Every mechanical system relies on a variety of interconnected elements that work in harmony to ensure functionality. In large vehicles, these elements are especially crucial, as they bear significant weight and face constant pressure. Proper understanding of these components is essential for maintaining performance and ensuring safety.
The mechanisms involved are not just simple parts but complex assemblies designed to handle various tasks. Whether it’s the components responsible for motion or those providing stability, each plays a unique role. Grasping the fundamentals of these systems can help in diagnostics, maintenance, and repair.
Identifying these elements requires a clear understanding of how they fit together and interact. From the exterior shell to the internal mechanisms, each piece contributes to the overall efficiency. By exploring these connections, one can gain a comprehensive view of the system’s operation.
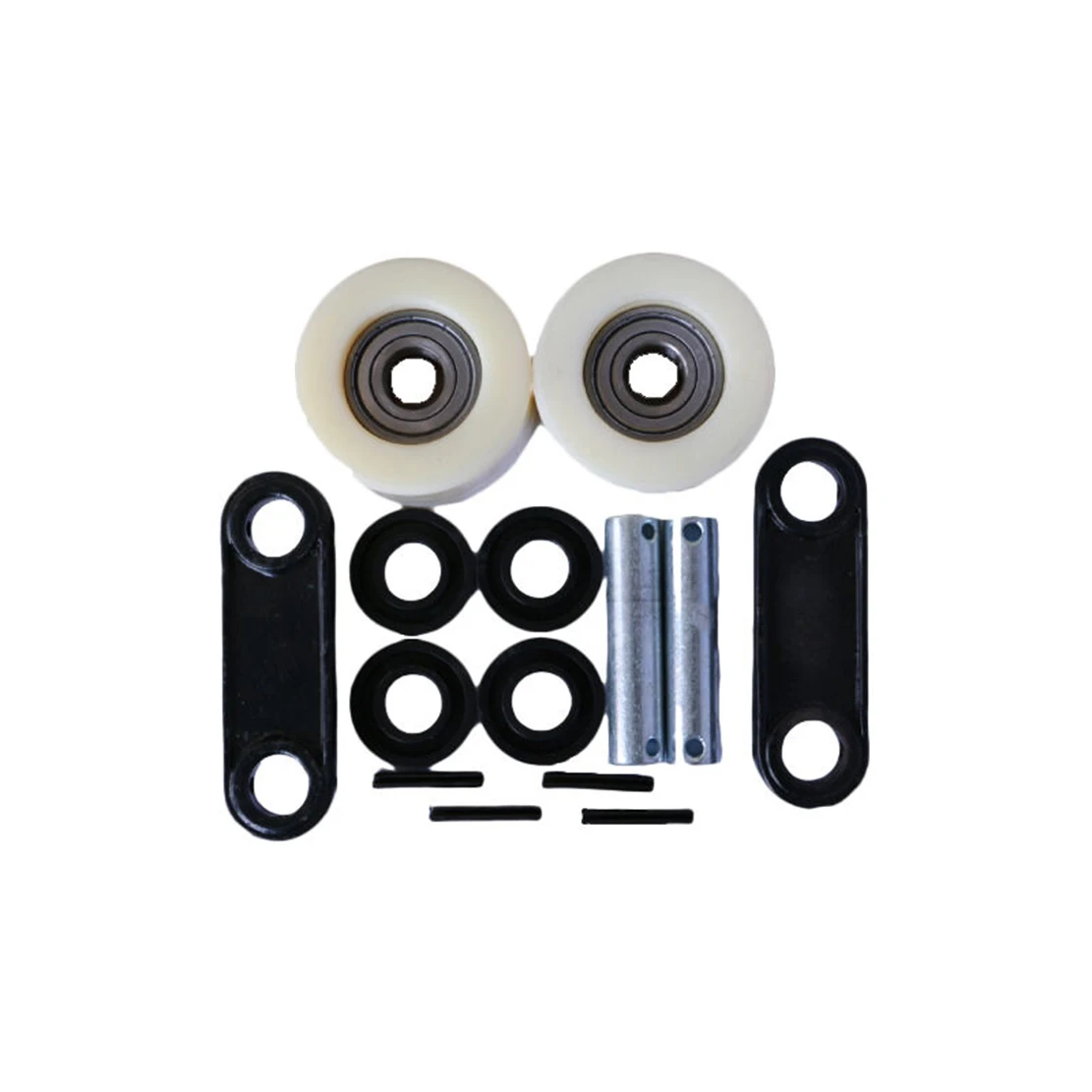
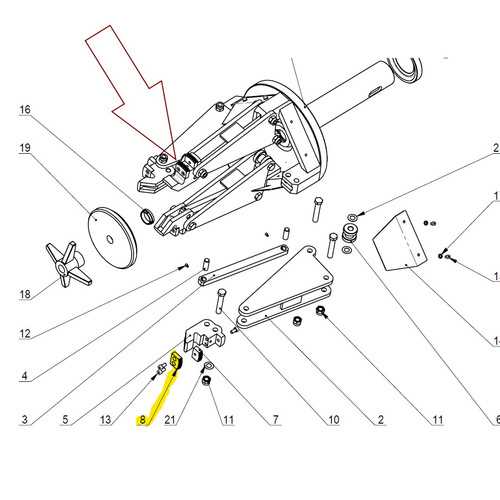
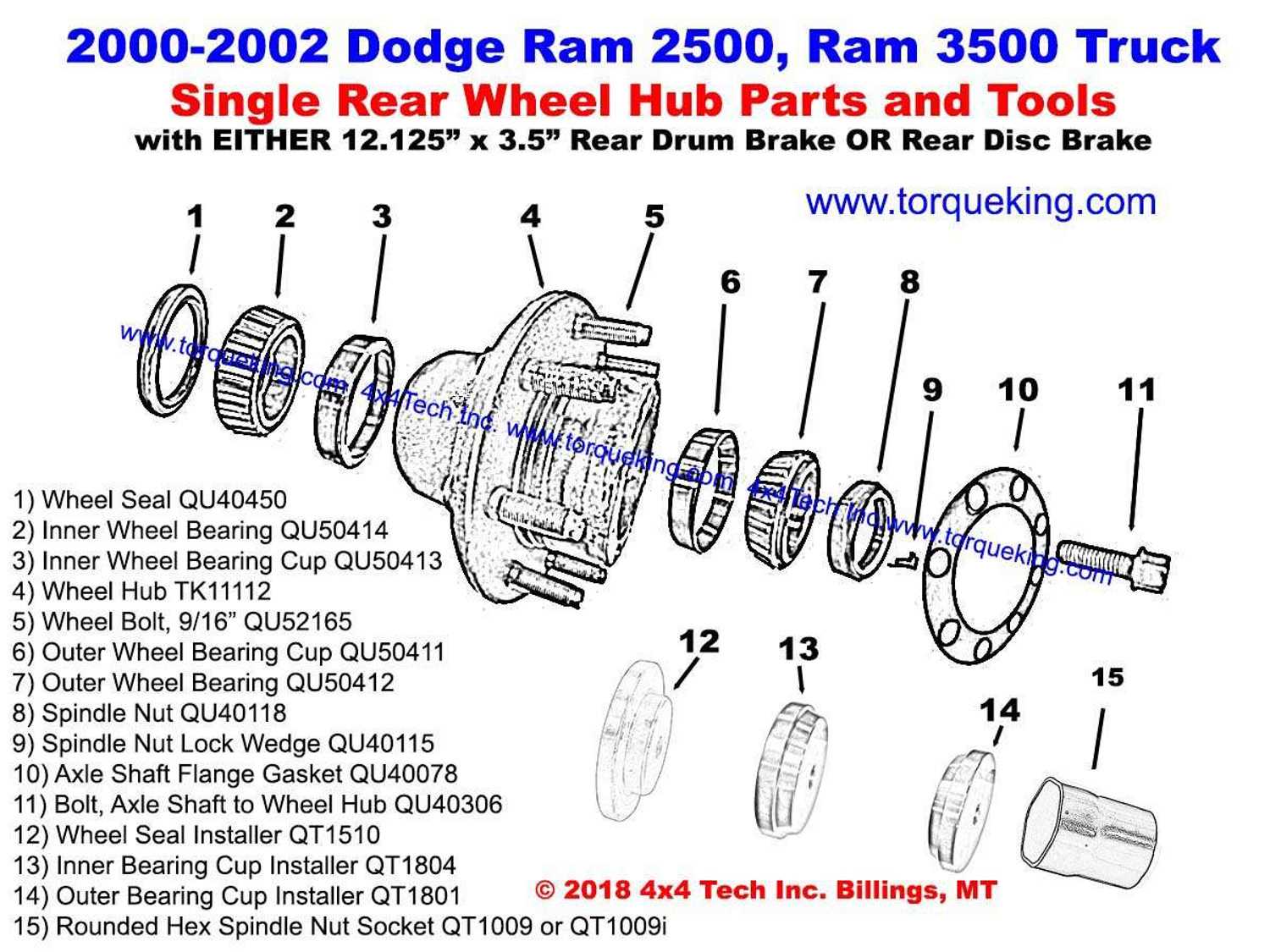
Truck Wheel Parts Diagram Overview
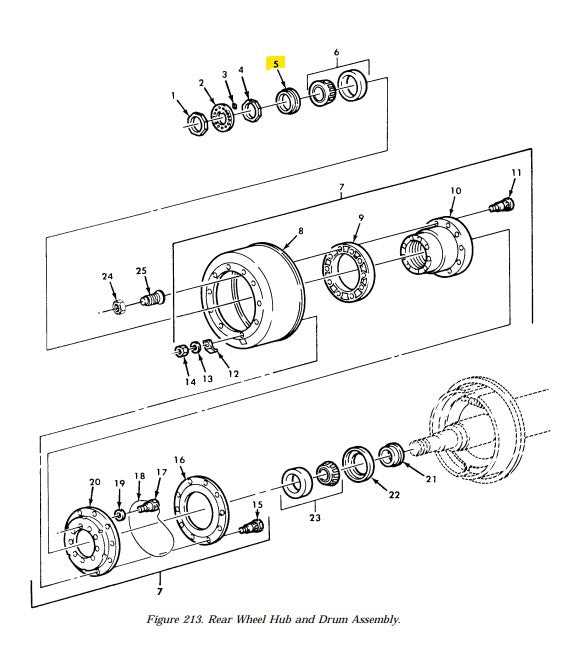
Understanding the layout and composition of a vehicle’s rotating assembly is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. This section provides a detailed look at the key components involved in the circular support mechanism and their roles in the overall system. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you can ensure proper maintenance and troubleshooting when necessary.
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hub | The central part where the axle connects, ensuring stability and rotation. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rim | Forms the outer edge, providing a foundation for the tire and overall structure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spokes | Connects the central hub to the outer edge, distributing weight evenly. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lugs | Fastening elements that secure the assembly to the vehicle’s structure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Hub Bearing | Facilitates smooth rotation by reducing friction between moving elements. |
| Mounting Flange | Serves as the attachment point for external elements, securing the system in place. |
| Spindle | Acts as the central axis, allowing the rotation to occur around a fixed point. |
| Grease Seal | Prevents debris and moisture from entering the system, maintaining the integrity of moving components. |
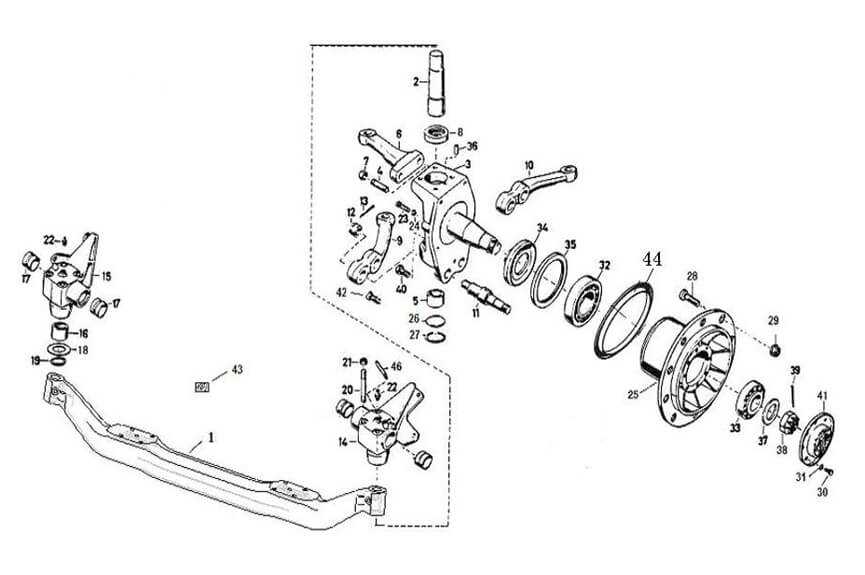
Axle Components Related to Wheels
The axle is a crucial structural element responsible for connecting and supporting rotating mechanisms. Various components ensure that the axle functions smoothly, offering stability and enabling proper movement. Each part works in unison to maintain performance and efficiency under diverse conditions.
Main Structural Elements

- Bearings: Critical for reducing friction and ensuring smooth rotation, these elements help the axle rotate freely without generating excessive heat or wear.
- Axle Shafts: These are the core elements that transmit motion from the drive system to the rotating elements, enabling controlled movement.
Supportive Mechanisms
- Seals: They prevent contaminants like dust or water from entering the axle assembly, ensuring longevity and minimizing maintenance.
- Mounting Brackets: These components secure the axle in place, providing stability and supporting the weight of the connected systems.
Role of Bearings in Wheel Assembly
Bearings play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of a vehicle’s rotation system. They minimize friction between moving components, allowing for efficient movement and reducing wear on critical elements. By supporting the load and maintaining stability, these components are essential for the longevity and safety of the entire system.
Types of Bearings
There are several types of bearings used, each with specific characteristics suited to different applications. Some common types include ball bearings, roller bearings, and tapered bearings, which offer various advantages in terms of load capacity and friction reduction.
Functionality and Maintenance
The performance of bearings is highly dependent on regular maintenance. Proper lubrication and timely replacement can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of the rotating system. Ensuring that bearings are inspected regularly helps maintain the overall efficiency of the machinery.
| Type of Bearing | Primary Use | Advantages | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Bearing | High-speed applications | Low friction, easy installation | |||||||||||||||
| Roller Bearing | Heavy load handling | Durable, supports radial loads |
| Symptom | Potential Issue | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding or rattling noise | Wear or damage to the rotation mechanism | Inspection and possible replacement |
| Vehicle pulling to one side | Uneven wear or damage to support components | Alignment check and repair |
| Excessive vibrations | Imbalance in the rotation system | Balancing or replacement of affected parts |
| Bulging or cracks | Structural damage or material fatigue | Replacement of damaged parts |