Understanding the inner workings of a vehicle’s systems is essential for proper maintenance and repair. In this guide, we delve into the detailed structure of various mechanical and electrical elements. Each section covers essential units, providing clarity on how they interact within the overall framework of the car.
The purpose of this resource is to make it easier to identify the essential mechanisms that ensure the vehicle’s functionality. From the powertrain to the smaller components, we explore their placement and how they work together to deliver optimal performance.
This detailed breakdown serves as a valuable reference for anyone looking to gain insight into the organization of critical systems. Whether for repair, customization, or general understanding, this guide is designed to offer a cl
Understanding the Layout of Volvo S80 Components

When exploring the internal structure of this vehicle model, it is important to comprehend how various mechanical and electrical elements are positioned. Each section of the system is designed to work in harmony, ensuring optimal performance. Familiarizing oneself with the arrangement of these systems helps not only in maintenance but also in the enhancement of vehicle longevity.
Below is a table outlining some of the primary sections and their corresponding functions within the overall assembly:
| Component Group | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powertrain | Responsible for delivering power to the wheels, this includes engines, transmissions, and related systems. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chassis | Supports the vehicle’s structure and includes suspension, steering, and braking systems. |
| Component | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master Cylinder | Converts the force from the driver’s foot into hydraulic pressure, which activates the brakes. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brake Pads | Friction materials that press against the rotors to reduce wheel speed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brake Rotors | Discs that rotate with the wheels, providing a surface for the brake pads to apply pressure. |
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Facilitates heat exchange, allowing coolant to release heat into the atmosphere. |
| Water Pump | Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring efficient temperature regulation. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on temperature, allowing for optimal engine heating and cooling cycles. |
| Coolant Reservoir | Holds excess coolant and allows for expansion and contraction during temperature fluctuations. |
| Hoses | Transport coolant between components, maintaining fluid circulation and pressure. |
Configuration Overview
The arrangement of the thermal management components is critical for achieving desired performance. Proper alignment and connections between these elements ensure effective heat exchange and fluid flow. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to prevent leaks and ensure that the system operates smoothly.
Transmission Components and Operation
The transmission system is a crucial element in any vehicle, facilitating the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Its design allows for the seamless modulation of speed and torque, ensuring efficient performance across various driving conditions. Understanding the key components and their functions is essential for anyone interested in automotive mechanics.
Key Components
The transmission comprises several vital parts that work together to achieve optimal functionality. Each component plays a specific role in the overall system, contributing to the smooth operation of the vehicle.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Gearbox | Transforms engine speed into torque, allowing for different driving speeds. |
| Clutch | Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, enabling smooth gear shifts. |
| Torque Converter | Allows for a smooth transition of power and acts as a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission. |
| Shift Linkage | Connects the gear lever to the transmission, facilitating gear selection by the driver. |
Operational Mechanics
The operation of the transmission is characterized by its ability to change gears automatically or manually, depending on the system design. In automatic systems, sensors and hydraulic systems work in tandem to determine the optimal gear ratio based on driving conditions. In contrast, manual systems require driver input to select gears, offering a more engaged driving experience.
Exhaust System Structure and Design
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a vehicle. Its primary function is to channel harmful gases away from the engine and reduce emissions while enhancing engine performance. The design and arrangement of components within this system are essential for optimal functionality and compliance with environmental regulations.
Typically, the exhaust system consists of several key components:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipes.
- Catalytic Converter: Converts harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
- Resonator: Aids in noise reduction and helps improve the exhaust note by tuning the sound frequency of the exhaust gases.
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the exhaust system, ensuring a quieter ride.
- Exhaust Pipes: Transport exhaust gases from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, where they are expelled into the atmosphere.
Designing an efficient exhaust system involves considering various factors, such as:
- Material Selection: Durable materials are essential for withstanding high temperatures and corrosive environments.
- Pipe Diameter: Proper sizing is critical to maintain optimal exhaust flow and engine performance.
- Component Arrangement: Strategic placement of components minimizes back pressure and maximizes efficiency.
- Noise Control: Effective noise dampening techniques are necessary to enhance the driving experience.
Overall, a well-designed exhaust system contributes significantly to engine efficiency, performance, and environmental sustainability.
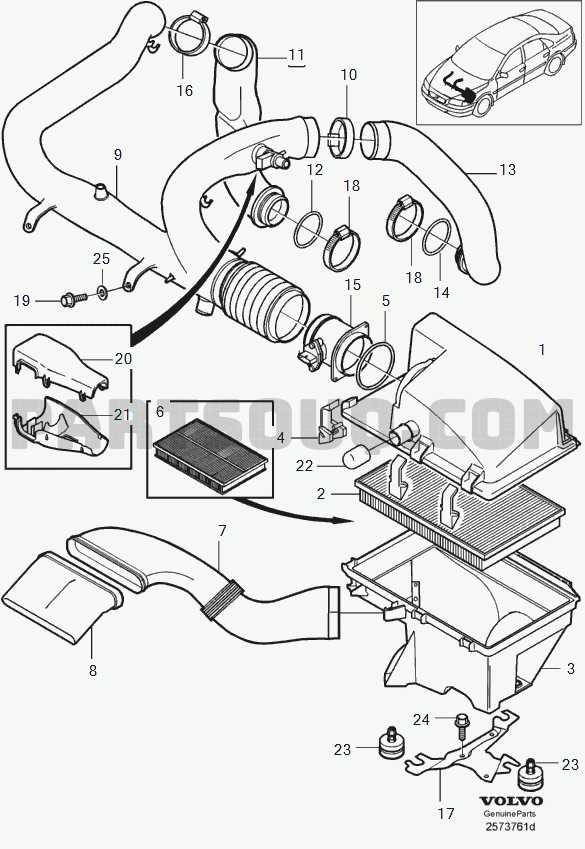
Fuel System Diagram and Functionality
The fuel system is a crucial component of any automobile, responsible for delivering the necessary fuel to the engine for optimal performance. Understanding its layout and operation helps in diagnosing issues and ensuring efficient functionality. This section will explore the key elements of the fuel delivery mechanism, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Key components of the fuel delivery system include:
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel until needed.
- Fuel Pump: Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel by removing impurities and contaminants before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel for efficient combustion within the engine cylinders.
- Fuel Lines: Transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors.
The operation of the fuel system can be summarized in the following steps:
- The fuel pump draws gasoline from the tank.
- As fuel travels through the lines, it passes through the fuel filter, where impurities are removed.
- The filtered fuel is then delivered to the injectors, where it is atomized and mixed with air.
- This mixture is drawn into the engine cylinders for combustion.
Regular maintenance of the fuel delivery components is essential to ensure reliable performance and prevent issues such as engine misfires or poor fuel efficiency. Identifying any signs of wear or damage in these components can help maintain the overall health of the vehicle.
Body Frame and Exterior Components
The structure and outer elements of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. This section explores the various components that comprise the framework and exterior design, ensuring durability, safety, and style. Understanding these features is essential for maintenance and enhancement of the overall performance and appearance of the automobile.
Key Structural Elements
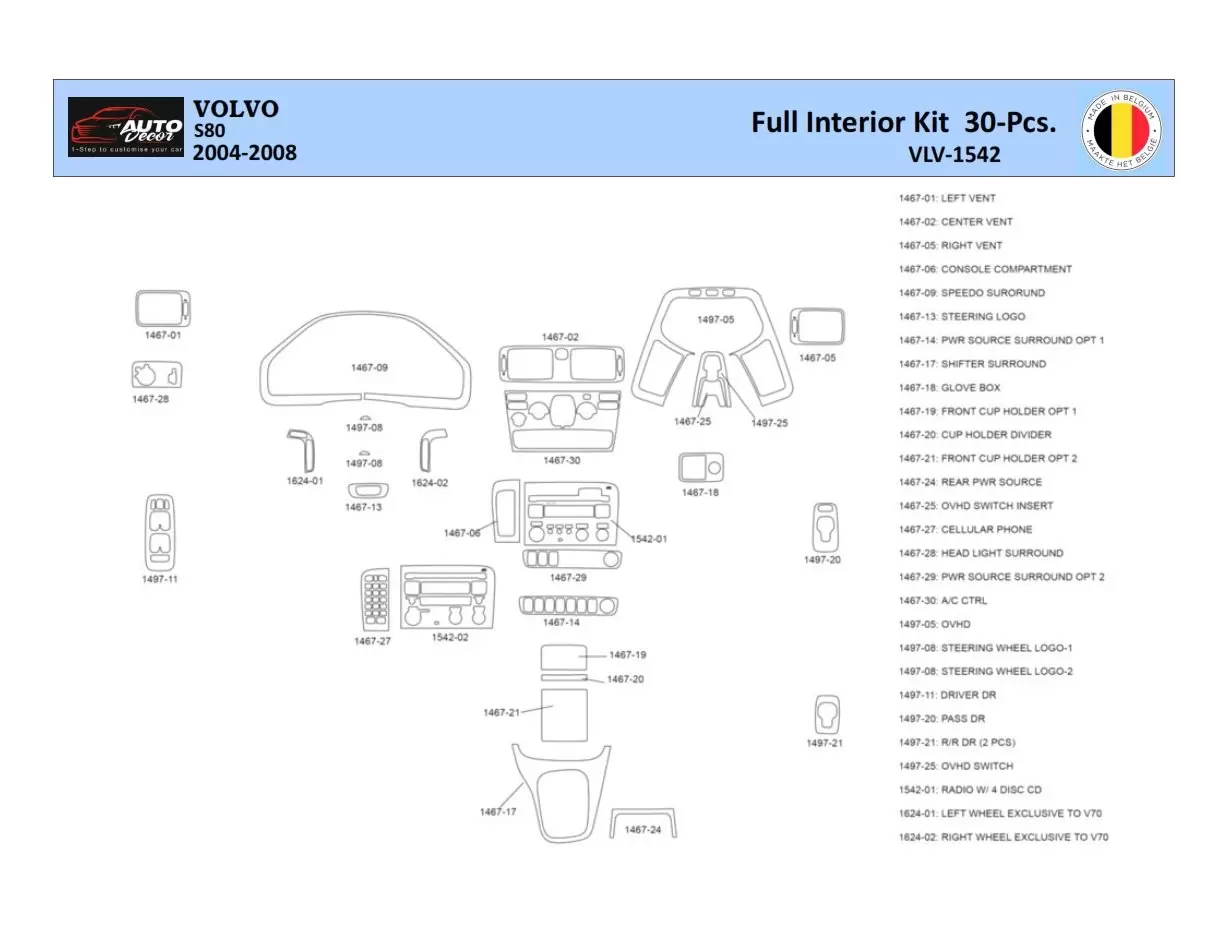
The main framework consists of several vital components that support the entire vehicle structure. These elements contribute to the integrity and rigidity of the automobile, providing protection to the occupants and internal systems. A detailed overview of these elements is presented in the table below.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Chassis | The main supporting frame that holds the entire vehicle together, providing strength and stability. |
| Fenders | The outer sections that cover the wheels, protecting them from debris and enhancing the vehicle’s aerodynamics. |
| Bumpers | Shock-absorbing structures designed to minimize damage during low-speed collisions, improving safety. |
| Hood | The hinged cover over the engine compartment, providing access for maintenance and protection from the elements. |
| Roof | The top part of the vehicle’s exterior, contributing to overall aerodynamics and passenger comfort. |
Exterior Finishing Touches
The outer design elements not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also improve functionality. Features such as lighting systems, mirrors, and trim details contribute to visibility, safety, and the overall style of the vehicle.
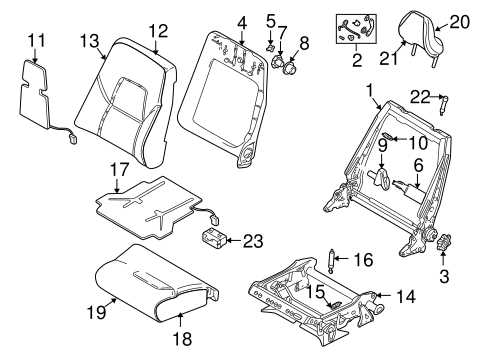
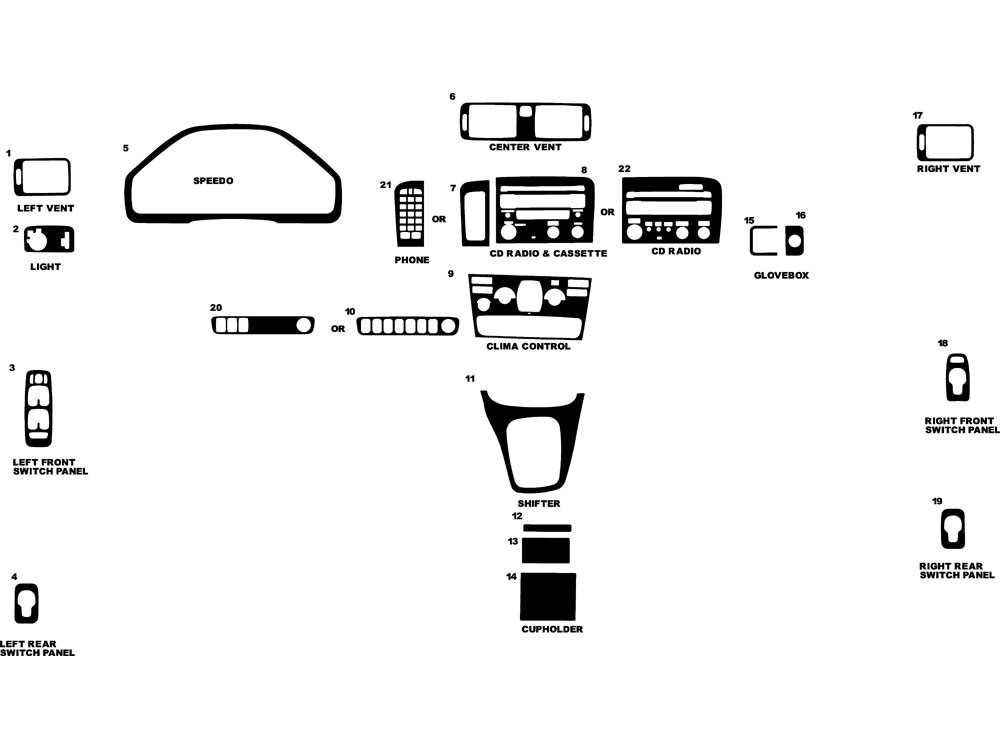
Interior Parts and Dashboard Configuration
The arrangement and components of the inner environment play a crucial role in both functionality and aesthetics. A well-structured interior enhances user experience, offering comfort and convenience while ensuring that essential controls and displays are within easy reach. Understanding the layout of these elements can significantly improve maintenance and customization efforts.
Key components of the interior typically include various panels, controls, and storage areas that contribute to the overall usability of the cabin. The dashboard serves as the central hub for instrument displays and driver controls, making it vital to comprehend its configuration.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Dashboard | The main panel that houses the speedometer, fuel gauge, and other essential instruments. |
| Center Console | Area located between the front seats, typically containing controls for the audio system and climate settings. |
| Infotainment System | Multimedia interface for navigation, audio playback, and communication features. |
| Steering Wheel | Control device that allows the driver to steer and often includes mounted controls for audio and cruise settings. |
| Door Panels | Interior sides of the doors, which can include armrests, storage compartments, and window controls. |
| Seats | Provide comfort and support for occupants, often featuring adjustable mechanisms and upholstery options. |
Grasping the configuration of these interior elements is essential for effective upkeep and customization, allowing for a more tailored driving experience.