Adjusts and maintains
How a Thermostat Regulates Heat

The thermostat plays a crucial role in maintaining consistent warmth by controlling the overall temperature of the system. Its primary function is to sense temperature changes in the surrounding environment and adjust accordingly to keep the space at a desired comfort level. Through internal mechanisms, the device ensures that heat output is either increased or decreased based on the preset preferences.
Temperature Sensing and Feedback

Thermostats are equipped with sensors that continuously monitor the surrounding air. When the air cools below a set threshold, the system receives a signal to activate. Similarly, when the environment reaches the chosen warmth, the signal cuts off the flow, preventing overheating.
Mechanisms of Control
Inside the thermostat, mechanical or electronic components manage the temperature regulation process. Based on the feedback from sensors, these components interact with control elements to either initiate or halt the flow of warmth, ensuring an effi
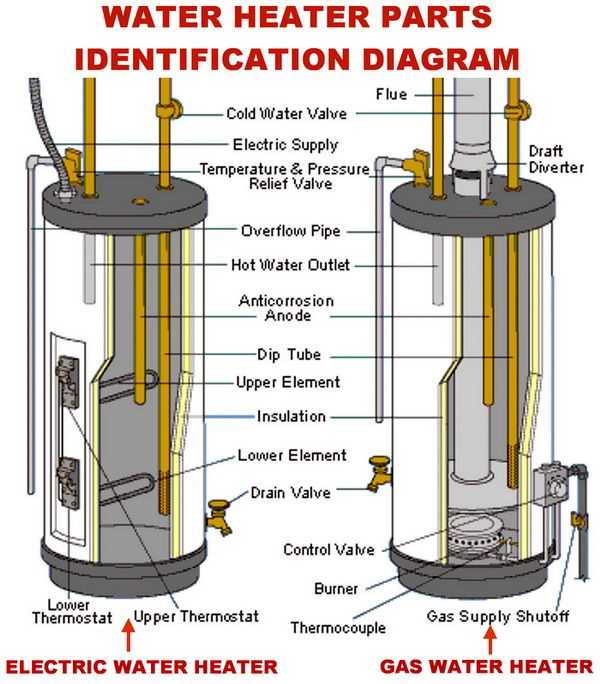
Identifying the Heating Element

The core component responsible for generating warmth is crucial to the overall function of the system. This part plays a vital role in converting energy into the desired thermal output, making it one of the most important aspects to recognize and understand within the unit.
Below is a simplified breakdown to help you visually locate and understand the arrangement:
| Component |
Description |
| Main conductor |
A metallic coil that transforms energy into heat when activated. |
| Support structure |
The framework that holds the conductor in place, ensuring stability and safety during operation. |
| Temperature control linkage |
A mechanism that interacts with the conductor to regulate thermal levels within the system. |
Wiring Setup for Efficient Operation
Proper connection and layout of the control system are essential for ensuring reliable functionality and optimal energy use. By aligning the various components in an efficient manner, the system can respond effectively to changes in temperature, providing consistent comfort.
Key Elements to Consider

- Thermostat Placement: Ensure the control unit is installed in a central location, away from direct heat sources or cold drafts, to maintain accurate readings.
- Circuit Pathways: Keep the flow of power unobstructed, using appropriately rated wiring for safe and stable performance.
- Grounding: Connect the protective conductor to safeguard the system against electrical faults, enhancing overall safety.
Connection Sequence
- Identify the main control switch and connect it according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Ensure that all connectors are secure, avoiding loose ends that could cause malfunctions.
Common Issues with Heating Systems
Heating systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable environment in homes and buildings. However, they can encounter various challenges that hinder their efficiency and effectiveness. Understanding these common issues is crucial for timely intervention and proper maintenance.
One prevalent problem is inadequate warmth. This can arise from various factors, including thermostat malfunctions or poor insulation, which prevent the system from reaching the desired temperature. Additionally, noisy operations may indicate underlying mechanical issues, such as loose components or air trapped in the system.
Another frequent concern is increased energy consumption. When systems operate inefficiently, energy bills can spike unexpectedly, often signaling the need for repairs or replacements. Regular maintenance checks can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Lastly, leaks or moisture accumulation can lead to serious damage over time. It’s important to monitor any signs of water buildup, which may indicate leaks in the system. Addressing these problems promptly can help prevent further complications and extend the lifespan of the heating infrastructure.
The Role of Heat Sensors
Heat sensors play a crucial role in regulating temperature within a thermal system. These devices are designed to detect and respond to variations in warmth, ensuring optimal performance and energy efficiency. By providing real-time feedback, they help maintain a comfortable environment while preventing overheating and potential damage to the system.
In addition to enhancing safety, these sensors contribute to energy conservation. When the detected warmth reaches a predetermined threshold, the sensors can signal the system to adjust its operation, either reducing output or shutting down completely. This responsiveness not only prolongs the lifespan of the equipment but also minimizes energy waste.
Furthermore, the integration of heat sensors facilitates automated control, allowing for the implementation of smart technology. With the ability to connect to home automation systems, these sensors can optimize heating based on occupancy and personal preferences. This advanced capability enhances user convenience and contributes to a more sustainable living space.
Exploring the Function of Fuses
Fuses play a crucial role in safeguarding electrical systems by interrupting the flow of current during overloads or short circuits. Their primary purpose is to prevent damage to devices and maintain safety within the circuit. By acting as a weak link, fuses ensure that excess energy is dissipated, thereby protecting more sensitive components from failure.
How Fuses Operate
When a circuit experiences an excessive current, the fuse’s conductive material heats up and ultimately melts. This process breaks the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing potential hazards such as fires or equipment damage. The speed at which a fuse reacts can vary, with some designed for quick responses and others for slower, delayed reactions based on their specific applications.
Types of Fuses
There are various types of fuses available, each designed for specific requirements. Cartridge fuses are commonly used in high-voltage applications, while glass tube fuses are more typical in household devices. Understanding the different kinds helps in selecting the appropriate fuse for a given situation, ensuring optimal protection and performance.
Understanding Fan-Assisted Models
Fan-assisted systems are designed to enhance warmth distribution within a room, offering an efficient solution for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures. These units incorporate a mechanical component that circulates air, optimizing the heating process and ensuring that warmth reaches all corners of the space. By employing a fan, these models reduce cold spots and promote a more even thermal environment.
Benefits of Fan-Assisted Units
Utilizing a fan in heating mechanisms provides several advantages. These include improved efficiency, faster temperature regulation, and a reduction in energy consumption. The circulation of warm air allows for quicker heating, which can lead to lower operational costs and increased comfort levels.
Key Components of Fan-Enhanced Systems
Understanding the fundamental components of these models is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Below is a table outlining the critical elements commonly found in fan-assisted systems:
| Component |
Description |
| Fan |
Moves warm air throughout the room, enhancing heat distribution. |
| Heating Element |
Generates warmth, typically through electrical resistance or hydronic processes. |
| Thermostat |
Monitors and regulates the temperature to maintain desired comfort levels. |
| Housing |
Encases the components, ensuring safety and aesthetic appeal. |
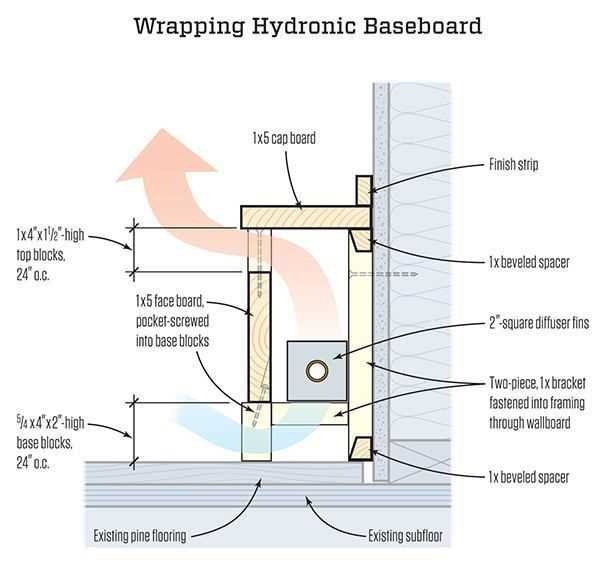
Mounting Techniques for Wall Units
Proper installation of wall-mounted units is essential for optimal performance and safety. The right techniques ensure that the units are securely attached, allowing for effective heat distribution throughout the space. This section outlines various methods for mounting these devices, focusing on best practices and considerations for various wall types.
Before starting the installation, it is important to gather the necessary tools and materials:
- Level
- Stud finder
- Drill and drill bits
- Screws and anchors
- Measuring tape
Here are several techniques for securely mounting wall units:
- Locate Studs: Use a stud finder to identify the wooden or metal studs in the wall. Attaching the units directly to these supports will provide maximum stability.
- Use Anchors: For walls without sufficient studs, toggle bolts or wall anchors can be employed. These help distribute weight evenly and prevent damage to the wall.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Always refer to the specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer for optimal installation procedures and recommendations.
- Ensure Level Alignment: Before securing the unit, check that it is level. This prevents potential operational issues and enhances aesthetic appeal.
- Double-Check Securement: After installation, gently tug on the unit to ensure it is firmly mounted. This step is crucial for safety and functionality.
By adhering to these mounting techniques, users can achieve a secure and effective installation of their wall-mounted units, ensuring safety and efficient operation.
Safety Features in Electric Heaters
Ensuring user protection is paramount when it comes to devices that generate warmth. Various mechanisms and designs are implemented to mitigate risks associated with overheating, electrical faults, and other hazards. These features are essential for promoting safe usage and preventing accidents in residential and commercial settings.
Overheat Protection

One of the most critical aspects of modern warmth-generating appliances is their ability to detect excessive temperatures. Overheat protection systems automatically shut off the device when it exceeds a specified threshold, reducing the risk of fire or damage. This feature is particularly important in environments where users may inadvertently obstruct airflow or place items too close to the unit.
Tip-Over Switch
Another vital safety component is the tip-over switch, which activates when the unit is accidentally knocked over. This mechanism promptly interrupts power, preventing any potential hazards associated with an unstable position. Devices equipped with this feature provide users with additional peace of mind, especially in homes with children or pets.
Tips for Replacing Worn-Out Parts
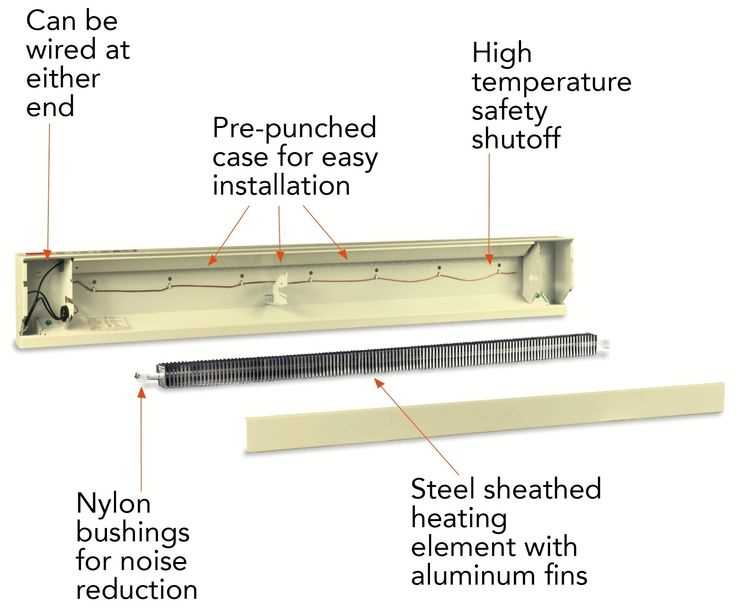
Replacing outdated components is essential for maintaining the efficiency and safety of your heating system. Understanding the common issues that arise with these fixtures will help ensure a smooth replacement process, ultimately enhancing performance and longevity.
Before beginning the replacement, it is crucial to gather the necessary tools and materials. Familiarize yourself with the components you intend to replace, as well as any specific requirements they may have. Proper preparation will streamline the process and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Here are some essential tips to consider:
| Tip |
Description |
| Turn Off Power |
Always ensure that the power supply is disconnected to avoid any risk of electrical shock. |
| Inspect Surroundings |
Check the area around the fixture for any obstructions or debris that may hinder the replacement process. |
| Use Quality Components |
Select high-quality replacements to ensure durability and optimal functionality. |
| Follow Manufacturer Guidelines |
Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific details regarding installation and compatibility. |
| Test After Replacement |
Once the installation is complete, restore power and test the unit to ensure everything is functioning correctly. |
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively replace outdated components, ensuring your heating system operates at peak efficiency.
Energy Efficiency of Wall-Mounted Systems
Wall-mounted heating solutions are designed to optimize energy consumption while providing warmth to living spaces. These systems utilize advanced technologies to ensure minimal waste of resources, making them an ideal choice for homeowners seeking to reduce their carbon footprint and utility bills. By focusing on insulation, programmable features, and effective temperature control, these installations can achieve remarkable efficiency in heating environments.
Insulation and Design Considerations
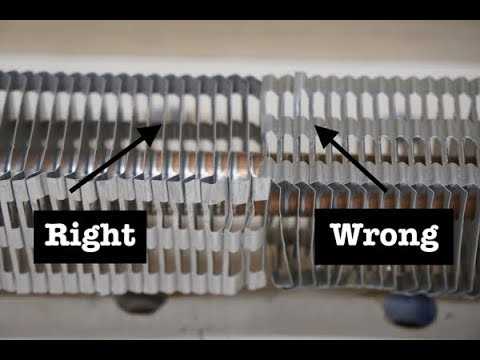
Effective insulation plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of wall-mounted systems. Properly insulated spaces retain heat longer, which allows the heating units to operate less frequently, ultimately conserving energy. Additionally, the design of these systems often includes features such as radiant heating elements that distribute warmth evenly, further contributing to efficient energy use.
Smart Technology Integration
Modern wall-mounted solutions frequently incorporate smart technology, enabling users to manage their heating preferences remotely. These innovations include programmable timers and smart thermostats that adapt to daily schedules, ensuring that energy is only used when needed. Such features not only enhance comfort but also significantly improve overall energy efficiency, making them a wise investment for environmentally conscious consumers.
|