
In today’s world, advanced climate control systems are an integral part of maintaining comfort in various environments. Whether used in residential or commercial settings, these systems provide efficient temperature regulation, ensuring a pleasant indoor atmosphere regardless of the external conditions. Understanding how these systems function and the critical elements that contribute to their performance is essential for both users and technicians.
This article explores the core elements of one such system, focusing on the internal and external mechanisms that work together to deliver reliable cooling and heating. By examining the layout and individual functions of these components, we can gain insights into the efficient operation and maintenance of this equipment.
With a comprehensive look at the essential parts, we will delve into how each unit works in harmony with others to ensure energy efficiency and consistent performance. Additionally, this guide will highlight how proper maintenance and timely replacements of certain elements can extend the lifespan of the entire system, preventing costly repairs in the future.
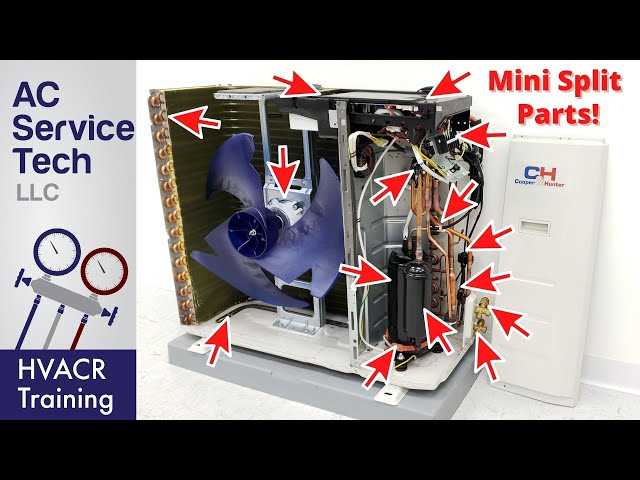
Understanding Mitsubishi MR Slim Components
When examining this cooling system, it’s essential to grasp the various elements that ensure smooth operation. Each part plays a unique role in regulating temperature, airflow, and overall performance. A clear understanding of how these elements interact allows for efficient troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Functional Elements
- Compressor Unit: This is the heart of the system, responsible for pressurizing the refrigerant and facilitating heat exchange.
- Evaporator Coil: Here, the cooling process takes place as warm air is absorbed and cooled air is released.
- Expansion Valve: Regulates the flow of refrigerant, ensuring optimal cooling performance based on the temperature settings.
- Fan Assembly: Works to circulate air through the unit and into the designated space, ensuring consistent airflow.
Electrical and Control Systems
- Control Board: Manages the operation of the system by processing inputs and adjusting settings accordingly.
- Sensors: Measure temperature and humidity to provide feedback for the system’s performance, ensuring it adapts to environmental conditions.
- Remote Interface:
Main Elements of the Cooling System
The cooling system is a complex structure designed to regulate temperature in various environments. It ensures the proper functioning of air distribution by maintaining an optimal balance of airflow, temperature control, and energy efficiency. This system is composed of several interconnected components, each playing a specific role in facilitating heat exchange and maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
Component Function Compressor The heart of the system, responsible for circulating refrigerant and increasing its pressure to initiate cooling. Evaporator Coil Absorbs heat from indoor air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the surrounding environment. Condenser Coil Releases absorbed heat outdoors by condensing the refrigerant back into liquid form. Expansion Valve Controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil, allowing for efficient heat absorption. Air Handler Distributes cooled or heated air through the ventilation ducts, ensuring even air circulation throughout the space. Key Electrical Connections in MR Slim
The internal system relies on several critical electrical linkages to ensure efficient operation. These connections play a fundamental role in managing the flow of power and signals between the main components, guaranteeing smooth performance across various functions. Understanding how these electrical points interact with each other is crucial for both installation and maintenance.
Power Distribution
One of the primary connections involves the power supply, which feeds electricity to the core system. This essential link is responsible for distributing energy to the major operating parts, ensuring that the unit can perform heating and cooling tasks effectively. Properly securing this connection minimizes the risk of malfunctions due to power inconsistencies.
Signal Control Pathways
Equally important are the signal pathways that manage communication between various modules. These connections allow the control system to monitor and adjust settings, such as temperature and airflow. Ensuring these pathways are intact helps maintain precise control over the entire system, allowing it to respond to changes quickly and efficiently.
Fan Unit Breakdown and Functions
The fan component is essential for ensuring proper airflow and maintaining optimal temperature regulation in a cooling system. By efficiently circulating air, the fan helps to distribute cool air evenly throughout the environment and prevents overheating of critical elements within the system. Understanding the breakdown of the fan and its roles can provide insight into the system’s overall efficiency and reliability.
Main Structural Elements
The fan assembly consists of several key parts that work together to create consistent airflow. The blades, typically made from lightweight materials, are shaped to maximize air movement while minimizing noise. These blades are connected to a motor that powers the rotation, ensuring constant airflow. Additionally, a casing or housing surrounds the fan unit to protect the internal components and guide airflow in the desired direction.
Operational Functions
The primary function of the fan is to assist in cooling by moving air across the system’s coils. This movement helps dissipate heat, allowing the system to operate at optimal performance levels. The fan’s speed is often adjustable, providing flexibility based on the cooling demands. In more advanced setups, the fan may also feature sensors to automatically adjust its speed, further enhancing the efficiency of the overall system.
Compressor Assembly Overview
The compressor is a crucial element in modern cooling systems, responsible for the efficient regulation of refrigerant flow. This component ensures that the refrigerant transitions through various stages, allowing the entire system to maintain optimal performance in different temperature conditions. Understanding the various parts involved in the compressor assembly helps in grasping its function and maintaining its efficiency.
Main Components of the Compressor
- Housing: The external casing that protects internal parts from environmental factors and maintains the structural integrity of the compressor.
- Pistons and Cylinders: The mechanisms inside the assembly responsible for compressing the refrigerant, ensuring proper pressure levels are maintained.
- Valves: These control the flow of refrigerant, ensuring that it moves correctly between the low and high-pressure sides of the system.
- Motor: Powers the movement of the pistons, providing the necessary force to compress the refrigerant effectively.
Operational Process
- The refrigerant enters the compressor in a low-pressure, gaseous state.
- The pistons compress the gas, increasing its press
Refrigerant Line and Valve Structure
The system responsible for circulating the cooling substance plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance in climate control systems. Understanding the configuration of the conduits and associated mechanisms can greatly enhance the efficiency and reliability of these systems. This section delves into the design and function of these essential components, providing insights into their importance within the overall framework.
Components of the Refrigerant Circuit
The network of tubes designed for the refrigerant is integral to the operation of cooling systems. These conduits are engineered to withstand high pressure and temperature variations, ensuring the safe transfer of the cooling medium. Insulation is often applied to minimize energy loss, while connectors and fittings ensure a secure and leak-proof system.
Valves and Their Functions
Control mechanisms within the system, such as valves, are vital for regulating the flow of the refrigerant. These devices enable precise adjustments to be made, allowing for optimal performance under varying operational conditions. Expansion valves and solenoid valves are particularly important, as they manage pressure and flow, ensuring that the cooling process remains efficient and effective.
Control Board Configuration and Features
The configuration of the control board plays a vital role in the overall functionality and efficiency of the unit. This component serves as the brain, managing various operations and ensuring smooth communication between different elements. Its layout and integrated features are designed to enhance performance and facilitate ease of maintenance.
Typically, the control board includes various connectors, relays, and microcontrollers that enable precise control over the system’s functions. Features such as fault detection, temperature regulation, and user interface options are often incorporated to provide intuitive operation and feedback. By utilizing advanced technology, these boards can adapt to different environmental conditions, optimizing performance while minimizing energy consumption.
Regular inspection and understanding of the control board’s configuration can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance. Familiarity with the layout helps technicians quickly identify components that may require attention, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the system.
Thermostat Interaction with MR Slim
The relationship between temperature control units and the cooling systems plays a crucial role in maintaining comfort within a space. These devices work together to ensure that the desired climate is achieved efficiently, optimizing both energy usage and user satisfaction. Understanding how these control units interact with the cooling system can lead to improved performance and longevity of the equipment.
Functionality of the Control Unit
The primary function of the temperature regulator is to monitor and adjust the environment’s temperature according to user settings. This device communicates with the cooling mechanism, sending signals to initiate or halt operation based on the ambient conditions. Effective interaction ensures that the system operates only when necessary, which can significantly enhance energy efficiency.
Impact on System Efficiency

When the temperature control unit operates effectively, it contributes to reduced wear and tear on the cooling equipment. Proper coordination between these components helps maintain a steady temperature, minimizing fluctuations that could lead to energy spikes. Furthermore, an efficiently functioning regulator can extend the lifespan of the cooling system, resulting in lower maintenance costs and improved overall performance.
Exploring the Drainage System Components
The drainage system is a crucial aspect of any cooling unit, ensuring the efficient removal of condensation and preventing water-related issues. Understanding its components can help in maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the system. This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to effective drainage, highlighting their roles and functions.
Key Elements of the Drainage Mechanism
At the core of the drainage mechanism lies the collection pan, designed to gather excess moisture generated during operation. This component channels the water towards the drainage outlet, facilitating proper disposal. Complementing the collection pan are various tubing and piping systems that transport the collected water away from the unit, minimizing the risk of leaks and water accumulation.
Importance of Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance of the drainage system is vital to ensure uninterrupted operation. Over time, debris and dirt can accumulate in the collection pan and tubing, leading to blockages. Routine inspections help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent costly repairs and system failures.
Air Filter Types and Maintenance
Effective air filtration is essential for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of cooling systems. Different varieties of filters serve unique purposes, ensuring that air circulation remains clean and free from pollutants. Understanding these types and their upkeep can enhance the efficiency of your system while promoting a healthier indoor environment.
Types of Air Filters: Various filter types are available, each designed to capture different contaminants. Fiberglass filters are the most basic option, effectively trapping larger particles but requiring frequent replacement. Pleated filters, with their increased surface area, can capture smaller particles and have a longer lifespan. For those needing advanced filtration, HEPA filters are highly effective at removing tiny allergens and pollutants, making them ideal for allergy sufferers.
Maintenance Tips: Regular maintenance is vital for all filter types to ensure they function efficiently. It is recommended to check filters monthly and replace them as necessary, typically every one to three months, depending on usage and filter type. Keeping the surrounding area clean and free of dust will also prolong filter life. In addition, consider scheduling professional inspections to ensure the entire cooling system operates optimally.
Sensor Locations and Roles
This section delves into the strategic positioning and functions of various detectors within the system. Understanding these components is crucial for effective operation and maintenance, as they play a vital role in monitoring and controlling various parameters.
Key Locations
- Indoor Unit Sensors: Positioned to gauge temperature and humidity, ensuring optimal comfort levels.
- Outdoor Unit Sensors: Located to monitor external environmental conditions, enabling efficient performance adjustments.
- Refrigerant Sensors: Found within the refrigerant circuit to track pressure levels and ensure system reliability.
Functions of Sensors
- Temperature Regulation: Adjusts the operational settings based on detected indoor and outdoor temperatures.
- Humidity Control: Monitors moisture levels, aiding in maintaining a comfortable environment.
- Pressure Monitoring: Ensures the refrigerant operates within safe parameters, preventing system failures.
Outdoor Unit and Its Components
The outdoor unit serves a crucial role in the overall functionality of the air conditioning system, housing essential components that facilitate the heat exchange process. This unit is designed to withstand various weather conditions while ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency.
Key Components
Understanding the main elements of the outdoor unit is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Below are the primary components found within the system:
Component Description Compressor Compresses refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure to circulate it through the system. Condenser Coil Allows heat to be released from the refrigerant, transforming it from a gas to a liquid state. Fan Promotes airflow across the condenser coil, enhancing heat dissipation and cooling efficiency. Expansion Valve Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, maintaining optimal pressure levels. Electrical Components Includes wiring, circuit boards, and relays that control the unit’s operation and safety features. Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep of the outdoor unit is vital for longevity and efficiency. Keeping the area around the unit clear, inspecting the components for wear and tear, and scheduling professional servicing can help prevent issues and ensure reliable performance.
Inspecting the Heat Exchanger Design
The efficiency and functionality of a thermal management system heavily rely on the design of the heat transfer component. This crucial element plays a significant role in regulating temperature, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. Understanding its layout and structure can greatly enhance the maintenance and troubleshooting processes, leading to improved system longevity.
Key Design Features
Several aspects define the effectiveness of a thermal exchange system. These include the material composition, surface area, and overall geometry. Each characteristic contributes to the component’s ability to transfer heat effectively, impacting the entire system’s performance. A well-engineered design minimizes energy loss and maximizes heat exchange, essential for achieving peak operational efficiency.
Common Inspection Parameters
Regular inspections of the heat transfer unit are vital for early detection of issues that may compromise system efficiency. Below are common parameters to assess during the evaluation:
Parameter Description Surface Condition Check for corrosion, fouling, or scaling that may hinder heat transfer. Flow Rate Ensure the fluid movement aligns with design specifications to maintain optimal performance. Temperature Differential Monitor the temperature difference across the exchanger to assess its operational efficiency. Leakage Inspect for any signs of leaks that could affect system integrity and performance.