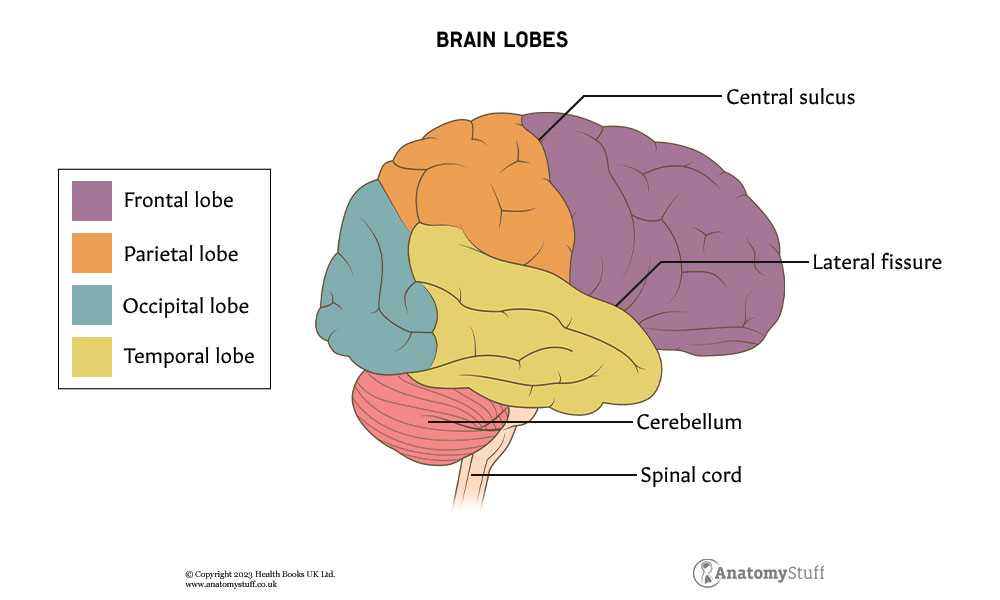
Understanding the complex organization of our cognitive system reveals a fascinating landscape of functions and responsibilities. Each section contributes uniquely to our overall experience, influencing thoughts, emotions, and actions.
Visual representations play a crucial role in grasping these intricate connections. By examining various regions, we can appreciate how they collaborate to support behavior and perception.
As we delve into this subject, it becomes clear that recognizing these anatomical elements is essential for comprehending the ultimate workings of human consciousness and interaction.
Understanding the Brain’s Structure
Grasping the organization of this complex organ is essential for comprehending its functions. Each section plays a crucial role in various processes, influencing everything from motor skills to emotional responses. By exploring its architecture, one can appreciate how interconnected systems work harmoniously to sustain life and behavior.
Main Regions
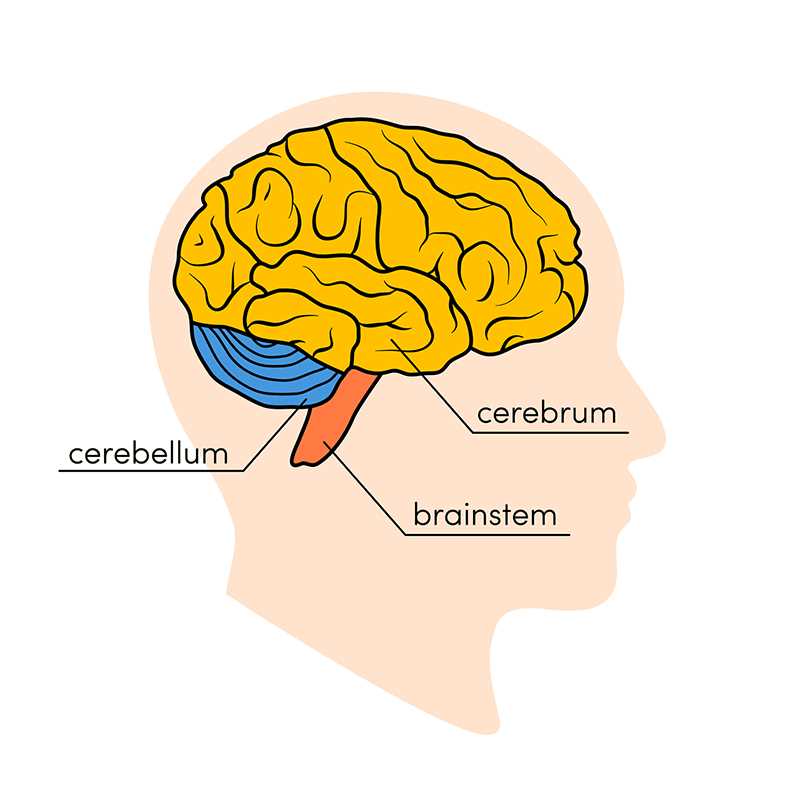
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
Each of these regions has specific responsibilities, contributing to overall functionality. For example, the largest area is primarily involved in higher cognitive functions, while another section manages coordination and balance.
- Neurons transmit signals rapidly, ensuring efficient communication.
- Synapses facilitate connections, allowing for information exchange.
- White matter connects different regions, promoting integration of diverse functions.
Understanding these networks enhances insight into how information flows, enabling rapid responses and adaptive behaviors. This intricate web ultimately shapes personality, thought, and actions.
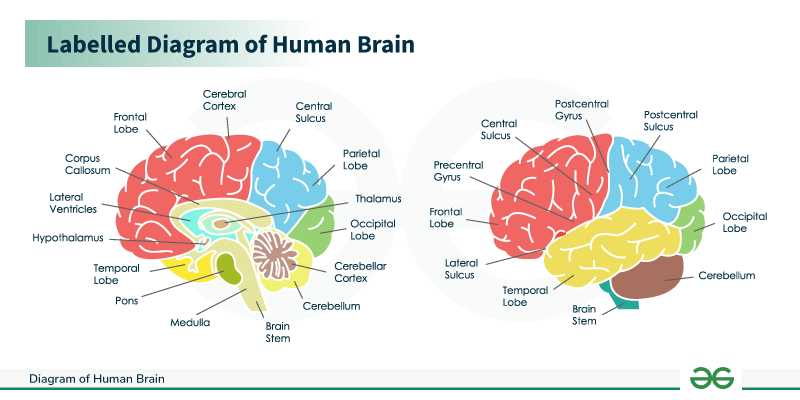
Major Regions of the Human Brain
The human central nervous system is a complex structure divided into several significant areas, each responsible for various functions and processes. Understanding these key zones is essential for grasping how our cognitive abilities, emotions, and motor skills operate.
Cerebrum
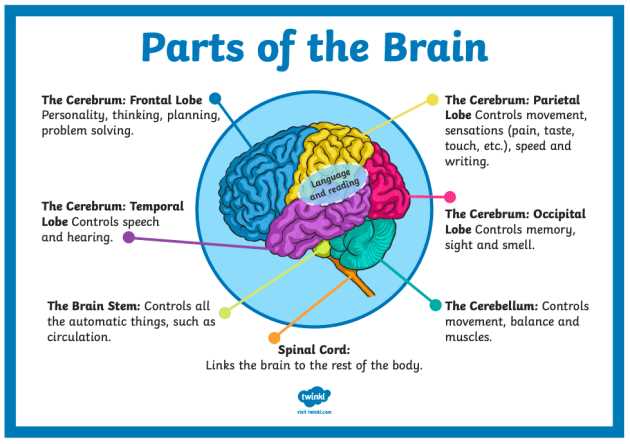
The cerebrum is the largest region, encompassing areas that govern reasoning, sensory perception, and voluntary movements. This section is further subdivided into hemispheres and lobes, each playing distinct roles in our daily experiences.
Cerebellum
Positioned beneath the cerebrum, the cerebellum coordinates movement and balance, ensuring smooth execution of motor tasks. It is crucial for fine-tuning motor activities and maintaining posture.
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Reasoning, sensory perception, voluntary movement |
| Cerebellum | Coordination, balance, fine motor skills |
| Brainstem | Basic life functions, reflexes, and autonomic control |
| Limbic System | Emotion regulation, memory processing, and motivation |
Functions of the Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex plays a crucial role in various cognitive functions and processes that define human experience and behavior. Its intricate structure allows for a wide range of activities essential for daily life.
- Perception: Interprets sensory information, enabling recognition and response to stimuli.
- Motor Control: Coordinates voluntary movements through motor planning and execution.
- Cognition: Involves higher-level thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making.
- Language: Facilitates comprehension and production of speech and writing.
- Emotion Regulation: Influences emotional responses and social interactions.
Understanding these functions provides insight into how this outer layer contributes to overall functionality and human behavior.
The Role of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordinating motor control and balance. This region is essential for smooth execution of voluntary movements and ensuring that actions are precise and fluid. Additionally, it contributes to cognitive functions and emotional regulation, highlighting its multifaceted importance in overall neurological performance.
Functions of the Cerebellum
Primarily associated with motor activities, this region helps fine-tune movements by processing sensory information and making real-time adjustments. It also engages in learning and memory related to motor tasks, which enhances skill acquisition over time.
Impact on Coordination and Balance
Maintaining equilibrium and coordinating physical actions are fundamental to daily life. The cerebellum ensures that the body responds effectively to changes in posture and movement, preventing falls and injuries.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor Coordination | Refines and adjusts movements for precision. |
| Balance | Maintains stability during activities. |
| Cognitive Processing | Involved in planning and executing tasks. |
| Emotional Regulation | Influences emotional responses and behavior. |
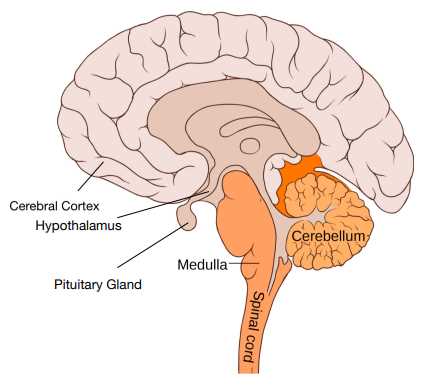
Brainstem: Control Center of Life
This vital structure serves as a fundamental hub for regulating essential functions, ensuring survival and maintaining equilibrium in our bodies. Its influence extends to both automatic processes and basic reflexes, underscoring its importance in daily life.
Functions of the Brainstem
Operating quietly yet effectively, this region manages a variety of crucial roles:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Breathing | Controls the rhythm and depth of respiration. |
| Heart Rate | Regulates the pace and force of cardiac contractions. |
| Consciousness | Plays a key role in alertness and sleep cycles. |
Impact on Daily Life
Without this crucial structure, many involuntary actions would falter, highlighting its role as a silent guardian. Understanding its functions helps appreciate how intricately our bodies are orchestrated.
Limbic System and Emotion Processing
The limbic system plays a crucial role in how individuals experience and manage emotions. This intricate network is essential for emotional regulation, influencing behaviors and responses to various stimuli. By understanding this system, we gain insights into how feelings shape human experiences and decision-making.
Components of the Limbic System
Key elements within this network include structures such as the amygdala, hippocampus, and cingulate gyrus. Each component contributes uniquely to emotional responses. For instance, the amygdala is primarily involved in processing fear and pleasure, while the hippocampus plays a significant role in forming emotional memories. Together, these structures create a dynamic interplay that affects how emotions are perceived and acted upon.
Emotional Regulation and Response
Emotional processing is not solely about experiencing feelings; it also encompasses how individuals regulate those emotions. Strategies such as reappraisal or suppression can significantly alter emotional responses. The limbic system helps coordinate these strategies, allowing individuals to navigate complex emotional landscapes. Understanding this regulation can lead to better mental health practices and improved emotional well-being.
Understanding Brain Lateralization
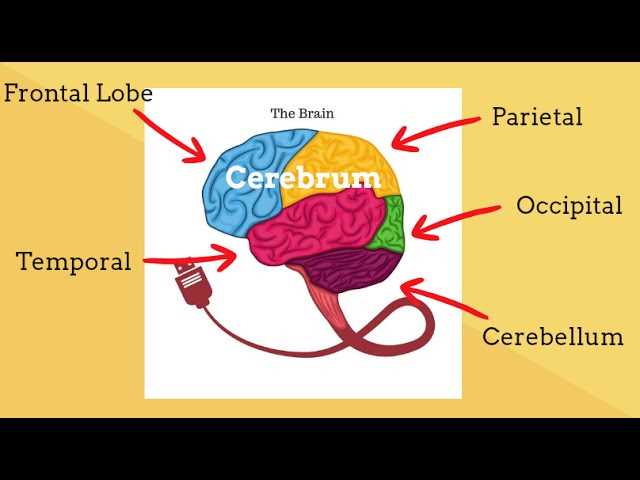
Lateralization refers to the tendency for certain cognitive functions and processes to be more dominant in one hemisphere than the other. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in how individuals perceive and interact with the world. By exploring this concept, one can gain insights into the complex workings of human cognition and behavior.
Cognitive Functions and Hemispheric Dominance
Research indicates that specific activities, such as language processing, often occur predominantly in the left hemisphere, while spatial abilities and creativity are more associated with the right hemisphere. This division of labor enhances efficiency and allows for a more nuanced understanding of various tasks, impacting learning and communication.
Implications for Learning and Development
Understanding lateralization can inform educational approaches and therapeutic strategies. Recognizing individual differences in cognitive processing can lead to tailored learning experiences, fostering strengths and addressing weaknesses. This awareness is particularly beneficial in developing programs that cater to diverse learning styles and preferences.
Mapping the Neuron Connections
Understanding how various neurons interconnect forms the foundation of exploring cognitive functions and behaviors. This intricate network facilitates communication throughout the entire organism, enabling responses to external stimuli and internal processes. Analyzing these connections unveils the complexity and elegance of neural pathways.
Neural Networks and Their Functions
Neurons communicate through synapses, creating a vast web of connections. Each neuron can form thousands of synapses, allowing for a rich tapestry of interactions. This interconnectivity supports essential functions, such as learning, memory, and sensory perception. Mapping these networks provides insight into how experiences shape the nervous system and influence overall well-being.
Visualizing Connectivity
Advanced imaging techniques have revolutionized our ability to visualize these connections. Tools like functional MRI and diffusion tensor imaging reveal the dynamic landscape of neuronal pathways. By studying these visual representations, researchers can identify patterns associated with various cognitive tasks and neurological conditions, paving the way for targeted interventions.
Impact of Brain Injuries on Function
Injuries to neural structures can lead to significant alterations in cognitive and physical abilities. Such traumas may disrupt normal operations, causing a range of impairments depending on the affected areas. Understanding these effects is crucial for recovery and rehabilitation efforts.
Common Consequences of Injuries
- Cognitive deficits
- Emotional instability
- Motor skill impairment
- Changes in behavior
Rehabilitation Strategies
- Physical therapy to enhance mobility
- Cognitive training to restore thinking skills
- Psychological support for emotional recovery
- Occupational therapy to improve daily functioning
Visualizing Brain Activity with Scans
Understanding how neural networks function and interact is crucial for advancements in cognitive science. Modern imaging techniques allow researchers to observe these dynamic processes, offering insights into the complexities of mental functions. By capturing real-time activity, scientists can correlate specific behaviors and thoughts with corresponding regions of neural tissue.
Techniques for Imaging
Several methodologies exist for monitoring cerebral functions, including functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). Each method provides distinct advantages, enabling comprehensive analysis of how various tasks engage different neural circuits. This information is vital for developing targeted therapies for neurological disorders and enhancing educational approaches.
Applications in Research and Medicine
Imaging techniques not only facilitate academic research but also play a significant role in clinical settings. They assist in diagnosing conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy, enabling healthcare professionals to create tailored treatment plans. Moreover, ongoing studies utilize these technologies to unravel the underlying mechanisms of consciousness and memory, paving the way for future innovations in mental health.
Future of Brain Research and Technology
Advancements in neuroscience and related technologies promise to revolutionize our understanding of cognitive functions and enhance human capabilities. Emerging methods and tools aim to explore complex neural networks, ultimately leading to breakthroughs in both medical and cognitive fields.
Innovative Techniques
New imaging modalities and neurostimulation techniques are being developed to map neural activity with unprecedented precision. These innovations could enable researchers to identify specific regions responsible for various cognitive tasks, paving the way for tailored therapeutic approaches.
Ethical Considerations
As we delve into the intricate workings of cognition, ethical dilemmas surrounding privacy, consent, and enhancement will become increasingly prominent. It is essential to navigate these challenges thoughtfully to ensure that technological progress benefits society as a whole.