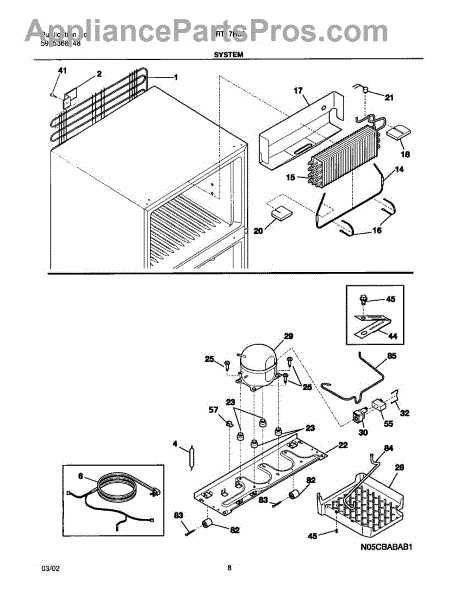
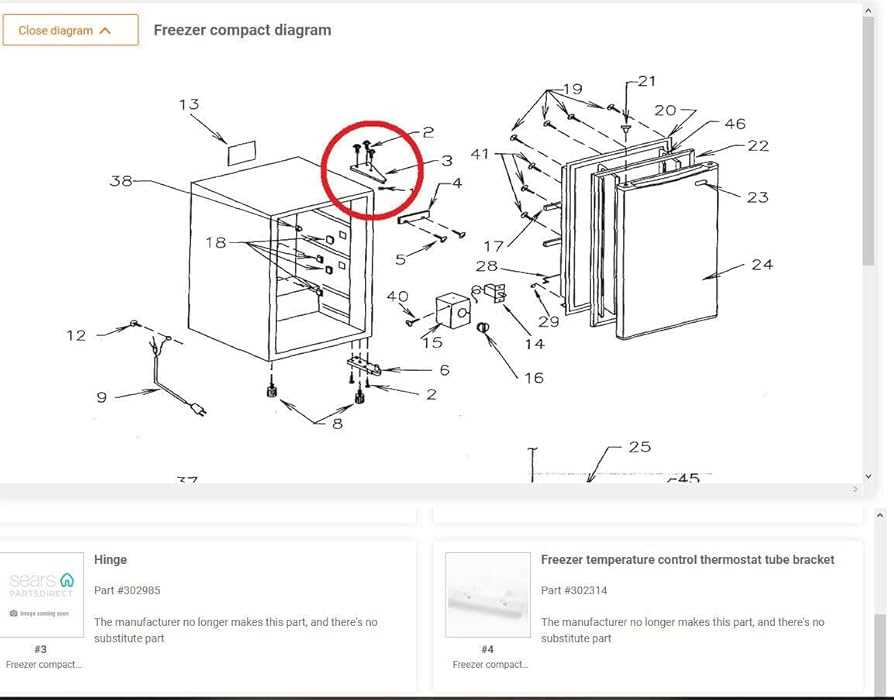
When it comes to maintaining an efficient cooling system, understanding how different elements function together is crucial. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance, from temperature regulation to energy consumption. This section will provide a detailed breakdown of the essential mechanisms involved in keeping a cooling unit operating smoothly over time.
In the following content, we will explore various critical sections, describing their functions and connections. With this knowledge, users can easily identify potential issues and make informed decisions about maintenance or repairs, ensuring the longevity of their cooling equipment.
By examining each section closely, you’ll gain insight into how to approach troubleshooting and recognize the importance of regular upkeep. These details will help you navigate and understand the internal workings of your unit, contributing to better overall management and efficiency.
Overview of Kenmore Freezer Components
Understanding the various elements within a cooling appliance is essential for ensuring efficient operation and maintenance. These machines are composed of multiple integral systems that work together to preserve food at optimal temperatures. Familiarity with each section allows users to identify potential issues and keep the device running smoothly.
Main Cooling Mechanism

The primary system responsible for maintaining low temperatures includes the compressor, condenser, and evaporator. Together, these parts ensure proper airflow and temperature control, efficiently removing heat from inside the unit. Regular inspection and cleaning can help extend the longevity of these components.
Internal Storage Structure
Inside the unit, the storage areas are designed to maximize space while providing easy access to stored goods. Shelving units and baskets are arranged to allow airflow, ensuring even cooling throughout the interior. Proper organization of this space contributes to optimal energy efficiency.
Understanding the Freezer’s Key Functions
To fully grasp the essential functions of this appliance, it’s crucial to look at how various systems work together to maintain optimal storage conditions. These mechanisms ensure consistent performance, preserving items over extended periods. Let’s explore the primary roles and processes that contribute to the unit’s efficient operation.
Temperature Regulation
The cooling system is designed to maintain a stable internal climate, crucial for preventing spoilage. This is achieved through a combination of sensors, compressors, and thermostats working in unison. When temperature levels fluctuate, these components adjust to restore balance, ensuring the preservation of stored items.
Air Circulation
Proper ventilation inside the unit is key to preventing frost buildup and ensuring even cooling. Fans and vents distribute cold air evenly, reducing temperature variations between shelves. This
Interior Parts and Their Purpose
The internal components of this cooling appliance are essential for ensuring consistent performance and maintaining the proper temperature for stored items. Each element serves a specific role in the overall functionality, contributing to the efficiency and user experience of the device. Understanding the purpose of these key components will help users optimize usage and maintain the unit effectively.
Shelves and Drawers
The shelving system is designed to organize contents, allowing easy access and maximizing storage capacity. Adjustable shelves provide flexibility for storing items of various sizes, while drawers help keep smaller or more delicate items separated and at the right temperature.
Cooling Mechanisms
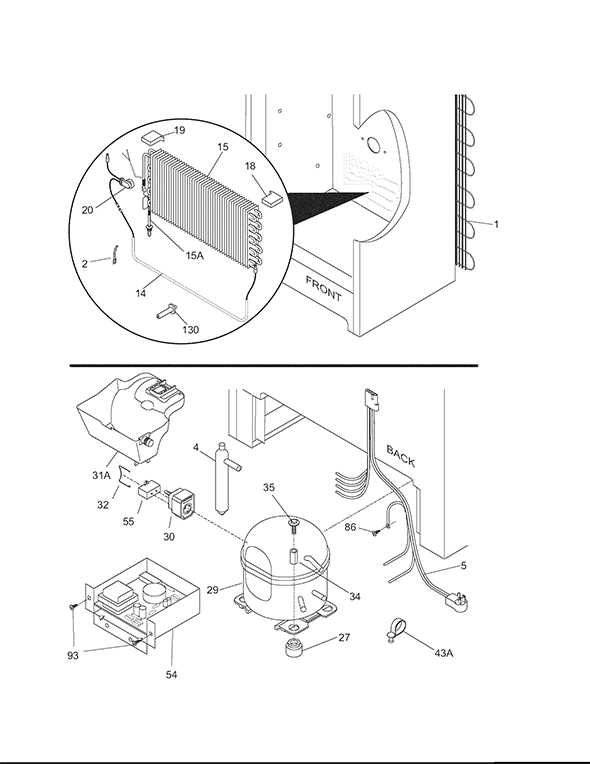
Cooling elements, such as fans and vents, distribute cold air evenly across the interior.
Detailed Breakdown of Internal Components

The internal structure consists of various interconnected systems that work together to ensure efficient performance. Each component plays a critical role in maintaining the overall functionality and ensures that all operations run smoothly.
Cooling Mechanism: At the heart of the system is the cooling mechanism, responsible for regulating temperature. This includes a compressor, condenser, and evaporator, all functioning together to maintain optimal conditions.
Storage Sections: The storage area is divided into multiple compartments. These are designed for organized placement, allowing for efficient use of space while ensuring proper air circulation.
Temperature Control Unit: The control system is essential for setting and maintaining desired temperatures. It typically consists of adjustable knobs or digital displays, offering precise management of internal climate.
Electrical System and Circuit Layout

The electrical system is a vital component responsible for ensuring efficient operation by managing power distribution across different functional areas. This section provides an overview of the general layout and structure of the circuitry involved in regulating key elements, including temperature control and power management.
Each electrical circuit is designed to carry specific current loads to essential components, ensuring stable performance under varying conditions. Proper connections between wires, relays, and switches allow for smooth communication between parts of the system, facilitating safe and reliable operation.
Key elements like safety mechanisms and
Key Aspects of Power and Control Systems
The efficiency and reliability of any refrigeration unit significantly depend on the integration of power and control mechanisms. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity by regulating energy consumption and operational parameters.
Power Supply Considerations
Understanding the fundamentals of power supply is essential for effective operation. Key factors include:
- Voltage Requirements: Different appliances require specific voltage levels for optimal functioning. Ensuring compatibility prevents potential damage.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient components reduces overall consumption and operating costs.
- Surge Protection: Incorporating surge protectors safeguards against voltage spikes that could harm sensitive electronic parts.
Control Mechanisms
Control systems are vital for monitoring and adjusting various operational aspects. Important elements involve:
- Thermostatic Control: Thermostats regulate temperature by switching the compressor on and off based on preset values.
- Humidity Regulation: Maintaining appropriate humidity levels is essential for preventing frost buildup and ensuring food preservation.
- Automated Alerts: Modern systems may include alerts for temperature fluctuations or system malfunctions, enhancing reliability.
Cooling Mechanism and Refrigeration Process
The efficiency of temperature regulation in storage appliances is primarily governed by a well-designed cooling system. This system operates by transferring heat from the interior to the exterior, thus maintaining a low temperature within the storage compartment. Understanding this process is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the appliance.
Key Components of the Cooling System
- Compressor: This component is responsible for compressing the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature before it enters the condenser.
- Condenser: Here, the high-pressure gas releases heat to the surroundings and transforms into a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve: This valve regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator, allowing it to expand and cool down.
- Evaporator: In this component, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the interior, causing the temperature to drop and maintaining the desired cold environment.
Refrigeration Cycle Overview
- The compressor compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its pressure and temperature.
- The gas flows into the condenser, where it releases heat and condenses into a liquid.
- The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature.
- The cold refrigerant enters the evaporator, absorbing heat from the surrounding area, thus cooling the interior.
- The cycle repeats as the refrigerant returns to the compressor.
Explaining the Freezer’s Cooling Cycle
The cooling process of a refrigeration unit is a vital mechanism that maintains low temperatures for food preservation. This system relies on a series of interconnected components working together to efficiently transfer heat away from the interior space.
At the heart of this operation is the compressor, which circulates the refrigerant through the system. The refrigerant begins as a low-pressure gas and is compressed into a high-pressure state, generating heat in the process. This heated gas then travels to the condenser coils, where it dissipates heat into the surrounding environment, transforming into a liquid state.
Next, the liquid refrigerant moves to the expansion valve, where it experiences a rapid decrease in pressure. This drop in pressure allows the refrigerant to cool significantly as it enters the evaporator coils. Inside the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the interior, returning to its gaseous state and effectively lowering the temperature of the unit.
The cycle then repeats as the gaseous refrigerant flows back to the compressor, ensuring continuous cooling. Understanding this cycle is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining the efficiency of the refrigeration system, allowing for optimal food storage and freshness.
Door Assembly and Seal Maintenance
Proper care of the door components and sealing mechanisms is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency. Regular inspection and maintenance ensure that these elements function effectively, preventing temperature fluctuations and potential spoilage of stored items.
The assembly of the door plays a vital role in preserving the internal climate. A well-functioning door not only enhances accessibility but also contributes to the overall energy efficiency of the appliance. Ensuring that the door seals tightly is essential to avoid cold air escape, which can lead to increased energy consumption.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect Seals | Monthly | Check for any wear or damage on the seals to ensure a proper fit and airtight closure. |
| Clean Door Surfaces | Biweekly | Wipe down door surfaces with mild soap and water to remove any residues that may affect seal integrity. |
| Adjust Hinges | As Needed | Ensure that door hinges are aligned properly and lubricated to facilitate smooth opening and closing. |
| Test for Air Leaks | Seasonally | Conduct a simple test using a flashlight or candle to identify any gaps where air may escape. |
Regularly maintaining these components not only prolongs the lifespan of the appliance but also ensures efficient operation, ultimately saving energy and reducing costs.
How to Maintain the Freezer Door Integrity
Ensuring the proper function of a chilling appliance is essential for preserving its efficiency and longevity. One critical aspect of this maintenance involves safeguarding the closure mechanism, which plays a significant role in temperature regulation and energy consumption. Regular attention to the door’s integrity can prevent costly repairs and enhance overall performance.
Regular Inspection

Conduct frequent examinations of the door seals and hinges. Look for any signs of wear, cracks, or debris that may compromise the seal. A tight closure is vital to maintaining optimal internal conditions, and any damage should be addressed promptly to prevent cold air from escaping.
Proper Cleaning Techniques
Utilize gentle cleaning agents and a soft cloth to wipe down the door and its components. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the materials. Keeping the surface clean not only improves appearance but also ensures a proper seal, as dirt and grime can hinder the door’s ability to close tightly.
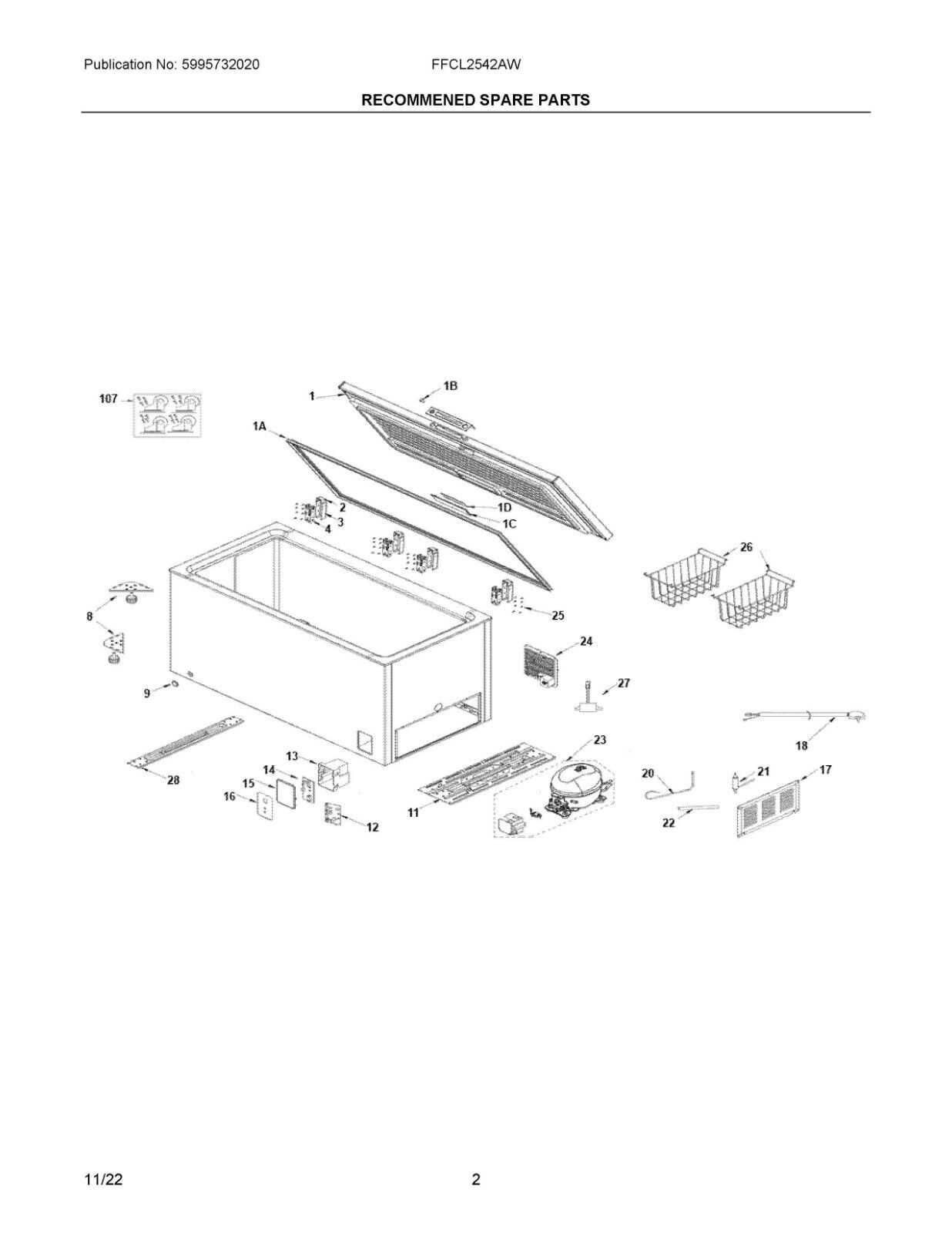
Shelves, Baskets, and Storage Options
Effective organization within cold storage units enhances accessibility and maximizes available space. Various components, such as racks and containers, play a vital role in maintaining an orderly environment. By understanding the different types of storage solutions available, users can optimize their storage approach to suit individual needs.
Racks and baskets come in various sizes and configurations, allowing for customization based on the items being stored. These elements can be easily rearranged or adjusted to accommodate different storage demands, making them essential for maintaining order.
| Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Shelves | Open design promotes airflow and visibility of items. | Lightweight, easy to clean, and adjustable. |
| Plastic Baskets | Durable containers for smaller items, providing easy access. | Stackable, versatile, and easy to remove. |
| Sliding Racks | Easy access to items stored in the back. | Maximizes space and improves organization. |
| Adjustable Dividers | Customizable sections within larger storage units. | Allows for organization of various item sizes. |
In conclusion, selecting the right combination of storage solutions ensures an efficient and tidy setup. By tailoring racks and baskets to specific needs, users can significantly enhance their overall experience.
Maximizing Space for Optimal Storage
Efficiently utilizing available space is crucial for maintaining an organized storage environment. By implementing strategic approaches, you can enhance the functionality of your storage unit, allowing for easy access and optimal use of each section. Whether you are looking to store food items, seasonal goods, or household essentials, maximizing every inch can lead to significant improvements in overall storage effectiveness.
Start by categorizing items based on size and frequency of use. Place frequently accessed products at eye level, while less commonly used items can be stored higher or lower. Additionally, consider utilizing modular storage bins or baskets to separate different categories. This not only aids in organization but also helps to minimize wasted space within the unit.
Another effective strategy is to take advantage of vertical space. Installing shelves or using stackable containers can create additional layers for storage, making it easier to find what you need without cluttering the available area. Moreover, labeling containers can simplify the retrieval process, ensuring that everything is easily identifiable and accessible.
Lastly, regularly evaluate the contents and adjust as necessary. By periodically reviewing stored items, you can eliminate expired or unused goods, thus optimizing the storage area. Maintaining a systematic approach ensures that your storage remains functional and adaptable to changing needs.
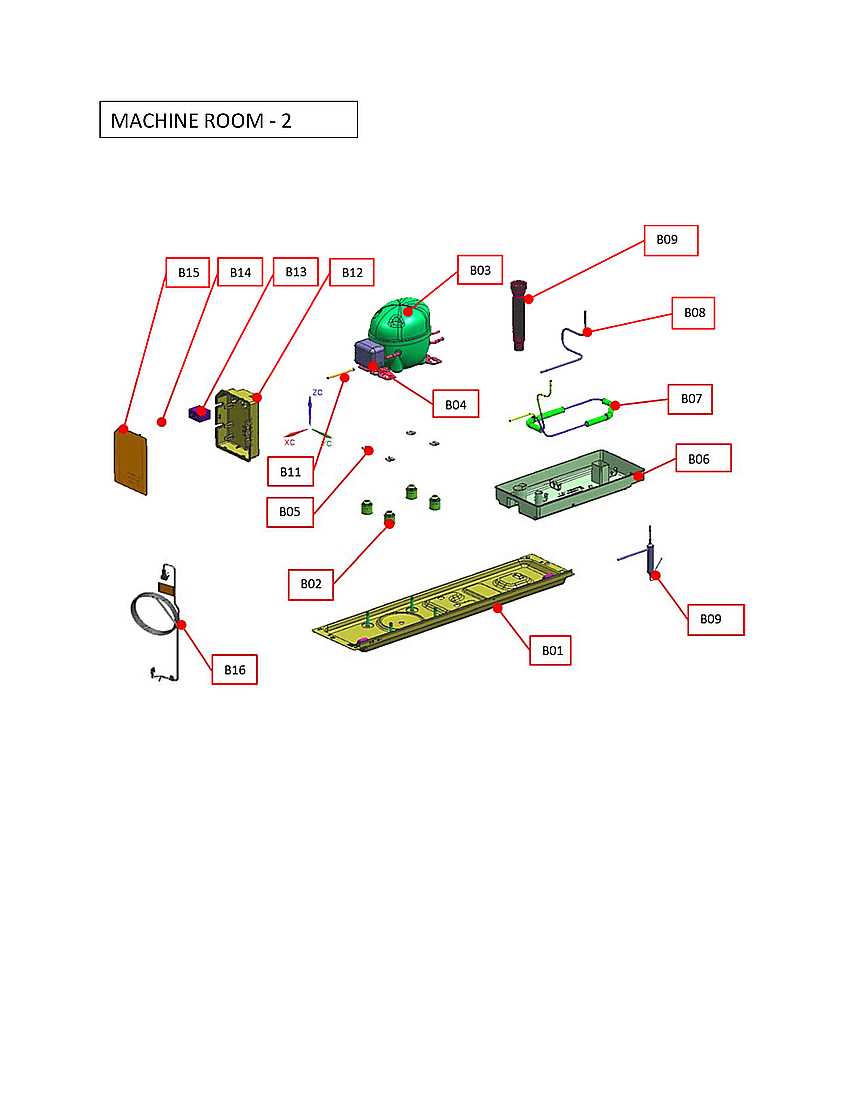
Compressor Unit and Related Components
The compressor unit is a crucial element in refrigeration systems, responsible for circulating refrigerant throughout the unit. This component plays a vital role in maintaining the desired temperature by compressing and moving the refrigerant through various stages of the cooling cycle. Understanding the structure and function of the compressor and its associated parts is essential for efficient operation and troubleshooting.
Key components related to the compressor include the condenser, evaporator, and various valves. Each of these elements works in conjunction with the compressor to ensure optimal performance of the refrigeration system. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of these components can significantly extend the lifespan and efficiency of the entire cooling apparatus.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Compressor | Mechanism that compresses refrigerant gas. | Facilitates refrigerant circulation in the system. |
| Condenser | Component that cools and condenses the refrigerant. | Removes heat from the refrigerant, turning it from gas to liquid. |
| Evaporator | Unit where the refrigerant absorbs heat. | Turns liquid refrigerant back into gas, cooling the surrounding area. |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. | Controls refrigerant expansion and pressure drop. |