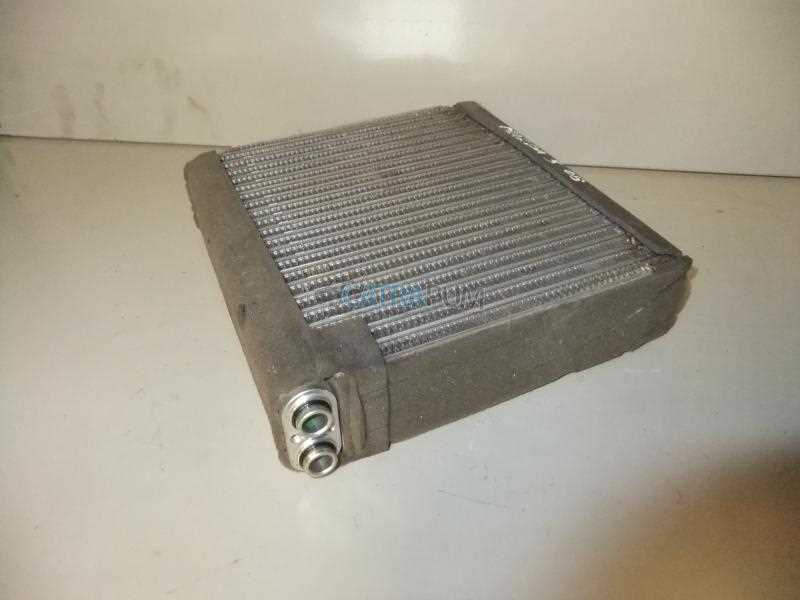
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
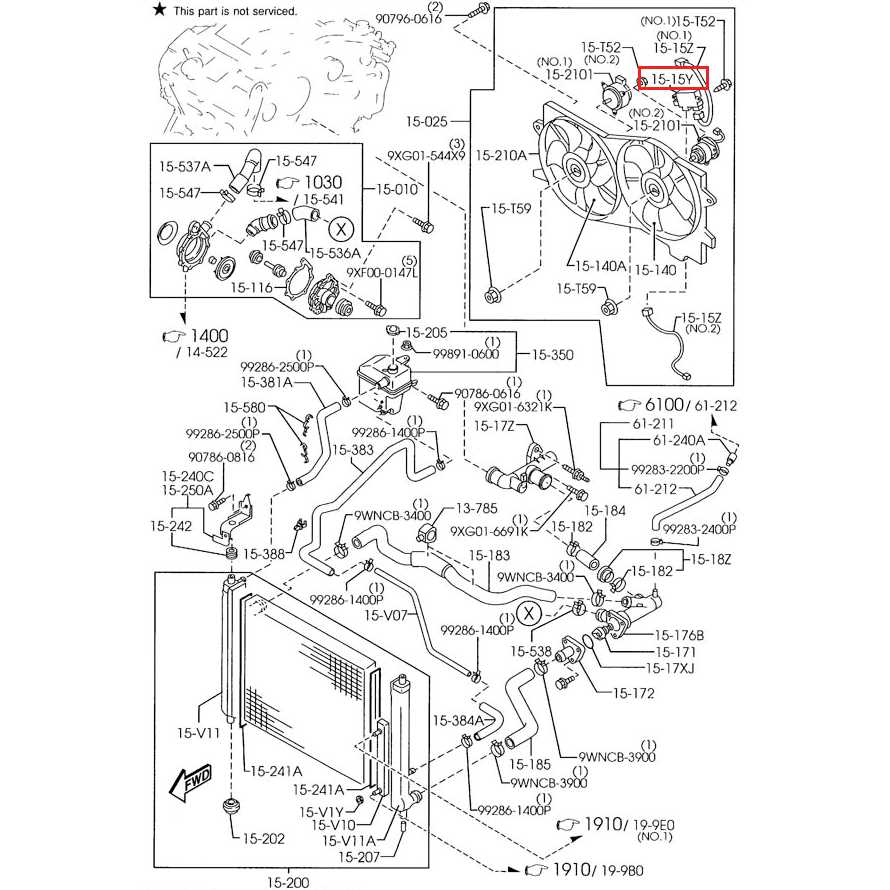
| Radiator | A heat exchanger that cools the engine coolant before it re-enters the engine. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the system, maintaining flow and pressure. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on temperature, ensuring efficient engine operation. |
| Cooling Fans | Assists in airflow over the radiator when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. |
| Hoses | Flexible tubes that transport coolant to and from various components. |
System Layout
Understanding the configuration of the cooling mechanism is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. The layout typically includes the components mentioned above, all interconnected to facilitate optimal coolant flow and heat dissipation.
Fuel System Assembly and Key Parts
The fuel system is a critical component of any vehicle, responsible for delivering the necessary fuel to the engine for optimal performance. Understanding the various elements involved in this assembly helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining efficiency. This section outlines the essential components that constitute the fuel delivery mechanism and their respective functions.
Essential Components
The fuel delivery system is composed of several vital components, each playing a specific role in ensuring a smooth flow of fuel. These elements include the fuel pump, injectors, filter, and lines, which work together to maintain the engine’s performance and longevity.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Pump | Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Injectors | Atomizes fuel for optimal combustion in the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, and engine. |
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance of the fuel system is crucial for enhancing the vehicle’s performance and efficiency. Inspecting components like the fuel filter and lines for leaks or blockages can prevent significant issues. Additionally, using high-quality fuel can help minimize deposits and ensure the longevity of injectors and other related parts.
Interior Components: Dashboard and Controls
The dashboard and control interface play a crucial role in providing an intuitive driving experience. These elements not only serve functional purposes but also contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of the vehicle’s cabin.
Key features of the dashboard include:
- Instrument cluster displaying vital information such as speed, fuel level, and engine temperature.
- Control buttons and knobs for adjusting climate settings, audio, and navigation systems.
- Display screens providing access to multimedia, communication, and vehicle settings.
The layout of these components is designed for easy accessibility, allowing drivers to operate them without distraction. Additionally, ergonomic considerations ensure that controls are within reach and comfortably positioned.
Various materials and finishes enhance the visual and tactile experience of the dashboard, contributing to a sophisticated environment. The integration of modern technology further elevates the functionality, making it essential for both comfort and safety.
Overall, the dashboard and its controls are integral to a pleasant driving experience, merging practicality with design in a seamless manner.
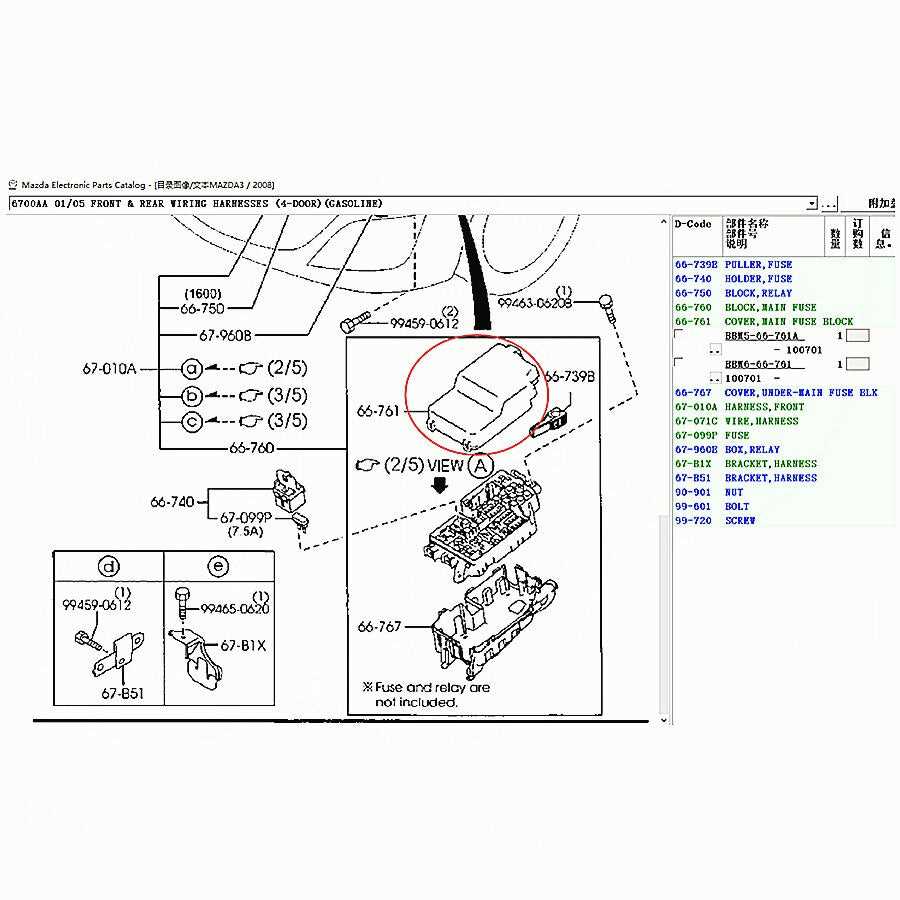
Lighting System and Electrical Connections
The lighting arrangement and electrical linkages play a crucial role in ensuring visibility and safety during operation. A well-designed illumination framework enhances the overall functionality of the vehicle, facilitating effective communication with other road users. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Illumination Framework
This system comprises various elements, including headlights, taillights, turn signals, and interior lighting. Each component is interconnected through a network of wires and connectors, which must be properly configured to ensure reliable performance. Regular inspections are necessary to identify any issues such as blown bulbs or corroded connections, which can hinder visibility and compromise safety.
Electrical Connection Insights
Electrical connections are vital for transmitting power throughout the vehicle. These linkages must be secure and free from corrosion to maintain efficient operation. Additionally, fuses and relays play a significant role in protecting the lighting system from electrical overloads. Familiarity with the layout and function of these components can aid in effective troubleshooting and repair.
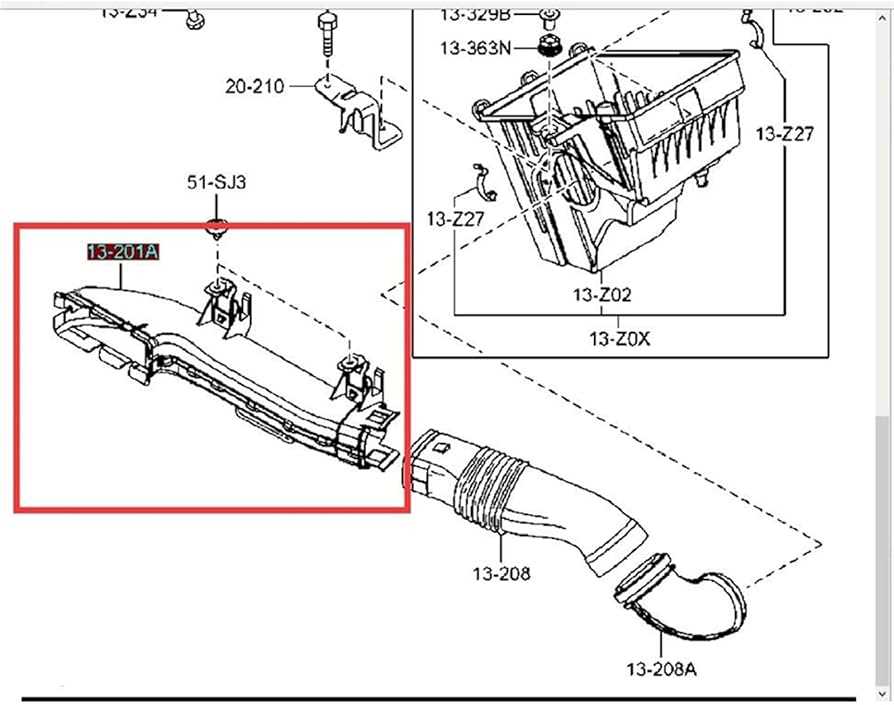
Air Intake System Overview
The air intake assembly plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance by regulating the flow of air into the combustion chamber. This system is designed to deliver a precise mixture of air and fuel, which is essential for efficient combustion. By managing airflow, it enhances power output and reduces emissions, contributing to the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Typically, the intake mechanism comprises several components, including the air filter, intake manifold, and throttle body. The air filter serves to remove contaminants from incoming air, protecting the engine from potential damage. The intake manifold distributes the air evenly to each cylinder, ensuring a balanced performance across the engine. Meanwhile, the throttle body controls the amount of air entering the engine based on the driver’s input, allowing for responsive acceleration and smooth operation.
In addition, the air intake system may feature sensors that monitor airflow and adjust performance parameters accordingly. This integration of technology aids in optimizing engine response and fuel economy, highlighting the importance of this assembly in modern vehicles.
Wiring Harness and Electrical Layout
The wiring harness serves as the central nervous system of the vehicle, interconnecting various electrical components and systems. Understanding its structure and layout is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. This section explores the arrangement and organization of electrical connections, emphasizing the importance of each segment in ensuring optimal functionality.
In modern vehicles, the wiring harness is designed to accommodate multiple circuits, facilitating communication between devices such as sensors, switches, and actuators. The layout is meticulously planned to minimize interference and protect against environmental factors. Below is a simplified representation of the electrical arrangement:
| Component | Function | Connection Type |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Power supply for all electrical systems | Positive and negative terminals |
| Fuse Box | Protects electrical circuits from overload | Plug-in fuses |
| Engine Control Unit (ECU) | Manages engine functions and performance | Connector pins |
| Body Control Module (BCM) | Controls interior and exterior lighting | Multi-pin connectors |
| Sensor Modules | Collects data for various systems | Plug connectors |
Each component plays a vital role in the vehicle’s overall performance. A well-organized electrical layout not only ensures efficient operation but also simplifies repairs and upgrades.
Steering System Parts and Functionality
The steering system is a crucial component in automotive design, responsible for directing the vehicle’s movement and ensuring driver control. This system encompasses a variety of elements that work together seamlessly, facilitating smooth navigation and responsive handling. Understanding these components helps in appreciating their roles and the overall functionality of the mechanism.
Key Components
Several essential elements contribute to the steering system’s operation. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring optimal performance and safety while driving.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | Allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. |
| Steering Column | Connects the steering wheel to the steering mechanism, transmitting the driver’s input. |
| Rack and Pinion | Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, allowing the wheels to turn. |
| Steering Linkage | Transmits movement from the rack and pinion to the wheels. |
| Power Steering Pump | Assists in reducing the effort needed to turn the steering wheel, enhancing maneuverability. |
Operational Mechanism
The steering system operates through a complex interaction between the components. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the motion is relayed down the steering column to the rack and pinion assembly. This assembly transforms the circular movement into a lateral shift, effectively guiding the vehicle’s wheels in the desired direction. Additionally, the power steering pump provides necessary assistance, making steering effortless, especially at low speeds or during tight maneuvers.