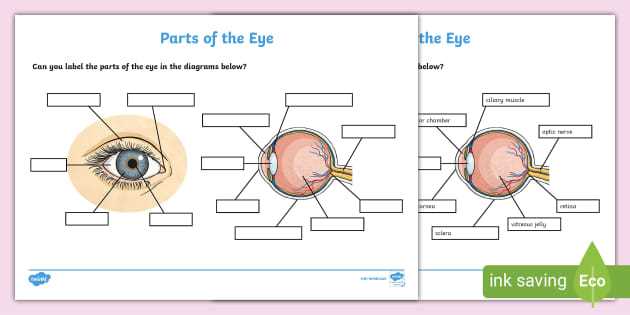
In the quest to comprehend how we perceive the world, it is essential to explore the intricate structures that contribute to our visual experiences. Each element plays a vital role in processing light and translating it into images that we can recognize and interpret. This exploration reveals the complexity of our visual system, highlighting how various structures work in harmony to enable sight.
From the outer layers that protect and filter light to the inner mechanisms responsible for translating visual information, the arrangement of these components is both fascinating and crucial. By examining these elements, one can appreciate the sophisticated design of the visual apparatus and its remarkable ability to adapt to different environments and conditions.
Gaining insight into this system not only enhances our understanding of vision but also underscores the importance of maintaining eye health. Awareness of how these various structures function can lead to better care and appreciation for our sensory capabilities, ensuring that we continue to experience the beauty of the world around us.
Understanding Eye Anatomy
The intricate structure of vision organs plays a crucial role in how we perceive the world around us. Each component contributes to the overall functionality, enabling the reception and processing of light to form clear images. By exploring the various elements involved, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and precision of this sensory system.
Components and Their Functions
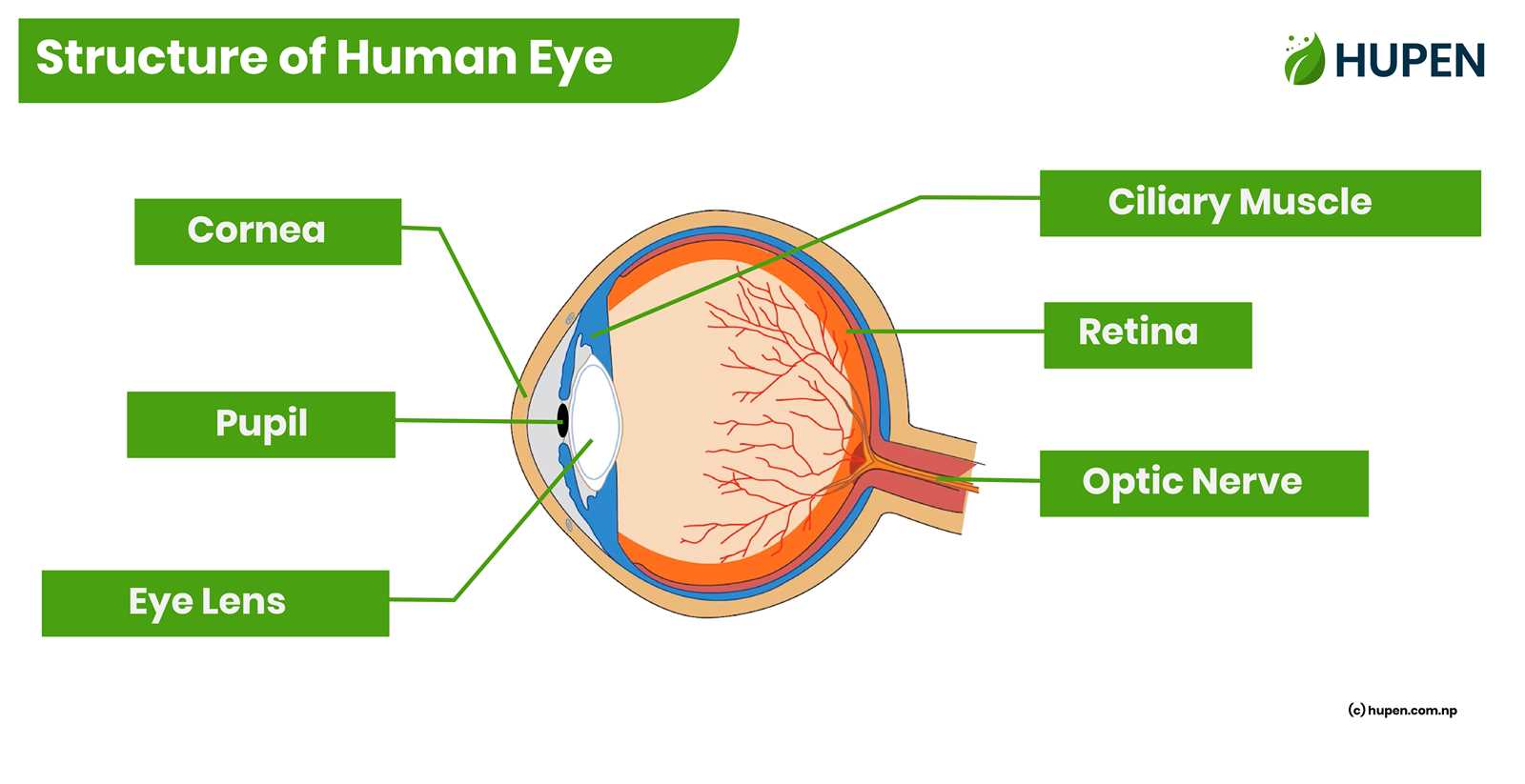
The major components include the outer covering, which protects and shapes the structure, along with various internal elements that focus light and transmit signals to the brain. These internal structures work harmoniously to ensure optimal vision, adjusting for distance and brightness, and allowing for detailed color perception.
Importance of Understanding
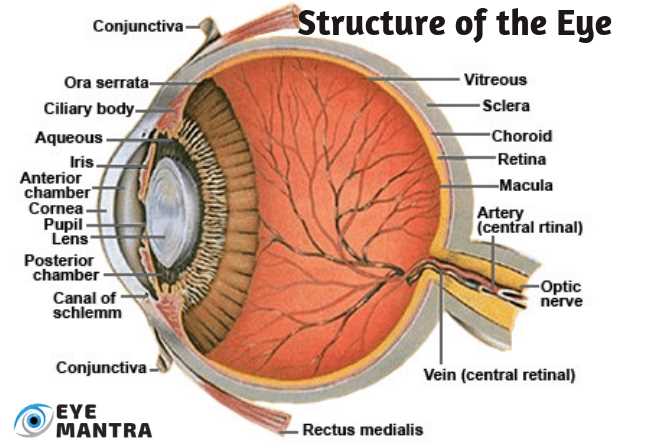
A comprehensive knowledge of these anatomical features not only enhances awareness of how vision functions but also emphasizes the significance of maintaining eye health. Conditions affecting any of these structures can lead to impaired vision or other complications, highlighting the need for regular check-ups and proper care.
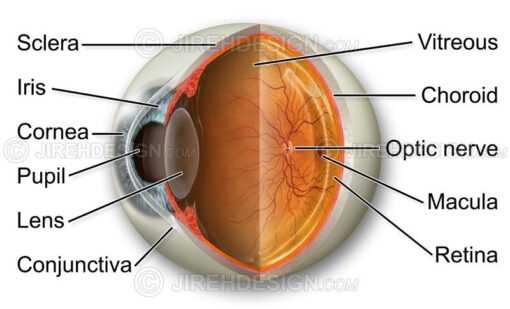
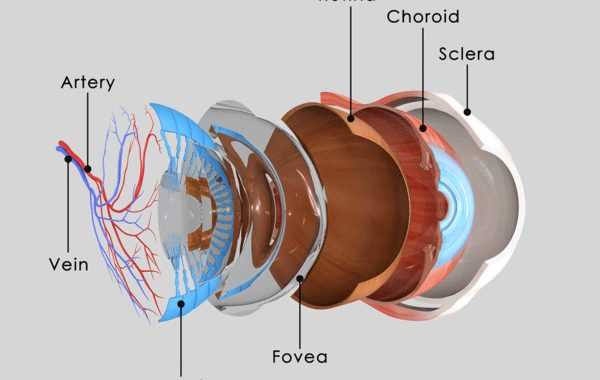
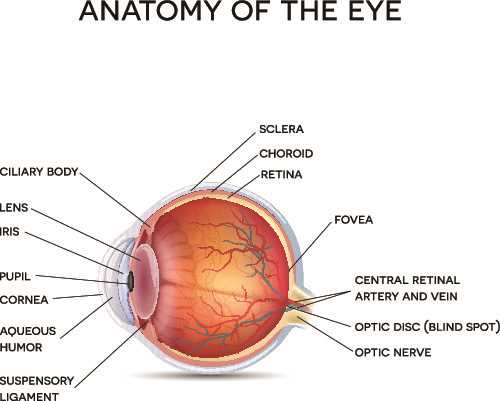
Components of the Human Eye
The human visual system comprises several intricate structures that work together to facilitate vision. Each component plays a vital role in the process of capturing and processing light, enabling us to perceive the world around us.
Key structures include:
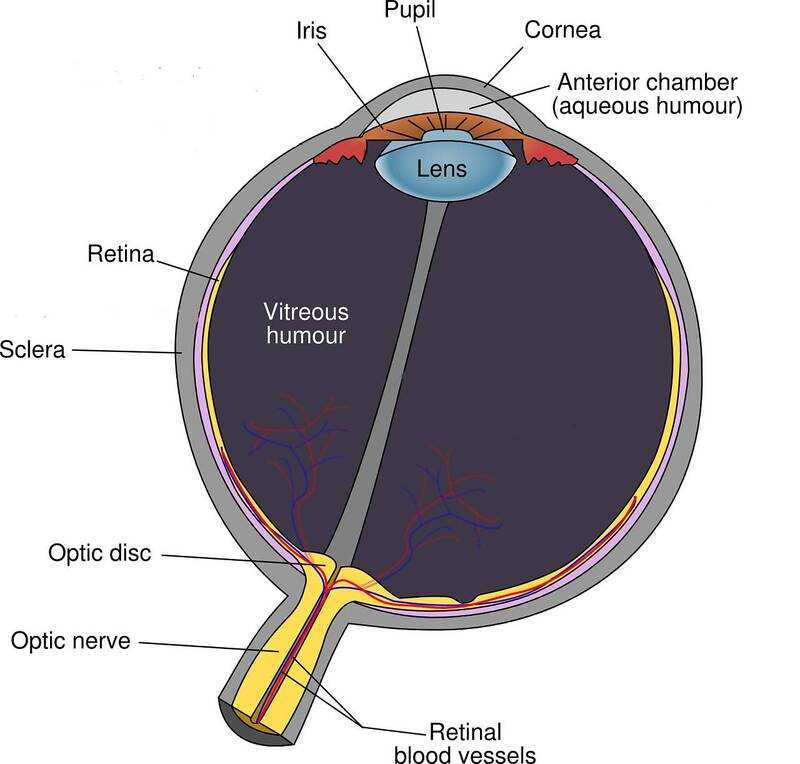
- Cornea: The transparent outer layer that helps focus incoming light.
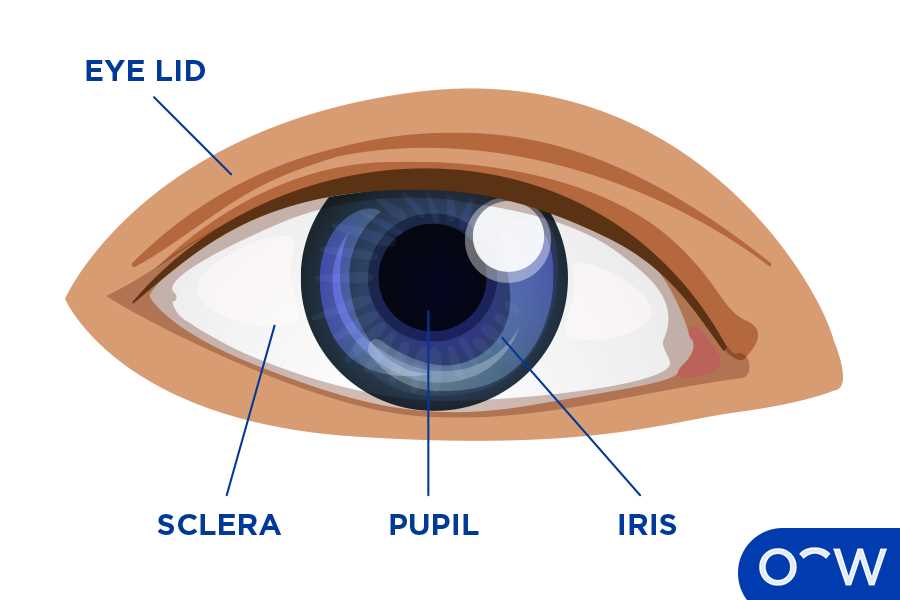
- Iris: The colored part that regulates the amount of light entering the chamber.
- Pupil: The opening at the center of the iris that adjusts size based on light intensity.
- Lens: A flexible structure that further refines the focus of light onto the retina.
- Retina: The inner lining that contains photoreceptor cells, converting light into neural signals.
- Optic Nerve: The pathway that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
Understanding these components is essential for grasping how vision functions and the complexity of the visual system.
Functions of Each Eye Part
The intricate structure of vision mechanisms enables the perception of the surrounding world. Each component plays a vital role in processing light and creating clear images. Understanding the specific responsibilities of these elements can enhance our appreciation for how we see and interpret our environment.
Cornea and Lens
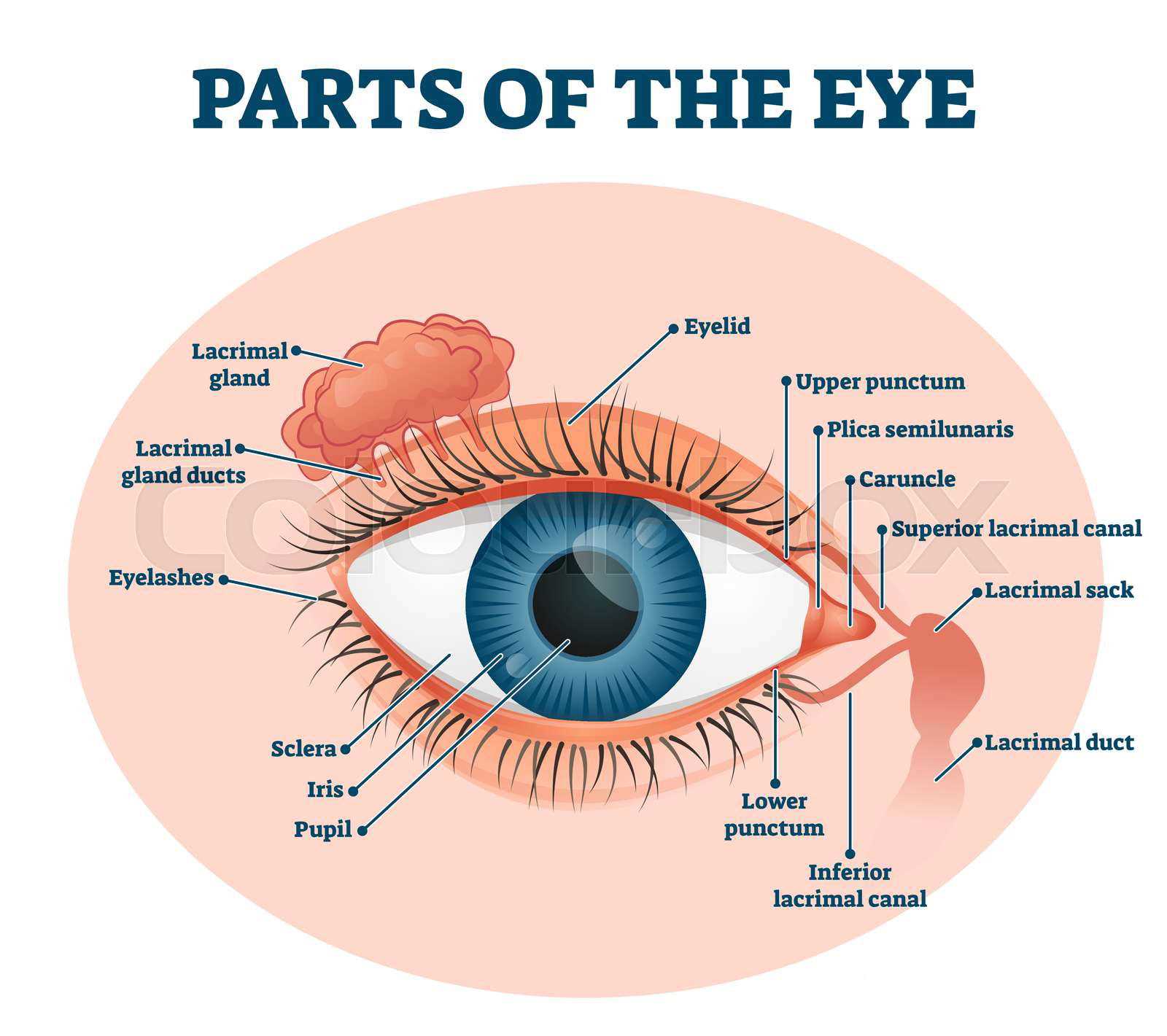
The cornea acts as the initial barrier, providing protection and helping to focus incoming light onto the retina. Its curved shape refracts light, ensuring that images are sharply focused. The lens further fine-tunes this focus, adjusting its shape through a process known as accommodation to help us see clearly at varying distances.
Retina and Optic Nerve
The retina is a light-sensitive layer that converts light into neural signals. It contains photoreceptors that respond to different wavelengths, allowing us to perceive colors. These signals are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as visual images, enabling us to understand what we see.
How Light Interacts with Eyes
The interaction of light with our visual system is a complex process that enables us to perceive the world around us. When light travels through the environment, it encounters various structures that play crucial roles in capturing and interpreting visual information. This section explores the mechanisms through which illumination affects our perception and the various factors influencing this interaction.
Refraction and Focus
As light enters the visual system, it undergoes a process known as refraction. This bending of light occurs at different interfaces, allowing it to converge on sensitive receptors. Proper focusing is essential for clear vision, and any distortion in this process can lead to visual impairments.
Color Perception
The spectrum of visible light comprises various wavelengths, each corresponding to different hues. Our ability to perceive colors is a result of how different structures detect and respond to specific wavelengths. Color vision is fundamental to our experience, influencing everything from art to navigation in our daily lives.
Common Eye Disorders Explained
Understanding various conditions that affect vision is essential for maintaining overall ocular health. These ailments can range from mild inconveniences to serious issues that may lead to impaired sight. Recognizing symptoms early can significantly enhance treatment outcomes and preserve clarity of vision.
Refractive Errors

Refractive errors are among the most prevalent vision disorders. They occur when the shape of the cornea or lens prevents light from focusing directly on the retina. Common types include myopia (nearsightedness), where distant objects appear blurry; hyperopia (farsightedness), where close objects are difficult to see; and astigmatism, which results in distorted or blurred vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea.
Cataracts
Cataracts develop when the lens becomes clouded, leading to decreased vision quality. This condition is often age-related and can result in symptoms such as blurred vision, glare from lights, and difficulty seeing at night. Timely intervention through surgical procedures can restore clarity and improve quality of life for those affected.
Importance of Eye Health
Maintaining the well-being of our visual system is crucial for overall quality of life. Healthy vision enables individuals to engage fully in daily activities, work, and leisure pursuits. Regular care and attention to this vital sense can prevent numerous issues and enhance life experiences.
Prevention of Common Disorders
Proactive measures play a significant role in averting common ailments that can affect sight. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help identify potential problems early. Early detection often leads to more effective treatments, thereby preserving functionality.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Adequate attention to visual well-being not only boosts individual comfort but also enriches social interactions and emotional health. Being able to see clearly fosters confidence and independence, allowing for participation in various activities and experiences.
In conclusion, prioritizing the health of the visual system is essential for a fulfilling life. By adopting preventative strategies and seeking timely care, individuals can safeguard their perception and overall health.
Vision Changes with Age
As individuals progress through life, various transformations occur in their ability to perceive the world. These alterations are a natural part of aging and can significantly influence daily experiences. Understanding these shifts is essential for adapting to new challenges and maintaining optimal clarity.
With advancing years, common issues such as decreased sharpness, diminished color perception, and heightened sensitivity to glare can arise. These factors may lead to a sense of frustration or confusion, particularly in low-light conditions or during activities that require fine detail.
Additionally, the gradual hardening of the lens can result in a condition known as presbyopia, which affects the ability to focus on nearby objects. Regular check-ups become increasingly vital as changes progress, allowing for timely interventions, whether through corrective lenses or other aids.
Staying informed about these developments enables individuals to make proactive choices regarding their vision health. Engaging in activities that promote visual wellness and seeking professional guidance can help mitigate some of the challenges associated with aging.
Embracing these changes with knowledge and preparation can enhance the quality of life, ensuring that the world remains vivid and accessible.
How Eyes Communicate with Brain

The interaction between visual organs and the central nervous system is a complex process that facilitates the perception of our surroundings. This communication pathway is essential for interpreting visual stimuli and responding to the environment.
When light enters the visual organs, it is transformed into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain. This process involves several steps:
- Light enters through the transparent surface.
- The light is focused onto a light-sensitive layer.
- Photoreceptors convert the light into electrical impulses.
- These impulses are sent through specific neural pathways to the brain.
Upon reaching the brain, these signals undergo further processing:
- The signals are analyzed for color, brightness, and motion.
- Different regions of the brain are activated to interpret various aspects of the visual information.
- This information is then integrated with other sensory inputs to form a coherent understanding of the environment.
This intricate network enables individuals to navigate their surroundings effectively, respond to visual cues, and engage with the world around them.
Protective Mechanisms of the Eye
The human visual organ is equipped with a variety of protective features designed to safeguard its delicate structures from potential harm. These mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining optimal functionality and health.
One of the primary defenses includes the outer coverings, which serve as a barrier against dust, debris, and harmful microorganisms. Additionally, a specialized fluid provides lubrication and nourishment, helping to prevent dryness and irritation.
Moreover, blinking serves as an essential reflex that not only protects against physical injury but also helps to keep the surface moist and clear. The eyelids, in conjunction with lashes, provide an additional layer of protection by filtering out larger particles.
Furthermore, various glands contribute to the production of tears, which play a significant role in cleaning and nourishing the visual organ. These tears help wash away any irritants that may come into contact with the surface.
In summary, the protective mechanisms are vital for ensuring the safety and well-being of the visual system, enabling it to function effectively in various environments.
Innovations in Eye Care Technology
Recent advancements in vision health have significantly transformed the way professionals diagnose and treat various conditions. Cutting-edge technologies are enabling earlier detection, improved accuracy, and more effective treatments, leading to enhanced patient outcomes. These developments are paving the way for personalized approaches that cater to individual needs and preferences.
One notable advancement is the introduction of smart contact lenses, which integrate sensors to monitor ocular health in real-time. These lenses can track vital signs and provide valuable data to both patients and healthcare providers, facilitating proactive management of conditions.
Additionally, the advent of telemedicine has revolutionized access to vision care. Patients can now consult specialists remotely, allowing for timely assessments without the need for in-person visits. This approach not only saves time but also ensures that individuals in underserved areas receive essential care.
Another exciting development is the use of artificial intelligence in diagnostic processes. AI algorithms can analyze images and data with remarkable precision, assisting practitioners in identifying diseases earlier than ever before. This technology enhances decision-making and ensures that treatment plans are tailored to each patient’s specific situation.
Moreover, innovations in surgical techniques have improved recovery times and outcomes. Procedures that once required extended hospital stays can now often be performed on an outpatient basis, minimizing disruption to patients’ lives. These
Comparative Eye Anatomy in Animals
The visual systems of various species exhibit remarkable diversity, shaped by their unique environments and lifestyles. By examining the anatomical structures responsible for vision across different animals, we gain insights into how evolution has influenced sensory adaptation. Understanding these variations allows for a deeper appreciation of the complexities involved in the perception of the world around us.
Structural Differences
Different organisms possess distinct configurations in their visual apparatus, tailored to their ecological niches. For example, some creatures, like eagles, have a highly developed system that enhances their ability to see distant objects with incredible clarity. In contrast, nocturnal animals often feature larger lenses and specialized retinal cells to maximize light capture in low-light conditions. These adaptations highlight the role of anatomical variation in optimizing visual performance.
Functional Adaptations
Functionality also varies significantly among species. Aquatic animals, such as fish, have adaptations that allow them to perceive light underwater, where conditions differ markedly from terrestrial environments. On the other hand, insects possess compound structures that enable them to detect movement and changes in light with remarkable sensitivity. These functional differences underscore the intricate relationship between form and function in the realm of vision.
Role of Eye in Perception
The visual organ plays a crucial role in how we interpret and understand the world around us. It acts as a gateway for light to enter, enabling the brain to process and make sense of the information received. This remarkable structure transforms light waves into signals, allowing us to perceive shapes, colors, and movements, which are essential for our daily interactions and experiences.
Through the intricate mechanisms of focus and depth, the visual system helps us navigate our environment, recognize faces, and appreciate art and beauty. The ability to perceive accurately is fundamental to communication, safety, and enjoyment of life. Understanding the significance of this organ reveals its vital contribution to our overall cognitive functions and emotional responses.
Furthermore, the connection between the visual system and the brain illustrates how perception is not merely a passive process but an active interpretation of sensory input. This interaction is essential for developing skills such as reading and learning, making it a pivotal component of human development and interaction. Ultimately, the significance of this organ extends far beyond mere sight; it is integral to our consciousness and experience of reality.