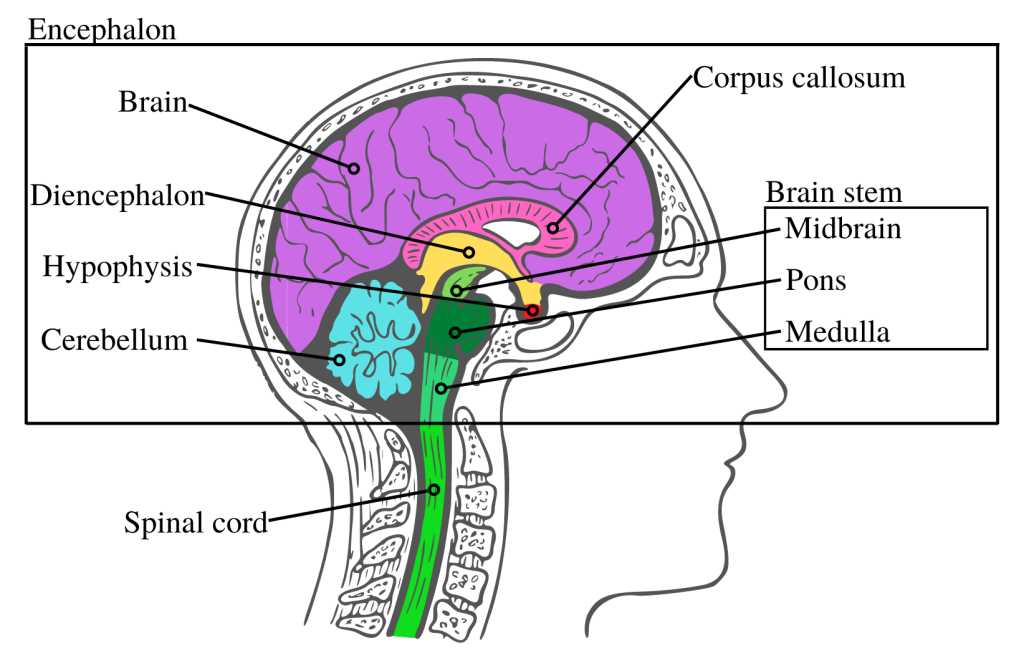
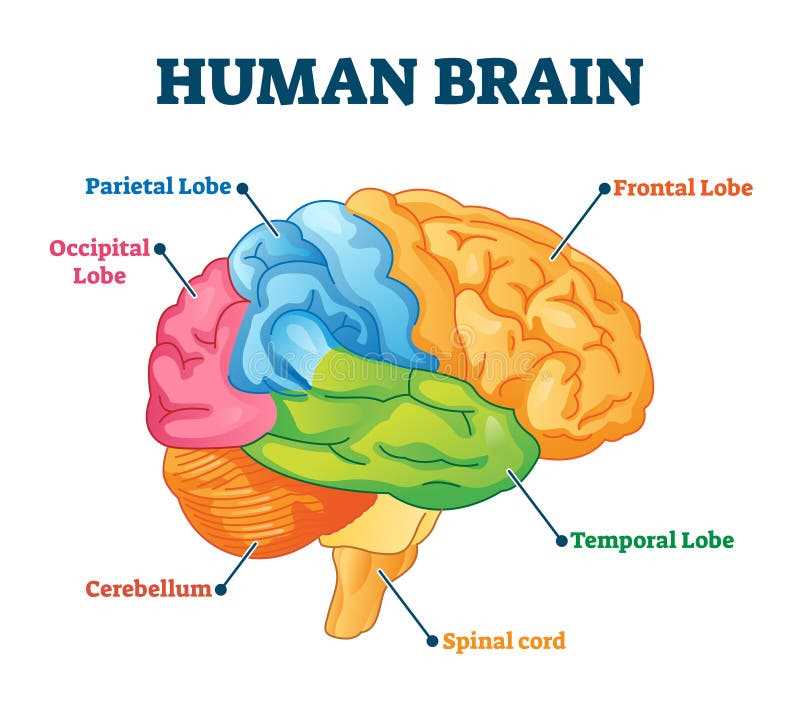
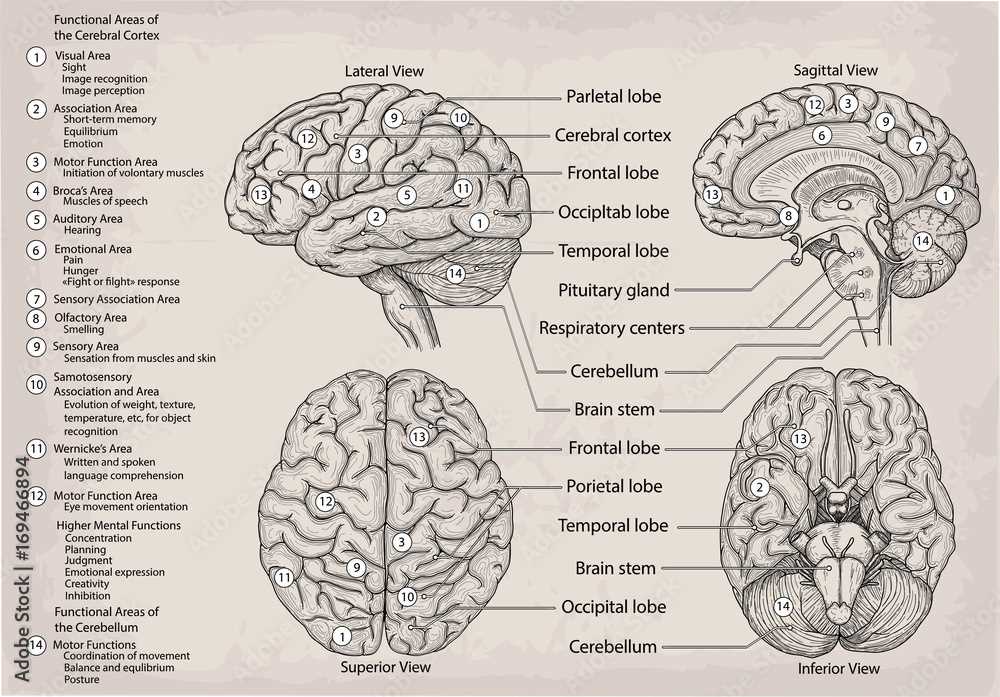
An intricate network exists within our bodies, serving as a command center for various functions and activities. Understanding this complex assembly is crucial for grasping how sensations, thoughts, and movements are orchestrated. Each section plays a vital role, contributing to the overall harmony of operations.
The exploration of these elements reveals how they interact and support each other, creating a seamless experience for individuals. By analyzing their arrangement and connections, one can appreciate the remarkable efficiency and adaptability inherent in this biological framework.
Visual representations can enhance comprehension, providing insight into the roles and relationships among these regions. This approach fosters a deeper understanding of not only how actions are executed but also how conditions can affect overall functionality.
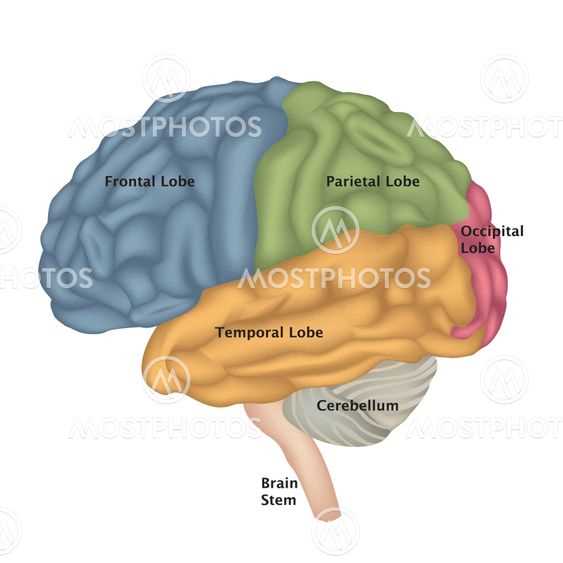
This section delves into a vital region responsible for fine-tuning motor activities and maintaining equilibrium. It plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and coordinated movements, allowing individuals to perform tasks with precision.
Functions of the Cerebellum
- Regulates posture and stability
- Coordinates voluntary movements
- Facilitates learning of motor skills
- Adjusts actions based on sensory input
Impact on Daily Activities
Effective functioning of this region is essential for various everyday tasks. From walking to writing, it enables seamless execution of movements. Impairments in this area can lead to difficulties in coordination, resulting in challenges in performing routine actions.
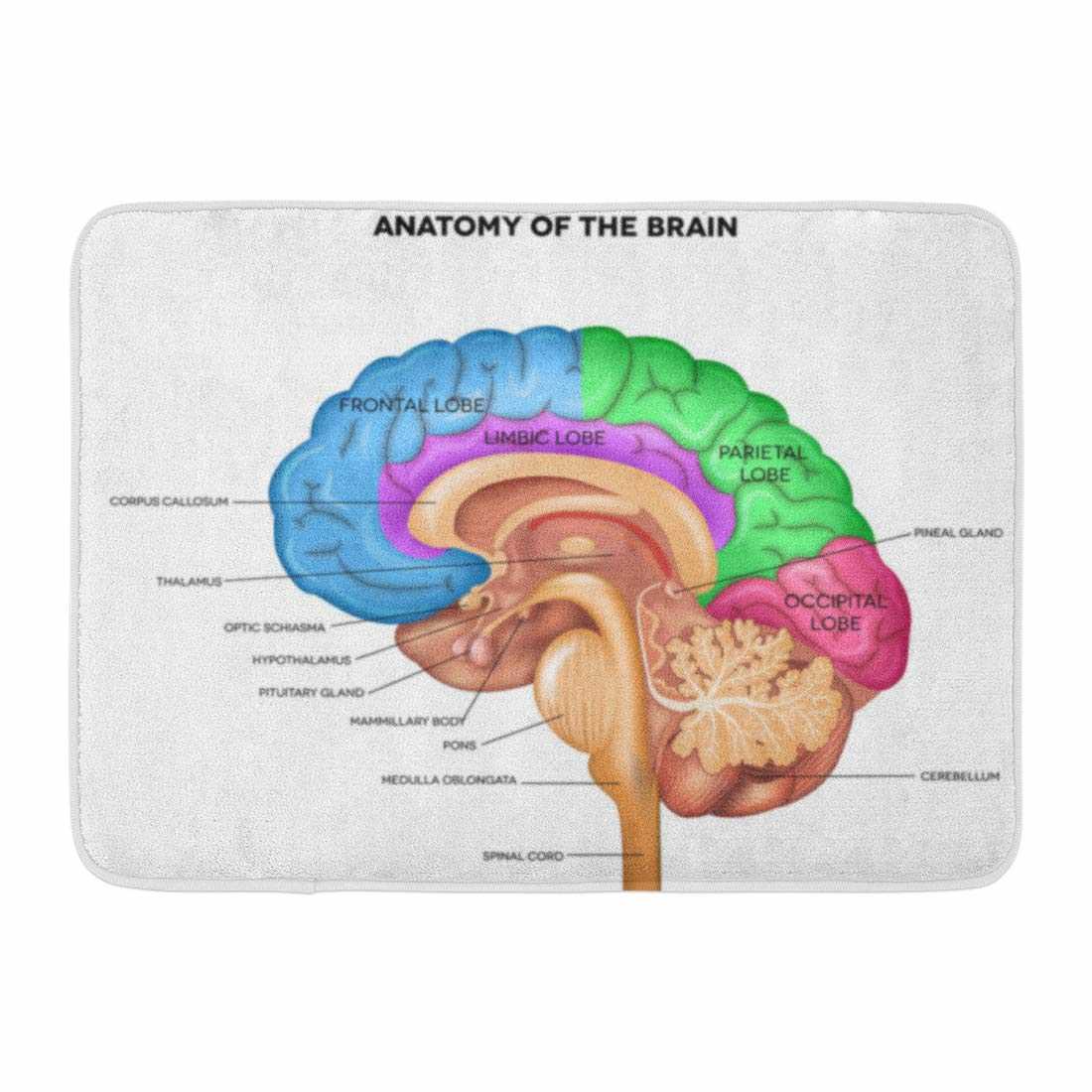
Brainstem: Vital Life Functions
The brainstem plays a crucial role in maintaining essential processes that support life. It acts as a control center, coordinating automatic functions necessary for survival.
This structure regulates critical activities such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure, ensuring that these functions operate smoothly without conscious thought. Its influence extends to the management of reflexes and responses to stimuli, making it vital for reacting to environmental changes.
Additionally, the brainstem serves as a communication pathway between different regions of the nervous system, facilitating the transmission of signals that impact various bodily functions. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it underpins many physiological processes essential for overall health.
Limbic System: Emotions and Memory
This intricate network plays a crucial role in regulating feelings and recollections. It serves as a bridge between instinctual responses and complex thoughts, influencing how experiences are processed and remembered. The structure is vital for understanding emotional reactions and forming lasting memories.
Components and Functions
Within this network, several key elements interact to shape emotional experiences. Structures like the amygdala and hippocampus are essential for processing emotions and storing memories. The amygdala, in particular, is known for its role in fear responses and emotional learning, while the hippocampus is critical for transforming short-term experiences into long-term memories.
Impact on Behavior
Emotional states greatly influence decision-making and behavior. The connections formed in this region help individuals navigate social interactions and adapt to various situations. Understanding how this system operates provides insight into the complexities of emotional well-being and cognitive functioning.
Frontal Lobe: Decision Making Center
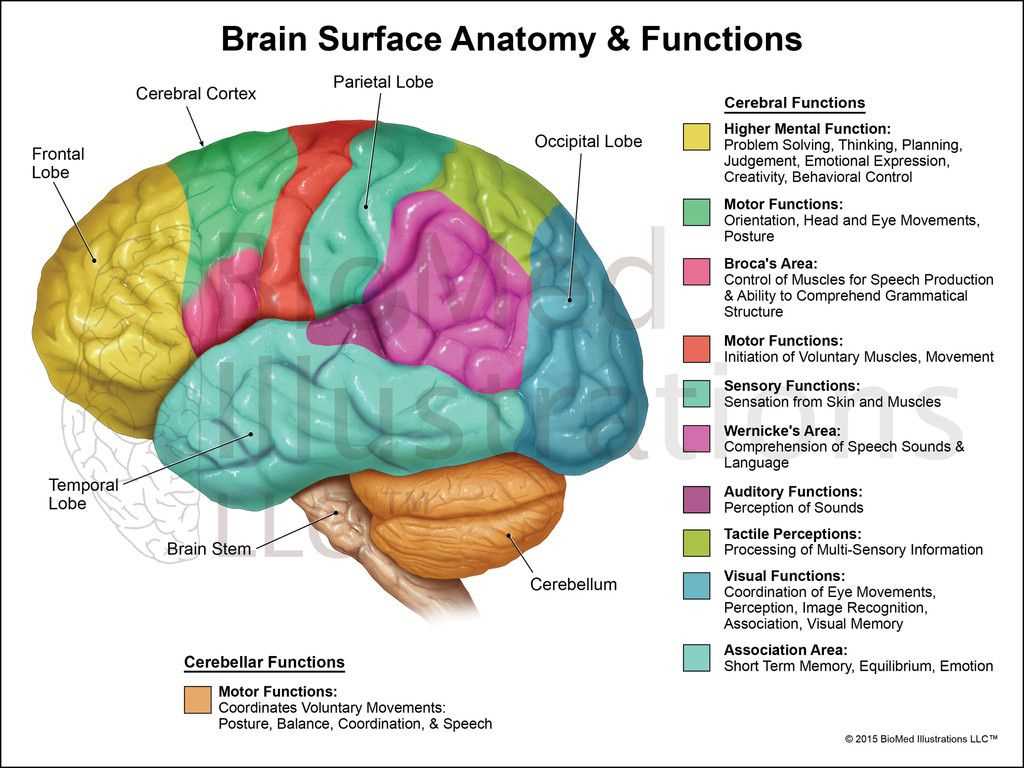
This region plays a crucial role in cognitive processes, serving as a hub for assessing choices and formulating plans. It influences various aspects of behavior and personality, making it essential for effective functioning in daily life.
Key Functions
Responsible for tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, and impulse control, this area allows individuals to evaluate situations and make informed decisions. Its involvement in social interactions also shapes how one navigates relationships.
Impact on Behavior
The functionality of this zone directly affects personality traits and emotional responses. Disruptions in its operation can lead to challenges in judgment and social behavior, highlighting its importance in overall well-being.
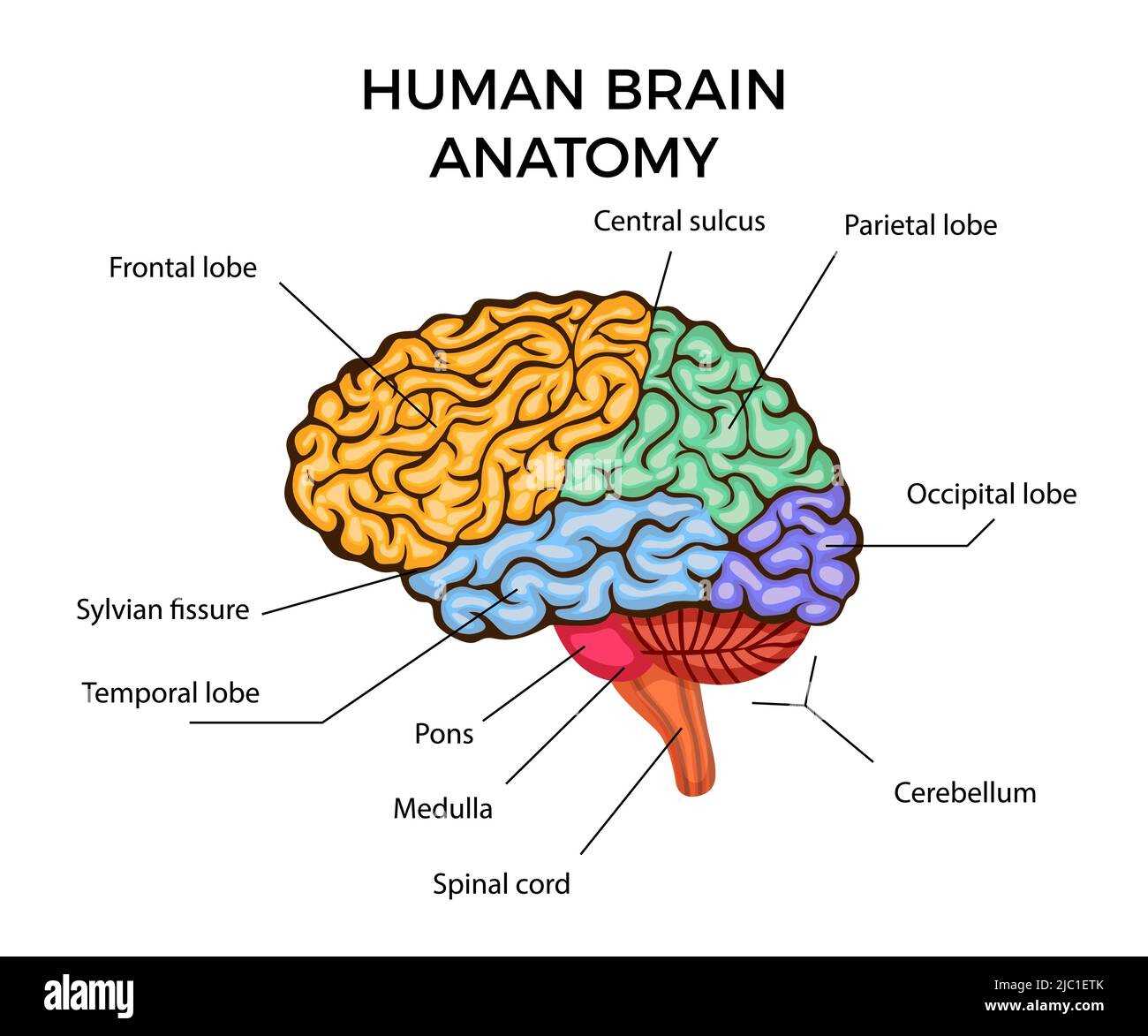
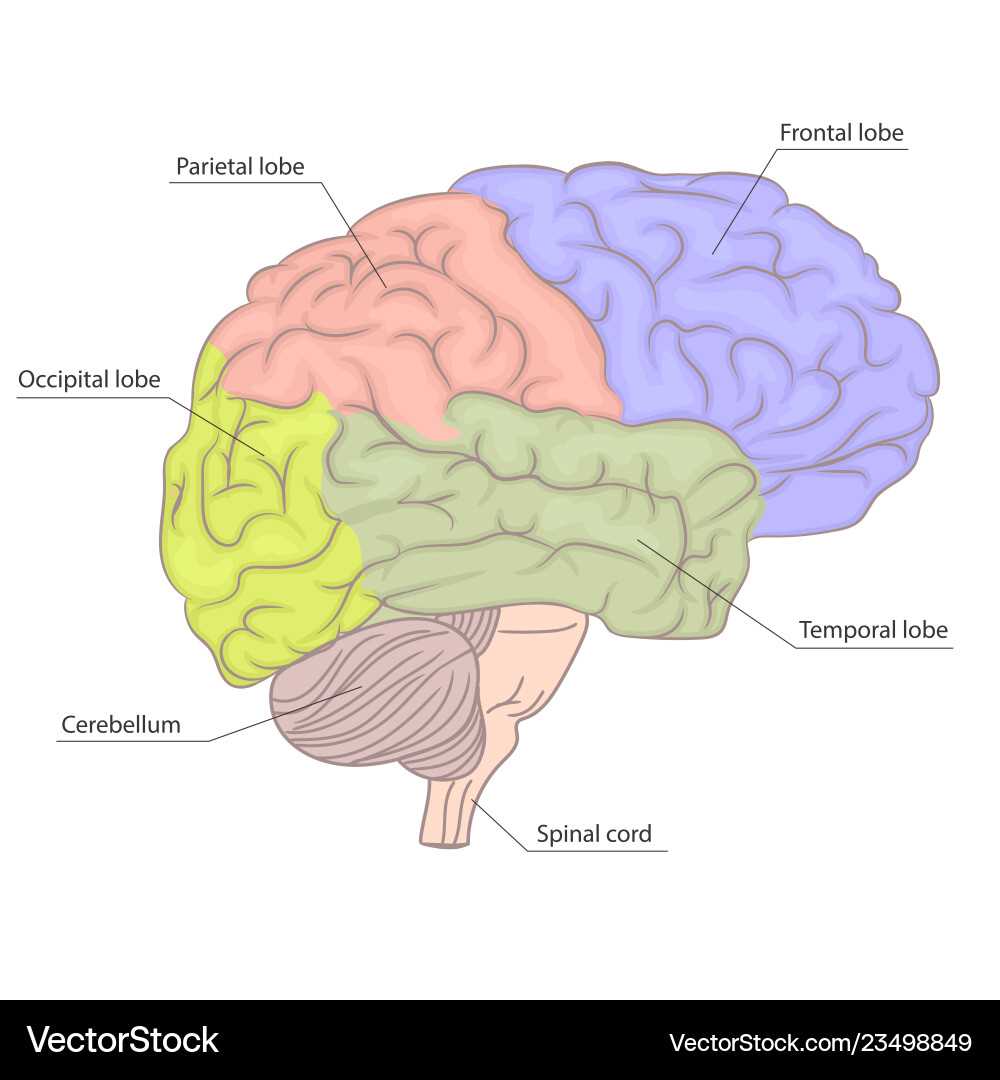
Parietal Lobe: Sensory Information Processing

The parietal region plays a crucial role in interpreting various types of sensory input. This area integrates information from multiple sources, allowing individuals to perceive their environment effectively. Its functionality is essential for tasks that involve spatial awareness and coordination.
Role in Sensory Integration
Within this region, different modalities such as touch, temperature, and pain are combined to form a cohesive understanding of surroundings. By processing sensory data, this area contributes to how one interacts with objects and navigates through space.
Importance for Spatial Awareness
Furthermore, the parietal region is vital for recognizing spatial relationships and distances. It assists in tasks such as reaching for objects or determining the position of items relative to oneself. This capability is essential for daily activities and complex motor functions.
Occipital Lobe: Visual Processing Area
This section explores a crucial region responsible for interpreting visual information. This area plays a significant role in how images are perceived, allowing individuals to recognize shapes, colors, and movement.
Functionality and Importance
Situated at the rear of the cranial structure, this zone is essential for processing stimuli received from the eyes. It converts raw data into comprehensible visuals, contributing to overall perception and understanding of surroundings.
Connections with Other Regions
Communication with various other areas is vital for integrating sensory inputs. This region works closely with auditory and associative parts to create a holistic perception, enhancing experiences through collaborative processing.
Temporal Lobe: Auditory Functions
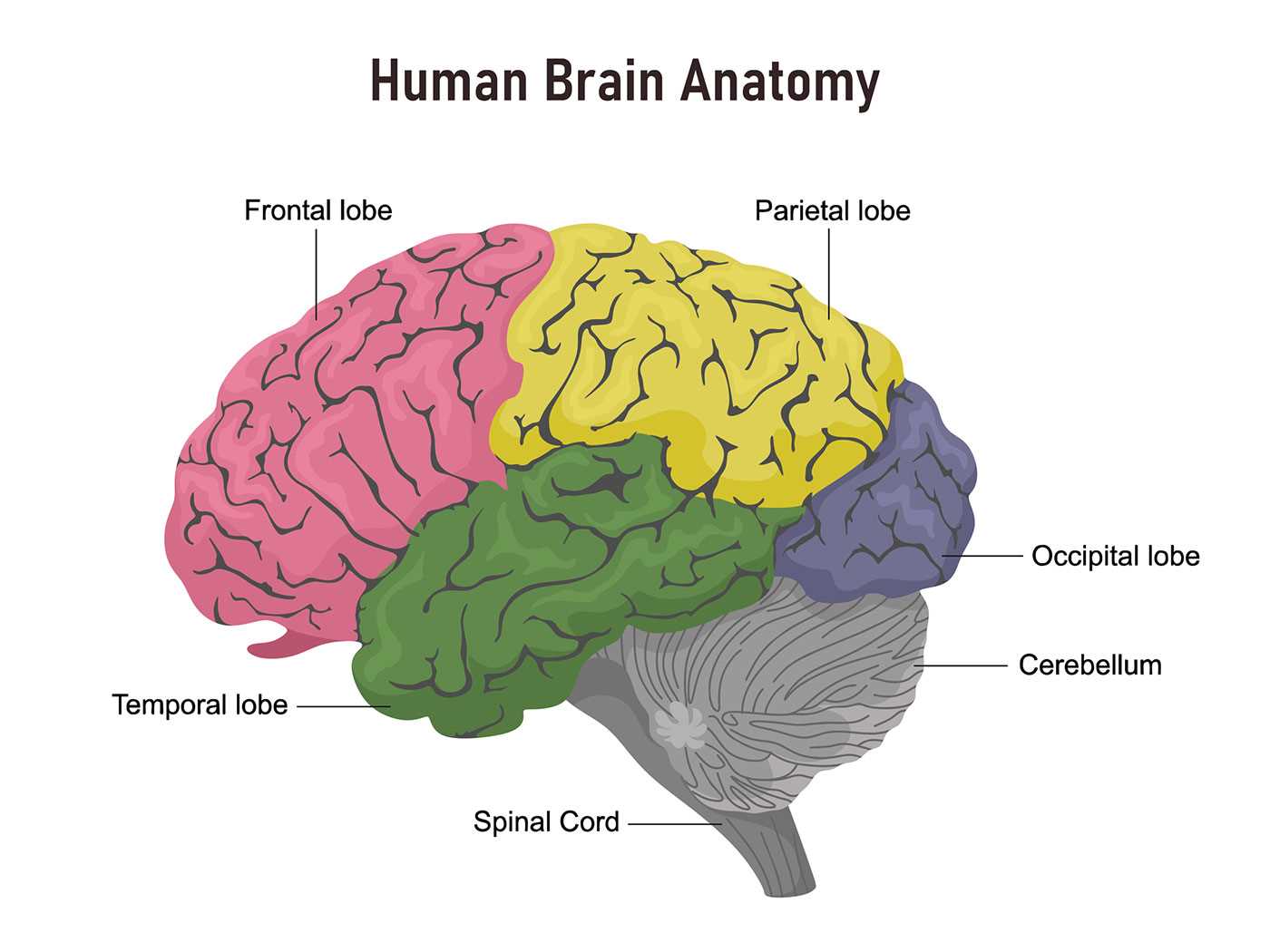
The temporal lobe plays a crucial role in processing sound and language, contributing significantly to our auditory experiences. This region is responsible for interpreting various auditory stimuli, allowing individuals to perceive and understand sounds in their environment.
Sound Processing: Within this area, specialized neurons work together to analyze different frequencies and tones. This intricate network ensures that auditory signals are transformed into recognizable information, enabling effective communication.
Language Comprehension: Additionally, the temporal lobe is essential for grasping spoken language. It assists in deciphering speech patterns, facilitating comprehension of conversations and verbal exchanges.
Memory Association: This region also connects auditory inputs with memory, linking sounds to past experiences. This connection enhances our ability to recall melodies or familiar voices, enriching our auditory memories.
Corpus Callosum: Brain Hemispheres Connector
This structure serves as a vital link between two cerebral hemispheres, facilitating communication and coordination between them. Its role is crucial for integrating functions and processing information efficiently.
Located centrally, this connector is composed of a dense bundle of nerve fibers, allowing signals to travel rapidly between both sides. This enables a harmonious interaction, essential for a variety of cognitive tasks.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Communication | Enables message transfer between hemispheres. |
| Coordination | Helps synchronize activities across both sides. |
| Cognitive Integration | Facilitates unified processing of information. |
Thalamus: Sensory Relay Station
The thalamus serves as a crucial hub for processing and transmitting sensory information to various regions within the central nervous system. This structure plays an integral role in filtering and relaying signals, ensuring that relevant data reaches appropriate areas for further interpretation.
Located at the top of the brainstem, this oval-shaped formation is involved in multiple sensory modalities, including vision, hearing, and touch. It acts as a gatekeeper, determining which signals deserve attention and which should be ignored, thus facilitating effective communication within the nervous system.
Moreover, the thalamus not only processes incoming stimuli but also participates in regulating consciousness and alertness. By coordinating sensory input, it contributes significantly to perception and overall cognitive function, highlighting its importance in daily experiences.
Hypothalamus: Regulating Bodily Functions
This vital structure plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. It acts as a central hub for various regulatory processes, ensuring that essential functions are balanced and coordinated efficiently.
Key Functions
The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating numerous physiological activities, including temperature control, hunger, thirst, and sleep cycles. By interacting with other systems, it influences behaviors that are essential for survival.
Hormonal Influence
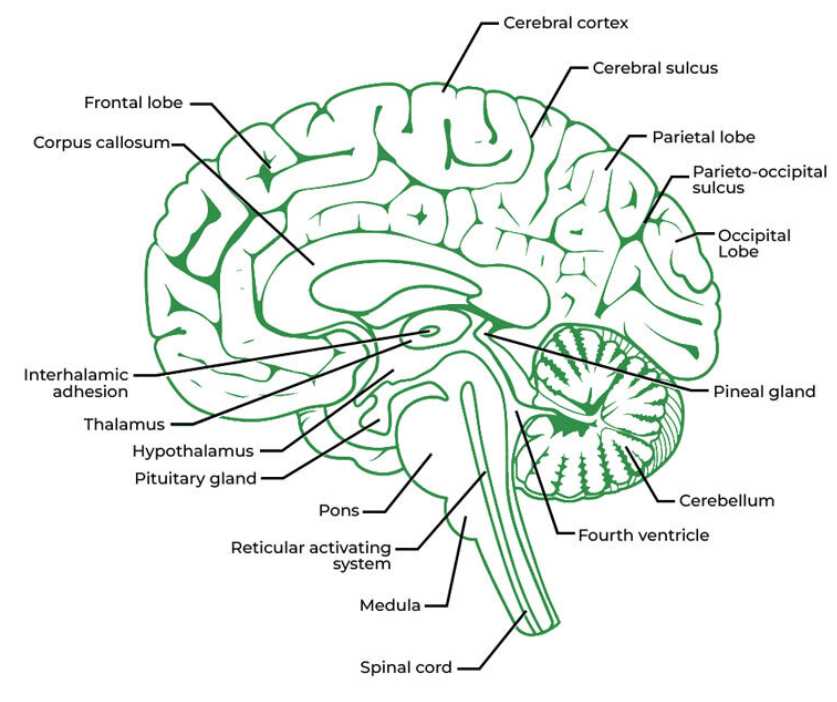
This region also produces hormones that affect various bodily processes, from growth to reproductive functions. Its connection to the endocrine system allows for precise regulation of hormone release.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Regulation | Maintains optimal body temperature through sweating or shivering. |
| Hunger Control | Signals feelings of hunger or satiety, influencing eating behavior. |
| Thirst Mechanism | Triggers thirst responses to maintain fluid balance. |
| Sleep-Wake Cycle | Regulates circadian rhythms, impacting sleep patterns. |