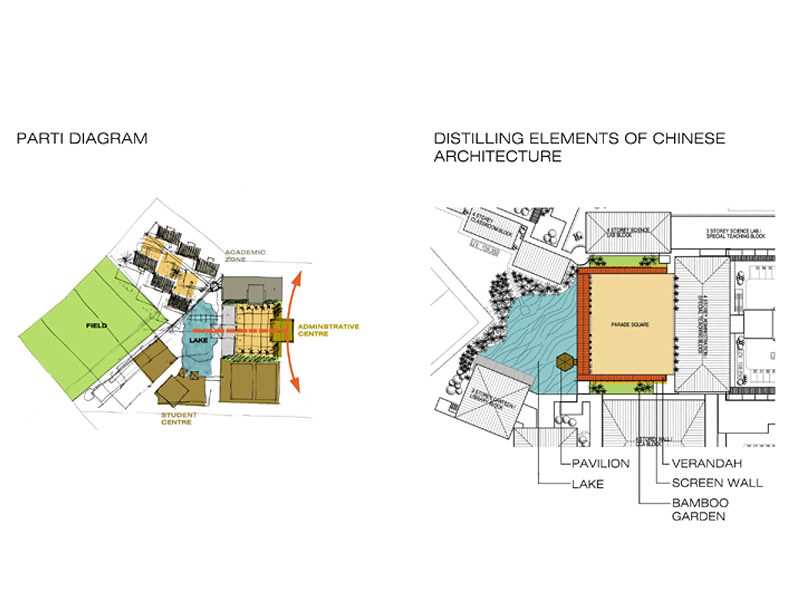
In the realm of architectural design, the visualization of ideas plays a crucial role in shaping the final outcome of a project. This representation serves as a foundational element, allowing architects to communicate complex concepts effectively. By breaking down a design into its essential components, creators can explore various possibilities and articulate their vision.
This approach not only aids in the initial stages of brainstorming but also fosters collaboration among team members. As ideas are mapped out, it becomes easier to identify key themes and relationships that inform the overall structure. The clarity provided by this method enhances the decision-making process and promotes innovative thinking.
Ultimately, the exploration of these visual tools leads to a deeper understanding of spatial dynamics and functionality. Engaging with this form of representation allows designers to delve into the interplay between form and purpose, ensuring that each aspect aligns harmoniously with the intended experience.
Understanding Parti Diagrams
This section explores the fundamental concepts of spatial representation in architectural design. By analyzing visual frameworks, we can appreciate how designers communicate their intentions and ideas effectively, often revealing the underlying structure of a project.
These visual representations serve as a powerful tool for architects to convey complex ideas succinctly. They break down intricate plans into easily digestible formats, allowing for better understanding and discussion among stakeholders.
| Key Elements | Description |
|---|---|
| Conceptual Clarity | Focus on essential ideas without extraneous details. |
| Spatial Relationships | Illustrate connections and organization within a design. |
| Visual Communication | Utilize symbols and sketches to convey meaning efficiently. |
By delving into these elements, one can gain insights into the ultimate purpose of such visualizations in the design process, enhancing both creativity and collaboration.
Historical Background of Parti Diagrams
The evolution of architectural representation has often mirrored the changing philosophies and methodologies within the discipline. A particular approach has gained prominence as a means of simplifying complex spatial concepts, allowing architects to convey essential ideas clearly and effectively. This technique emphasizes the fundamental elements of design, serving as a visual shorthand that encapsulates the core principles driving a project.
Tracing back to the early 20th century, this form of representation emerged as a response to the burgeoning modernist movement. Influential figures sought ways to distill their architectural intentions into accessible visuals, paving the way for new interpretations of space and form. This practice not only reflected contemporary ideas but also served as a bridge between abstract thought and practical application, influencing educational methodologies in architecture.
Over the decades, this mode of visual communication has been adapted and refined by various architects, each contributing unique perspectives that align with their individual design philosophies. Its usage in prominent projects has illustrated the versatility of this technique, making it an essential tool in the arsenal of modern architecture. As a result, it has become synonymous with the clarity and precision that characterize contemporary design practices.
In the latter part of the 20th century, the rise of digital tools further transformed how architects engage with this form of visual expression. Digital platforms have allowed for greater experimentation and innovation, enhancing the ability to convey complex ideas in a straightforward manner. As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, this particular representation remains a vital aspect of conveying design narratives, adapting to the needs of both practitioners and audiences alike.
Components of a Parti Diagram
The essence of a visual representation in architecture is to distill complex ideas into fundamental elements that convey the overall design intent. Understanding these foundational aspects allows for a clearer interpretation and communication of spatial relationships and functional organization.
- Spatial Organization: This element illustrates how different areas interact and relate to one another, highlighting the flow and connectivity.
- Mass and Volume: Representing the physical forms, this aspect emphasizes the scale and proportions of structures within the design.
- Circulation: A crucial component that maps out movement paths for users, ensuring accessibility and ease of navigation throughout the space.
- Hierarchy: This element demonstrates the importance and relationship of different spaces, guiding the viewer’s understanding of the design’s focus.
- Context: Addressing the surrounding environment, this aspect situates the design within its larger setting, considering both natural and built influences.
By analyzing these elements, one can better grasp the underlying principles that shape a coherent architectural vision.
Importance in Architectural Design
The role of conceptual representation in architecture cannot be overstated. It serves as a foundational element that influences the overall design process, guiding architects in visualizing spatial relationships and functional organization. By establishing a clear vision, these representations help streamline communication among stakeholders and foster a cohesive design approach.
Enhancing Clarity and Communication
Utilizing such representations allows architects to convey complex ideas in an accessible manner. This clarity not only aids in discussions with clients but also facilitates collaboration with engineers and contractors, ensuring that all parties are aligned on the project’s objectives.
Driving Creative Solutions
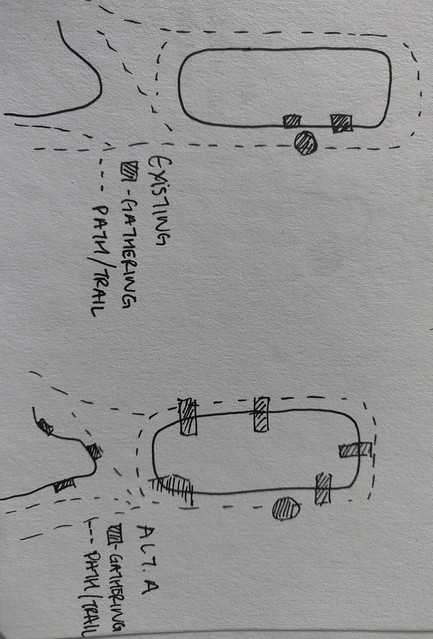
Moreover, these visual tools inspire innovative thinking by encouraging architects to explore various design possibilities. By distilling the essence of a project into simple forms, they can identify unique solutions that might otherwise remain obscured in more detailed planning stages.
How to Create a Parti Diagram
Understanding the early conceptual layout of a project is key to successful design. This type of visual representation provides a clear overview of the fundamental relationships between the main components of a design, helping to guide decisions throughout the process.
To create this kind of schematic, follow these steps:
- Identify the core elements that define the project. These can include physical spaces, functions, or key influences like sunlight or wind.
- Determine the main relationships between these components
Examples of Effective Parti Diagrams
Successful architectural concepts often rely on clear and simplified visual representations that communicate the core ideas of a design. These illustrations allow designers to express relationships between spaces, functions, and forms, helping to convey the main message without unnecessary complexity. They serve as a tool for clarity, aiding in the decision-making process and ensuring that the overall composition is easily understood by all involved parties.
A well-crafted sketch emphasizes the primary features of the design, focusing on essential connections between elements. In various cases, these visuals highlight circulation patterns, structural alignments, or the hierarchy of spaces within the project. By utilizing a minimalistic approach, these examples prioritize the central theme, making it stand out and ensuring that the design intent remains at the forefront.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working through the conceptual process of visualizing an architectural or design solution, there are frequent missteps that can lead to unclear or ineffective outcomes. Recognizing these common errors can help prevent misunderstandings and improve the overall clarity and functionality of the final product.
Overcomplication
A common issue is adding too many elements, which can confuse the intent or focus. Simplifying and focusing on the key aspects allows for a more streamlined and understandable representation.
Lack of Clarity
Another frequent mistake is failing to communicate the main objectives clearly. It’s important to emphasize the core elements, ensuring that the message is easily understood and not lost in unnecessary details.
Applications in Urban Planning
In the context of shaping modern cities, structured visual representations play a pivotal role in organizing and optimizing spatial layouts. These tools help planners to visualize relationships between spaces, paths, and key structures, aiding in decision-making processes that impact the functionality and aesthetics of urban environments. By simplifying complex design elements, they provide an effective way to explore potential developments and address urban challenges.
Visualizing Spatial Relationships
Urban planners use these techniques to illustrate the connections between buildings, open spaces, and transport networks. This visual approach allows for better coordination of infrastructure, ensuring harmony between different areas of the city and improving accessibility. It fosters a more sustainable urban growth by highlighting key factors such as density, flow, and zoning.
Parti Diagrams in Landscape Architecture In landscape design, creating a clear concept is essential for communicating the relationship between different elements in outdoor spaces. These simplified sketches capture the core vision, showcasing the overall structure and flow of a project. By focusing on the key features and how they interact with the surrounding environment, designers can present ideas in a way that is both accessible and visually compelling.
Key Visual Elements
Incorporating strategic lines, shapes, and textures helps emphasize the main components of an outdoor layout. These visual tools allow the designer to illustrate functional aspects, such as pathways, water features, and green areas, highlighting the connections between them. This approach ensures that the primary intent of the design is easy
Comparing Parti Diagrams and Site Plans
When exploring the initial concepts of architectural designs, it’s crucial to understand the distinction between the early conceptual sketches and detailed layout representations. Each serves a different purpose, shaping how a project is envisioned and ultimately built. One focuses on core ideas and spatial relationships, while the other dives into technical details that guide the construction phase.
Purpose and Approach
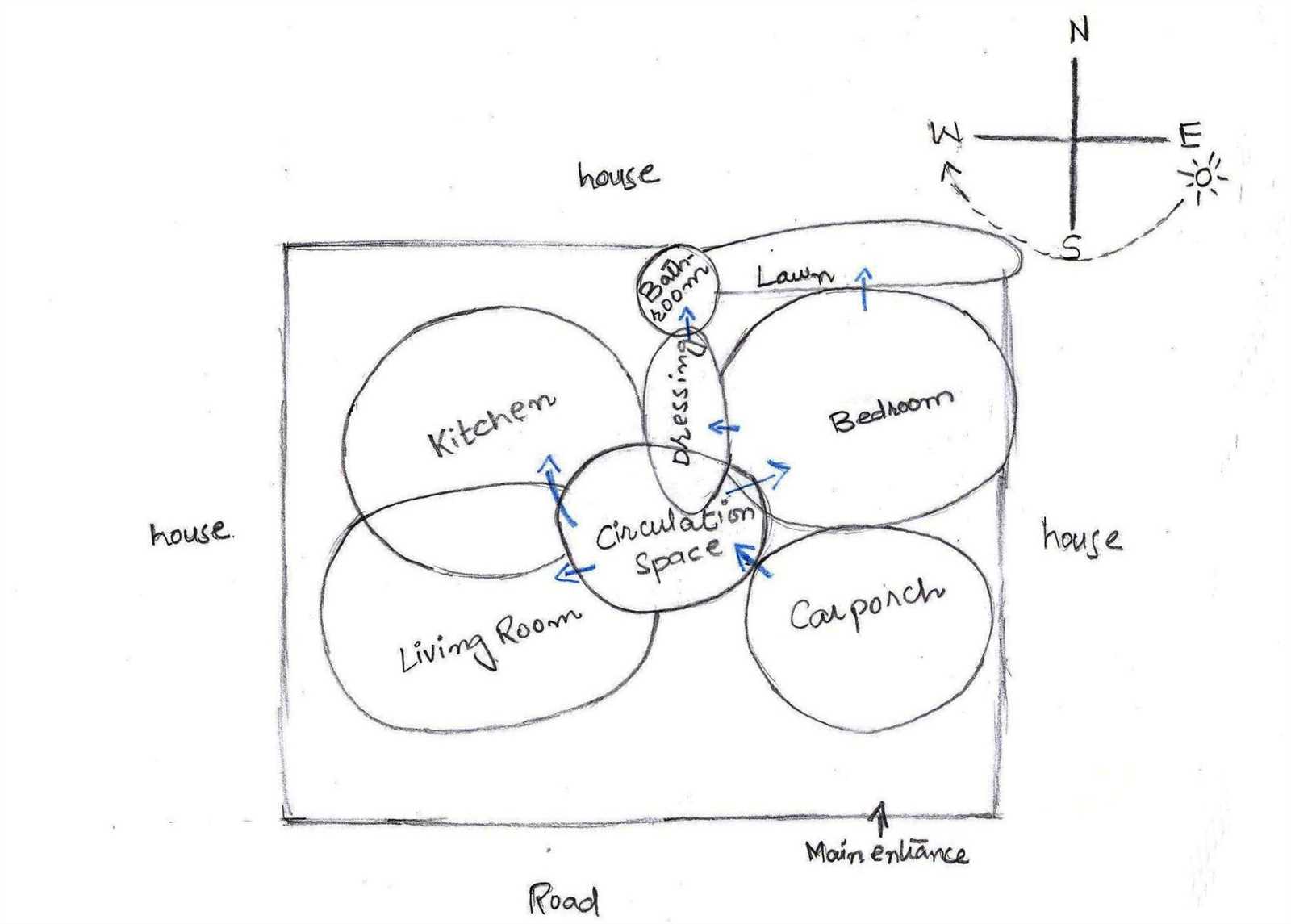
The first visual representation is often focused on conveying the essence of a structure, showing fundamental spatial organization and overall design intent. It emphasizes the key zones and their relationships. In contrast, the technical layout is more precise, detailing exact measurements, locations of elements, and adherence to regulatory standards. This second type ensures that the broader vision can be executed correctly in the physical environment.
Key Differences
Conceptual Drawing Interpreting Spatial Relationships Understanding how different elements are arranged within a space is essential for creating meaningful and functional designs. The placement of objects, their proximity, and how they relate to one another visually impact the way we perceive and interact with the environment. By analyzing these spatial connections, we can uncover the underlying logic behind various configurations.
Analyzing Proximity
The distance between objects can indicate relationships such as grouping or separation. Elements that are positioned closer to each other often suggest a connection or a shared purpose, while those placed further apart may signify distinction or independence.
- Close spacing can create a sense of unity or interaction.
- Wide spacing may emphasize individuality or contrast.
- Balanced proximity can help guide the observer’s attention.
Future Trends in Diagram Usage
As visualization tools continue to evolve, the way we represent complex ideas and systems is undergoing significant changes. Emerging technologies are driving new methods for creating clear, efficient, and dynamic visual representations. These advancements make it easier to process information quickly, enhancing decision-making processes and communication efficiency in various fields.
Interactivity is becoming a core feature, allowing users to engage with visual models in real-time, making them adaptable to specific needs or scenarios. This interactive capability fosters a deeper understanding of the data being presented.
Incorporating automation through AI is another major trend. Automated systems can now generate complex visual structures based on real-time data inputs, reducing human