
Understanding the intricate components and systems behind fabric-making devices can greatly enhance your approach to efficient production. These mechanical systems, though often complex, consist of key elements that work in harmony to achieve the desired result. Each aspect of the structure serves a specific function, contributing to the overall operation of the device.
The key to maximizing efficiency lies in familiarizing yourself with the various elements involved in these machines. Whether it’s understanding the framework or the moving mechanisms, each detail plays a role in ensuring smooth functionality. By gaining insight into these structures, you will be better equipped to manage and optimize their performance.
Mastering the connections between different components can help to solve common challenges that arise during operation. Proper maintenance and a deep understanding of each aspect of the machine will allow you to prevent disruptions and ensure long-term reliability.
Loom Components Overview
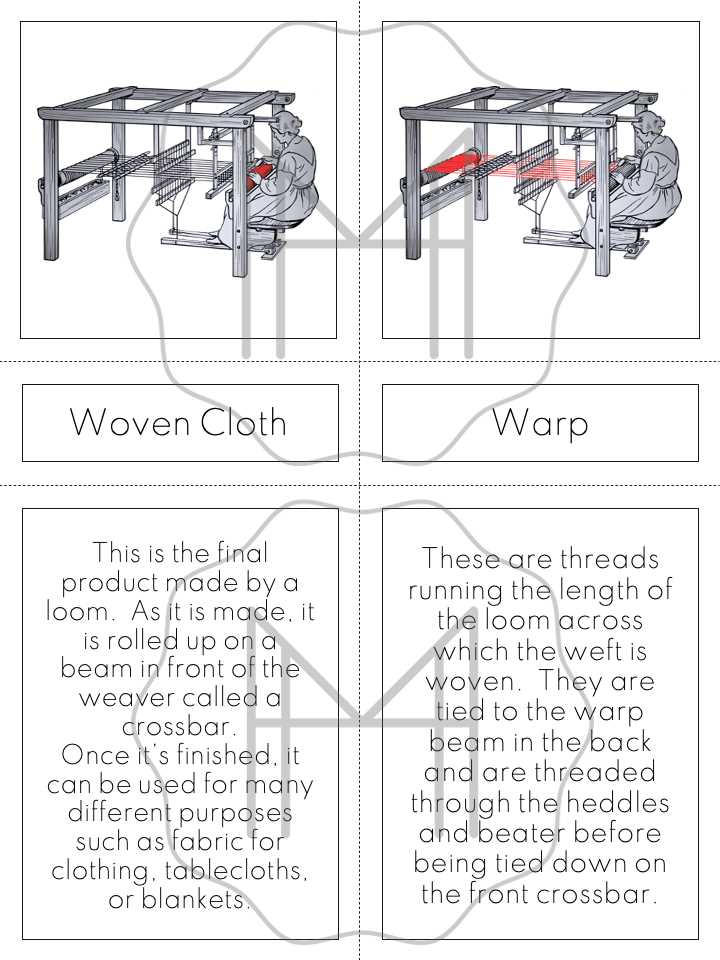
The structure of weaving machines involves various interconnected elements, each designed to perform specific tasks. These components work together to ensure the smooth operation and efficiency of the equipment.
Primary mechanisms typically manage the movement of threads, maintaining tension and alignment, while secondary elements assist in guiding, cutting, or adjusting the materials throughout the weaving process. These elements are integral to achieving accurate and consistent results in fabric production.
Understanding how these pieces interact is crucial for anyone working with weaving machines, as it ensures smoother operation and helps in identifying potential improvements or issues.
Understanding Loom Frame Structure
The framework of weaving equipment plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall stability and efficiency of the machine. By ensuring that each component is properly aligned, the structure supports the smooth operation of all the essential processes involved in fabric creation.
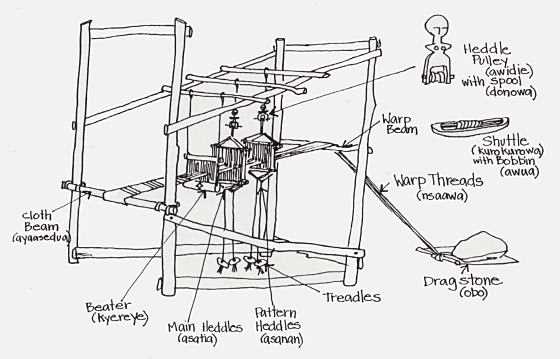
Main Elements of the Structure
The primary components of this framework include vertical and horizontal supports, which work together to hold the machine steady. These supports are designed to handle significant stress, ensuring the integrity of the equipment during continuous use. Proper alignment of these elements is critical for seamless production.
Support and Adjustability
The design also often incorporates adjustable parts to accommodate various fabric types. These adjustments are essential to ensure the precise tension and positioning required for high-quality production. Flexibility in the structure allows for adaptation to different weaving conditions.
Essential Parts for Warp Control
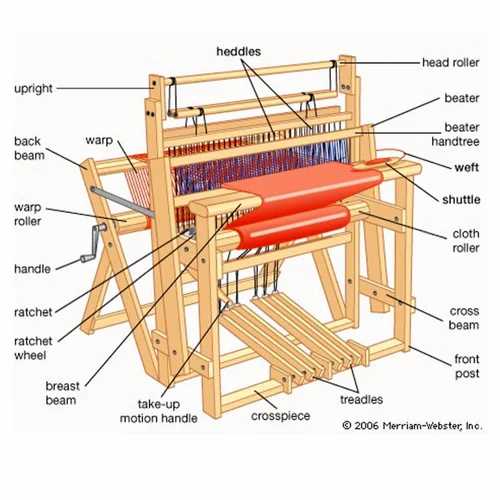
Maintaining tension and precision in the warp threads is crucial for smooth fabric production. Various components work together to ensure consistent alignment, tension, and movement throughout the process. These elements play a vital role in the overall efficiency of the weaving operation.
- Tensioning devices: Regulate the tightness of the threads, ensuring they remain uniform and controlled throughout weaving.
- Guiding mechanisms: Help in directing the threads accurately, preventing misalignment and ensuring a steady weaving process.
- Brake systems: Manage the stopping and starting of the process, preventing unwanted slack or tightness in the threads.
- Roller assemblies: Assist in smooth thread delivery, helping to maintain consistency in thread feed.
Guide to Weaving Mechanism Functions
Understanding the intricacies of how various components work together in a textile machine is crucial for efficient fabric production. Each mechanism plays a specific role, ensuring smooth and synchronized operations. These functions collectively form the backbone of the entire weaving process, transforming threads into finished fabric with precision and speed.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Shedding | This action raises and lowers threads to create the path for the shuttle to pass through. |
| Picking | The shuttle is moved across the machine, inserting the crosswise threads into place. |
| Beating | The inserted threads are packed tightly into the fabric by the reed, ensuring uniformity. |
| Take-Up | The woven fabric is gradually rolled onto a beam as more fabric is produced. |
Beam and Roller Systems Explained
The interaction between beam and roller mechanisms forms the foundation of various textile processes. These components ensure smooth movement and precise control of materials during operation. Each element plays a vital role in supporting and guiding materials efficiently, ensuring consistent tension and alignment.
Main Components Overview
Beam systems serve as core structural elements, holding and controlling the material as it is processed. Roller systems, in turn, facilitate material flow, reducing friction and enhancing movement consistency.
Key Functions
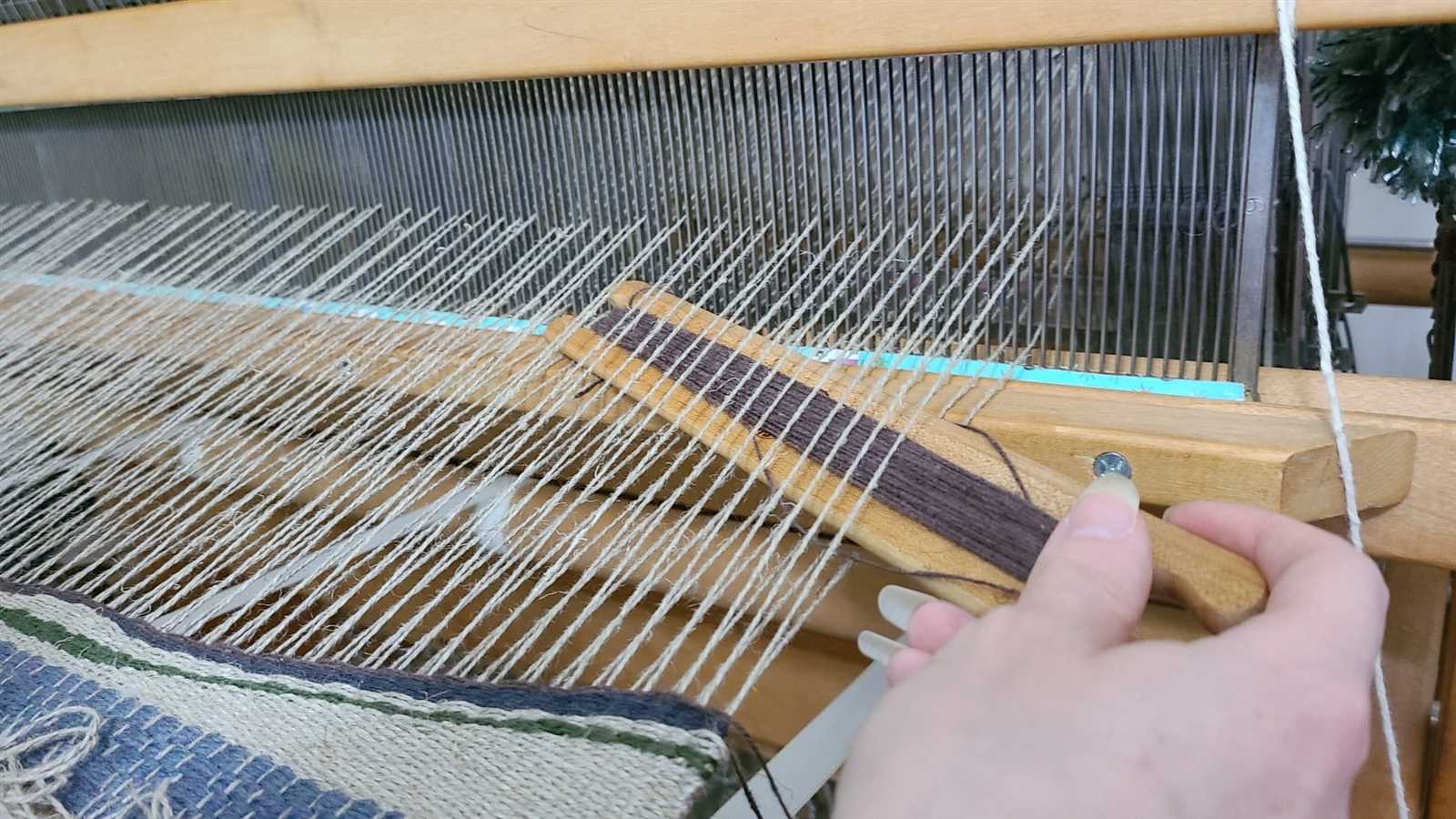

| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Beam | Supports and holds material, ensuring stability during operation. |
| Roller | Guides the material and maintains even tension throughout the process. |
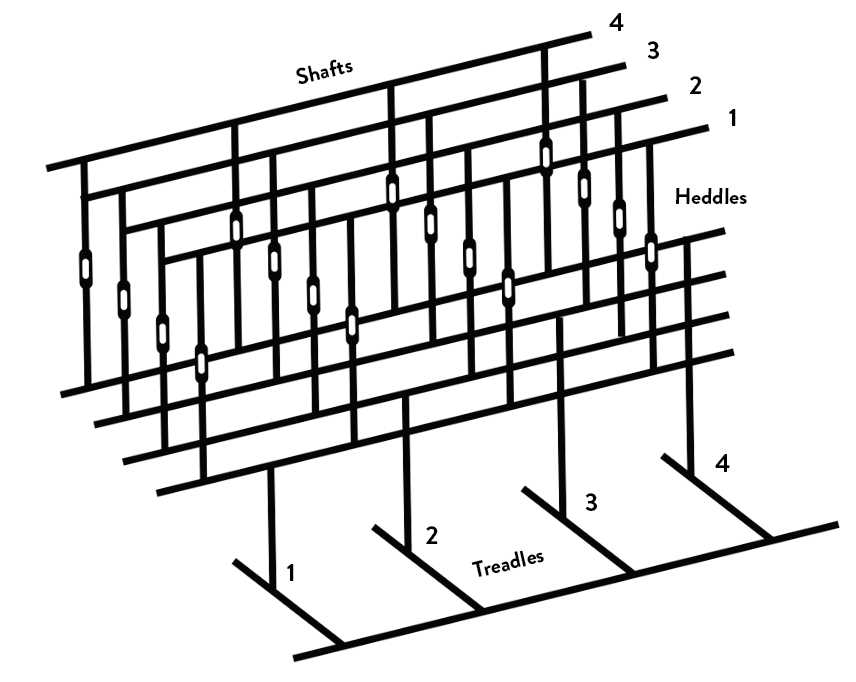
The Role of Heddles in Weaving
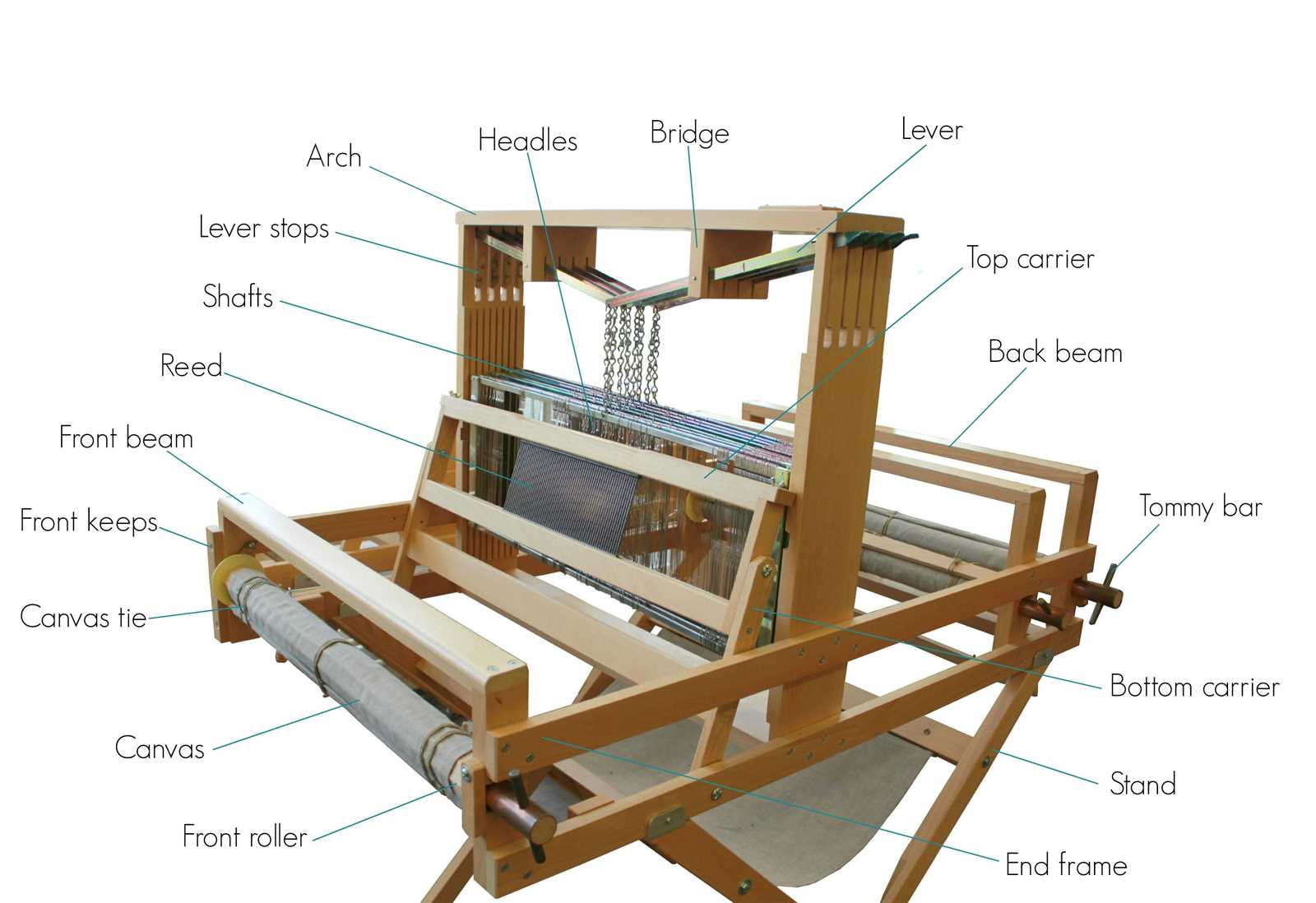
Heddles are crucial elements in the process of textile creation, serving to guide and separate threads during the interlacing phase. They facilitate the efficient movement of warp strands, allowing the weaver to produce intricate patterns and textures. By managing the arrangement of these threads, heddles play a vital role in ensuring a consistent and precise fabric structure.
When incorporated into the weaving mechanism, heddles contribute to the overall efficiency of the operation. Their design and arrangement directly impact the speed and quality of the finished product. Below is a table summarizing the primary functions of heddles in weaving.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Thread Separation | Allows for the individual placement of warp threads, preventing tangling. |
| Pattern Formation | Enables the creation of various designs by controlling which threads are raised or lowered. |
| Thread Tension | Helps maintain even tension across the warp threads, crucial for fabric integrity. |
Shuttle and Bobbin Interaction
The relationship between the shuttle and the bobbin is crucial in the process of textile creation. These two components work together seamlessly to ensure the effective movement of thread during weaving, contributing to the overall efficiency and quality of the fabric produced. Understanding their interaction can provide insights into the functionality and operation of weaving mechanisms.
The shuttle plays a vital role in carrying the thread across the width of the material being crafted. It is designed to move swiftly, enabling quick insertion of the thread into the weave. On the other hand, the bobbin serves as the storage unit for the thread, releasing it as needed to facilitate the shuttle’s movement. This coordinated effort between the two components is essential for maintaining tension and consistency in the woven fabric.
When analyzing their interaction, one can observe that any disruption in the shuttle’s motion or the bobbin’s thread supply can lead to complications in the weaving process. For instance, if the bobbin runs low on thread, it may cause the shuttle to halt, interrupting the workflow. Hence, a well-functioning system relies on the harmonious operation of these two elements to produce high-quality textiles efficiently.
How Reed Contributes to Fabric Density
The role of the reed in textile production is essential for achieving the desired density in the final fabric. This component not only helps to separate the threads but also plays a pivotal role in maintaining uniform tension across the width of the material.
By influencing the space between the warp threads, the reed ensures that the weaving process produces a consistent and cohesive structure. Several factors highlight the importance of this element:
- Thread Separation: The reed’s design promotes even spacing of warp threads, which is crucial for preventing tangling and ensuring smooth operations.
- Tension Regulation: It helps maintain optimal tension, reducing the risk of thread breakage and contributing to overall fabric integrity.
- Density Control: Adjusting the reed’s characteristics allows for variations in fabric density, enabling manufacturers to create textiles that meet specific requirements.
- Enhanced Weave Structure: The reed aids in forming a structured weave, which impacts the aesthetic and functional qualities of the fabric.
In conclusion, the reed is a critical factor in the weaving process, significantly affecting the density and quality of the finished textile. Understanding its contributions allows for better control over production outcomes.
Tension Adjustment for Smooth Weaving
Ensuring the correct level of pressure during the weaving process is essential for achieving a flawless finish. Proper regulation of this force not only affects the overall quality of the fabric but also influences the efficiency of the entire operation. A balanced approach helps maintain uniformity and prevents issues such as fraying or uneven tension.
Understanding the Importance
The right amount of pressure is crucial for controlling how the threads interact with each other. If the pressure is too tight, it can lead to breakage or excessive wear on the fibers. Conversely, if it is too loose, the material may become slack, causing distortions in the final product. Therefore, achieving the optimal balance is necessary for seamless production.
Techniques for Adjustment
Several techniques can assist in fine-tuning the pressure. Regularly checking the settings and making small incremental adjustments can lead to significant improvements. Additionally, observing the behavior of the threads during the process provides valuable insights into whether further modifications are needed. Using appropriate tools for measuring and adjusting this force will enhance overall performance and fabric quality.
Examining Treadles and Their Movements
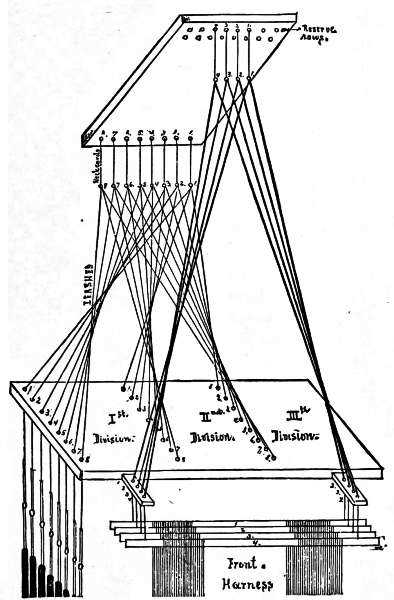
The foundation of a weaving mechanism lies in the functionality of its foot-operated components. These elements are essential for controlling the motion of threads, enabling intricate patterns to emerge through the rhythmic coordination of movement. Understanding how these mechanisms operate enhances the weaver’s ability to create and manipulate fabric effectively.
Functionality of Foot Components
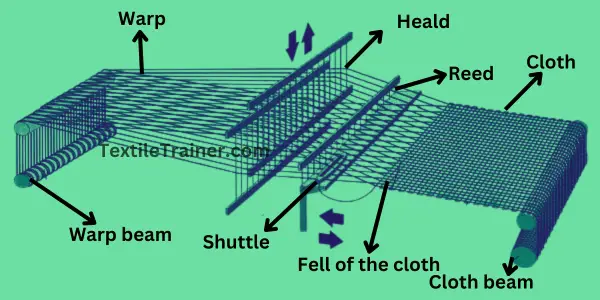
Foot-operated mechanisms are designed to facilitate the lifting and lowering of threads with precision. By applying pressure on these components, the operator can initiate various movements that influence the weaving process. The design and arrangement of these elements play a critical role in determining the ease of use and efficiency during weaving.
Impact on Weaving Technique
Mastering the operation of foot components can significantly enhance the overall weaving technique. Skilled artisans leverage these mechanisms to produce complex designs, demonstrating how crucial their understanding is in achieving artistic goals. A deeper insight into their movements enables weavers to adapt their styles and techniques, ultimately refining their craft.
Maintenance Tips for Loom Efficiency
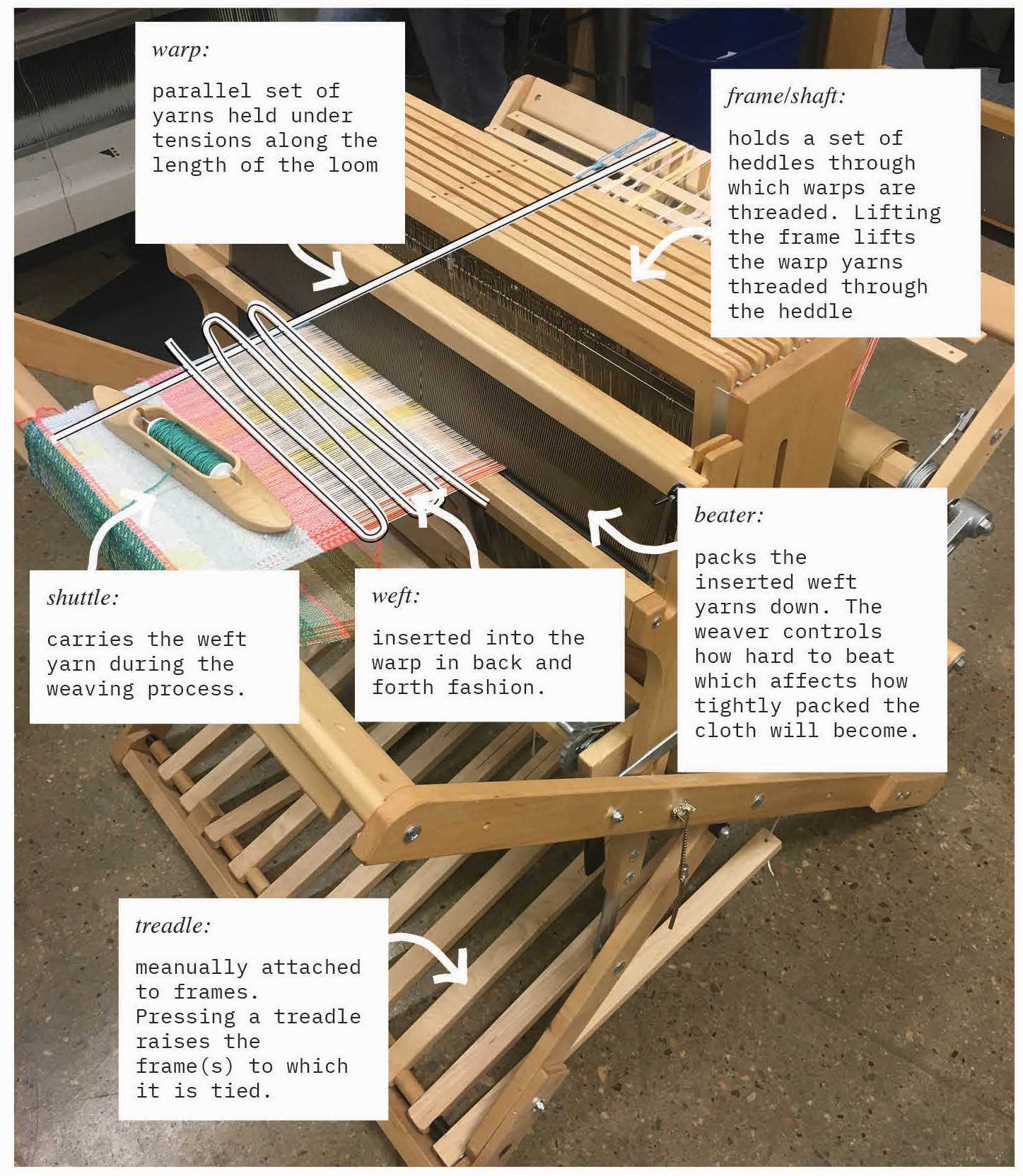
Regular upkeep of textile machinery is essential for maintaining optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment. Implementing effective maintenance strategies not only enhances productivity but also minimizes unexpected downtimes.
Here are some valuable suggestions for ensuring the smooth operation of your textile equipment:
- Routine Cleaning: Regularly remove dust, lint, and debris from all components to prevent build-up that can hinder operation.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts as per the manufacturer’s guidelines to reduce friction and wear.
- Inspection: Conduct frequent visual checks for signs of wear or damage on critical components. Early detection can prevent more significant issues.
- Calibration: Periodically verify and adjust settings to ensure that the machine operates within specified tolerances, optimizing efficiency.
- Training: Ensure that operators are well-trained in proper handling and maintenance practices to maximize operational effectiveness.
By following these guidelines, operators can maintain high efficiency and reliability in their textile production processes.
Upgrading Your Loom for Modern Use
Enhancing your weaving equipment to meet contemporary demands can significantly improve your crafting experience. By integrating new technologies and materials, you can streamline your workflow and elevate the quality of your creations. This section explores various approaches to modernizing your setup, ensuring it remains efficient and relevant in today’s textile landscape.
Here are some key areas to consider when upgrading:
- Technology Integration: Implementing digital solutions can optimize your operations.
- Material Upgrades: Using advanced fibers and threads enhances durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Workspace Optimization: Rearranging your setup can improve accessibility and comfort.
Additionally, consider the following enhancements:
- Automated Systems: Incorporating automation can reduce manual effort and increase precision.
- Accessory Enhancements: Upgrading tools like shuttles and reeds can improve overall functionality.
- Educational Resources: Engaging with online tutorials and courses can expand your skills and techniques.
By focusing on these aspects, you can ensure your weaving apparatus meets modern standards while preserving the artistry of traditional craftsmanship.