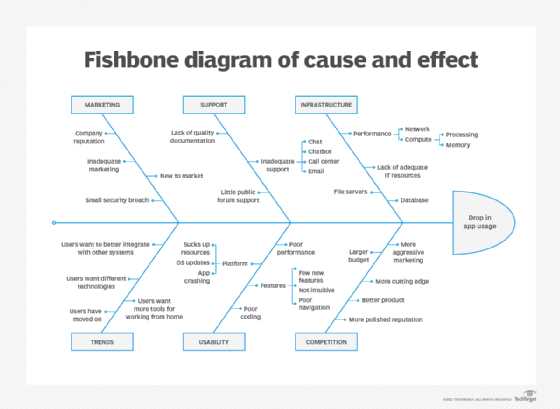
The exploration of interconnections among various elements provides valuable insights into how outcomes arise from specific factors. This analytical approach enables individuals and organizations to identify underlying reasons for particular results, fostering a deeper understanding of complex systems.
By utilizing visual representations, one can effectively illustrate the relationships between different influences. Such tools enhance clarity, allowing for a systematic examination of how various components contribute to an overall situation.
This methodology is particularly beneficial in problem-solving contexts, where recognizing the interplay between causes and outcomes aids in developing effective strategies for improvement. Ultimately, this approach not only enhances comprehension but also empowers informed decision-making.
Understanding Cause-and-Effect Diagrams
Exploring the connections between actions and outcomes is essential for effective problem-solving. This approach helps to identify underlying issues and their ramifications. By visually representing relationships, individuals can gain insights into complex situations, making it easier to pinpoint the root causes of challenges.
The framework facilitates brainstorming sessions, allowing teams to collaboratively discuss potential factors influencing a specific issue. Each element plays a role, contributing to a holistic understanding of the scenario. This method not only enhances communication but also supports decision-making processes.
History of Cause-and-Effect Analysis
The exploration of relationships between actions and outcomes has deep historical roots, evolving through various methodologies to enhance problem-solving and decision-making processes. This analytical approach has been employed in diverse fields, from manufacturing to healthcare, highlighting its versatility and importance in understanding complex systems.
| Era | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| Early 20th Century | Introduction of systematic analysis techniques in engineering and management. |
| 1950s | Emergence of quality control methods, leading to formalized analytical frameworks. |
| 1980s | Widespread adoption in various industries for quality improvement initiatives. |
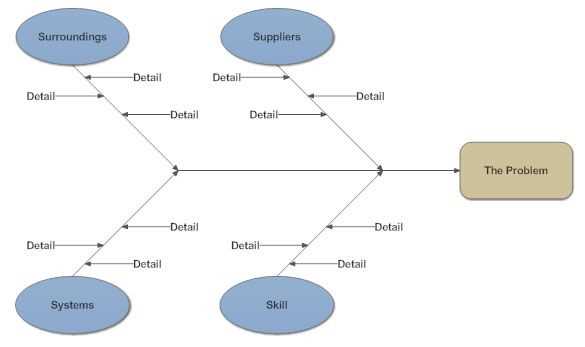
Key Components of Diagrams
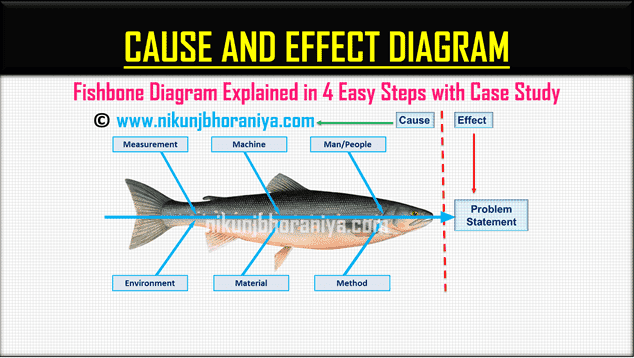
This section explores the essential elements that contribute to the effective representation of relationships and influences within various scenarios. Understanding these building blocks can enhance clarity and facilitate analysis.
Core Elements

- Entities: These are the main subjects or factors that impact outcomes.
- Connections: Lines or arrows that illustrate the relationships between entities.
- Categories: Groups that classify entities based on specific criteria.
- Descriptions: Brief explanations that clarify the nature of each entity or connection.
Additional Features
- Color Coding: Utilizing different hues to signify various categories or levels of importance.
- Shapes: Various forms used to distinguish between different types of entities.
- Legends: Guides that provide meaning to symbols or colors used within the representation.
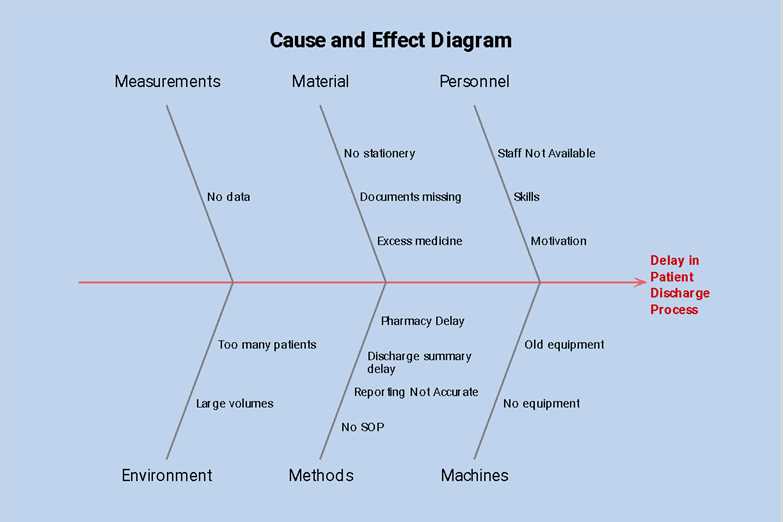
Applications in Various Industries
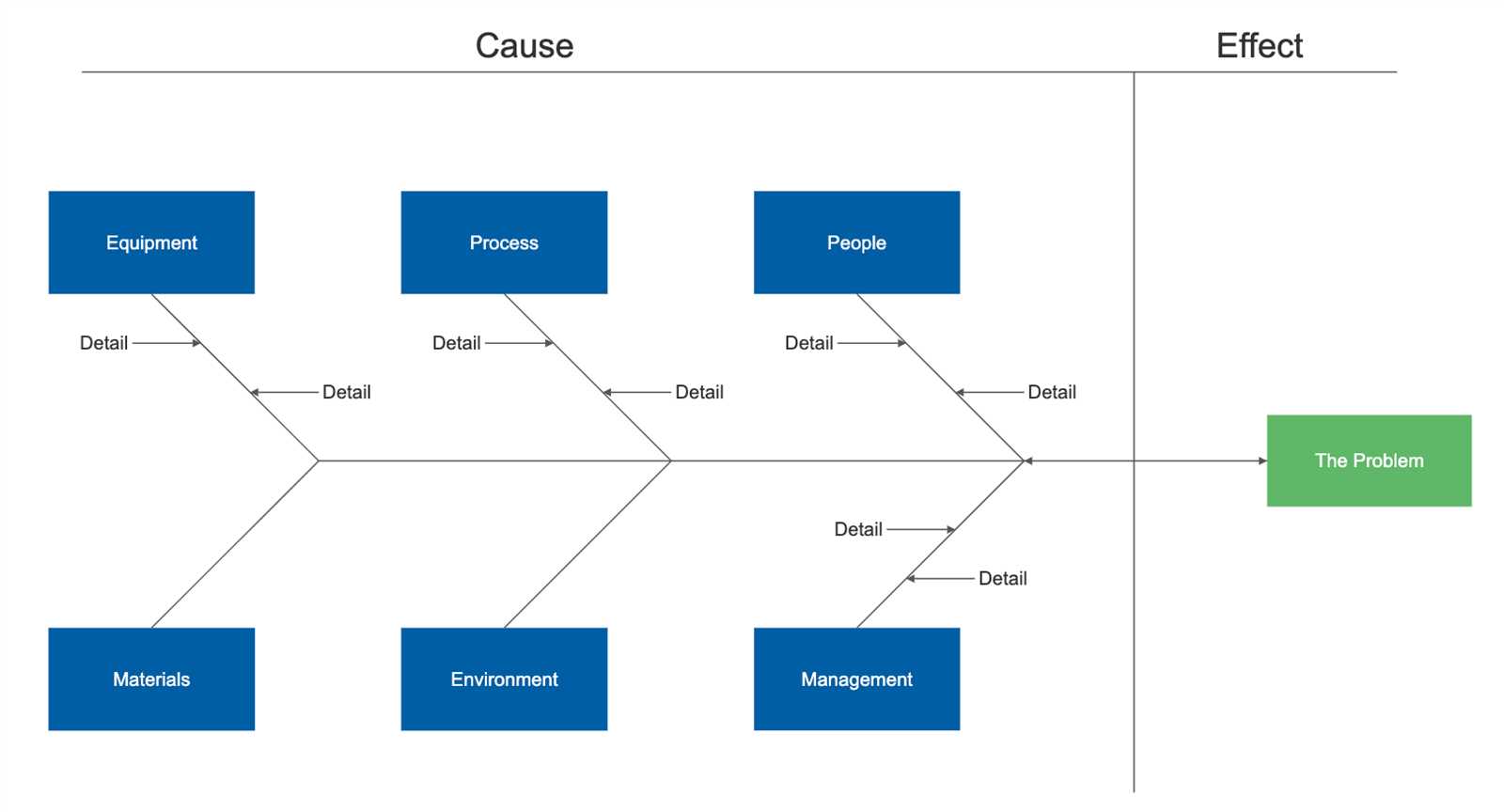
Visual representations of relationships between variables are widely utilized across multiple sectors. These tools help identify underlying factors contributing to issues, enabling professionals to devise effective solutions. Their versatility makes them essential in areas such as manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries.
Manufacturing Sector
In manufacturing, these tools are instrumental in quality control and process improvement. By mapping out potential issues, teams can enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
- Identifying defects in production lines
- Streamlining operations
- Enhancing product quality
Healthcare Industry
The healthcare sector employs these visual tools to analyze patient care processes and improve outcomes. They assist in identifying root causes of delays or errors in treatment.
- Improving patient safety
- Enhancing workflow efficiency
- Reducing medical errors
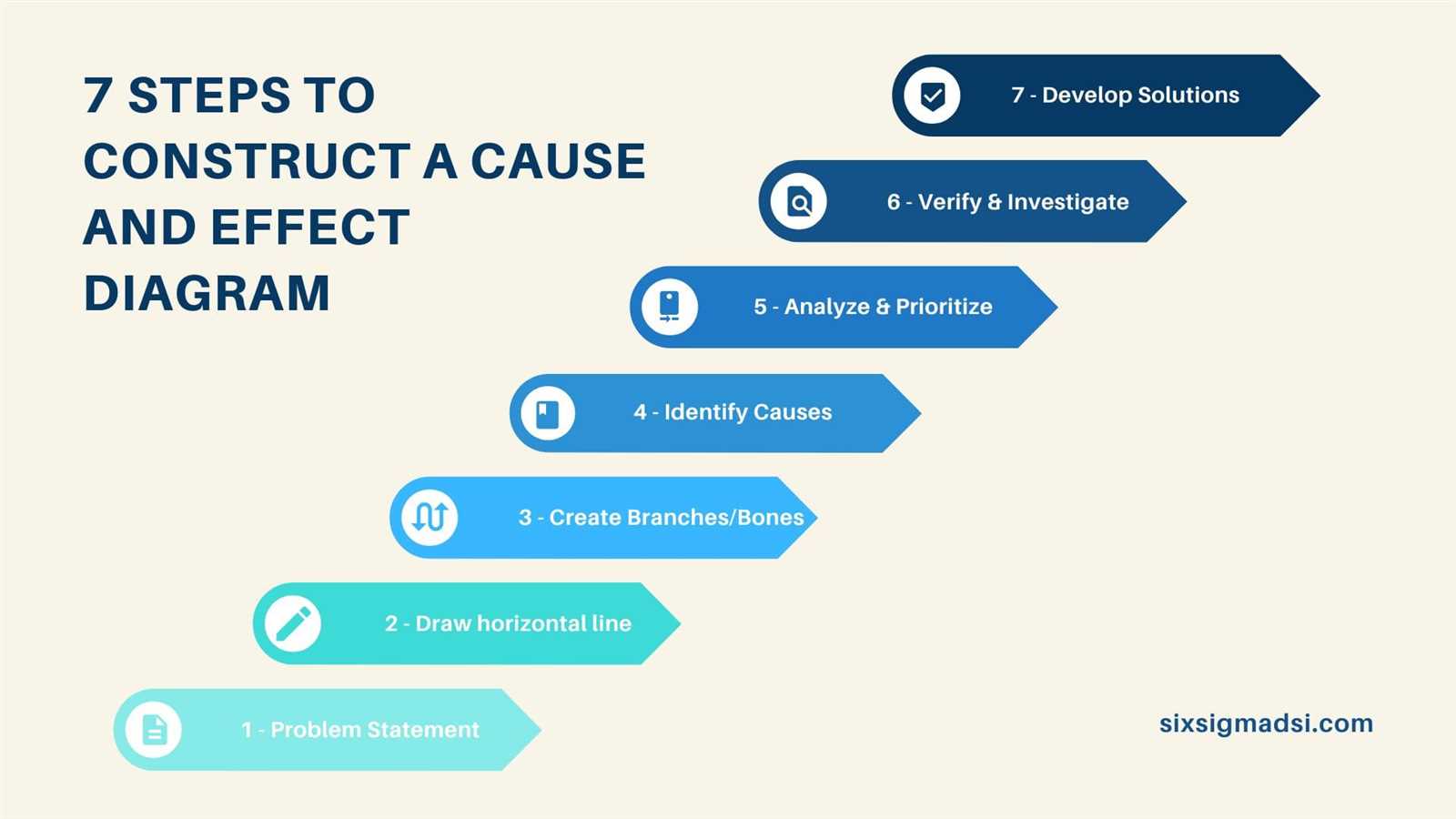
Steps to Create Effective Diagrams
Creating a visual representation of relationships and influences can enhance understanding and communication. A structured approach ensures clarity and effectiveness in conveying complex information.
Identify the Purpose
Before starting, clarify the main objective of the visual tool. Determine what specific information you aim to convey and who your audience is. This focus will guide your decisions throughout the process.
Gather Relevant Information
Collect data and insights related to the topic. Engage with stakeholders to understand their perspectives. This comprehensive collection will provide a solid foundation for your visual representation, ensuring all critical elements are included.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding the pitfalls in analytical processes can significantly enhance the quality of your work. Identifying errors early on can lead to clearer insights and more effective solutions. Below are some frequent missteps that individuals encounter.
Lack of Clarity
Failing to define the central issue can lead to confusion and misalignment among team members. Clear articulation of the problem ensures everyone is on the same page and focused on relevant factors.
Overlooking Details

Neglecting minor aspects can result in major oversights. Every element contributes to the overall picture, and overlooking these can skew your analysis and outcomes.
Benefits of Using Diagrams

Utilizing visual representations can significantly enhance understanding and communication within various fields. These tools provide clarity, allowing individuals to quickly grasp complex relationships and processes.
One major advantage is the ability to simplify intricate concepts. By breaking down information into visual elements, it becomes easier to analyze and interpret data. This visual clarity fosters better problem-solving skills and encourages collaborative discussions.
Additionally, these tools can serve as effective aids in presentations. They capture attention and facilitate retention, making it simpler for audiences to follow along and engage with the material. The use of visuals can lead to more productive meetings and brainstorming sessions.
In summary, integrating these representations into workflows can enhance efficiency, promote understanding, and ultimately lead to better decision-making. Their role in visual communication cannot be overstated, as they bridge gaps between abstract ideas and tangible insights.
Tools for Diagram Creation
Creating visual representations of relationships between various elements can greatly enhance understanding and analysis. A variety of resources and applications exist to facilitate this process, making it easier for users to design effective visuals that communicate their ideas clearly.
Popular Software Options
- Lucidchart
- Microsoft Visio
- Draw.io
- Creately
Key Features to Consider
- Ease of use and intuitive interface
- Collaboration features for teamwork
- Template availability for quick start
- Integration with other applications
Case Studies: Success Stories
This section explores various instances where analytical tools have played a pivotal role in achieving remarkable outcomes. By examining different scenarios, we highlight how systematic approaches can lead to significant improvements and innovations within organizations.
One notable example is a manufacturing company that implemented these analytical methods to enhance production efficiency. By identifying key factors contributing to delays, the team was able to streamline processes, resulting in a notable reduction in lead times and increased output.
Another success story involves a healthcare organization that utilized these techniques to improve patient care. Through careful analysis of patient feedback and treatment processes, the staff identified areas for enhancement, leading to improved patient satisfaction scores and better health outcomes.
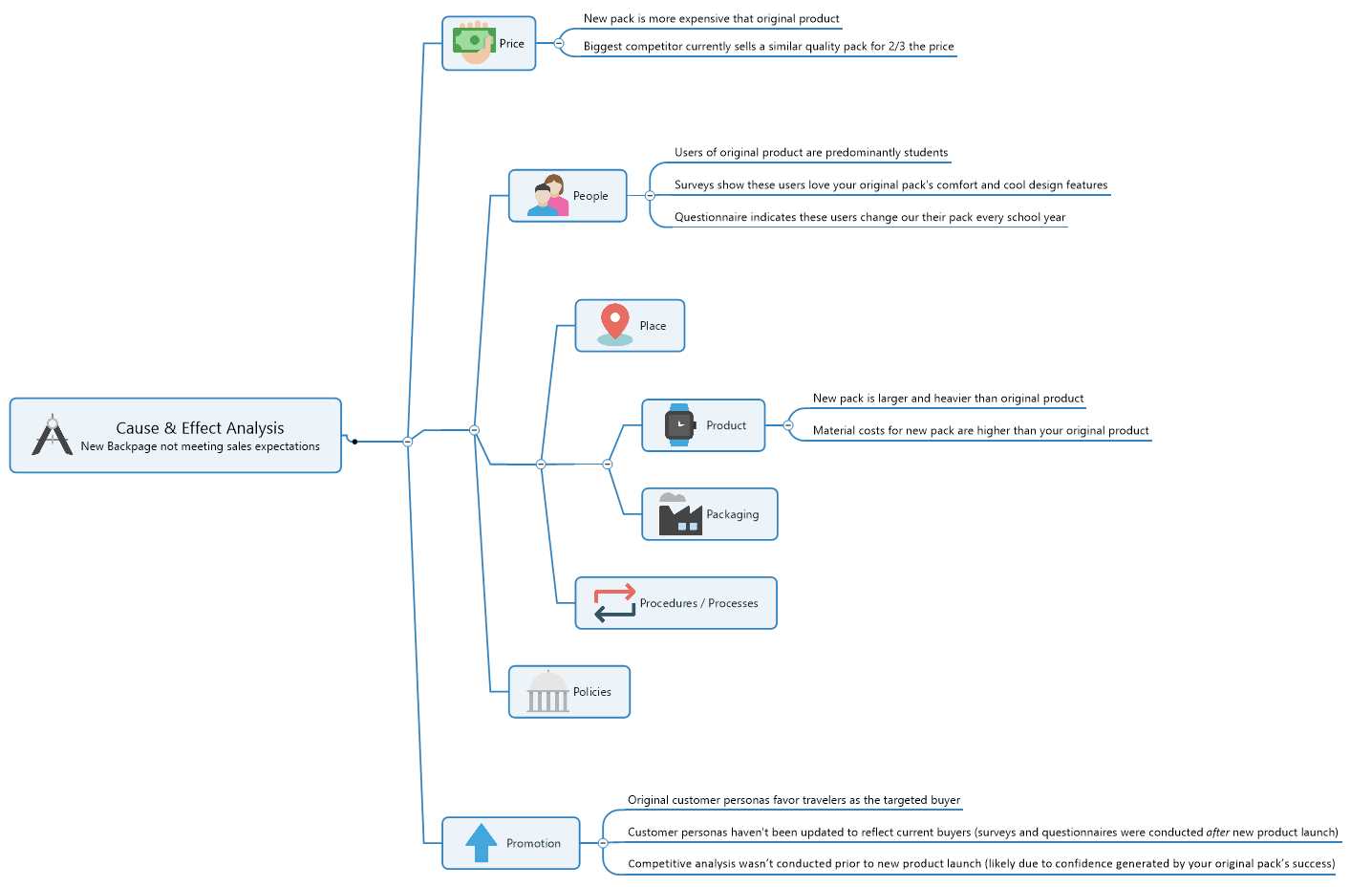
Integrating Diagrams with Other Methods
Combining visual representations with various analytical techniques enhances understanding and problem-solving capabilities. This approach fosters clearer communication among team members, streamlining processes and promoting collaboration. By utilizing multiple methodologies, one can uncover deeper insights and drive effective solutions.
Benefits of Integration
Incorporating these visual tools alongside other frameworks offers several advantages:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Clarity | Visual aids simplify complex information, making it easier to comprehend. |
| Enhanced Collaboration | Teams can align their understanding and work towards common goals. |
| Streamlined Processes | Combining methods can lead to more efficient workflows and faster decision-making. |
Practical Applications
Integrating these representations with techniques like brainstorming, root cause analysis, or strategic planning can yield substantial results. Each method complements the others, creating a comprehensive toolkit for addressing challenges effectively.
Future Trends in Analysis Techniques
As the landscape of analytical methodologies evolves, emerging trends are shaping the way professionals approach problem-solving and decision-making. Innovations in technology and data processing are leading to more efficient and insightful analysis practices.
One significant trend is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advancements enable analysts to uncover patterns and insights from vast datasets with greater accuracy and speed.
Key areas of focus in future analytical techniques include:
- Data Visualization: Enhanced visual tools that provide clearer insights and facilitate quicker understanding of complex information.
- Predictive Analytics: Techniques that allow organizations to forecast future outcomes based on historical data, improving strategic planning.
- Real-Time Analysis: The ability to analyze data as it is generated, enabling immediate responses to changing conditions.
- Collaborative Analysis: Increased emphasis on teamwork and cross-functional collaboration to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise.
These trends highlight a shift towards more dynamic, responsive, and collaborative analytical practices that can adapt to the rapidly changing business environment.