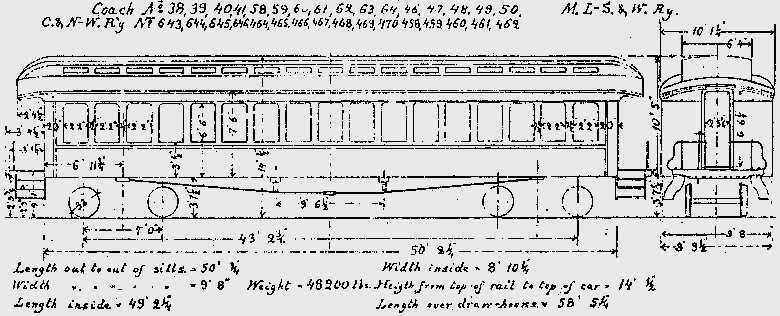
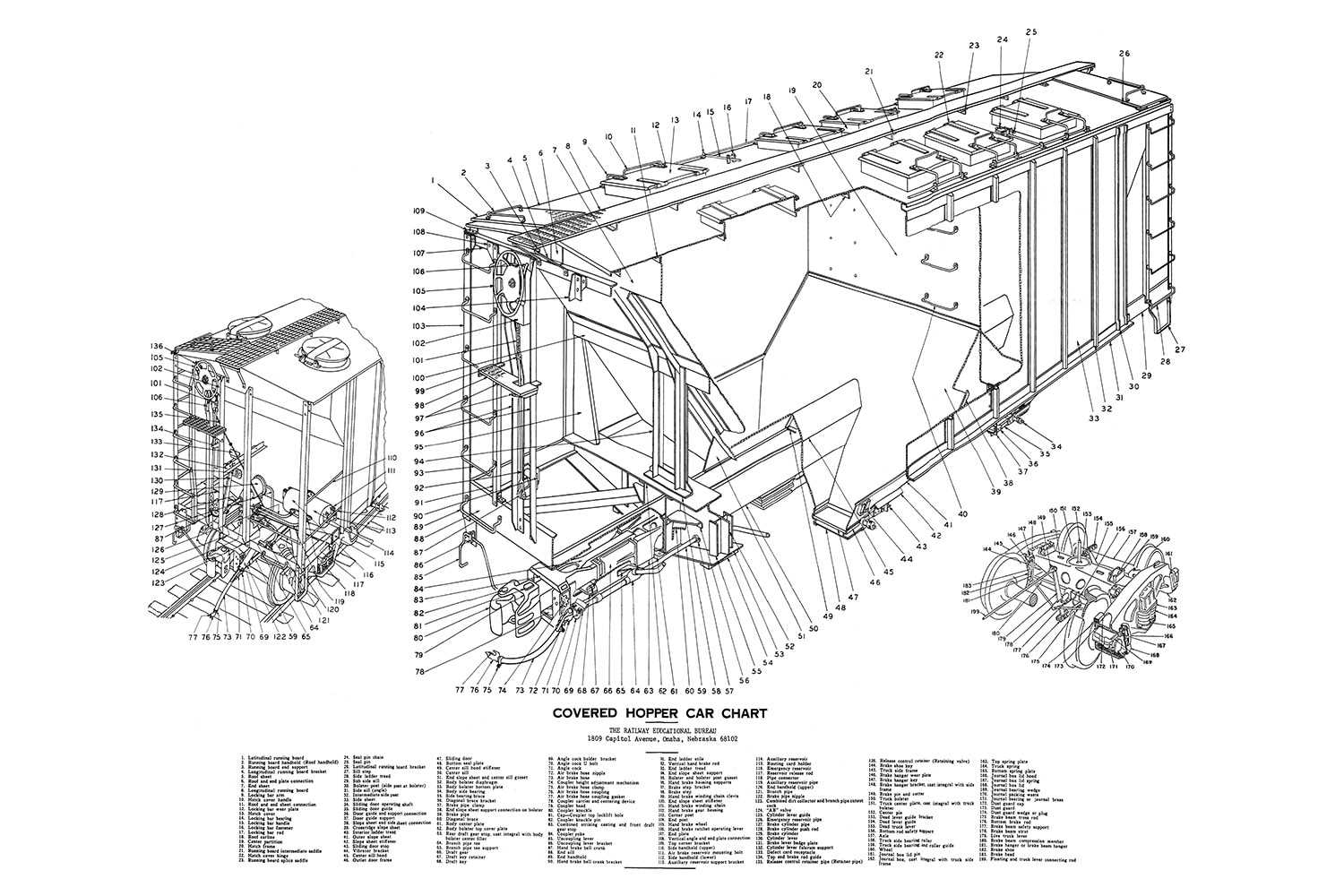
Effective maintenance and repair of complex transport units require a deep knowledge of their internal systems. Each element serves a unique role in ensuring smooth operations and safety during movement. The layout of these elements provides technicians with a clear understanding of how different sections interact and depend on one another.
To achieve seamless functionality, it is crucial to identify and examine the relationships among mechanical components, connectors, and subassemblies. This overview offers insights into the essential structures that form the core of such systems, helping to streamline troubleshooting processes and upgrades.
The following exploration dives into the key modules and configurations, providing a technical view of their arrangement. This breakdown facilitates more efficient diagnostics and enhances the overall management of moving equipment, minimizing downtime and ensuring long-term reliability.
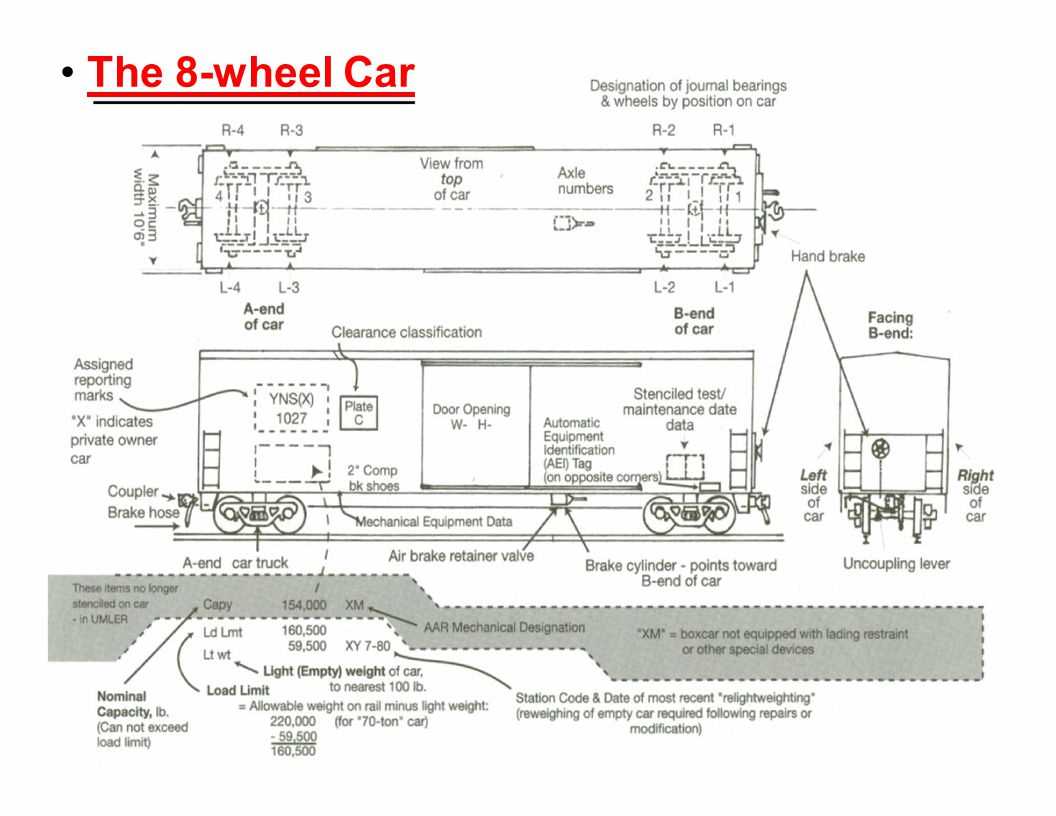
Overview of Rail Car Components
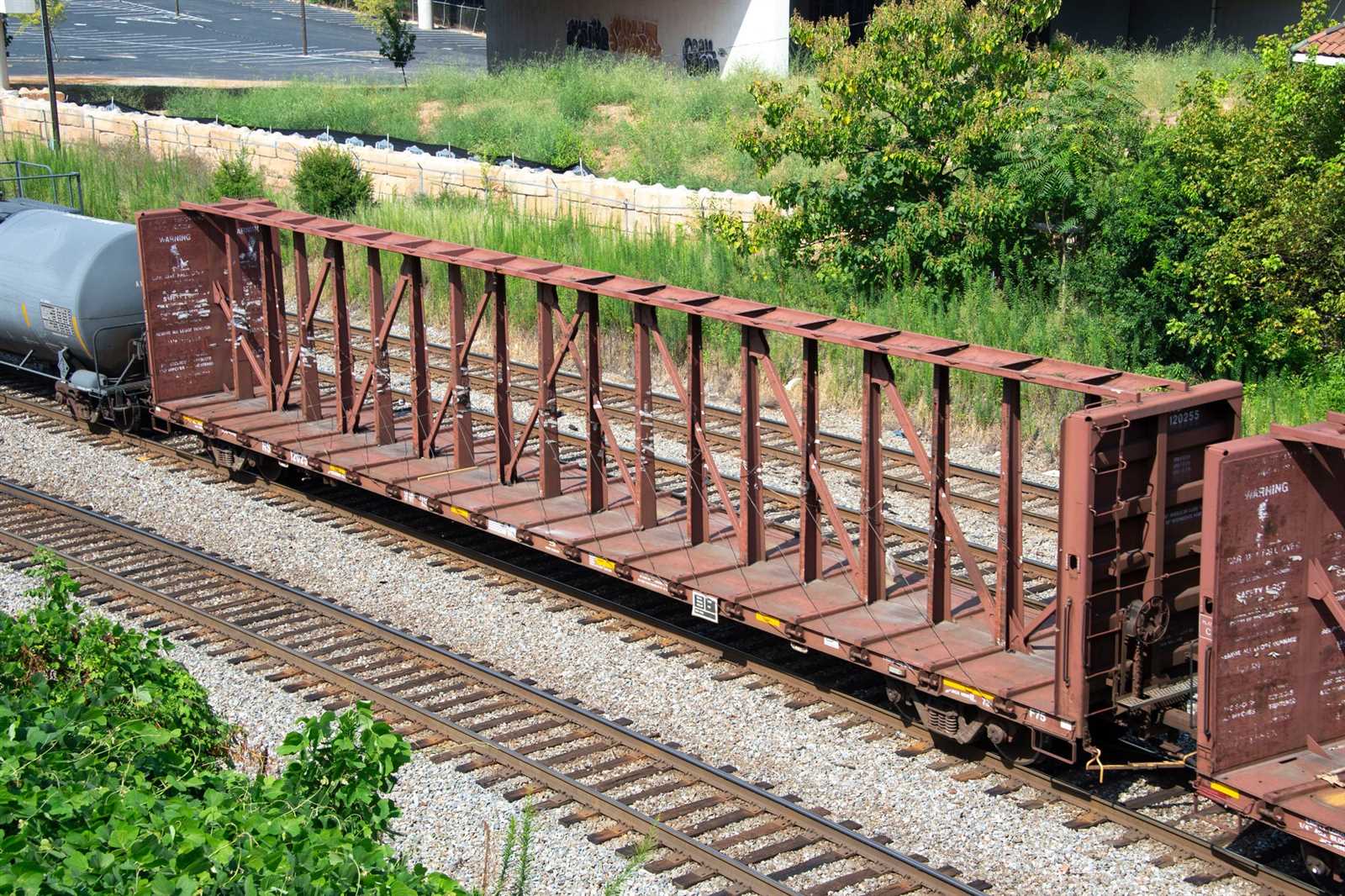

This section provides a concise explanation of the essential elements found in transportation vehicles designed for running on tracks. These systems include a variety of interconnected structures and mechanical features that ensure smooth operation and stability during movement.
- Chassis and Framework: The underlying structure supports the entire unit and distributes weight evenly across the wheels.
- Coupling Systems: Specialized mechanisms connect individual units, allowing them to operate as a continuous assembly.
- Suspension: Springs and dampers reduce vibrations, ensuring comfortable rides and protecting internal cargo or passengers.
- Braking Equipment: Devices designed to control speed and ensure safe deceleration when necessary.
- Axles and Bearings: Critical rotating elements that allow smooth wheel movement and transfer forces effectively.
The harmonious interaction of these components guarantees both safety and efficiency, ensuring that the vehicle performs reliably under varying conditions and meets operational demands.
Structural Frame and Chassis Details
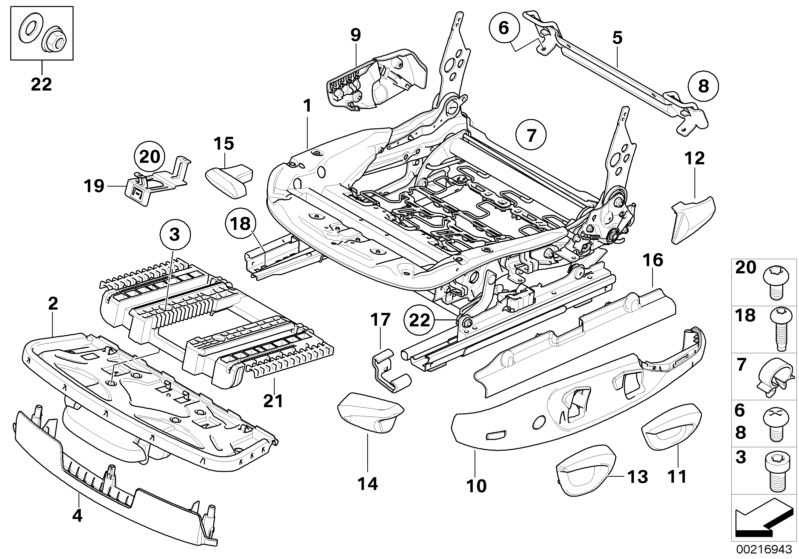
The framework and undercarriage provide the essential foundation for large vehicles, ensuring stability and strength under various loads. These components form the backbone of the overall structure, designed to distribute weight evenly and maintain balance during operation.
The main framework consists of beams and cross-sections, carefully arranged to enhance rigidity and reduce stress under heavy use. The undercarriage supports not only the weight of the entire structure but also ensures smooth movement by integrating with suspension systems and axles.
Attention to material quality and design precision is critical in these areas, as any structural weakness can lead to mechanical failures or safety risks. Proper inspection and maintenance routines are necessary to prevent wear and ensure long-term reliability.
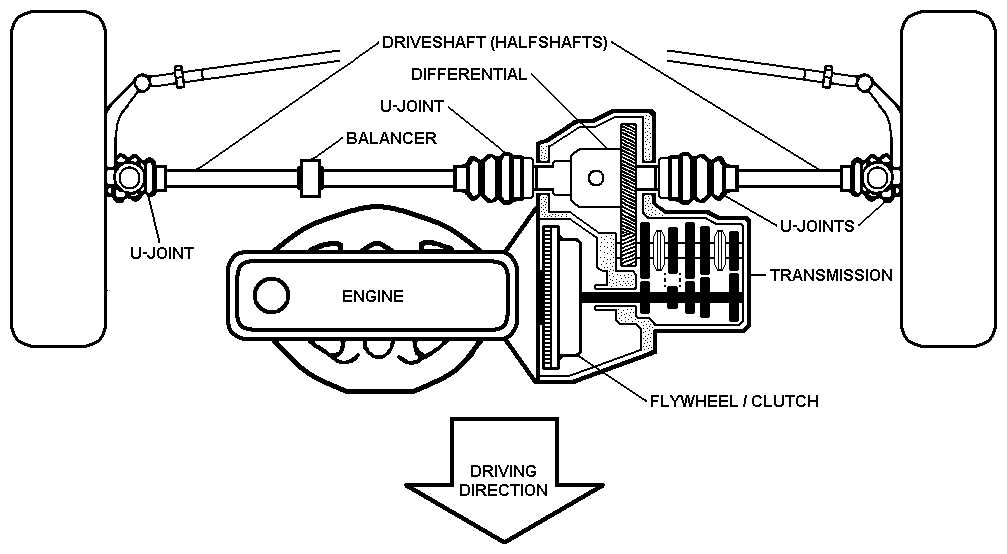
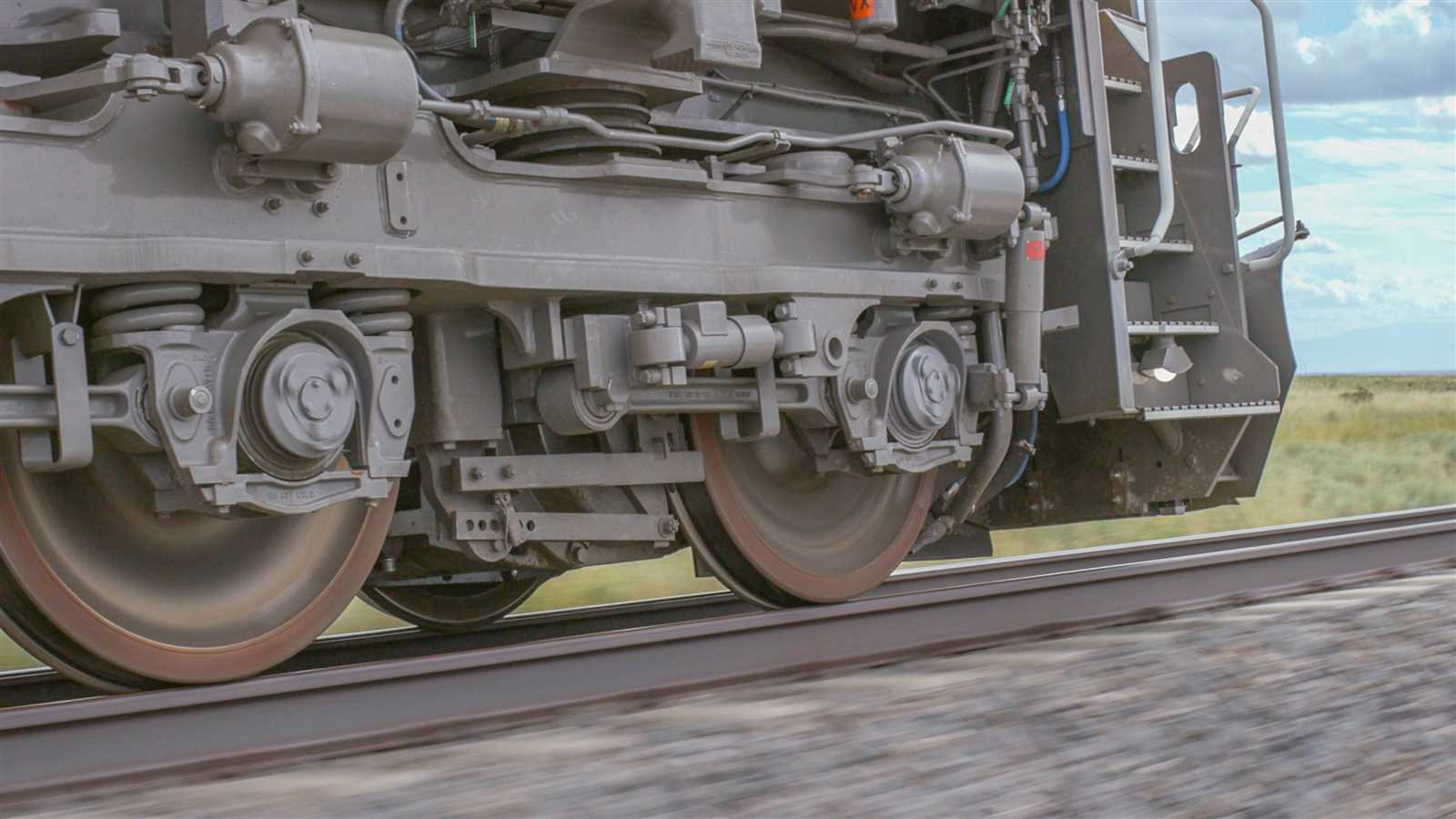
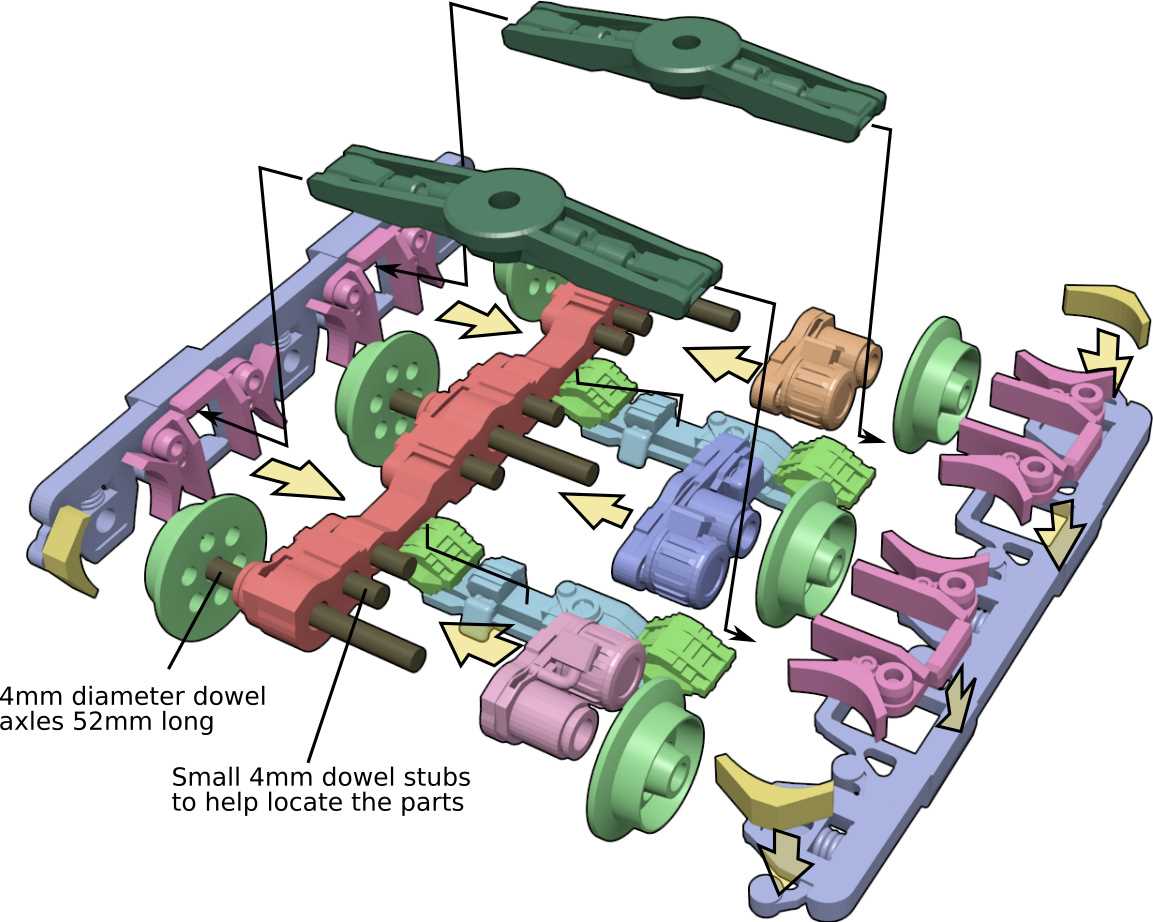
Axles and Suspension Systems
Axles and suspension systems are essential for ensuring smooth movement and stability during operation. These components work together to provide support and balance, enabling the structure to handle various loads while maintaining consistent functionality. The interaction between these elements is critical for maintaining performance and safety under different conditions.
Axle Functionality

The primary role of axles is to support weight and facilitate motion. They transfer force from the engine or drive system to the wheels, ensuring efficient movement. Strong and well-designed axles are crucial for handling various stress factors such as load shifts and uneven terrain.
Suspension Systems
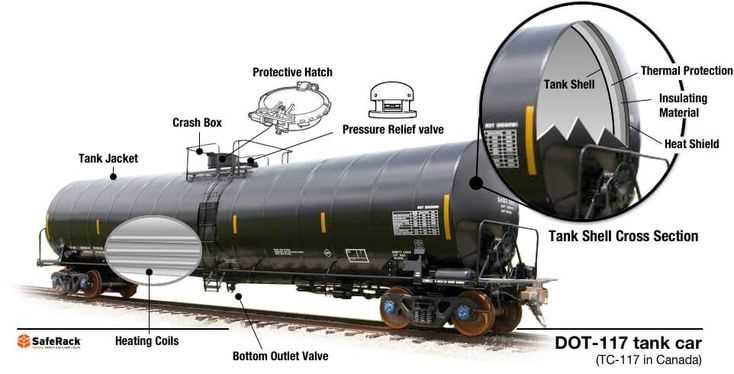
Suspension systems are designed to absorb shocks and vibrations, creating a smoother operational experience. These systems reduce wear on components and enhance comfort, especially when moving over rough surfaces. A well-functioning suspension system ensures better control and longevity of the entire setup.
Brake Mechanism and Safety Features
The braking system plays a crucial role in controlling movement, ensuring smooth deceleration, and preventing accidents. It integrates several components that work together to manage speed effectively, providing both operational control and emergency stopping power when needed. Safety features embedded within the system further enhance reliability and minimize risks.
Braking Operation: The mechanism employs a combination of friction-based elements and force modulation to achieve controlled slowing. Hydraulic or pneumatic pressure often regulates the braking force, ensuring consistent performance across varying loads and speeds.
Emergency Safety Measures: Modern designs incorporate fail-safe features to prevent malfunctions. Automatic braking can engage if the system detects a sudden loss of control, reducing the chance of hazardous situations. Additionally, sensors monitor critical components to alert operators to potential issues early.
Continuous advancements in braking technology focus on improving energy efficiency and response time. Redundancy is also a key element, ensuring that backup systems are available to maintain safety even in the event of primary system failure.
Electrical Wiring and Control Units

Electrical systems ensure the proper functioning of machinery by facilitating power distribution and signal communication between various components. These systems rely on complex networks of connections and controllers to maintain operational efficiency and safety in diverse environments.
Wiring configurations play a critical role in distributing energy to key devices and sensors. Robust cabling minimizes signal interference and ensures that components operate within their designed parameters. Proper routing and labeling of wires also enhance maintenance efficiency.
Control units act as the brain of the system, processing data from sensors and issuing commands to actuators. These controllers monitor performance, trigger safety protocols, and adjust parameters to optimize function. Modern designs often incorporate programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to allow for flexible automation and real-time adjustments.
Efficient electrical layouts and reliable control units are essential for the smooth operation of machinery in demanding industrial and transport settings. Regular inspections and updates are necessary to prevent malfunctions and ensure continued performance.
Coupling Devices and Connection Points
The efficiency and safety of transport systems greatly depend on the mechanisms that allow different units to connect and interact seamlessly. Understanding the various coupling devices and their corresponding connection points is essential for ensuring reliable operations and maintenance. These components serve as the backbone for secure linkages, facilitating the transfer of forces and loads between units.
Types of Coupling Devices
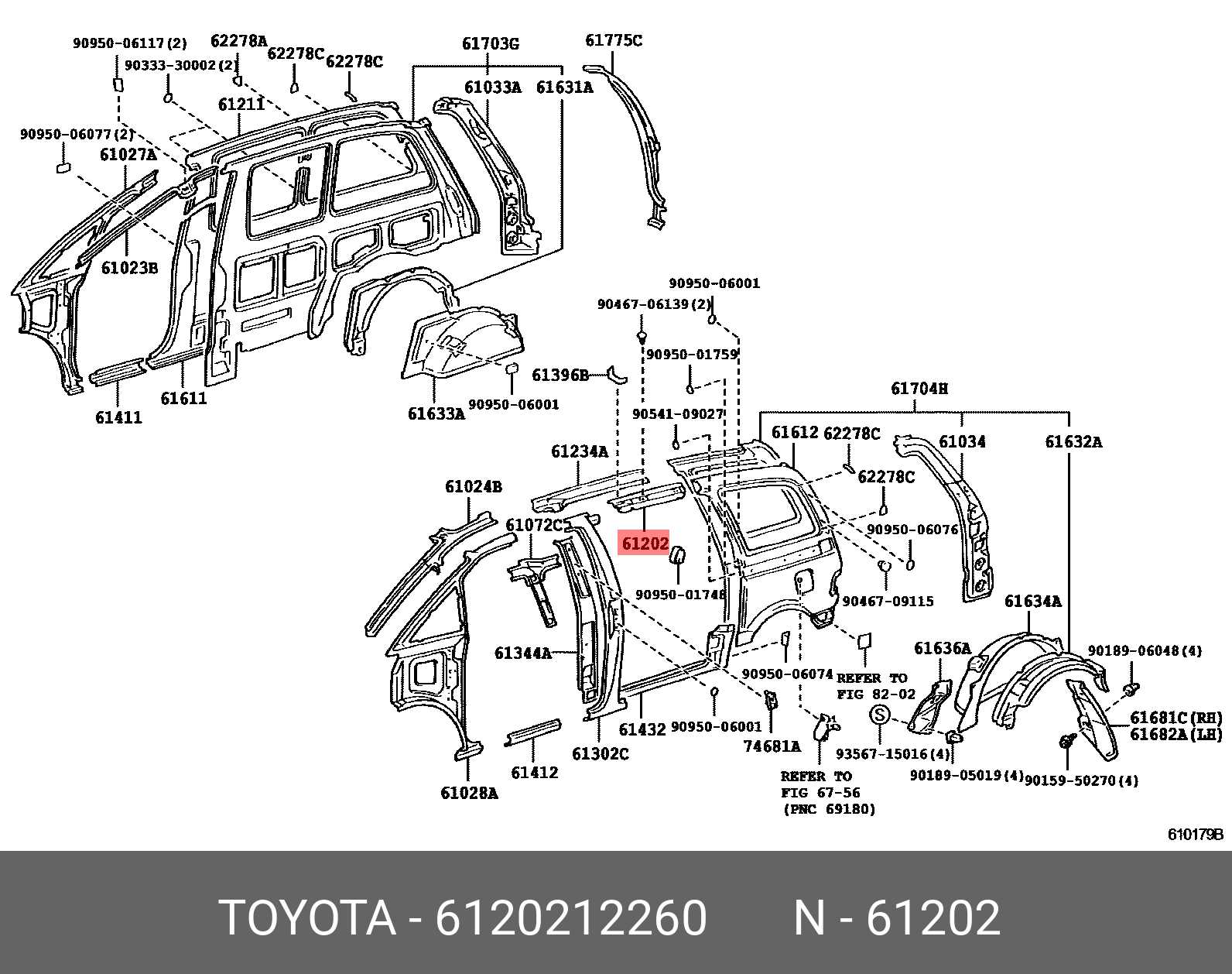
- Mechanical Couplers: These are typically employed to create strong physical connections between units. They may include hooks, pins, or specialized clamps designed to withstand significant stress.
- Flexible Couplings: These devices allow for some degree of movement or misalignment between connected units. They are particularly useful in accommodating variations in load or terrain.
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic Couplings: These types involve the use of fluid power to create secure connections, often found in systems requiring high force transmission.
Connection Points and Their Importance
Connection points are critical for ensuring that coupling devices function properly. Each point must be designed to handle specific loads and forces, preventing failures during operation. Factors to consider include:
- Material Strength: The durability of connection points is vital for long-term performance, necessitating the use of high-quality materials.
- Alignment and Precision: Proper alignment between coupling devices ensures effective load transfer, reducing the risk of wear and tear.
- Maintenance Access: Designing connection points for easy access simplifies inspections and repairs, contributing to operational efficiency.
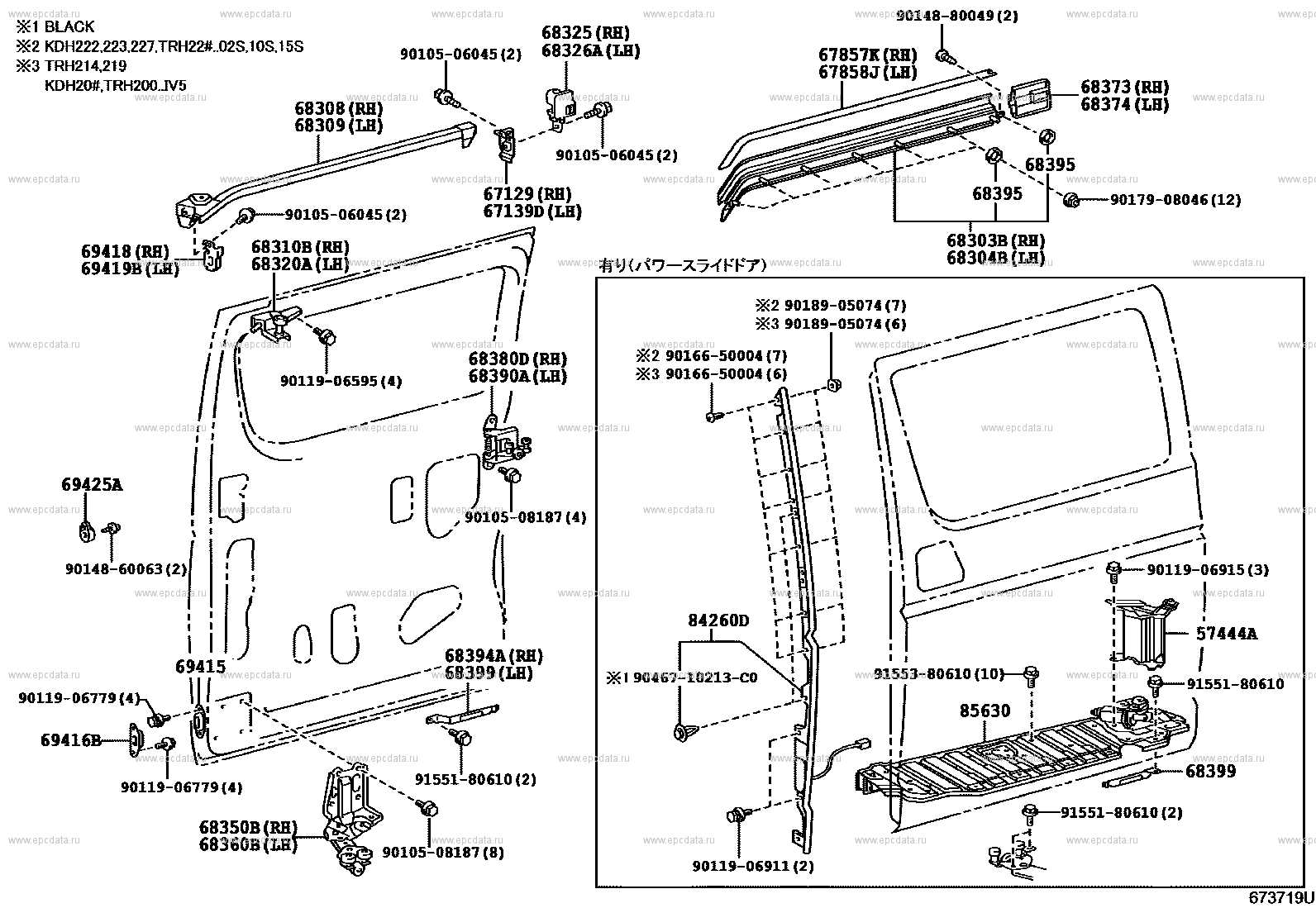
Doors, Windows, and Access Systems
Access mechanisms, openings, and transparent panels are crucial for the functionality and safety of transportation units. These components not only provide entry and exit but also ensure the comfort and visibility of passengers. Understanding their design and operation is essential for maintaining an efficient system.
Access Mechanisms
The various entry points utilized in these transportation units play a vital role in the overall experience. The following aspects are essential to consider:
- Types of Doors: Different designs are used, including sliding, hinged, and folding doors, each serving specific operational needs.
- Security Features: Modern access systems incorporate advanced locking mechanisms to enhance passenger safety.
- Accessibility: These systems are designed to accommodate all passengers, including those with reduced mobility.
Transparent Panels

Windows are integral for providing visibility and natural light within the unit. Key considerations include:
- Material Selection: The choice of materials, such as tempered glass or polycarbonate, affects durability and safety.
- Sealing and Insulation: Proper sealing is crucial to prevent air leaks and enhance energy efficiency.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Regular upkeep ensures clear visibility and aesthetic appeal.
Seating Arrangements and Interior Fixtures
The design of seating layouts and interior elements plays a crucial role in enhancing comfort and functionality within a transport vehicle. Various configurations aim to optimize space while ensuring that passengers have access to essential amenities and an enjoyable travel experience.
Seating arrangements can vary significantly depending on the intended use and capacity of the vehicle. Options may include single seats, bench seating, or modular designs that allow for flexibility in layout. Such configurations can cater to different travel needs, from family trips to professional commutes.
In addition to seating, the incorporation of interior fixtures is vital for improving the overall ambiance and utility of the space. Features such as lighting, storage compartments, and accessibility aids contribute to a more pleasant and convenient environment. The strategic placement of these elements ensures that passengers can navigate and utilize the area efficiently.
Furthermore, attention to material selection and aesthetic design enhances the visual appeal while providing durability and ease of maintenance. Combining comfort, functionality, and style is essential for creating an inviting atmosphere that meets the diverse needs of all travelers.
HVAC and Climate Control Solutions
Effective management of indoor climate is essential for ensuring comfort and functionality in any enclosed environment. This section explores various strategies and technologies designed to regulate temperature and air quality, enhancing the overall experience for occupants.
Key Components of HVAC Systems
- Heating Units: Devices that provide warmth, often utilizing gas, electricity, or renewable energy sources.
- Cooling Units: Equipment designed to lower temperatures, including traditional air conditioning systems and innovative cooling technologies.
- Ventilation Systems: Mechanisms that facilitate the exchange of indoor and outdoor air, promoting a healthy atmosphere.
- Control Systems: Smart technology that allows users to adjust settings for optimal comfort and efficiency.
Benefits of Advanced Climate Control Solutions
- Improved Comfort: Tailored temperature settings and air quality management contribute to a pleasant environment.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern systems are designed to minimize energy consumption while maintaining optimal performance.
- Enhanced Air Quality: Effective filtration and ventilation reduce pollutants and allergens, promoting better health.
- Smart Integration: Automation and connectivity enable remote monitoring and adjustments for added convenience.
Storage Compartments and Cargo Spaces
Efficient organization and management of storage areas are crucial for maximizing the utility of transportation units. These designated spaces are designed to accommodate a variety of goods, ensuring safe and secure transport while optimizing available capacity.
Storage compartments are strategically placed to enhance accessibility and functionality. Their layout allows for easy loading and unloading, facilitating smooth operations during transit. Additionally, these compartments are often equipped with safety features to protect the contents from damage.
Cargo spaces, on the other hand, play a pivotal role in defining the overall capacity of the unit. They are engineered to support different types of loads, from bulk items to specialized freight. The design of these areas considers factors such as weight distribution and stability, ensuring safe transport across various terrains.
Monitoring Sensors and Diagnostic Tools
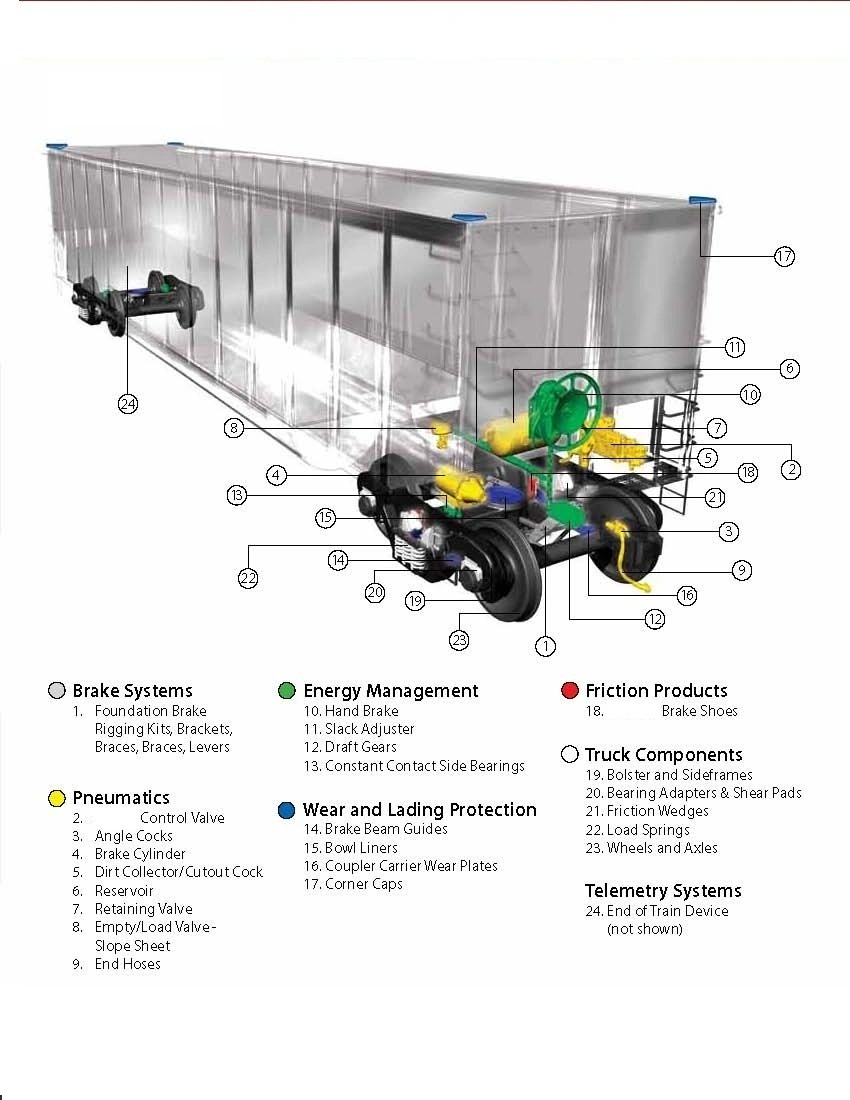
Effective oversight of vehicle systems relies heavily on advanced monitoring mechanisms and analytical instruments. These technologies play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and preemptively identifying potential issues. By leveraging a combination of sensors and diagnostic equipment, operators can maintain safety and efficiency throughout the entire operational lifespan.
Sensors are vital components that continuously collect data related to various operational parameters. They monitor conditions such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, allowing for real-time assessments of system health. The information gathered enables timely interventions, preventing minor faults from escalating into major failures.
Diagnostic tools complement these sensors by providing in-depth analyses of collected data. These instruments facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance processes by pinpointing exact problems within the system. By utilizing these technologies, maintenance personnel can enhance their response times and improve the overall reliability of the vehicle.
Maintenance Guidelines for Key Parts
Regular upkeep of essential components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the maintenance requirements can prevent unexpected failures and enhance reliability. By adhering to specific recommendations, operators can ensure their machinery remains in top condition.
Inspecting Connections: Regularly examine all connections for signs of wear or loosening. Tightening fasteners and checking for corrosion can significantly improve stability and prevent operational issues.
Lubrication Practices: Applying appropriate lubricants to moving elements is vital. This process reduces friction, minimizing wear and tear. Follow manufacturer guidelines for the type and frequency of lubrication to maintain efficiency.
Cleaning Procedures: Keeping surfaces free of debris and contaminants is essential. Regular cleaning not only enhances appearance but also prevents malfunctions caused by buildup. Use recommended cleaning agents to avoid damaging sensitive areas.
Monitoring Performance: Implementing routine performance checks can identify potential problems early. Pay attention to unusual sounds or changes in operation, as these may indicate underlying issues requiring immediate attention.
Documentation: Maintain a detailed log of maintenance activities and inspections. This record helps track the history of upkeep and can be invaluable for future assessments or troubleshooting.