Understanding the various elements that make up a cooling system is essential for maintaining efficiency and ensuring smooth operation. Each component plays a unique role, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the unit. Whether you’re dealing with maintenance, troubleshooting, or simply exploring the structure, a detailed breakdown of the system’s elements can be incredibly helpful.
In this section, we will delve into the key elements that form the foundation of these cooling units. By analyzing the core parts and their arrangements, you can gain a clearer understanding of how the system functions as a whole. This knowledge not only aids in repairs but also in the general upkeep, prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
By familiarizing yourself with the inner workings of such systems, you can make informed decisions when it comes to replacements or upgrades. Our detailed guide will offer insights into the primary components, shedding light on their specific functions and how they interact within the system.
Overview of Hoshizaki Ice Maker Components
The cooling appliance consists of various interconnected elements that ensure seamless production of chilled cubes. Understanding each element’s function can help in maintaining efficiency and addressing any technical issues. This section provides a detailed look at the key components found within these refrigeration units.
First, there is the cooling system, which is essential for maintaining the required temperatures. This includes a compressor, which circulates the refrigerant, and a condenser, where heat exchange occurs to ensure proper cooling. Additionally, the evaporator plays a crucial role by converting liquid into frozen cubes, completing the freezing process.
Another important aspect is the water distribution mechanism. This system manages the flow and distribution of water to the freezing unit, ensuring a consistent supply for the production process. Proper flow
Key Elements of Ice Maker Assembly
Understanding the essential components of a cooling appliance can greatly enhance its maintenance and performance. Each element plays a critical role in the overall operation, ensuring smooth production and reliable output. Familiarity with these components helps in troubleshooting and optimizing efficiency.
The core assembly typically includes a refrigeration system, which cools the internal environment, and a control mechanism that regulates operation. A compressor circulates refrigerant through the system, while an evaporator aids in cooling by absorbing heat. Additionally, a condenser expels unwanted warmth, maintaining the correct temperature within the unit.
Another vital aspect involves the water supply mechanism, which ensures a consistent flow and proper distribution. Valves, tubes, and pumps work together to manage the intake and movement of water throughout the system. Proper alignment and connection of these elements guarantee seamless performance and prevent common issues like leaks or blockages
Understanding the Ice Machine Mechanism
The process of generating frozen cubes involves a series of interconnected components working together seamlessly. The mechanism is designed to efficiently convert water into solid, chilled forms through a cycle of cooling, freezing, and harvesting.
The operation can be broken down into several key stages:
- Water Intake: The unit begins by drawing in a steady flow of liquid from a connected supply. This ensures that the system has a continuous source of fluid to transform.
- Cooling Process:
Identifying Common Replacement Parts
Understanding the essential components of cooling units can greatly aid in maintaining and repairing them. Various elements work together to ensure smooth operation, and over time, some may require substitution due to wear and tear. Recognizing which pieces need attention is key to prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
Commonly, the most replaced elements include motors, water valves, and condensers. Motors are crucial for driving the mechanical processes, and issues with them can cause disruptions. Water valves play a vital role in regulating the flow, and their malfunction could lead to performance inconsistencies. Condensers, responsible for heat exchange, often face problems related to blockages or inefficiencies, making them another frequent target for replacements.
Wiring and Electrical Connections Explained
Understanding the electrical setup is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and safety. Properly connecting the wiring not only helps maintain efficiency but also reduces the risk of electrical faults. This section will provide a clear overview of how to manage the electrical connections for equipment, including guidelines on essential components and configurations.
Key Components in Electrical Setup
Several essential elements are involved in the wiring system, each playing a specific role. These include power cables, control wires, and grounding. Proper arrangement of these components ensures smooth operation and prevents potential hazards. It is important to check the compatibility of the wires and connectors during the installation process.
Guidelines for Secure Connections
When connecting the
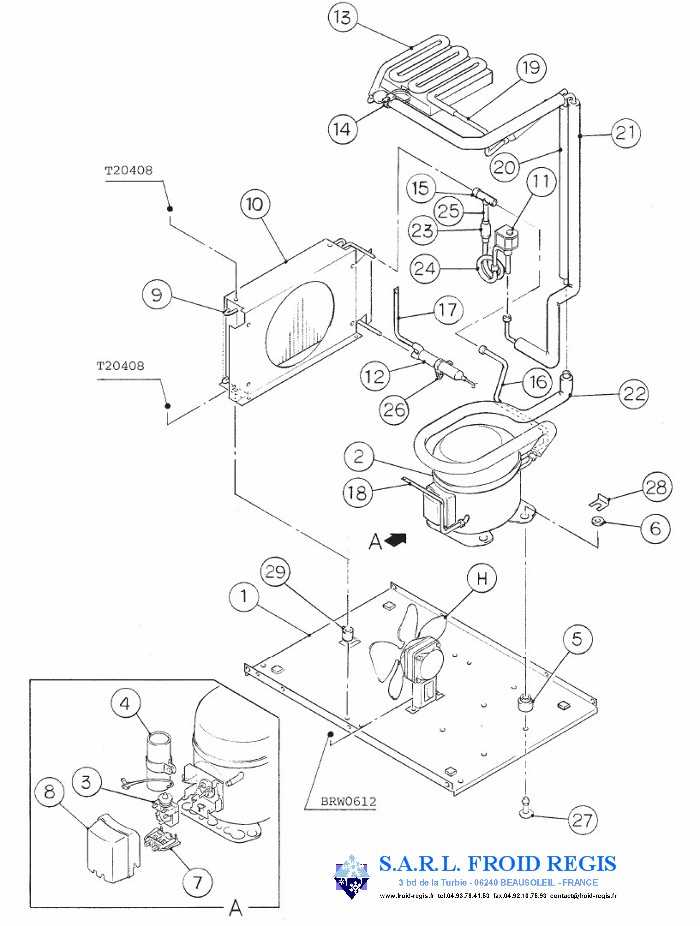
Cooling System Structure and Design
The efficiency and functionality of a refrigeration unit rely heavily on its cooling mechanism. A well-designed cooling system ensures optimal performance by effectively regulating temperature and enhancing the overall operational longevity of the device. Understanding its structure is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance, allowing users to appreciate how various components work together to achieve desired outcomes.
At the core of the cooling system is the evaporator, which absorbs heat from the surrounding environment. This process transforms the refrigerant from a liquid state into gas, effectively drawing heat away. Following this, the compressor plays a pivotal role by pressurizing the gaseous refrigerant, which raises its temperature and prepares it for condensation.
Once compressed, the refrigerant travels to the condenser, where it dissipates heat to the outside air, converting back into a liquid. The expansion valve then regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, maintaining the necessary pressure levels for efficient cooling. This cycle continues, forming a closed loop that is crucial for maintaining low temperatures.
In summary, a well-structured cooling system is fundamental to achieving effective refrigeration. Each component, from the evaporator to the expansion valve, plays a significant role in the seamless operation of the system, contributing to its reliability and efficiency.
Water Flow and Distribution Channels
Understanding the dynamics of fluid movement and its routing within refrigeration systems is crucial for optimal performance. Proper distribution mechanisms ensure that liquid is efficiently transported to various components, promoting effective cooling and freezing processes.
In these systems, water is channeled through a series of strategically designed pathways that facilitate uniform distribution. Channels and conduits are engineered to minimize blockages and maintain consistent flow, allowing for timely access to essential areas. The layout of these routes is critical, as it affects not only efficiency but also the overall lifespan of the unit.
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to keep the flow pathways clear of debris and buildup. By ensuring that these channels remain unobstructed, the system can function at peak efficiency, providing reliable cooling solutions without interruptions.
Compressor and Condenser Arrangement
The configuration of the compressor and condenser plays a vital role in the efficiency and performance of cooling units. Proper placement and integration of these components ensure optimal heat exchange and effective refrigerant flow, which are crucial for maintaining the desired operating conditions. Analyzing the layout allows for better understanding of how these elements work together to achieve effective thermal regulation.
The compressor is responsible for circulating the refrigerant and compressing it, increasing its pressure and temperature before it reaches the condenser. In contrast, the condenser dissipates heat from the refrigerant, allowing it to transition into a liquid state. The arrangement of these units is designed to facilitate efficient airflow and thermal transfer, which significantly impacts overall functionality. Ensuring adequate spacing and alignment enhances cooling performance and prolongs the lifespan of the equipment.
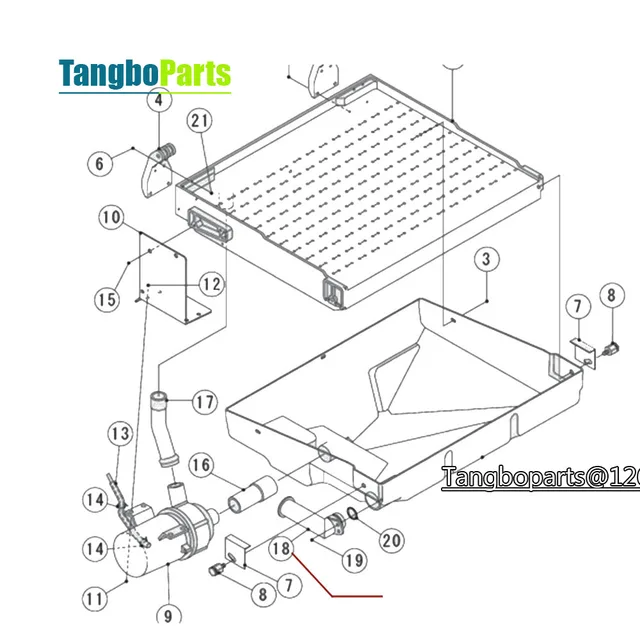
Exploded View of Machine Components
This section provides a detailed overview of the various elements within the equipment, showcasing how each component fits into the overall structure. Understanding the arrangement of these parts is essential for effective maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal functionality.
The following components are typically featured in the exploded view:
- Compressor: Responsible for circulating refrigerant and maintaining temperature.
- Condenser: Facilitates heat exchange, cooling the refrigerant before it enters the evaporator.
- Evaporator: Where the refrigerant absorbs heat, creating the cooling effect.
- Expansion Valve: Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, controlling the cooling cycle.
- Water Reservoir: Stores the water necessary for the freezing process.
- Control Panel: Allows users to adjust settings and monitor the machine’s performance.
- Fan: Helps circulate air, enhancing efficiency during operation.
Each component plays a vital role in the machine’s operation, and recognizing their locations and functions aids in troubleshooting and service procedures.
By examining the exploded view, users can gain insights into the relationships between various elements, fostering a deeper understanding of the machinery’s design and enhancing repair skills.
Control Panel and Sensor Layout
The control interface and sensor arrangement are crucial components in ensuring the efficient operation of refrigeration units. Understanding their configuration helps users effectively manage settings and monitor performance. This section explores the primary elements of the control system and the positioning of sensors that contribute to optimal functionality.
Key Components of the Control Interface
- Display Screen: Shows operational status and alerts.
- Buttons and Switches: Allow users to adjust settings and activate features.
- Indicators: Visual signals that inform about the system’s condition.
Sensor Placement and Functions
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor the internal temperature to maintain optimal conditions.
- Pressure Sensors: Ensure that the pressure levels are within the required range for effective operation.
- Level Sensors: Detect the quantity of the substance to prevent overflow or shortages.
Maintenance Tips for Ice Maker Parts
Proper upkeep of your freezing appliance is crucial for its longevity and efficiency. Regular attention to specific components can help prevent common issues and ensure smooth operation. Implementing a maintenance routine will not only enhance performance but also extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Regular Cleaning
Routine sanitation of the device is essential. Accumulated debris and mineral buildup can hinder functionality. Utilize a gentle cleanser to wipe down surfaces and components. Pay special attention to areas that are prone to moisture, as these are more likely to harbor bacteria. A clean machine operates more effectively and produces better results.
Component Inspections

Regularly examine individual elements for signs of wear and tear. Look for any cracks, frayed wires, or loose fittings. Addressing small issues promptly can prevent more significant failures. Additionally, ensure that all connections are secure to maintain optimal performance. Keeping a checklist can assist in monitoring the condition of each part over time.