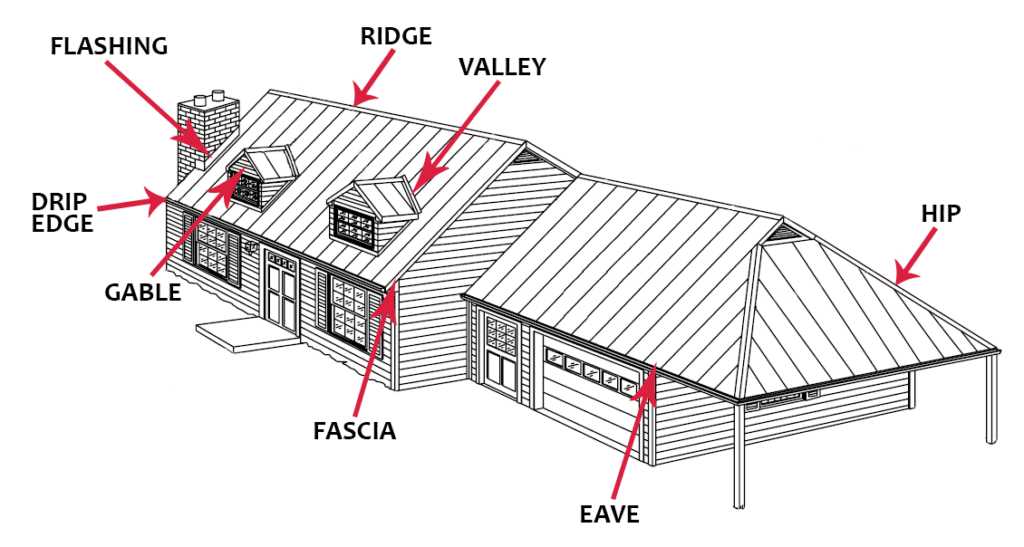
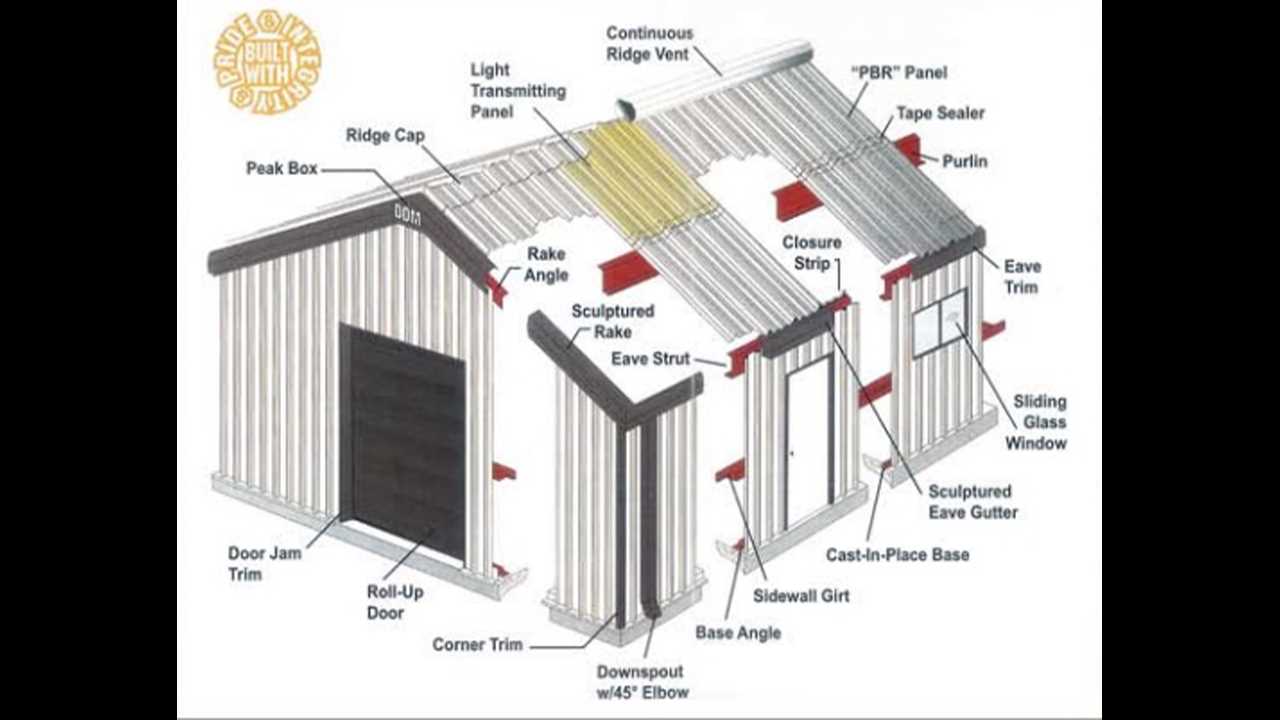
In the world of construction and design, the framework of protective coverings plays a crucial role in ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal. These structures consist of various elements that work harmoniously to provide shelter and enhance functionality. Each component, though distinct, contributes significantly to the overall integrity of the assembly.
To truly grasp the functionality and arrangement of these elements, one must delve into their specific roles and interconnections. A comprehensive exploration reveals how each segment is designed to withstand environmental factors while maintaining the visual charm of the edifice. This investigation will illuminate the ultimate composition and engineering behind these robust systems.
By examining these critical features, homeowners and builders can make informed decisions regarding installation and maintenance, leading to lasting benefits. Understanding the interplay of these components not only enhances knowledge but also promotes efficient and effective building practices.
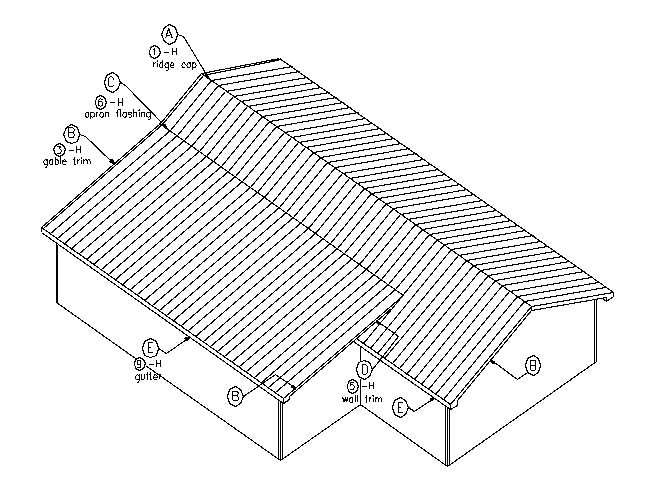
Understanding Metal Roof Components
Exploring the various elements involved in the construction of a durable and efficient overhead covering reveals the complexity and importance of each individual piece. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring the longevity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the structure.
Key Elements Involved
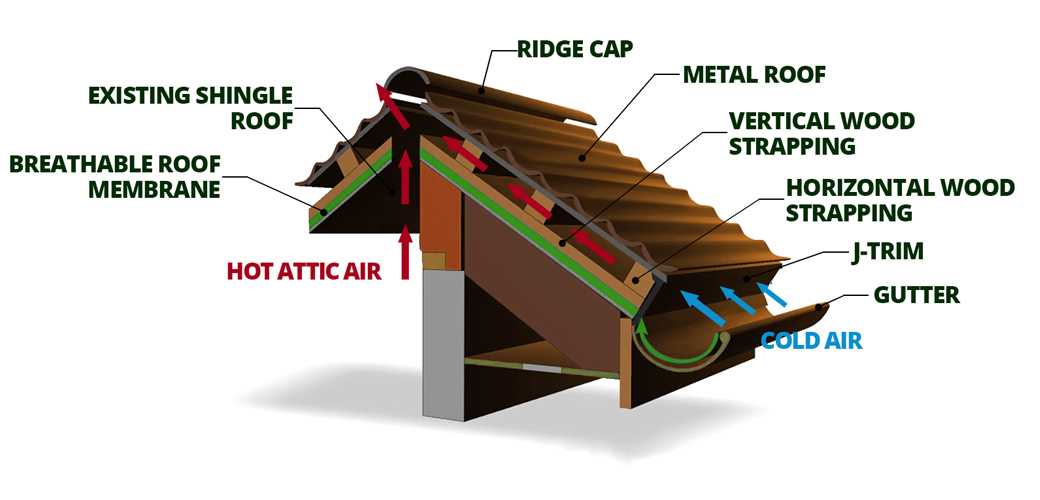
- Framework: This provides the essential support and stability needed for the entire assembly.
- Covering Sheets: These are the visible elements that protect against weather conditions and contribute to the overall appearance.
- Flashing: Critical for directing water away from joints and seams, preventing leaks and damage.
- Underlayment: A protective layer that adds insulation and moisture resistance beneath the covering sheets.
- Fasteners: These secure all components together, ensuring structural integrity and resistance to high winds.
Functions of Each Component
- Support: The framework distributes weight and provides a foundation for the entire system.
- Weather Protection: Covering sheets shield against rain, snow, and UV rays, enhancing durability.
- Moisture Management: Flashing and underlayment work together to redirect water, safeguarding the underlying materials.
- Structural Security: Fasteners keep everything in place, maintaining stability during severe weather.
By understanding these essential elements and their functions, one can appreciate the intricacies involved in creating a reliable and visually appealing overhead covering.
Types of Metal Roofing Materials
When selecting materials for overhead coverings, various options exist, each with unique characteristics and benefits. Understanding these variations is crucial for making an informed choice that meets both aesthetic preferences and functional needs.
Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for coastal areas. Its reflective properties help in energy efficiency, keeping structures cooler.
Steel offers durability and strength, often coated with zinc for enhanced protection against rust. It comes in various styles, including galvanized and galvalume, catering to different aesthetic requirements.
Copper is revered for its distinctive appearance and longevity, often developing a green patina over time. Its unique style and resistance to corrosion make it a premium option for those seeking elegance.
Zinc is another high-quality choice, recognized for its self-healing properties. It effectively resists weathering and is environmentally friendly, making it a sustainable option for conscientious builders.
Each material type provides distinct advantages, allowing for customization based on personal preference and regional demands.
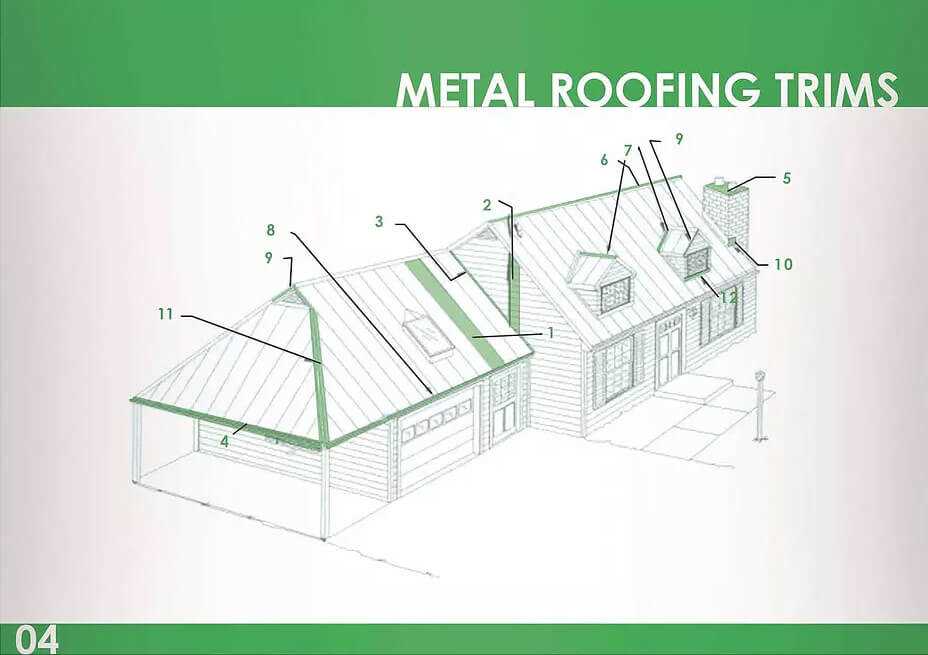
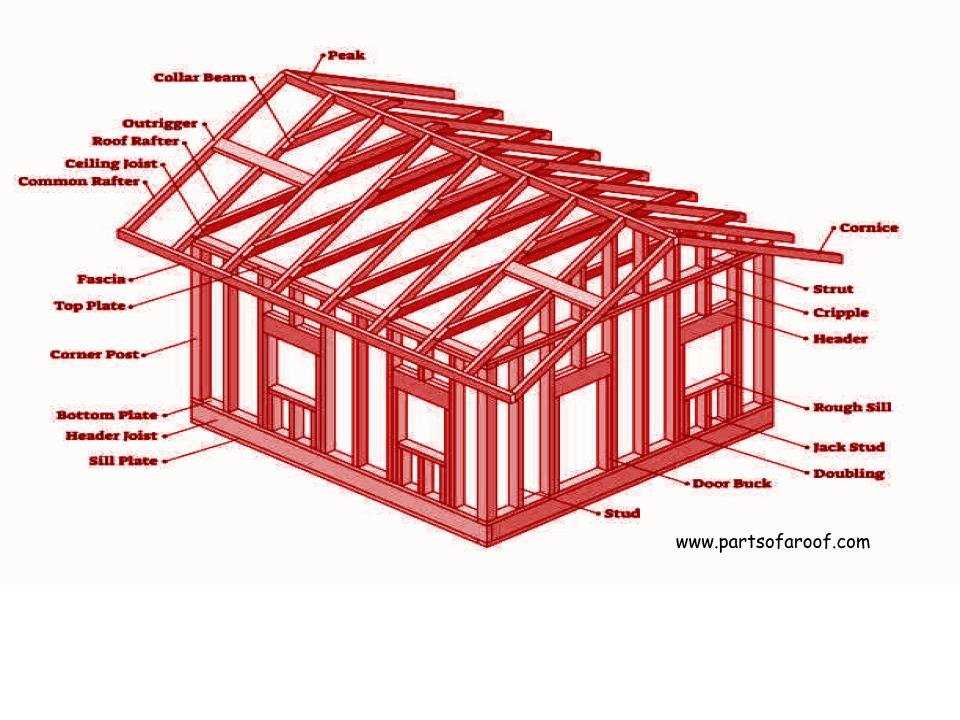
Essential Parts of Metal Roofs
Understanding the critical components that contribute to the overall structure is vital for anyone considering a durable covering. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring stability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
- Panels: The primary elements that provide coverage and protection.
- Underlayment: A protective layer that enhances insulation and moisture control.
- Flashing: Used to direct water away from seams and joints, preventing leaks.
- Gutters: Essential for directing rainwater away, safeguarding the foundation.
- Fasteners: Critical for securing elements in place, ensuring long-term stability.
- Ventilation: Important for regulating temperature and moisture levels within the structure.
Each of these components collaborates to create a robust and efficient system, providing lasting protection and enhancing the overall value of the building.
Benefits of Metal Roofing Systems
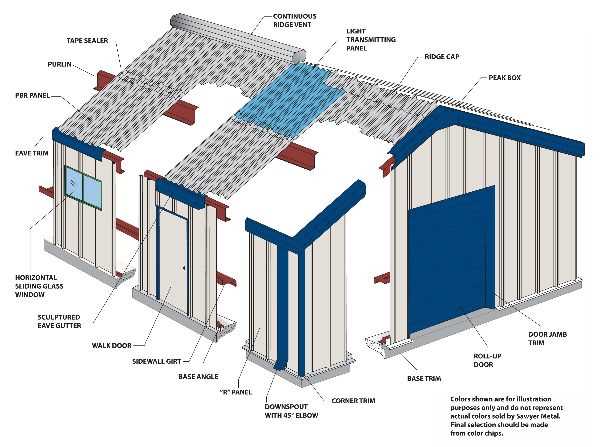
Choosing a durable covering for a structure brings numerous advantages, enhancing longevity and performance. These systems are increasingly favored for their resilience and energy efficiency, making them a worthwhile investment for any property owner.
Durability and Longevity
- Exceptional resistance to harsh weather conditions.
- Longevity, often exceeding 50 years with minimal maintenance.
- Non-corrosive materials that withstand rust and decay.
Energy Efficiency
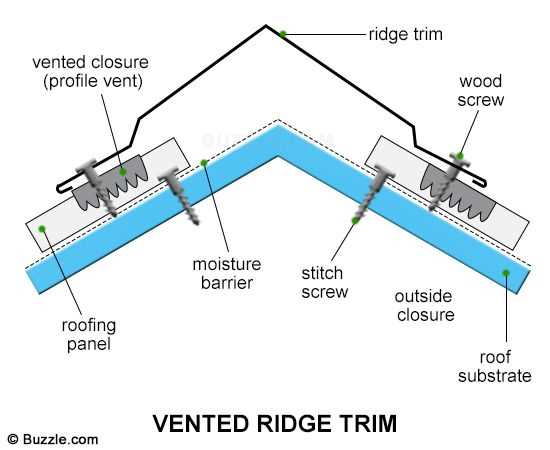
- Reflective surfaces that reduce heat absorption.
- Potential for lower energy bills due to improved insulation.
- Environmentally friendly options that contribute to sustainability.
Common Metal Roof Styles Explained
This section explores various popular styles of coverings used in construction, each offering distinct aesthetics and functional benefits. Understanding these designs can aid homeowners and builders in making informed choices that suit their preferences and requirements.
Standing Seam: This style features raised seams that interlock, providing excellent durability and water resistance. Its sleek appearance is favored for modern architecture.
Corrugated Panels: Characterized by their wavy pattern, these panels are lightweight and easy to install. They are commonly used in agricultural buildings and shed structures.
Shingle Style: Mimicking traditional shingles, this design combines the durability of metal with the classic look of asphalt or wood, offering a versatile aesthetic for residential properties.
Tile Effect: These panels are crafted to resemble clay or slate tiles, providing a sophisticated look while maintaining the advantages of lightweight materials and longevity.
Batten Panels: This style features horizontal battens over vertical panels, creating a textured appearance. It’s known for its strength and ability to handle extreme weather conditions.
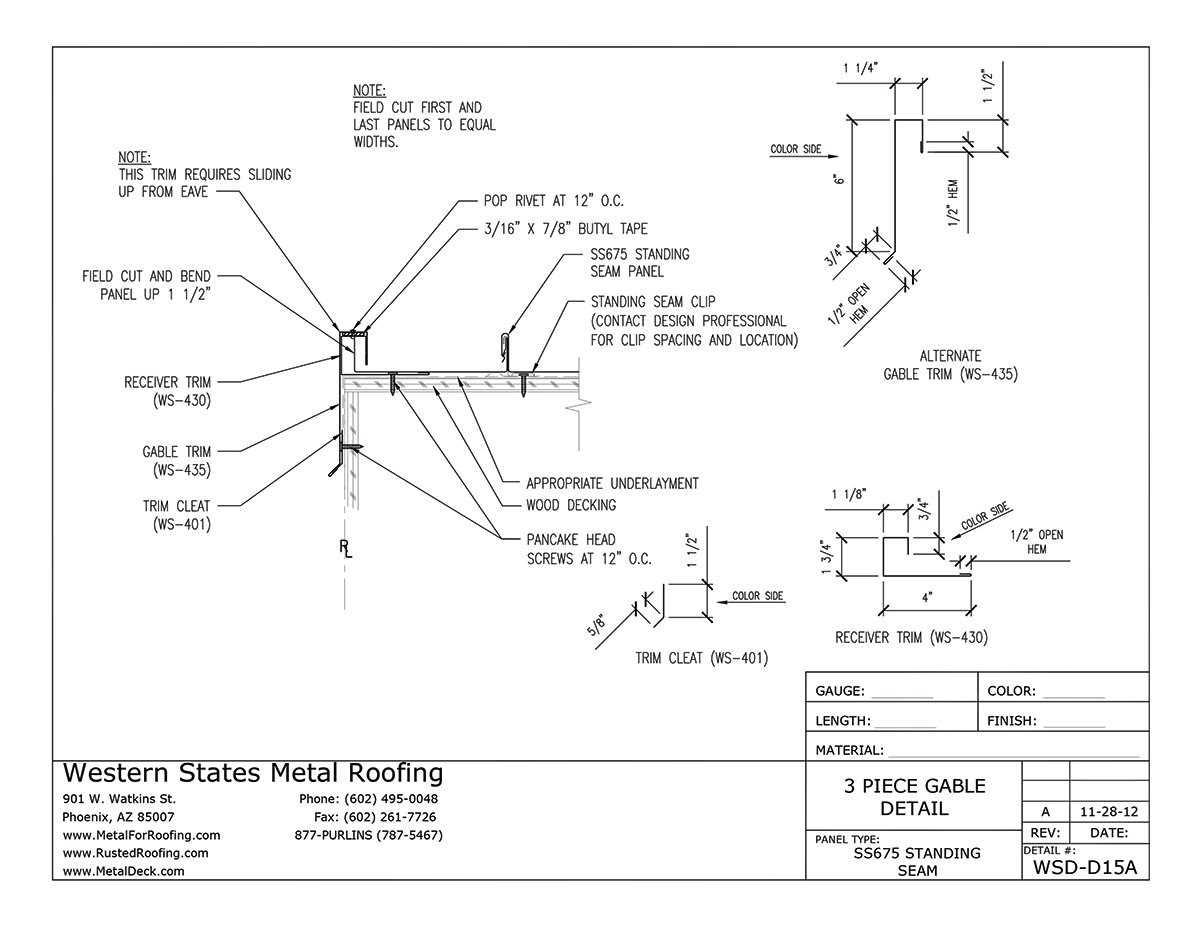
Installation Process of Metal Roofs
Understanding the procedure for setting up a durable overhead system is essential for ensuring longevity and efficiency. Each phase plays a crucial role in the overall success, from preparation to final inspection. Proper techniques and tools can significantly enhance performance and aesthetics.
Preparation Steps
Before commencing, assess the structure’s condition and gather necessary materials. Ensure all safety measures are in place, including protective gear. Clear the area of debris and make any necessary repairs to the underlying surface.
Installation Steps
Begin by laying down underlayment, which acts as a barrier against moisture. Next, attach the primary panels, securing them firmly to withstand adverse weather. Finally, install the finishing elements, ensuring everything is tightly sealed for maximum protection.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Assess and prepare the structure |
| 2 | Install underlayment |
| 3 | Attach primary panels |
| 4 | Add finishing elements |
Maintenance Tips for Metal Roofs

Proper care is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of your structure’s exterior covering. Regular attention can prevent minor issues from escalating into costly repairs, thereby preserving the overall integrity and appearance. Here are some key practices to keep in mind.
Regular Inspections
Conduct periodic evaluations of the surface, especially after extreme weather events. Look for signs of wear, such as loose seams, rust, or any debris accumulation. Timely detection of problems allows for prompt intervention, which can save both time and money.
Cleaning Techniques
Maintaining cleanliness is crucial. Use a gentle detergent and soft-bristle brush to remove dirt, algae, and other buildup. Avoid abrasive materials that can damage the finish. Routine cleaning helps maintain aesthetic appeal and functional efficiency.
Factors Influencing Metal Roof Lifespan
The longevity of a covering system is determined by various elements that interplay throughout its lifecycle. Understanding these factors can help ensure optimal performance and durability, ultimately protecting the underlying structure and enhancing property value.
Material Quality
The selection of high-grade materials significantly affects the durability of the covering. Premium options often resist corrosion, wear, and extreme weather conditions better than lower-quality alternatives.
Installation Techniques
Proper installation is crucial for the longevity of any covering system. Skilled workmanship and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can prevent issues like leaks and thermal expansion, which could compromise integrity over time.
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | High-quality materials enhance resistance to elements and reduce maintenance needs. |
| Installation Techniques | Proper installation minimizes risks of damage and prolongs effective life. |
| Maintenance Practices | Regular inspections and timely repairs prevent minor issues from escalating. |
| Climate Conditions | Harsh weather can accelerate wear; local climate should guide material choice. |
Tools Required for Installation
Successful setup of your structure demands the right tools, ensuring efficiency and safety throughout the process. Proper equipment not only streamlines tasks but also enhances the overall quality of the work done.
Essential Equipment
Basic implements like hammers, screwdrivers, and drills are fundamental for any installation project. Additionally, measuring tapes and levels are crucial for achieving accuracy and alignment.
Safety Gear
Personal protective equipment, such as helmets, gloves, and goggles, is vital to safeguard against potential hazards. Ensuring you have the appropriate safety gear will help prevent injuries during the installation process.
Cost Considerations for Metal Roofing
When evaluating the financial aspects of durable covering options, it’s essential to examine various factors that contribute to overall expenses. From initial investment to long-term savings, understanding these elements can significantly impact decision-making.
| Cost Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Costs | Quality and type of material greatly influence the price. |
| Installation | Professional installation can add to overall expenses. |
| Maintenance | Some options require less upkeep, impacting future costs. |
| Longevity | Investing in a more durable choice can yield savings over time. |
Comparing Metal Roofs to Other Materials
When evaluating various coverings for structures, it’s essential to consider their characteristics, longevity, and overall performance. Different materials offer unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact aesthetics, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This section will delve into how one type stands against alternatives, highlighting key factors that influence decision-making.
One of the primary benefits of using this type is its impressive lifespan, often outlasting traditional choices. While asphalt shingles may need replacement every couple of decades, this option can endure for 50 years or more with proper maintenance. Additionally, it reflects sunlight, contributing to energy efficiency and reducing cooling costs.
In contrast, traditional options tend to be more susceptible to weather conditions, leading to potential damage over time. For example, wood may provide a classic look but often requires regular upkeep to prevent decay and insect infestation. Furthermore, synthetic materials might offer a lower upfront cost, yet they may not achieve the same level of durability or sustainability.
Ultimately, choosing the right material involves weighing immediate costs against long-term benefits, environmental impact, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences helps ensure a well-informed decision that aligns with individual needs and preferences.