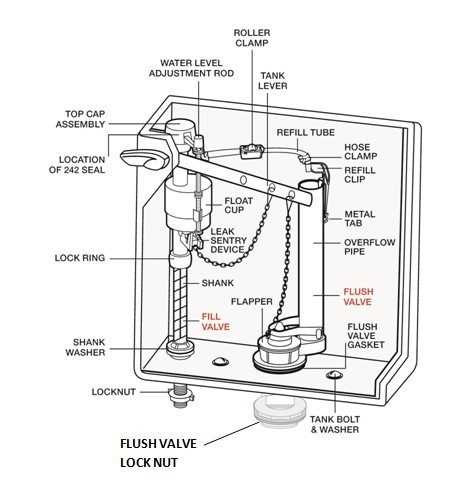
The intricate design of a common sanitary fixture plays a crucial role in modern hygiene and convenience. Each element within this essential apparatus contributes to its functionality and efficiency, ensuring that daily tasks are performed seamlessly. By examining the various sections, we can appreciate how they work together to maintain cleanliness and promote comfort in our lives.
Every segment of this apparatus serves a specific purpose, from water management to waste disposal. Understanding these segments not only enhances our knowledge but also empowers us to troubleshoot issues that may arise. By exploring these interconnected elements, we gain insight into the engineering that supports our daily routines.
Furthermore, a comprehensive grasp of this subject can aid in making informed decisions during maintenance or renovations. Whether for personal use or professional guidance, recognizing the significance of each component is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the fixture. This exploration serves as a valuable resource for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of such a ubiquitous feature in our lives.
Understanding Toilet Bowl Components
This section delves into the essential elements that make up a sanitary fixture, focusing on their functions and importance. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring proper operation and efficiency, contributing to the overall experience of users.
- Chamber: The main area where waste is collected and stored until it is flushed away.
- Flushing Mechanism: This system initiates the removal of waste, often activated by a lever or button.
- Water Tank: A reservoir that holds water, supplying the necessary volume for effective flushing.
- Trapway: The passageway that allows waste to flow from the chamber to the plumbing system.
- Seat: The surface on which individuals sit, designed for comfort and hygiene.
Understanding these elements enhances one’s knowledge of functionality and maintenance. Each component works in harmony to promote efficiency and cleanliness, making it vital to comprehend their roles.
- Regular maintenance can prolong the life of these essential fixtures.
- Awareness of how each element functions aids in troubleshooting common issues.
- Improper care can lead to malfunctions, emphasizing the importance of familiarity with these components.
In summary, a clear grasp of these individual elements and their interactions is key to ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the fixture.
Essential Parts of a Toilet

Understanding the fundamental components of sanitation fixtures is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring proper functionality and hygiene in any restroom environment. By familiarizing oneself with these essential items, users can enhance their overall experience and address issues when they arise.
Key Components

Among the most vital elements are the cistern, which stores and releases water for flushing, and the seat, designed for user comfort. The flapper valve controls the flow of water from the cistern to the drainage area, ensuring an effective clean with each use. Additionally, the trap prevents unpleasant odors from escaping into the restroom.
Additional Features
Modern fixtures may also include features such as a float mechanism that regulates water levels and a water supply line to ensure a consistent flow. Understanding these elements not only aids in troubleshooting common issues but also emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance for optimal performance.
Functionality of the Toilet Bowl
The core purpose of this essential fixture revolves around efficient waste management and hygiene. It plays a crucial role in ensuring sanitary conditions while providing ease of use for individuals.
Water Mechanism
The flow of water is pivotal in the flushing process, effectively removing waste and maintaining cleanliness. This mechanism operates through gravity and pressure, which allows for a swift and thorough clean.
User Experience
Comfort and accessibility are vital aspects that enhance the overall experience. Design elements are tailored to cater to diverse needs, ensuring that users can utilize the fixture with convenience and ease.
Common Issues with Toilet Mechanisms
Understanding the frequent challenges encountered with flushing systems can greatly enhance maintenance and efficiency. Many of these problems stem from wear and tear, improper installation, or general neglect. By recognizing these common faults, users can ensure their fixtures operate smoothly and avoid unnecessary repairs.
Frequent Challenges
- Inconsistent Flushing: Often caused by a faulty flush valve or chain issues.
- Constant Running: This may result from a worn flapper or issues with the fill valve.
- Weak Flush: Often linked to clogs or improper water levels.
- Leakage: Can occur at seals or connections due to deterioration over time.
Prevention and Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Check for signs of wear or leaks at least once a month.
- Water Level Adjustment: Ensure the tank water level is appropriate for optimal flushing.
- Cleaning Components: Regularly clean parts to prevent mineral buildup.
- Prompt Repairs: Address any issues immediately to prevent further damage.
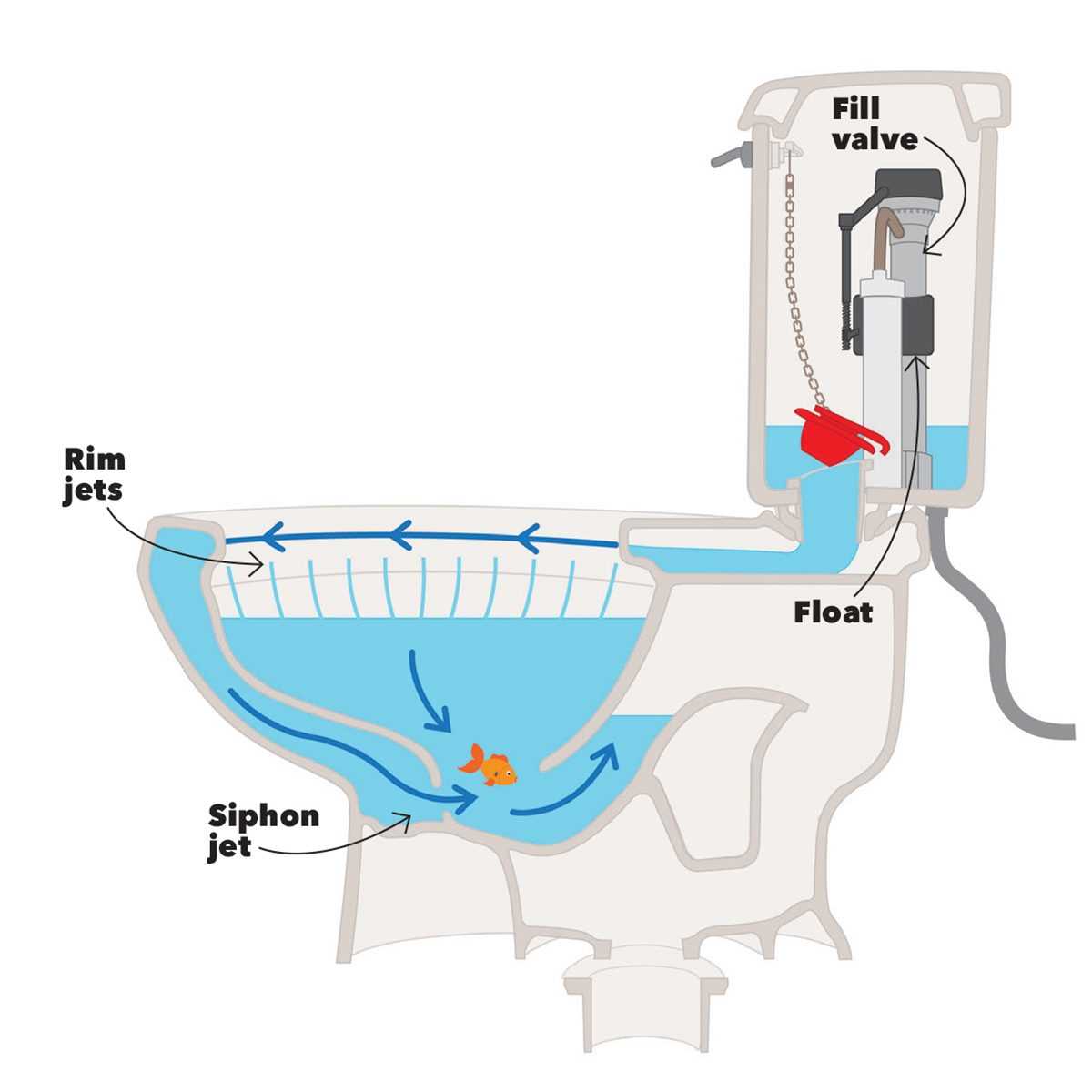
How a Flush Works Explained
Understanding the mechanics behind a flush reveals a fascinating process that ensures efficient waste removal. This system relies on a series of components working in harmony to create a powerful flow of water that clears the chamber effectively.
The Mechanism of Action
When the lever is activated, it initiates a chain reaction. Water is released from a reservoir, cascading down into the chamber. This sudden influx generates pressure, which helps push waste through the drainage pathway. The force is crucial for a complete and swift cleansing.
Return to Normalcy
Once the cycle completes, the mechanism resets itself. Water refills the reservoir, preparing for the next use. This automatic restoration ensures that the system remains ready and functional, contributing to a seamless experience.
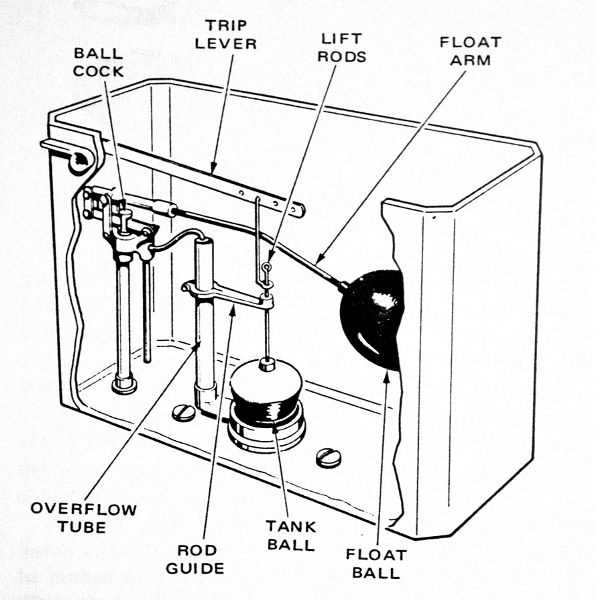
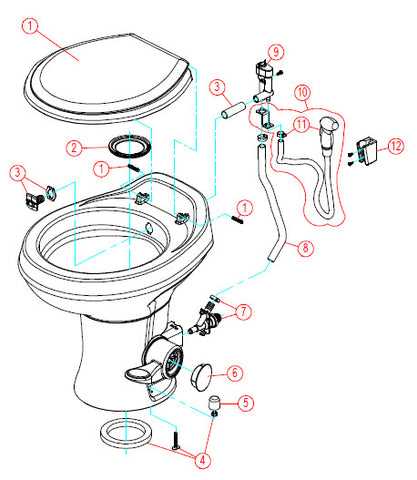
Parts of a Toilet Diagram Overview
This section provides a comprehensive insight into the various components that make up a typical restroom fixture. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting, as each section plays a vital role in the overall functionality.
Essential Components: Key elements include the base, which provides stability, and the seat, designed for comfort. Additionally, the mechanism for flushing ensures efficient waste disposal.
Functionality: Each component contributes to the overall system, ensuring a seamless experience. Recognizing the role of these sections allows users to appreciate the engineering behind everyday conveniences.
Importance of Each Component
Understanding the significance of individual elements within a sanitation fixture is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality and hygiene. Each section plays a specific role, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system.
Key Roles of Various Elements
- Water Control Mechanism: This part regulates the flow of water, crucial for maintaining cleanliness and preventing leaks.
- Waste Management Channel: Essential for the removal of waste, it directs materials to the sewage system.
- Sealing Mechanism: Prevents unpleasant odors from escaping and ensures a tight fit between components.
Impact on Performance
- Enhanced efficiency leads to reduced water consumption.
- Properly functioning elements minimize maintenance needs and extend the lifespan of the system.
- Ensuring each part operates effectively contributes to a more pleasant and hygienic environment.
Comparing Different Toilet Designs
Exploring various designs reveals a spectrum of options, each tailored for distinct user needs and preferences. Understanding these differences can guide individuals in selecting the most suitable model for their spaces.
Types of Designs
- Two-Piece: Features a separate cistern and bowl, allowing easier transport and installation.
- One-Piece: Combines the cistern and bowl into a single unit, providing a sleek appearance and easier cleaning.
- Wall-Mounted: Installed directly on the wall, saving floor space and enhancing aesthetics.
Functional Considerations
- Height: Varying heights cater to different users, enhancing comfort and accessibility.
- Flushing Mechanisms: Different systems offer various levels of water efficiency and effectiveness.
- Shape: Oval or round designs can affect both comfort and space efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and efficient operation of your sanitation fixture requires regular attention and care. By adopting a few simple practices, you can significantly extend its lifespan and enhance performance.
Regular Cleaning
Maintaining cleanliness is essential to prevent buildup and discoloration. Consider the following tips:
- Use a gentle cleaner to avoid damaging surfaces.
- Implement a weekly cleaning routine to remove stains and prevent mineral deposits.
- Pay attention to areas prone to grime accumulation, such as seals and connections.
Inspect for Leaks
Routine inspections can help identify issues early. Look for:
- Signs of moisture around fittings and connections.
- Unusual sounds indicating leaks or malfunctions.
- Flushing inconsistencies that might suggest a problem.
Taking these proactive steps can contribute to the longevity of your plumbing fixture and ensure a hassle-free experience.
Innovations in Toilet Technology
Advancements in sanitation technology have significantly transformed personal hygiene experiences. Modern innovations focus on enhancing comfort, efficiency, and sustainability, reflecting the evolving needs of users. These developments aim to improve overall functionality while minimizing environmental impact.
Smart Features
Contemporary models integrate advanced technology, providing features such as automatic flushing, heated seats, and personalized settings. These enhancements offer convenience and elevate user satisfaction, catering to individual preferences.
Water Efficiency
Innovations also prioritize water conservation. Many modern designs incorporate dual-flush systems and optimized water usage, reducing waste while maintaining effective cleaning. These eco-friendly approaches contribute to sustainable living.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automatic Flushing | Enhances hygiene and convenience |
| Heated Seats | Increases comfort |
| Dual-Flush Mechanism | Reduces water consumption |
| Self-Cleaning | Maintains cleanliness with minimal effort |
Environmental Impact of Toilets
The use of sanitary fixtures plays a significant role in environmental sustainability. Their design and function can have both positive and negative effects on ecosystems and resource consumption.
- Water Usage: Many models consume large volumes of freshwater, contributing to depletion of local water supplies.
- Waste Management: Improper disposal can lead to pollution, affecting soil and waterways.
- Energy Consumption: Manufacturing and maintenance require energy, contributing to carbon emissions.
Innovations in design focus on reducing resource consumption and promoting sustainability.
- Low-flow systems minimize water use.
- Composting alternatives reduce waste impact.
- Smart technologies enhance efficiency and tracking.
Addressing these factors is essential for a more sustainable future.
Signs of Malfunctioning Parts
Identifying issues within essential components of restroom fixtures can prevent more significant problems. Recognizing early warning signs allows for timely intervention and maintenance, ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the lifespan of the unit.
Unusual Noises: If you hear gurgling, hissing, or whistling sounds, it may indicate a malfunction. These noises often signal air leaks or issues with the internal mechanisms.
Water Leaks: Continuous dripping or pooling around the base suggests potential failures in seals or connections. Regularly inspecting for moisture can help catch issues early.
Slow or Incomplete Flushing: If the mechanism struggles to clear waste effectively, it may point to clogs or problems within the flushing system. Monitoring the efficiency of each flush is crucial.
Odors: Persistent foul smells can indicate leaks or decay, often a sign that certain elements are not functioning correctly. Regular checks can help maintain a fresh environment.
DIY Repairs for Toilet Issues

Homeowners often encounter common problems related to their sanitation fixtures that can disrupt daily routines. Understanding basic troubleshooting techniques can empower individuals to resolve these issues without the need for professional assistance.
Identifying Leaks: A prevalent concern is the presence of leaks, which can lead to water wastage. Start by checking for dampness around the base and ensure that connections are secure. If necessary, replace worn seals to restore functionality.
Addressing Flushing Problems: If the flushing mechanism is malfunctioning, it might be due to a faulty valve or chain. Inspect these components and make adjustments or replacements as needed. This can often restore proper operation quickly.
Dealing with Clogs: Clogs are another frequent issue that can cause frustration. Utilize a plunger or a plumbing snake to clear blockages effectively. Regular maintenance can help prevent these occurrences in the future.
By tackling these common issues with confidence and basic tools, homeowners can maintain their fixtures and ensure smooth operation in their homes.