
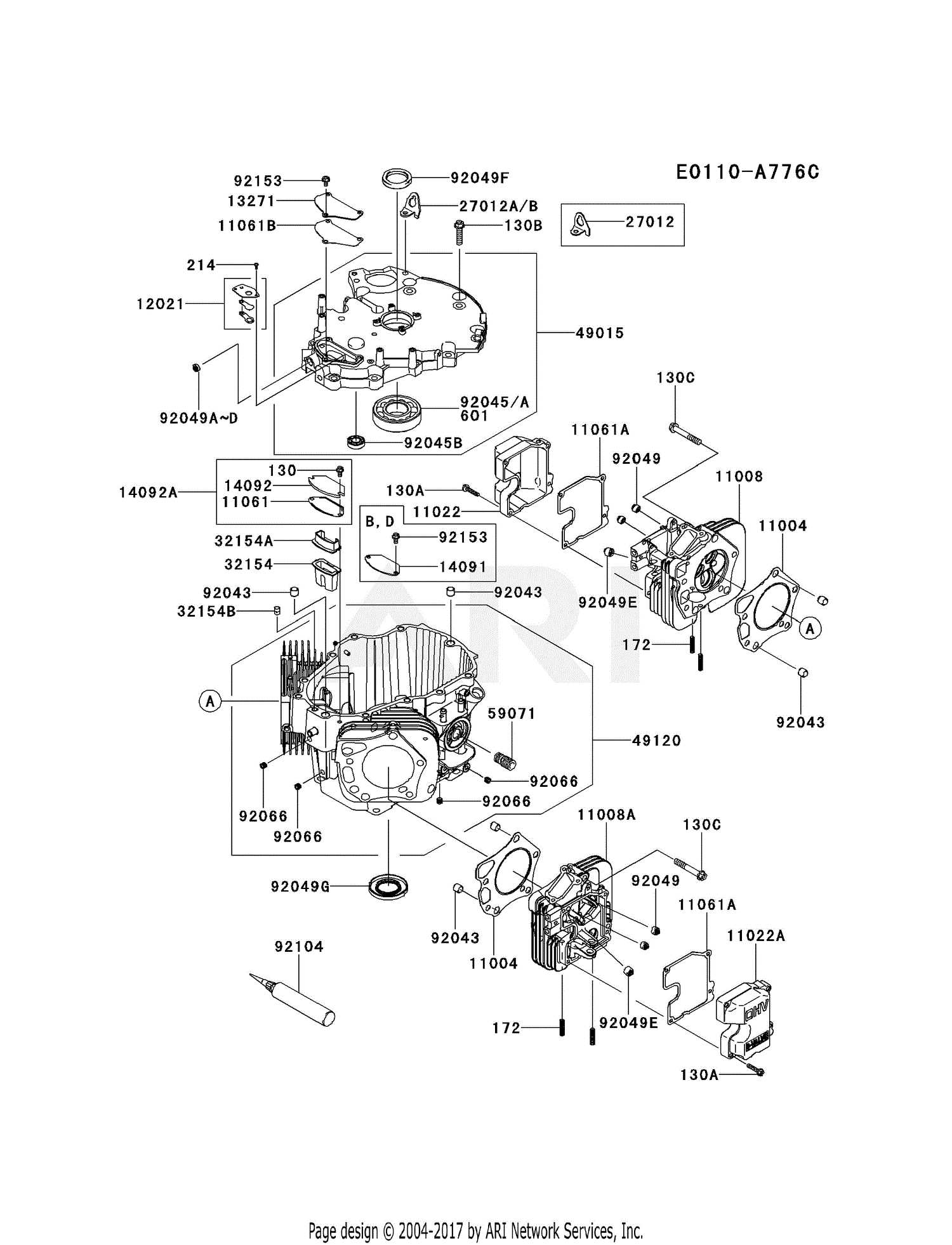
Exploring the intricate layout of a two-cycle motor reveals a fascinating interplay of essential elements that work in harmony to generate power. Each component plays a pivotal role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the system. This exploration will provide insights into how these vital parts collaborate to create movement.
By dissecting the various elements, one can appreciate the design and engineering behind this machinery. Understanding these components helps in grasping their individual functions and how they affect the performance of the motor. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, having knowledge of these essentials is crucial for maintenance and enhancement of operational capabilities.
Furthermore, delving into the specifics allows for a clearer perspective on troubleshooting and optimization. Familiarity with these components empowers users to make informed decisions regarding repairs and modifications, ultimately leading to improved performance and longevity.
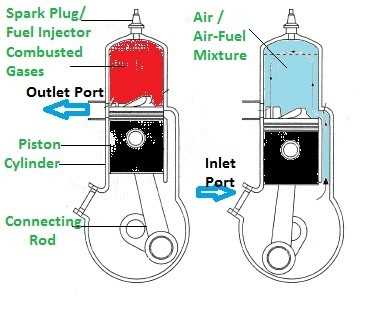
Understanding Two-Stroke Engine Basics
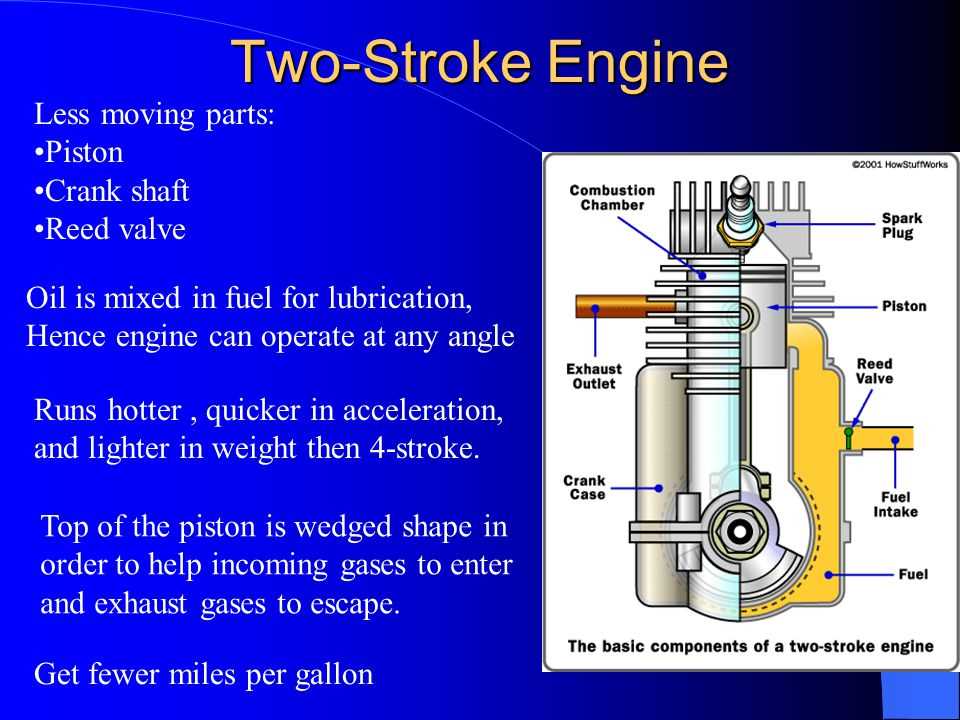
This section delves into the fundamental principles of a particular type of internal combustion mechanism, which operates through a simplified cycle, allowing for efficient power generation in a compact form. The process is characterized by a unique sequence that combines intake, compression, power, and exhaust in just two movements of the piston.
Central to this design is a variety of components that work in harmony to achieve optimal performance. Each element plays a critical role in facilitating the swift cycle, contributing to both power output and efficiency.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Piston | Moves to compress the fuel-air mixture and transmit power during combustion. |
| Crankshaft | Converts linear motion from the piston into rotational movement. |
| Combustion Chamber | Where the fuel-air mixture ignites to produce energy. |
| Intake Ports | Allow the entry of the fuel-air mixture into the chamber. |
| Exhaust Ports | Facilitate the exit of burnt gases after combustion. |
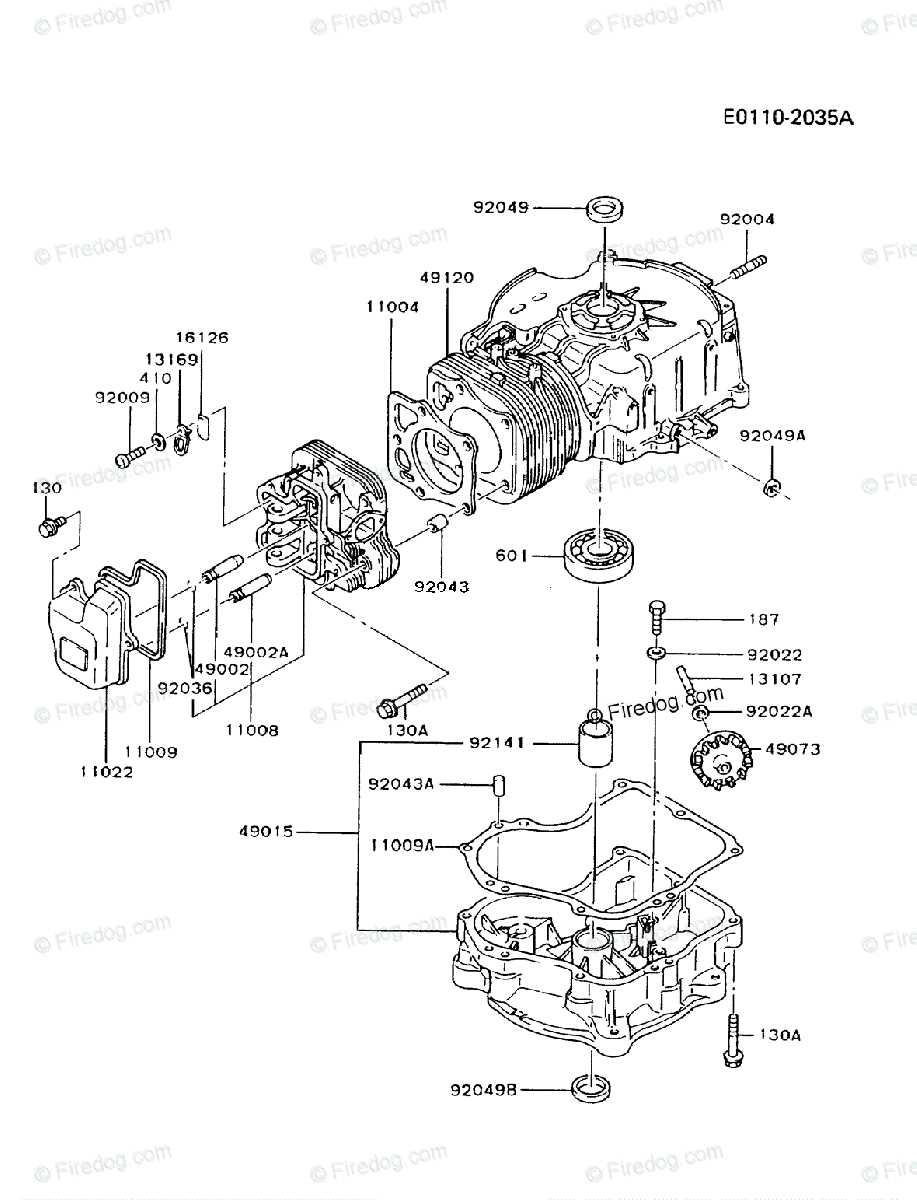
Key Components of Two-Stroke Engines
Understanding the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of a two-cycle power unit is crucial for enthusiasts and technicians alike. Each component plays a pivotal role in the overall operation, influencing efficiency, performance, and durability.
Fuel and Air Mixture System
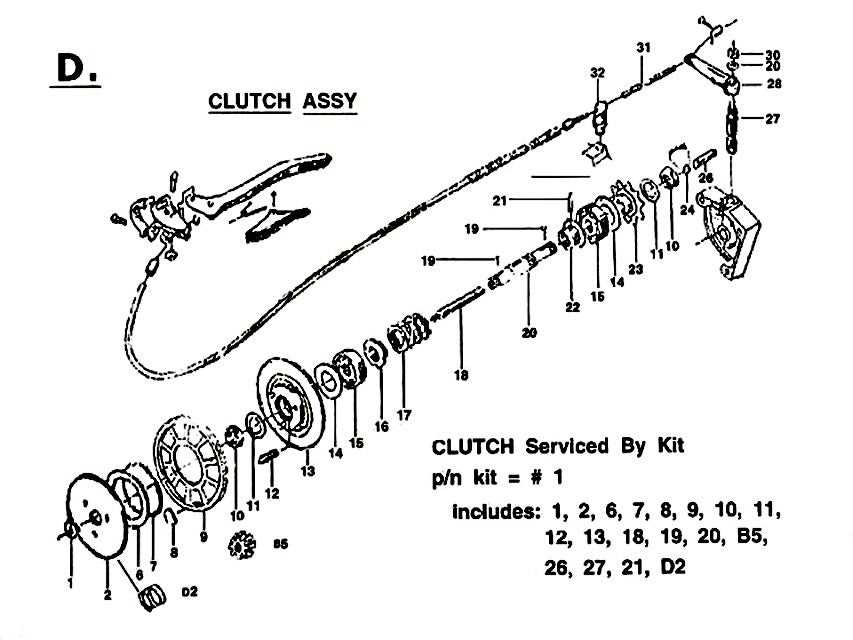
The first crucial aspect is the system responsible for mixing fuel and air. This blend is vital for combustion, and its composition can significantly affect the output. Components like carburetors or injectors ensure the right mixture reaches the combustion chamber, promoting optimal power generation.
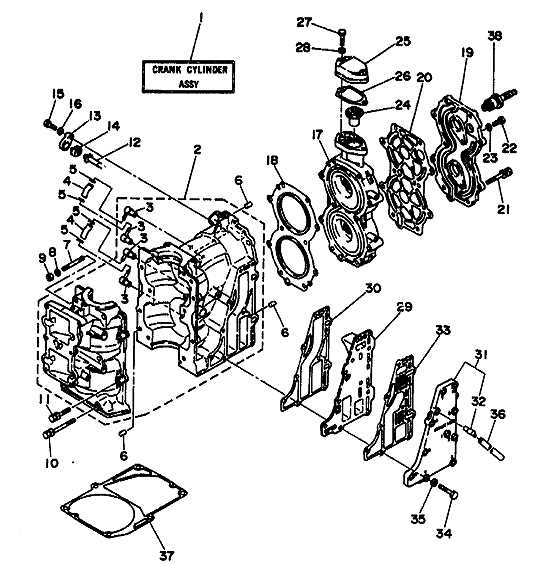
Combustion Chamber Mechanics
Another significant area is the mechanics of the combustion chamber itself. This section houses elements such as the piston and the connecting rod, which work in harmony to convert the energy from the fuel mixture into mechanical work. The design and integrity of these components are essential for achieving high efficiency and reliability in operation.
Fuel and Oil Mixture Explained
The proper combination of fuel and lubricants is crucial for the optimal performance of two-stroke machinery. This mixture ensures that moving components receive adequate lubrication while providing the necessary energy for operation. Understanding the right proportions and types of these substances can enhance efficiency and prolong the lifespan of the equipment.
Importance of the Mixture
Using the correct blend of fuel and oil offers several advantages:
- Reduces wear and tear on internal components
- Minimizes the risk of overheating
- Enhances combustion efficiency
- Prevents carbon buildup in the combustion chamber
Recommended Ratios
The ideal ratio of fuel to lubricant varies depending on the specific application. Here are some common mixtures:
- 50:1 – Typical for many recreational machines
- 40:1 – Common in certain lawn equipment
- 32:1 – Often used in high-performance applications
Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure the best results for your specific machinery.
Differences Between Two-Stroke and Four-Stroke
Understanding the distinctions between these two mechanical designs reveals significant variations in their operation and efficiency. Each type has unique characteristics that affect performance, maintenance, and application.
Power Cycle: The two types differ in how they complete their power cycles. The first system generates power every revolution, resulting in a more compact and lighter build. In contrast, the latter produces power every two revolutions, leading to a more complex configuration.
Efficiency: Generally, the first design is known for its simplicity and lighter weight, making it suitable for portable applications. The second design, while heavier, tends to offer better fuel efficiency and longevity due to its more comprehensive operation.
Lubrication: The method of lubrication also varies significantly. The first system typically mixes oil with fuel, which can result in higher emissions. The second relies on a separate lubrication system, leading to cleaner operation and reduced environmental impact.
Applications: These differences make each type suitable for various applications. The first is often favored in smaller tools and vehicles requiring agility, while the latter is preferred in larger machines where durability and efficiency are prioritized.
Working Principle of Two-Stroke Engines
The functioning of a two-cycle mechanism is based on a unique process that completes a power cycle in just two movements of the piston. This design allows for higher power output relative to size, making it popular in various applications, from small appliances to larger machines.
Operational Phases
In this configuration, the cycle consists of two main phases:
- Compression Phase: During this phase, the piston moves upward, compressing the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber.
- Power Phase: Upon reaching the top, the mixture ignites, forcing the piston downward, generating power for the next cycle.
Advantages of This Mechanism
- Higher power-to-weight ratio.
- Simpler design with fewer components.
- Continuous power delivery due to its operational cycle.
Common Applications of Two-Stroke Engines
Two-cycle power units are widely utilized across various sectors due to their compact design and efficient operation. Their ability to deliver high power-to-weight ratios makes them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and portable solutions.
Popular Uses
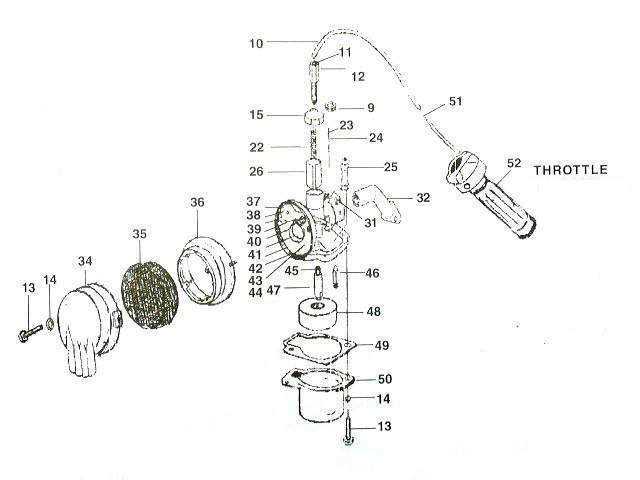
These compact mechanisms are commonly found in tools and vehicles where mobility and performance are crucial. They excel in situations that demand quick acceleration and a lightweight profile.
Typical Applications
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Chainsaws | Preferred for their power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for cutting tasks. |
| Outboard Motors | Common in marine activities for their lightweight nature and high efficiency. |
| Lawn Mowers | Used in small gardening tools for quick maneuverability and ease of use. |
| Motorcycles | Popular in lightweight bikes for their rapid response and performance capabilities. |
| Snowmobiles | Utilized for their power and agility in snowy conditions. |
Maintenance Tips for Two-Stroke Engines
Proper upkeep of small power units is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular care not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of mechanical issues. Understanding key aspects of maintenance can greatly benefit users in the long run.
Regular Cleaning
Keep the components clean to prevent the buildup of dirt and debris, which can hinder functionality. Use a soft brush and appropriate cleaning agents to maintain surfaces and internal areas. Ensuring that air passages are unobstructed will promote better airflow and efficiency.
Fuel Quality and Mixing

Utilize high-quality fuel and adhere to correct mixing ratios to ensure optimal combustion. Regularly check fuel lines for leaks and replace them as necessary. Proper fuel maintenance can prevent numerous operational issues and extend the life of your machinery.
Typical Problems in Two-Stroke Engines
Two-stroke mechanisms are known for their simplicity and lightweight design, but they often encounter specific challenges that can affect performance and longevity. Understanding these common issues is essential for proper maintenance and optimal operation.
Fuel and Oil Mixture Issues
One prevalent concern is the improper ratio of fuel to lubricants. An incorrect mixture can lead to excessive carbon buildup, resulting in reduced efficiency and potential damage. Regular checks of the mixture can help prevent these complications.
Overheating and Cooling Problems
Inadequate cooling is another critical issue. Without sufficient cooling, components can overheat, causing severe damage. Ensuring that cooling systems are functioning correctly and free from obstructions is vital for maintaining operational integrity.
Upgrades for Enhanced Engine Performance
Improving the overall efficiency and power of your mechanical system can significantly enhance its capabilities. By implementing various modifications, enthusiasts can unlock higher output and better responsiveness. These enhancements not only optimize functionality but also elevate the riding experience.
Air Intake Systems: Upgrading the air intake allows for improved airflow, which is crucial for maximizing combustion efficiency. Enhanced filtration systems can also help keep harmful debris out, ensuring cleaner operation.
Exhaust Systems: A high-performance exhaust setup can reduce back pressure, allowing for more effective exhaust gas expulsion. This modification can lead to noticeable gains in power and sound, enhancing the overall character of the unit.
Ignition Timing: Adjusting the ignition timing can improve fuel combustion, leading to a more powerful output. Electronic ignition systems offer precise timing adjustments that can be fine-tuned for optimal performance.
Fuel Quality: Using higher-octane fuel can lead to better combustion efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for systems designed to handle advanced tuning and modifications.
Weight Reduction: Reducing unnecessary weight from the overall setup can significantly improve acceleration and handling. Lightweight materials or removing non-essential components are effective strategies.
Implementing these modifications can lead to a remarkable improvement in performance, making the mechanical unit more responsive and enjoyable to operate.
Choosing the Right Engine Parts
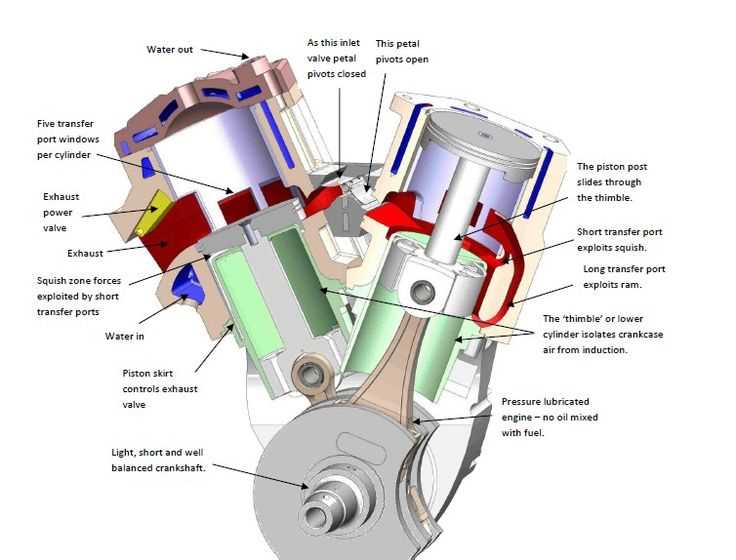
Selecting appropriate components for a combustion mechanism is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the specific requirements of your application can significantly enhance efficiency and reliability. It’s essential to consider quality, compatibility, and the intended use of each element.
When making your selection, it’s beneficial to evaluate various options based on key characteristics. Below is a table that outlines important factors to consider when choosing components for a combustion mechanism.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | Choose durable materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. |
| Compatibility | Ensure that each element fits correctly with other components to prevent malfunctions. |
| Performance Ratings | Look for specifications that indicate efficiency and power output potential. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Consider how often each component will need servicing and its overall upkeep. |
| Brand Reputation | Select from manufacturers known for reliability and customer satisfaction. |
Making informed decisions regarding each component can lead to enhanced functionality and extended service life for your machinery.