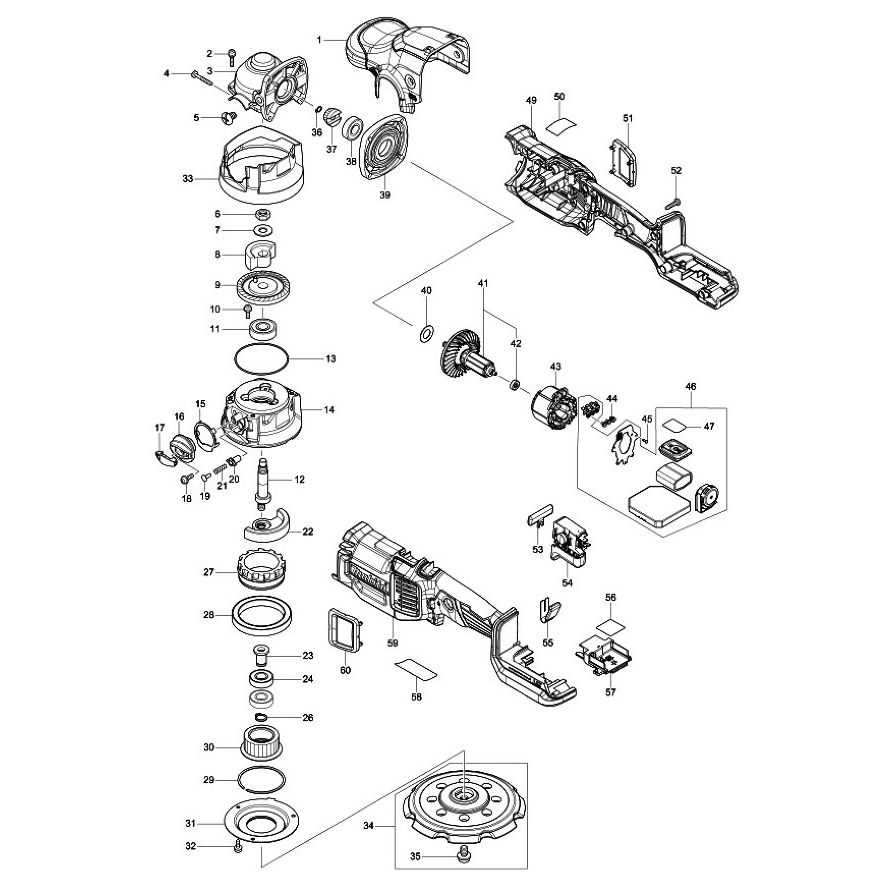
The internal structure of precision equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Understanding how various elements work together can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance, helping to extend the longevity of the tool.
This guide offers a breakdown of the key elements and their interactions within a high-performance device. Knowing the function of each individual element will make it easier to perform necessary adjustments or replacements over time.
Maintaining performance often requires a deeper knowledge of how components are arranged. By exploring each section, you will gain valuable insights into how to maintain optimal functionality and address any potential issues that arise.
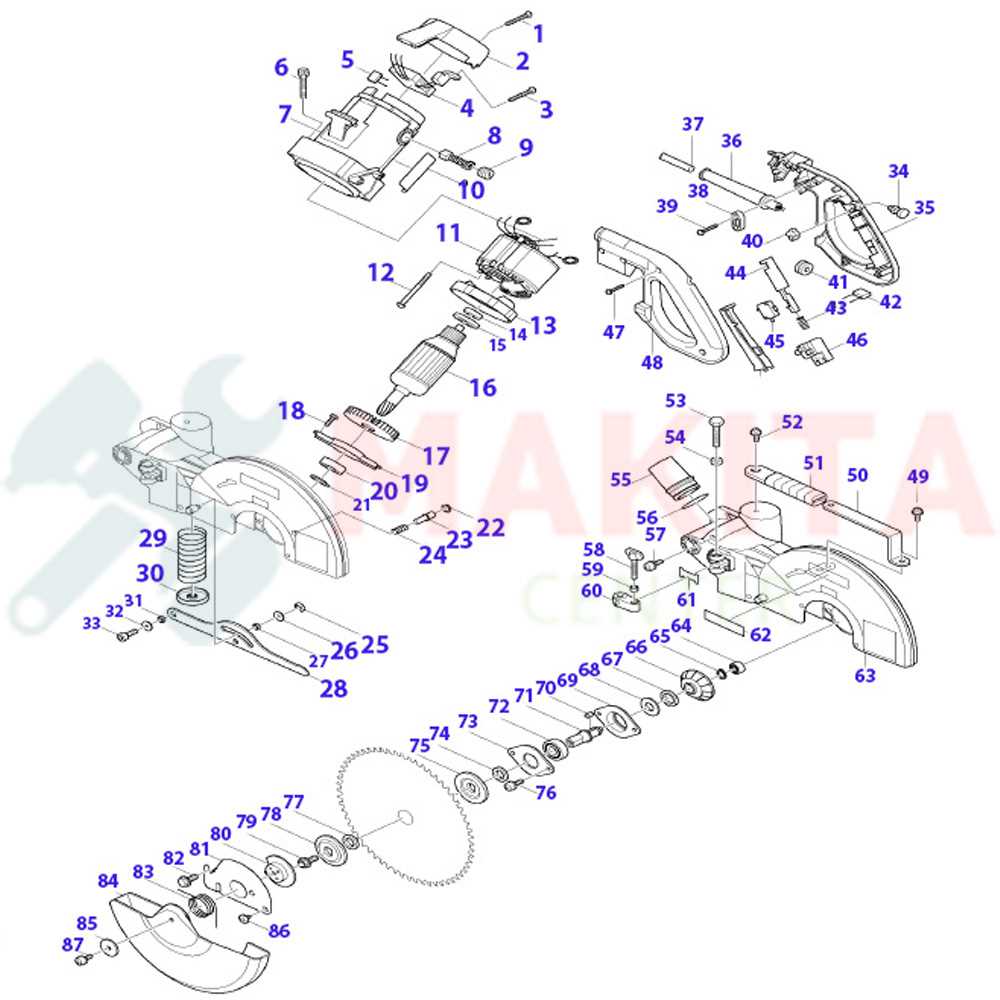
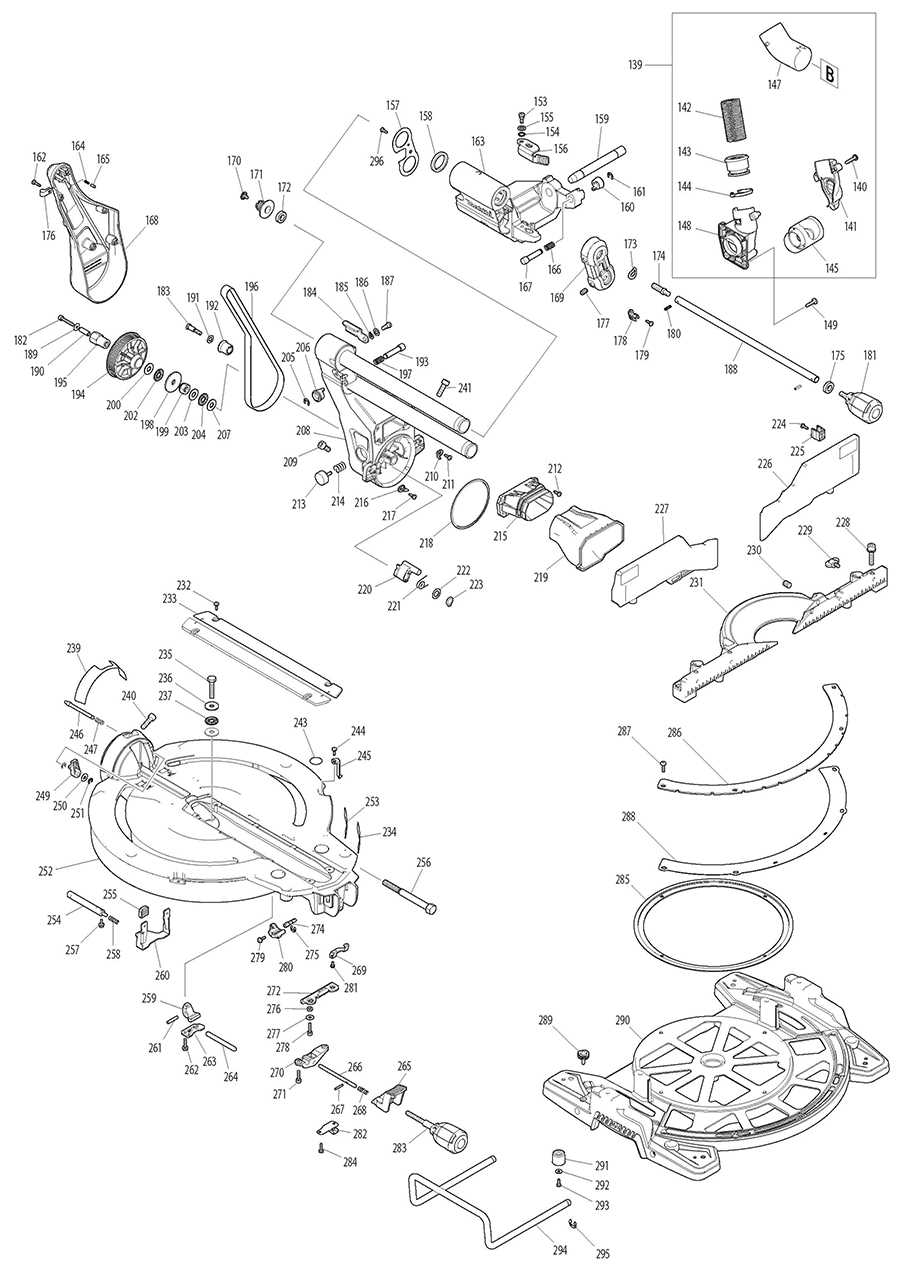
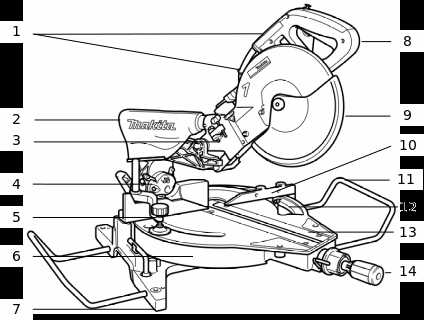
Overview of Makita LS1013L Components
This section provides a detailed look into the essential elements of this versatile tool, helping users understand its functionality and assembly. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and precision in various cutting tasks.
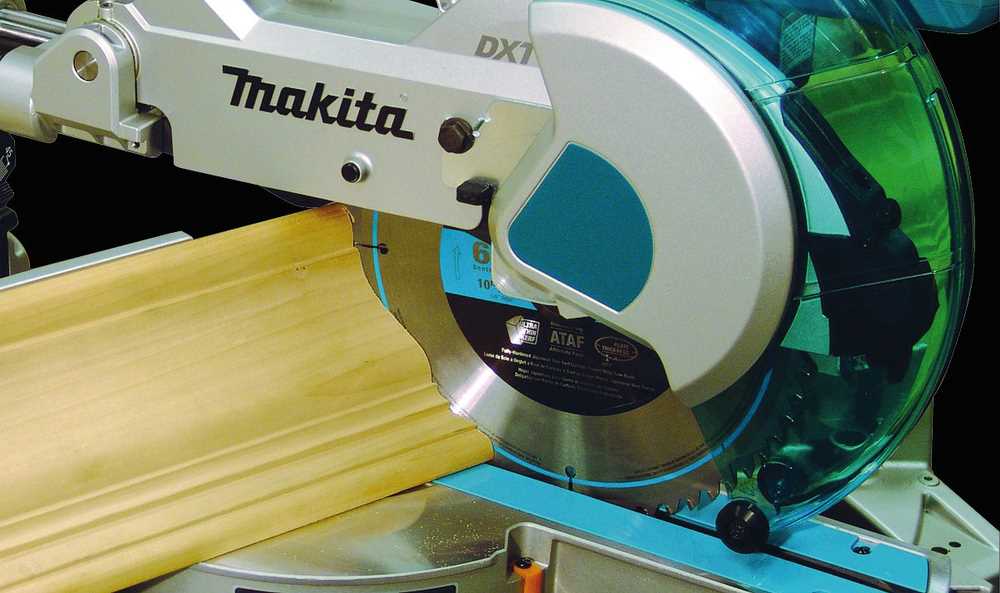
- Blade Assembly: The central cutting feature, designed for smooth, accurate cuts across different materials.
- Bevel and Miter Scales: These scales enable the operator to set precise angles, offering flexibility for diverse cutting applications.
- Fence System: A crucial part that holds materials in place, ensuring stability during operation.
- Dust Collection Port: This helps maintain a clean workspace by channeling sawdust away from the cutting area.
- Power Trigger: The control mechanism that powers the tool, providing the operator with full command over the cutting process.
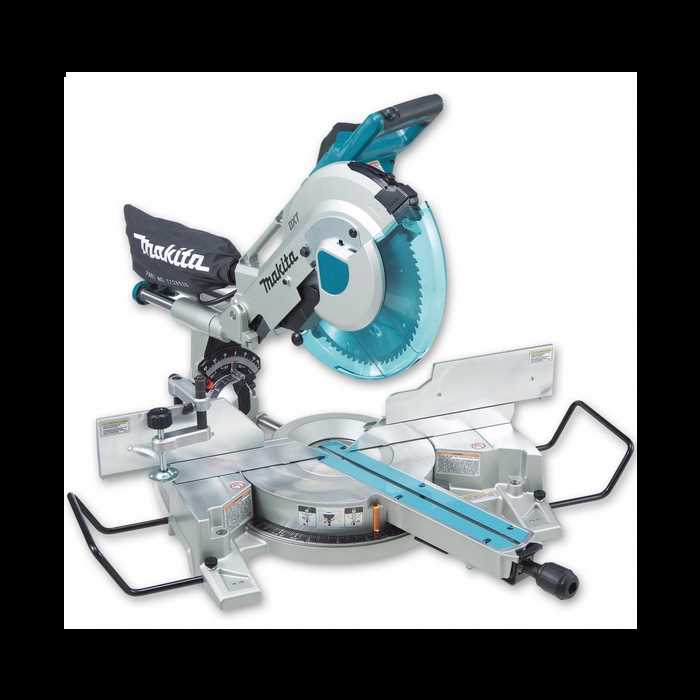
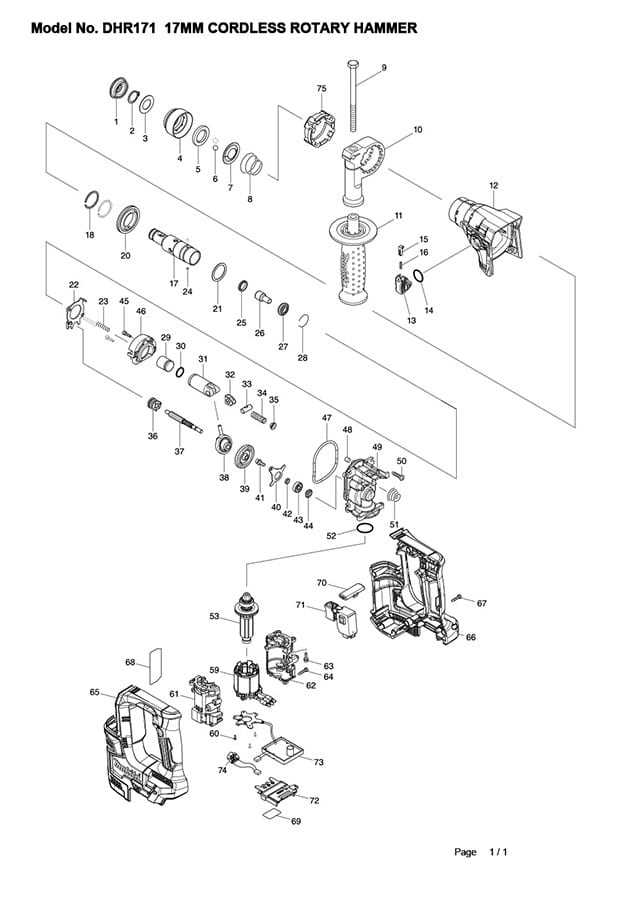
Main Structure of the LS1013L Saw
The structure of this saw model is designed to ensure stability, precision, and durability. Its components are arranged to offer smooth operation while allowing accurate and clean cuts in various materials. Below is a breakdown of the key elements that make up the core framework of the tool.
Base and Support

The foundation of the saw is a sturdy platform that provides balance and support during use. It is built to handle a range of materials and offers a secure base for cutting operations.
- Wide base for enhanced stability
- Adjustable supports to accommodate different workpiece sizes
- Non-slip surface to prevent material movement
Cutting Mechanism
At the heart of the tool’s design is the cutting mechanism, engineered for precision and control. This section ensures that the saw performs efficiently under various conditions.
- Rotating blade arm for flexible cutting angles
- Easy-to-adjust angle settings for miter cuts
- Locking system to secure the blade in place during operation
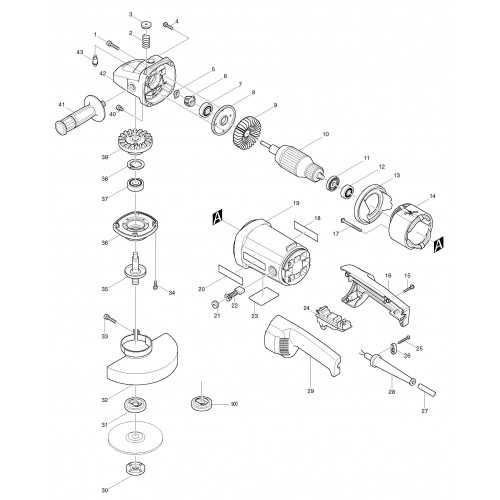
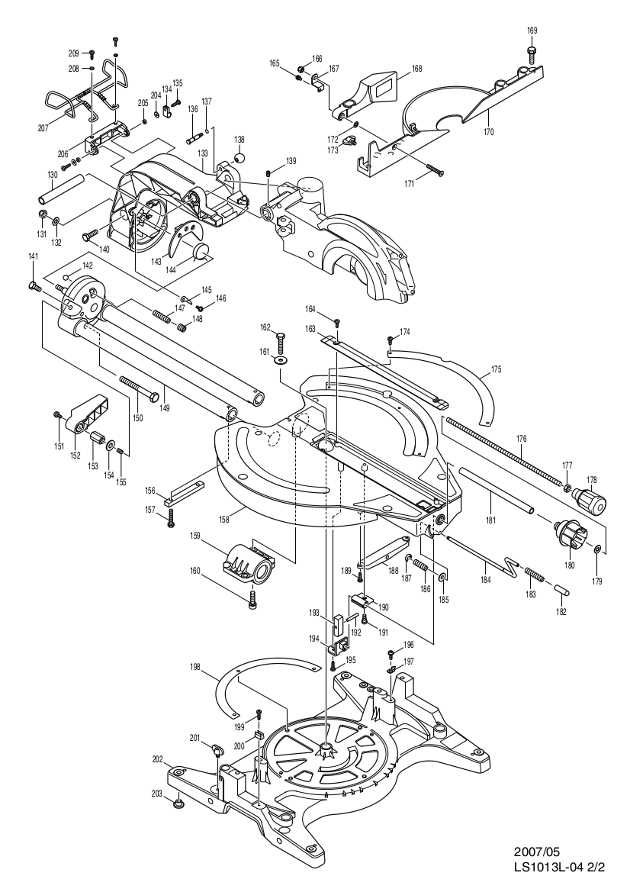
Blade Mechanism and Its Parts
The cutting mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring the precision and efficiency of the tool. Understanding its components is vital for maintaining smooth operation, safety, and long-term performance. Below, we explore the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of the blade system.
Main Components

The blade assembly consists of several interconnected elements designed to support accurate cuts. These parts include the rotary blade, the support bracket, and the adjustment knob. Each component must function in unison to provide the best results. Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent damage and prolong their life span.
Adjustment and Safety Features
Proper alignment and safety mechanisms are key to avoiding operational hazards. The blade guard, angle locks, and tension screws ensure that the blade remains stable during use. Each of these features is designed to offer protection while optimizing the tool’s performance.
| Component | Function | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Blade |
| Component | Signs of Wear | Recommended Replacement Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Blade | Dullness, chipping, uneven cuts | Every 6 months or as needed |
| Drive Belt | Squeaking noise, slippage | Annually or as needed |
| Brushes | Reduced power, sparking | Every 3-6 months |
| Switch | Intermittent operation, difficulty in starting | As needed |
| Housing | Cracks, excessive wear | Inspect regularly; replace if damaged |
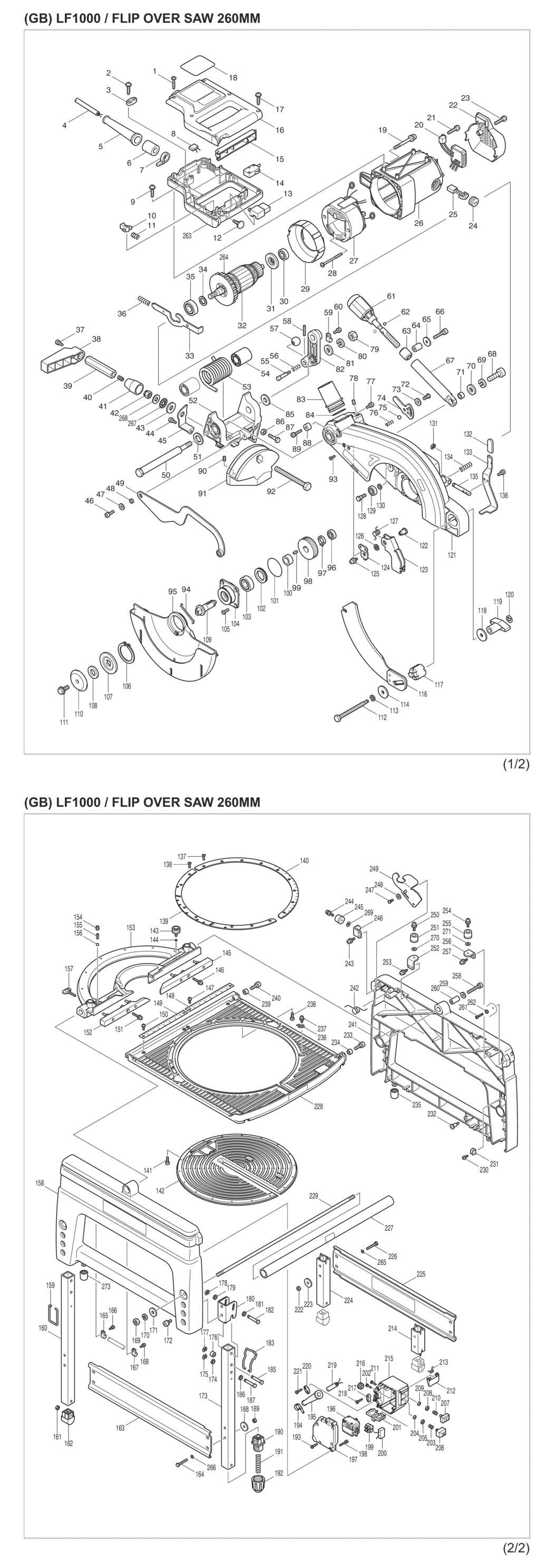
Mounting Hardware and Accessories
Proper mounting elements and supplementary tools play a vital role in ensuring stability and efficiency in various applications. These components are essential for securely attaching equipment and enhancing overall performance.
Essential Mounting Components

- Bolts: Used to connect parts firmly, ensuring a secure fit.
- Nuts: Paired with bolts to create a strong hold.
- Washers: Help distribute the load and prevent damage to surfaces.
- Screws: Useful for fastening items where additional grip is needed.
- Brackets: Provide support and stability to mounted components.
Additional Accessories
- Safety Guards: Protect users from accidental contact with moving parts.
- Extension Cords: Allow for greater flexibility in power supply locations.
- Tool Kits: Include various implements for installation and maintenance.
- Storage Cases: Keep hardware organized and easily accessible.
Electrical Wiring and Connectors
The effective functioning of power tools relies heavily on the integrity of their electrical systems. This section discusses the various components involved in the electrical wiring of these devices, focusing on the connectors and their roles in ensuring a safe and efficient operation.
Types of Connectors
Connectors are essential for establishing reliable electrical connections. Here are some common types:
- Terminal Connectors: These are used to connect wires to circuit boards or other components.
- Splice Connectors: Ideal for joining two wires together, providing a secure and insulated connection.
- Plug and Socket Connectors: Commonly used for detachable connections, allowing easy disconnection of parts.
Wiring Considerations
When dealing with the electrical wiring of power equipment, certain factors should be taken into account:
- Wire Gauge: Selecting the appropriate wire gauge is crucial to handle the current without overheating.
- Insulation Quality: Ensuring high-quality insulation prevents short circuits and enhances safety.
- Connection Security: All connections should be secure to prevent intermittent faults and ensure smooth operation.