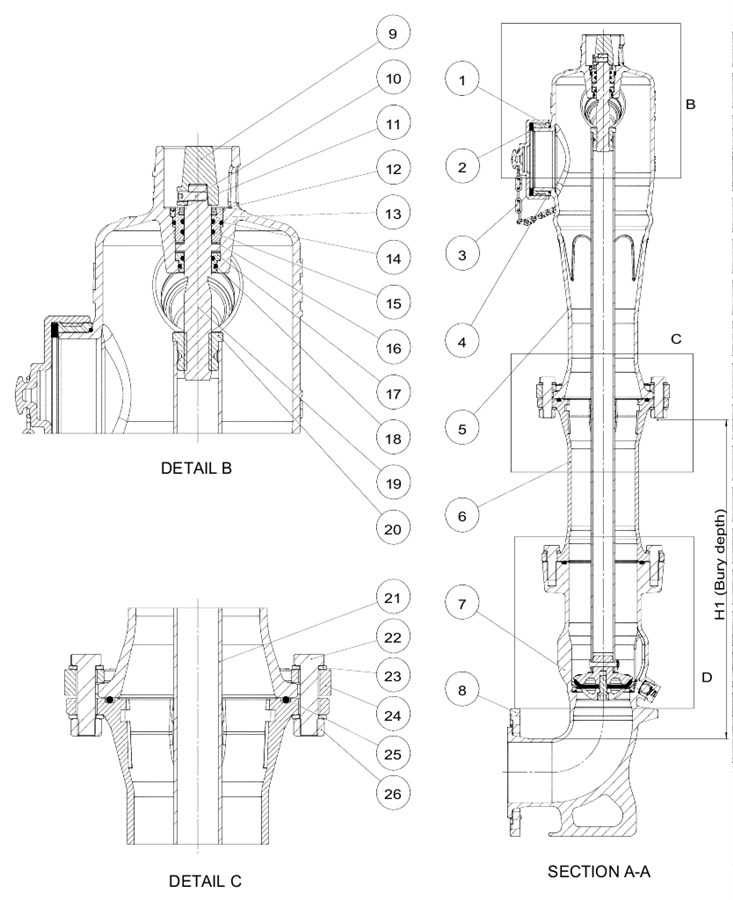
In the realm of fire safety, comprehending the intricate elements that constitute crucial apparatus is vital for effective usage and maintenance. Each element serves a unique function, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system designed to combat emergencies.
Exploring these components can provide insight into their operational synergy, enhancing knowledge for both professionals and enthusiasts alike. Whether it’s for installation, troubleshooting, or routine inspections, a thorough grasp of the essential mechanisms ensures optimal performance when it matters most.
By delving into the relationships and configurations of these essential components, one can appreciate their ultimate importance in safeguarding lives and property. This exploration empowers users to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades, ultimately promoting a safer environment for all.
Understanding Fire Hydrant Components

Firefighting systems rely on various crucial elements that work together to ensure effective water supply during emergencies. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of these systems. Grasping the intricacies of these essential features is vital for maintenance and operation.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Valve | Controls water flow and pressure. |
| Nozzle | Discharges water towards the fire. |
| Body | Houses internal mechanisms and provides durability. |
| Cap | Seals openings and prevents contamination. |
| Outlet | Connects to hoses for direct access to water. |
Essential Parts of a Hydrant
Understanding the critical components that contribute to the effective functioning of a fire suppression system is vital for ensuring safety and reliability. Each element plays a unique role in maintaining the efficiency and accessibility of water during emergencies.
Key Components
- Body: The main structure that houses various internal mechanisms.
- Valve: A crucial element that controls water flow, allowing for quick activation and deactivation.
- Nozzles: Outlets where hoses can be connected to deliver water to the required area.
- Cap: Protects the nozzle when not in use and ensures proper sealing.
- Bonnet: The cover that provides access to internal components while also supporting the structure.
Additional Features
- Drain Valve: Helps to expel residual water, preventing freeze damage in cold climates.
- Indicator: A visible mark or device indicating whether the system is operational or requires maintenance.
- Reflector: Enhances visibility, especially in low-light conditions, guiding firefighters to the location.
These components work together seamlessly, ensuring that water is readily available when needed most, thus playing a vital role in fire safety measures.
Functionality of Each Component
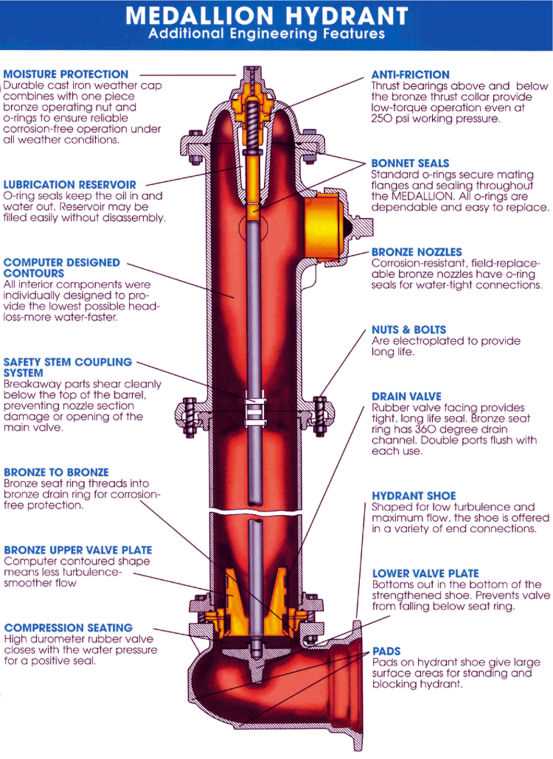
Understanding the functionality of each element within a fire suppression system is crucial for ensuring its effective operation. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall performance and reliability of the assembly. From the mechanism that controls water flow to the fittings that ensure secure connections, every piece is designed with a specific purpose in mind.
Valve: The valve serves as the primary control unit, regulating the flow of water. By opening or closing, it allows firefighters to manage the discharge effectively, ensuring that water is delivered where it is needed most.
Nozzle: The nozzle is responsible for shaping the water stream. It can be adjusted to produce various spray patterns, enabling users to target flames with precision, maximizing the system’s efficiency.
Body: The body of the assembly provides structural integrity and houses the internal components. Its durable construction is essential for withstanding high pressures and environmental conditions, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Cap: The cap protects the opening from debris and contaminants when not in use. It is crucial for maintaining the cleanliness and functionality of the system, preventing any obstruction during emergencies.
Coupling: The coupling connects different sections of the assembly, allowing for flexible configurations. It ensures a secure link between components, which is vital for maintaining a seamless flow of water.
Drainage System: The drainage system prevents the accumulation of water, reducing the risk of rust and damage to the internal components. Proper drainage is essential for maintaining operational readiness and extending the lifespan of the assembly.
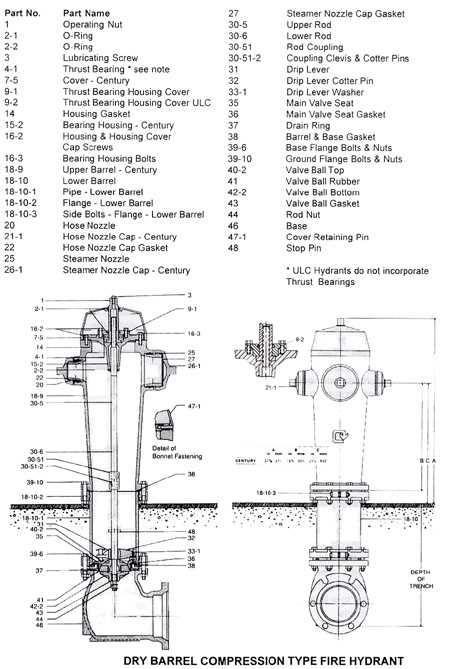
Hydrant Diagrams Explained
Understanding the intricate components of fire-fighting infrastructure is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Visual representations serve as essential tools, offering clarity on the various elements involved in water access systems. These illustrations simplify complex structures, allowing for a comprehensive grasp of how each segment functions together to ensure safety and efficiency in emergency situations.
Importance of Visual Representation
Visual aids not only enhance comprehension but also facilitate training and communication among professionals. They highlight relationships between different sections, illustrating how they interact during activation and usage. By referencing these graphics, individuals can quickly identify issues and implement solutions, ultimately leading to improved performance during critical times.
Common Features Highlighted
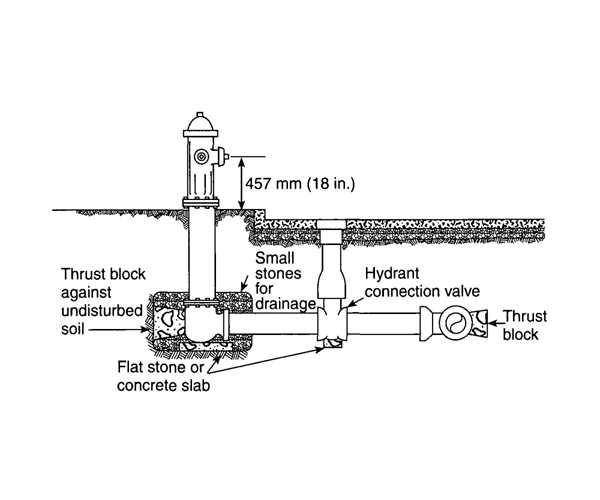
Such illustrations typically showcase the main sections, including valves, fittings, and connection points. Key functionalities are emphasized, helping users recognize vital components like flow control mechanisms and pressure gauges. This knowledge is essential for ensuring readiness and reliability in fire response scenarios. Understanding each feature’s role contributes to the overall effectiveness of safety measures.
Types of Fire Hydrants Available
Understanding the different varieties of water access points is crucial for effective firefighting and urban planning. Each type serves specific purposes and environments, catering to the diverse needs of emergency responders.
- Wet Barrel: Common in warmer climates, these structures maintain water at all times.
- Dry Barrel: Ideal for colder regions, they remain empty until activated to prevent freezing.
- Post Indicator Valve: These are often used in industrial areas and are marked visibly for quick identification.
- Wall-Mounted Units: Convenient for urban settings, these are fixed to building exteriors.
Each option has unique features and benefits, making it essential to select the right type based on local conditions and requirements.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Consistent upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of vital systems. Neglecting this crucial aspect can lead to malfunctions, increased repair costs, and potential safety hazards. Regular attention not only enhances performance but also safeguards the investment made in equipment.
Benefits of Routine Care
- Improved reliability and functionality
- Extended lifespan of equipment
- Prevention of costly repairs
- Enhanced safety for users
Key Maintenance Practices
- Regular inspections to identify issues early
- Timely replacements of worn-out components
- Lubrication and cleaning to prevent buildup
- Documentation of maintenance activities for tracking
Common Issues with Hydrant Parts
Maintenance of essential components in water distribution systems often reveals several recurring challenges. These problems can significantly affect functionality and efficiency, leading to potential hazards and inefficiencies.
Leaking Seals: One prevalent issue arises from worn or damaged seals, resulting in unwanted leaks. This not only wastes resources but can also lead to further complications within the network.
Corrosion: Metal components frequently suffer from corrosion, particularly in environments with high moisture levels. This deterioration can weaken structures and impair performance.
Blockages: Accumulation of debris or sediment can obstruct flow, making it crucial to regularly inspect and clean these systems to ensure optimal operation.
Misalignment: Improper alignment during installation can lead to mechanical stress and premature failure. Ensuring correct positioning is vital for longevity.
Addressing these issues promptly is essential for maintaining system integrity and ensuring reliable service.
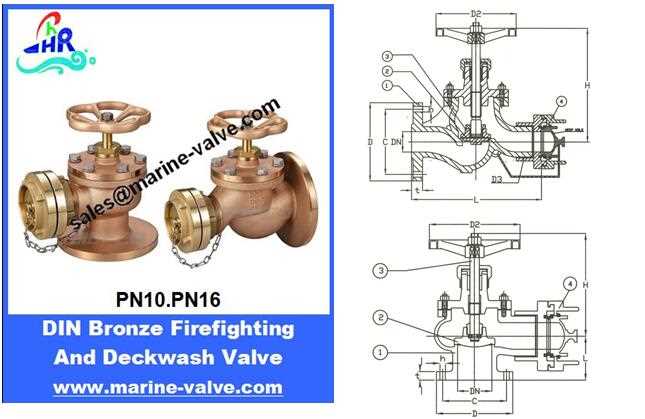
How to Read Hydrant Schematics
Understanding visual representations of equipment is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. These illustrations provide essential information about the components, their relationships, and functionality. Familiarity with these visuals allows users to identify parts, troubleshoot issues, and perform necessary repairs with confidence.
Key Elements to Identify
When analyzing these illustrations, focus on the various symbols and notations used. Each component is typically represented by a specific shape or icon, accompanied by labels indicating their names and functions. Colors may also signify different materials or states of operation, making it easier to discern critical details at a glance.
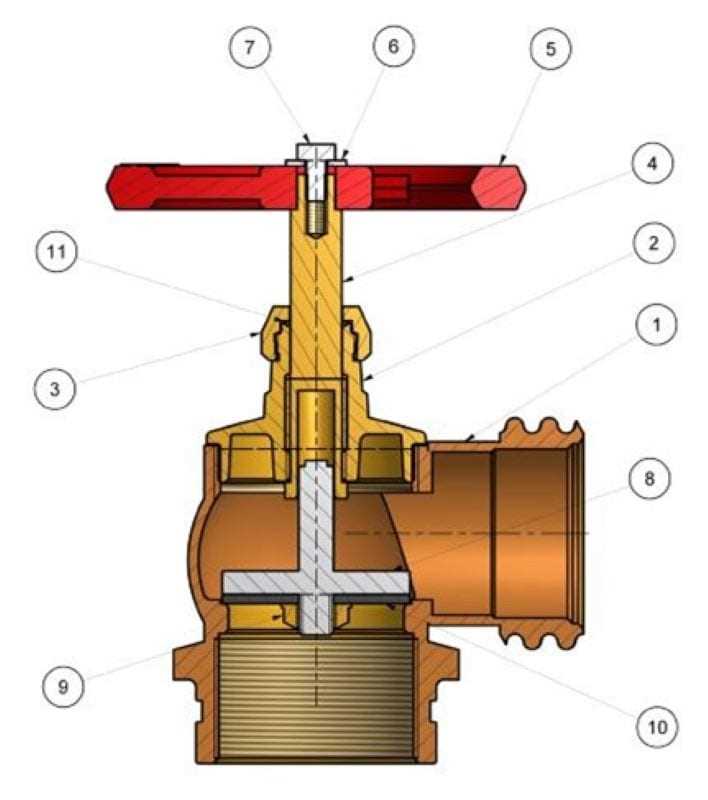
Understanding Connections and Flow
In addition to individual components, pay attention to the lines and arrows that indicate connections and the flow of fluids. These elements reveal how different parts interact and the direction of movement, which is vital for troubleshooting. Recognizing these pathways can help diagnose problems and guide repairs effectively.
Safety Measures During Repairs
Ensuring a safe working environment is paramount when conducting maintenance activities. Proper precautions help mitigate risks and protect both workers and the surrounding area from potential hazards.
| Safety Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Always wear appropriate gear such as gloves, goggles, and helmets to safeguard against injuries. |
| Area Inspection | Conduct a thorough inspection of the work site to identify any potential hazards or obstructions. |
| Tool Check | Ensure all tools and equipment are in good working condition before beginning repairs. |
| Emergency Procedures | Familiarize all personnel with emergency protocols in case of an accident or unforeseen incident. |
| Communication | Establish clear lines of communication among team members to ensure everyone is aware of the ongoing activities. |
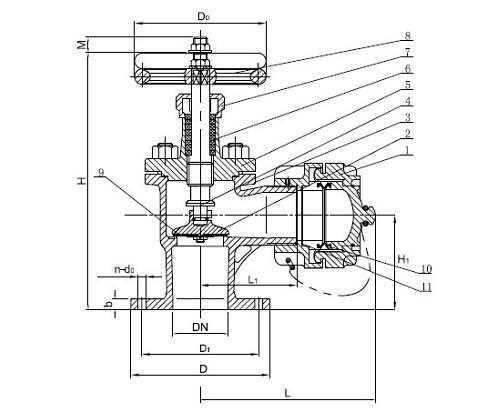
Installation Process for New Hydrants
The successful setup of a new water discharge system involves several essential steps, ensuring that it operates efficiently and meets safety standards. Proper preparation and execution during this process are critical to achieving optimal performance and longevity of the unit.
Preparation and Site Assessment
Before installation, a thorough site assessment is necessary. This includes checking the soil type, existing utility lines, and accessibility for maintenance vehicles. Identifying the optimal location will facilitate effective water flow and reduce the risk of future complications. Ensure that all necessary permits and local regulations are adhered to.
Installation Steps
The installation begins with digging a hole that accommodates the size and depth of the unit. It’s essential to create a stable base using gravel or similar material to promote drainage. After positioning the assembly, connect it securely to the main water line. Make sure all connections are watertight. Finally, backfill the surrounding area, compacting the soil to eliminate air pockets that may affect stability.
In conclusion, meticulous planning and execution during the installation process will contribute significantly to the functionality and durability of the water discharge system.
Hydrant Specifications and Standards
This section delves into the essential criteria and regulations governing the design and functionality of fire suppression devices. Understanding these specifications is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in emergency situations, as well as for compliance with local and international safety standards.
General Requirements
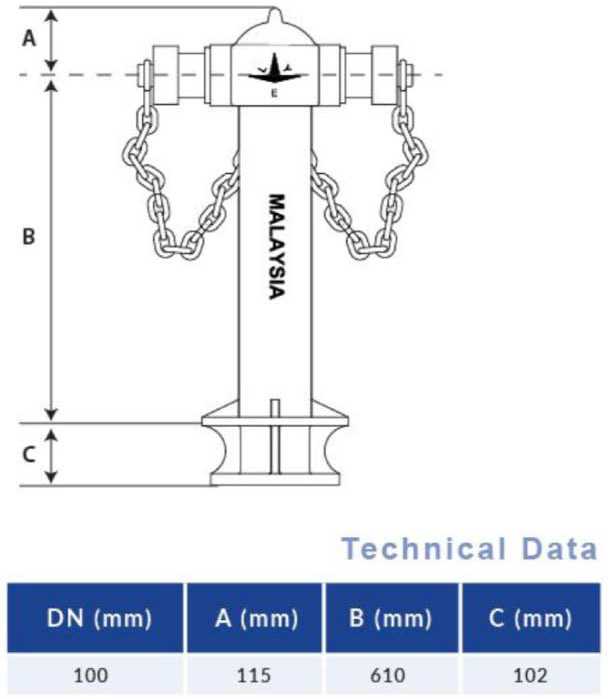
The primary aim of these devices is to provide reliable access to water in emergencies. Specifications often include factors such as flow rate, pressure ratings, and material durability. Compliance with standards set forth by organizations such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the American Water Works Association (AWWA) is mandatory to guarantee optimal performance.
Installation and Maintenance Standards
Proper installation and routine maintenance are vital for functionality. Guidelines typically dictate spacing, accessibility, and compatibility with local infrastructure. Regular inspections ensure that all components remain in good condition, allowing for immediate readiness in the event of a fire.
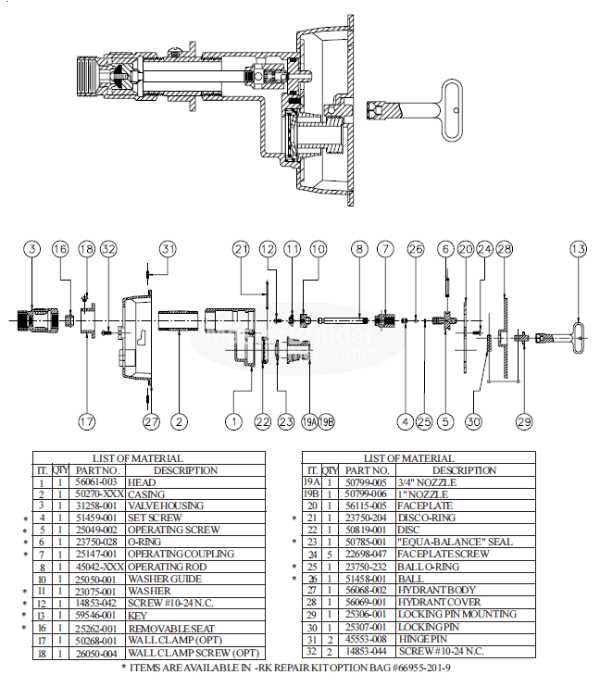
Tools Needed for Repairs
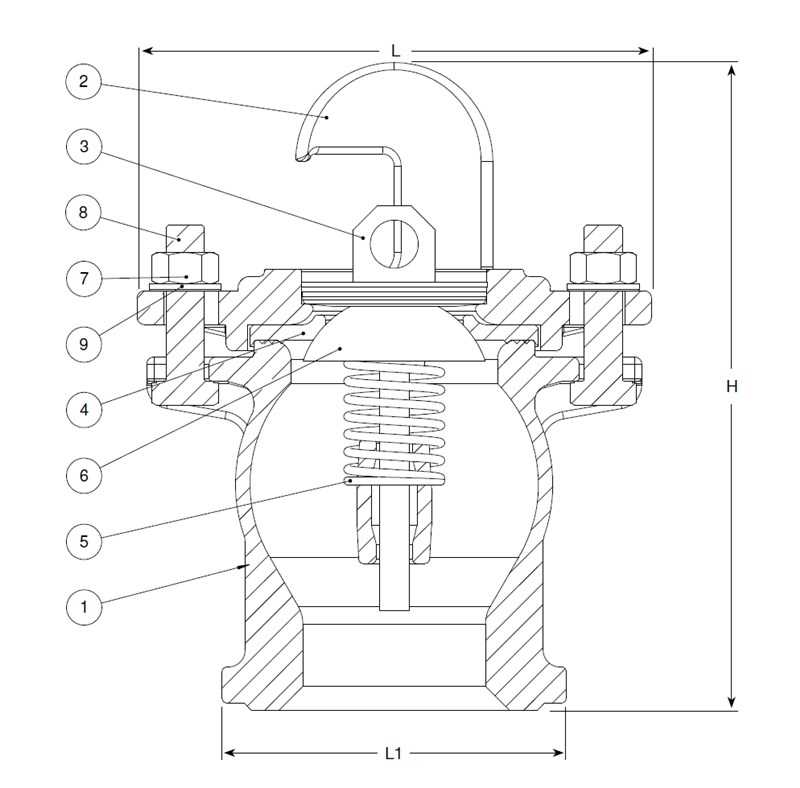
When tackling maintenance tasks, having the right instruments is essential for achieving efficiency and effectiveness. This section outlines the necessary equipment that can make the repair process smoother and more successful.
Wrenches are crucial for loosening and tightening various components. A set of pliers can provide the grip needed for handling smaller parts. Additionally, a reliable screwdriver set is necessary for addressing screws of different sizes.
For precise adjustments, a measuring tape ensures accuracy, while a rubber mallet can be used to avoid damaging surfaces. Finally, don’t forget to have a cleaning brush on hand to clear debris and ensure everything is in top condition.
Innovations in Hydrant Design
Recent advancements in the field of emergency water delivery systems have significantly transformed their functionality and efficiency. These developments aim to enhance accessibility, reliability, and ease of use for first responders, ultimately improving public safety during critical situations.
Smart Technology Integration
One of the most notable trends is the incorporation of smart technology. Devices equipped with sensors can now provide real-time data on water pressure, flow rates, and maintenance needs. This information not only assists emergency services in responding more effectively but also aids municipalities in managing their resources more efficiently. Remote monitoring systems enable quick diagnostics and timely repairs, reducing downtime and ensuring optimal performance.
Ergonomic Designs and Materials

Another innovation is the shift towards ergonomic designs and the use of advanced materials. Lightweight, durable composites are replacing traditional metals, making these systems easier to handle and install. Additionally, new shapes and mechanisms enhance usability, allowing for quicker access and deployment. Sustainability is also a focus, with many manufacturers now producing eco-friendly options that minimize environmental impact while maintaining high performance standards.