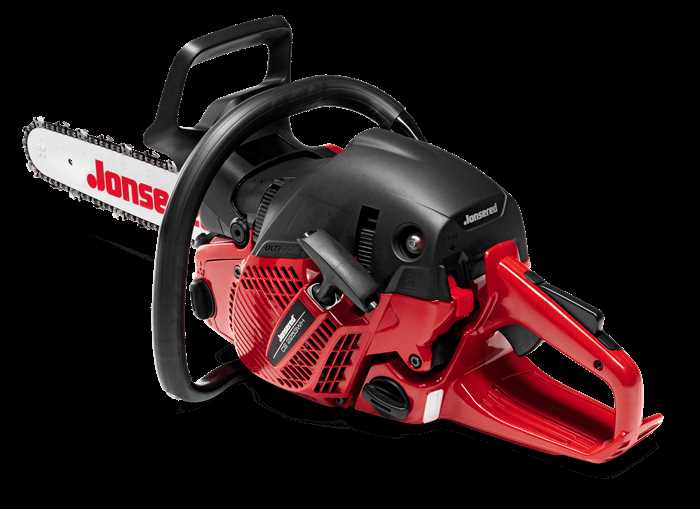

Understanding the essential elements and how they interact within a machine is crucial for its maintenance and repair. Each component has a specific role, and together, they ensure the optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. Identifying these elements and knowing their functions can make a significant difference in addressing technical issues effectively.
Exploring the internal mechanisms is vital for ensuring smooth operation. By familiarizing yourself with the different sections, you can prevent potential breakdowns and maintain the equipment’s functionality over time. Recognizing the key points of wear and tear helps in replacing or repairing components before major issues arise.
Maintenance routines are more efficient when the inner workings are fully understood. Knowing which parts require regular attention can save time and reduce the likelihood of unexpected malfunctions. A deeper dive into the structural makeup offers valuable insights for both professionals and hobbyists alike.
In this section, we will provide a detailed look at the essential components and their functionality. The aim is to offer a broad understanding of how each element contributes to the overall performance and longevity of the equipment. Each key part will be discussed to ensure that the reader gains a comprehensive perspective on maintenance and replacement needs.
- Introduction to essential elements and their roles
- Key features that influence performance
- Understanding the most common replacement parts
- Best practices for upkeep and ensuring longevity
- Frequent issues and troubleshooting strategies
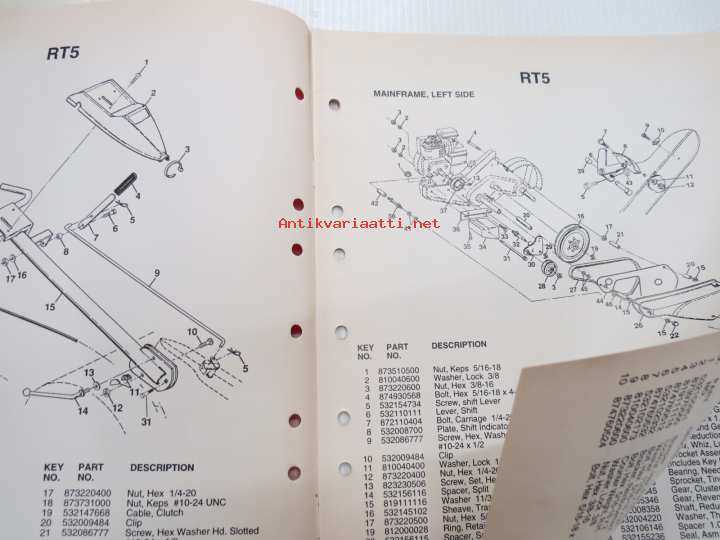
Main Components and Their Functions
The assembly of essential elements plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient performance of any mechanical tool. These components work together to provide stability, power, and precision, making the equipment reliable for various tasks.
Key Mechanical Elements
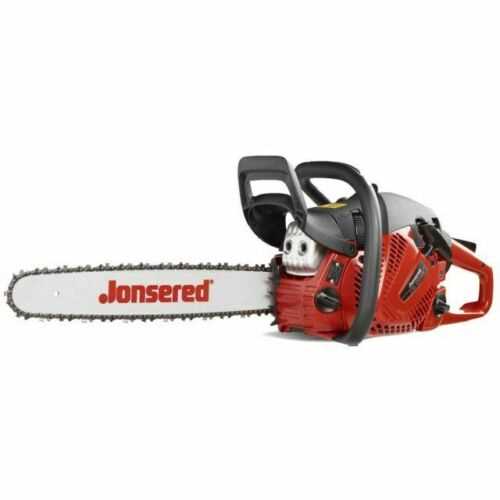

- Engine Unit: The core of the machine that powers all other functions, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Cutting Mechanism: This part is responsible for the primary operation, handling tasks like cutting or trimming with precision.
- Fuel System: Ensures proper fuel delivery to the engine, maintaining smooth operation and power output.
Supporting Features
- Handle Assembly: Designed to provide the user with control and stability while operating the equipment.
- Safety Features: Includes mechanisms that protect the operator and prevent
Engine Structure and Key Parts
The internal structure of the engine is composed of several essential components that work together to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding these elements can help in maintaining and repairing the machinery effectively. Below is a breakdown of the core elements that form the engine’s architecture.
Core Components
- Cylinder and Piston: The heart of the engine where combustion occurs, driving the piston to move and generate power.
- Crankshaft: Converts the piston’s linear motion into rotational energy, essential for transferring power to the drive mechanism.
- Connecting Rod: Links the piston to the crankshaft, allowing the conversion of motion from one form to another.
- Carburetor: Controls the air-fuel mixture, ensuring proper combustion within the cylinder.
- Ignition Coil: Converts the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to create a spark.
- Spark Plug: A vital component that delivers the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
- Flywheel: Contains magnets that, when spun, generate the electrical charge necessary for ignition.
Chainsaw Chain and Bar Assembly
The chain and bar of a chainsaw are essential components that work together to ensure efficient cutting performance. Proper alignment and maintenance of these parts contribute to the tool’s overall functionality, reducing wear and tear while enhancing safety during use. Understanding how the chain and bar interact can help users optimize their chainsaw’s longevity and performance.
Assembling the Chain

Begin by carefully positioning the chain along the bar, ensuring that the teeth face the correct direction. The drive links should fit securely into the guide bar groove, allowing for smooth movement when the chainsaw is in operation. It’s crucial to ensure proper tension in the chain to avoid unnecessary strain on the motor.
Installing the Bar
Once the chain is correctly positioned, secure the bar in place. The bar mount should align perfectly with the saw’s body, pro
Fuel System: Elements and Maintenance
The fuel system in modern chainsaws plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance. It consists of several components that work together to supply fuel efficiently to the engine. Proper care and timely maintenance of these elements can significantly extend the life of the tool and improve its operation.
Main Components: The key elements of the fuel system include the tank, filter, lines, and carburetor. Each part has a specific role in managing the flow and quality of fuel. Regular inspection and cleaning of the filter and lines are necessary to prevent blockages, which can cause reduced efficiency or malfunctions.
Maintenance Tips: It is essential to check for any wear or leaks in the system. Regularly replacing worn-out parts and cleaning the carburetor helps in maintaining smooth operation. Using high-quality fuel and following
Ignition System Breakdown
The ignition system plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of the engine. This section will explore the key elements that make up the system, focusing on the components involved in generating the necessary spark to ignite the fuel. Understanding how these parts work together can help with troubleshooting and maintaining optimal performance.
Key Components
Common Issues
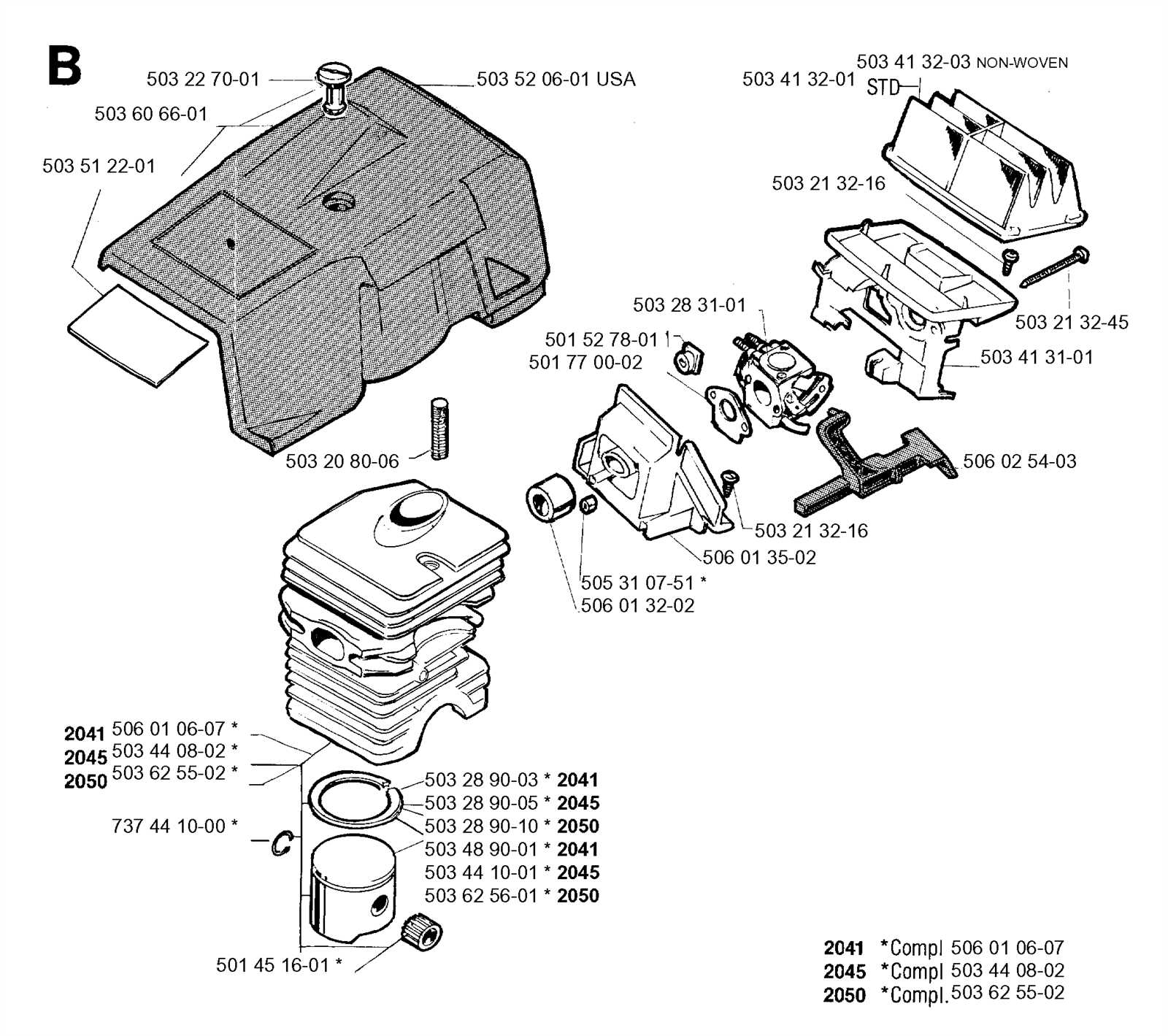
Air Filter and Carburetor Diagram
The air filter and carburetor are key components for ensuring proper air-fuel balance in machinery. Maintaining and understanding how these parts function together can significantly improve the performance of the equipment.
Main Components of the Air Filter
- Filter housing
- Filter element
- Mounting bracket
- Clamps and fasteners
Carburetor Mechanism Overview
- Throttle valve
- Float chamber
- Idle adjustment screw
- Fuel inlet
Regular inspection and cleaning of both the air filter and carburetor are crucial for maintaining optimal airflow and fuel delivery. Ensuring these components are free of debris will prevent issues such as engine
Handle and Vibration Dampening Parts
Proper ergonomics and reduced vibrations are essential for long-term usage of any equipment. The right components in the handle and vibration reduction system help ensure user comfort and safety during extended work periods.
- Handlebars – These are designed to offer a firm and comfortable grip, allowing the user to maintain control while operating the tool.
- Anti-vibration mounts – These components absorb excess vibrations, preventing them from reaching the user’s hands and arms, thus reducing fatigue.
- Grip covers – Often made from soft materials, they enhance comfort by minimizing direct contact with hard surfaces and absorbing small shocks.
- Mounting brackets – Securely hold the handlebars in place while ensuring the stability of the entire unit, contributing to overall
Exhaust and Muffler Layout
The exhaust system and muffler configuration play a crucial role in managing the engine’s emissions and noise levels. A well-designed layout helps to optimize engine performance by efficiently directing exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing harmful pollutants, and maintaining an acceptable noise level. Understanding the arrangement and components involved in this system is essential for ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the life of the engine.
Component Function Muffler Reduces noise and controls emissions by filtering exhaust ga Guide for Replacing Wearable Parts

Maintaining the efficiency and longevity of your equipment depends heavily on regular replacement of its consumable components. These elements are subject to wear due to frequent use and must be monitored for deterioration to ensure optimal performance. By addressing worn-out parts promptly, you can prevent larger mechanical failures and extend the overall lifespan of your tool.
Identifying Key Components
Before starting the replacement process, it’s essential to identify the components most likely to wear out. These typically include items like belts, seals, and chains, which are subject to constant stress. Regular inspections can help detect signs of wear, such as fraying, cracking, or excessive stretching.
Steps for
Safety Features and Mechanisms

Modern chainsaws come equipped with various safety systems to ensure the user is protected during operation. These features help prevent accidents and ensure that the equipment can be used effectively without compromising safety. Below are some key safety mechanisms commonly found in such tools.
Chain Brake System
One of the most important safety features is the chain brake. It is designed to stop the movement of the cutting chain in case of kickback or sudden movements. This reduces the risk of injury by halting the blade quickly.
- Inertia-activated brake: Engages automatically when rapid movement is detected.
- Manual brake: Can be activated by the operator when needed.
Hand Guard and Safety Switch
A protective hand guard and a safety switch are additional mechanisms that enhance user control and reduce the chance of accidental activation.
- Hand
Common Issues and Solutions

In the realm of machinery maintenance, users often encounter various challenges that can hinder performance. Understanding these common problems and their respective solutions is crucial for efficient operation and longevity.
1. Insufficient Power: One frequent issue is a lack of power during operation. This can be caused by factors such as a clogged air filter or fuel line. Regularly inspecting and cleaning these components can restore optimal functionality.
2. Overheating: Machines may experience overheating, which can lead to severe damage if not addressed. Ensuring proper lubrication and coolant levels can significantly reduce this risk. Additionally, checking for obstructions in the cooling system is advisable.
3. Unusual Noises: Unexplained noises can signal underlying problems, such as worn bearings or misaligned parts. Conducting routine inspections and replacing any damaged components promptly can help mitigate these issues.
4. Difficulty Starting: If starting becomes problematic, it may be due to battery issues or faulty ignition systems. Regular maintenance checks, including battery health assessments, can enhance reliability during start-up.
By being proactive and addressing these common concerns, users can maintain the efficiency and durability of their equipment.