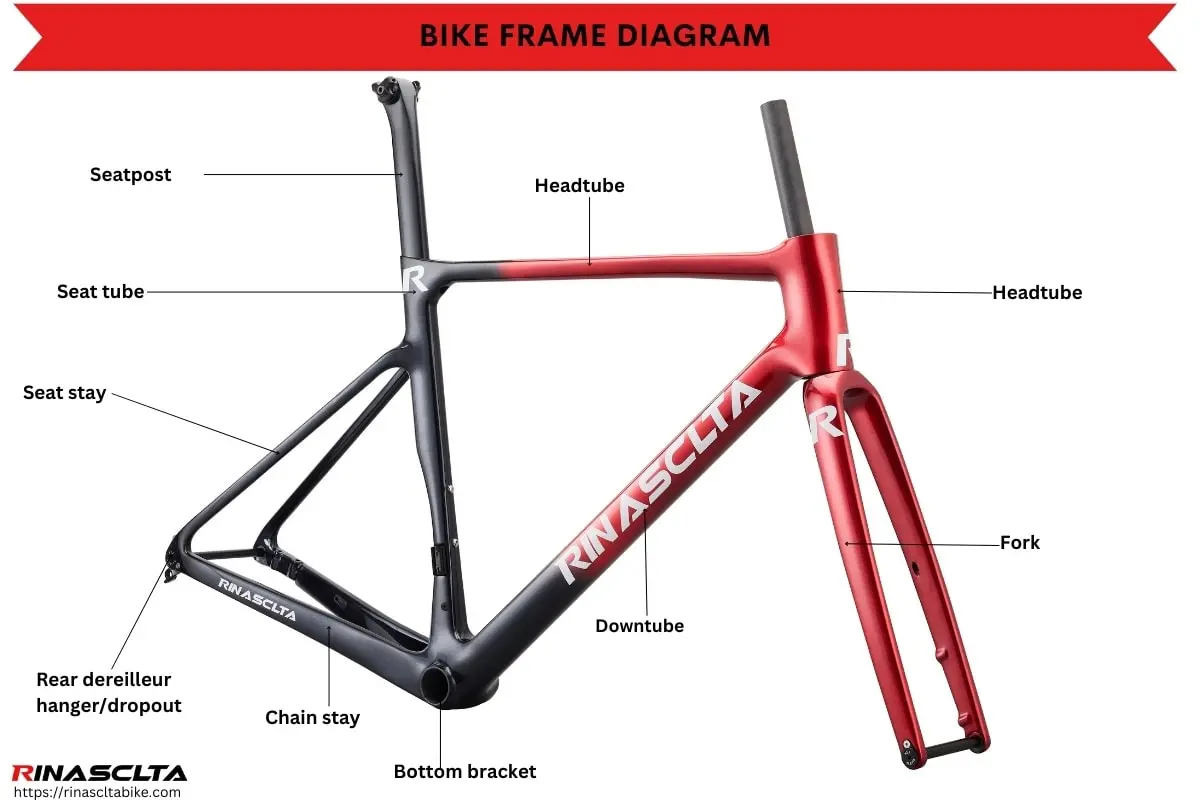

In the world of cycling, the construction of a two-wheeled vehicle is a crucial aspect that influences performance and comfort. This intricate assembly consists of various elements, each serving a distinct purpose that contributes to the overall functionality. Exploring these components can enhance your appreciation for the engineering behind your ride.
Each section plays a vital role, from providing stability to ensuring smooth navigation. Recognizing how these individual segments interact allows enthusiasts to make informed choices, whether for maintenance or upgrades. This knowledge ultimately leads to a more enjoyable experience on the road.
As we delve into the specifics, you’ll discover the ultimate framework that supports riders of all levels. Understanding these essentials is not just about mechanics; it’s about enhancing your connection with the journey ahead.
Understanding Bike Frame Anatomy
The structure of a two-wheeled vehicle is fundamental to its performance and comfort. Grasping the intricacies of its composition allows for better customization and maintenance, enhancing the riding experience. Each element serves a unique purpose, contributing to overall stability and efficiency.
Key Components
Top Tube: This horizontal element connects the head tube to the seat tube, playing a crucial role in overall rigidity. It influences handling and rider position, affecting comfort during long rides.
Geometry and Fit
Seat Tube: Serving as the foundation for the saddle, this vertical component directly impacts the cyclist’s posture. An appropriate angle and length ensure optimal power transfer and reduce fatigue.
Understanding these essentials not only aids in selecting the right setup but also enhances one’s connection with the vehicle.
Key Components of a Bicycle Frame

The structure of a two-wheeled vehicle is composed of several essential elements that contribute to its overall functionality and performance. Understanding these components is crucial for enthusiasts and riders alike, as they play a significant role in the cycling experience.
Top Tube: This horizontal element connects the front and rear sections, providing stability and support. It often influences the overall geometry and handling.
Down Tube: Positioned at a steep angle, this vertical component is vital for transferring power from the pedals to the rear wheel, enhancing propulsion and speed.
Seat Tube: This upright structure holds the saddle in place and can affect rider comfort and leg extension during pedaling.
Chainstays: Located at the rear, these tubes connect the rear wheel to the main structure, playing a key role in power transfer and overall balance.
Seat Stays: These components support the rear triangle and help maintain structural integrity, ensuring a smooth ride over various terrains.
Head Tube: This front section houses the steering mechanism, allowing for precise control and maneuverability while navigating different environments.
Delving into these critical elements reveals their ultimate importance in creating a reliable and efficient riding experience, tailored to meet diverse cycling needs.
Importance of Frame Geometry in Cycling
Understanding the structure and layout of a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for optimizing performance and comfort. The arrangement of various components significantly influences the rider’s experience, affecting handling, stability, and efficiency during movement.
| Aspect | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
| Rider Position | Affects aerodynamics and power transfer. |
| Stability | Influences cornering and control in various terrains. |
| Handling | Determines responsiveness to steering input. |
| Comfort | Impacts long-distance endurance and fatigue levels. |
By delving into these elements, enthusiasts can make informed choices, ultimately enhancing their riding experience and achieving better results in their endeavors.
Identifying the Main Frame Tubes
Understanding the key structural elements of a two-wheeled vehicle is essential for both enthusiasts and those new to cycling. Each section plays a vital role in overall performance, handling, and comfort. Recognizing these components can greatly enhance your ability to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, and customizations.
Key Structural Elements
- Top Tube: This is the horizontal bar connecting the front and rear sections. It influences the ride height and overall stability.
- Down Tube: Positioned below the top tube, this vertical element provides support and strength, especially during acceleration.
- Seat Tube: This upright section holds the saddle and plays a crucial role in determining the rider’s position and comfort.
- Chainstays: Located at the rear, these tubes connect the bottom bracket to the rear axle, affecting stability and power transfer.
- Seatstays: These components extend from the rear section to the top tube, contributing to the overall rigidity and responsiveness.
Recognizing Their Importance
Each element not only contributes to the structure but also affects various aspects of the riding experience. Familiarity with these tubes allows riders to appreciate how design choices influence handling, weight distribution, and comfort. Moreover, when considering modifications or repairs, knowing these key sections can aid in making educated choices.
Material Choices for Bicycle Frames
The selection of materials for constructing two-wheeled vehicles significantly influences their performance, weight, and overall ride quality. Each substance offers unique characteristics that cater to different riding styles and preferences, allowing cyclists to find the perfect match for their needs.
Aluminum
Aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It provides a responsive feel, making it ideal for those who prioritize agility and speed. Additionally, aluminum structures can be easily manipulated into various shapes, enhancing aerodynamics and comfort.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber stands out for its exceptional durability and minimal weight. This material absorbs vibrations effectively, offering a smooth ride even on rough terrains. While generally more expensive, its performance benefits make it a preferred option for competitive riders seeking the ultimate in responsiveness and performance.
Ultimately, the choice of materials is crucial in determining the experience of every cyclist, blending comfort, durability, and efficiency to suit individual preferences.
How Frame Size Affects Performance
The dimensions of a cycle’s structure play a crucial role in influencing overall efficiency and comfort during rides. Selecting the appropriate size can significantly enhance the experience, ensuring that the rider’s body aligns well with the machine, thus optimizing energy transfer and stability.
Impact on Comfort

A well-fitted structure allows for a natural riding posture, reducing strain on muscles and joints. This comfort leads to longer, more enjoyable rides, allowing enthusiasts to delve deeper into their journeys without fatigue becoming an issue.
Influence on Handling
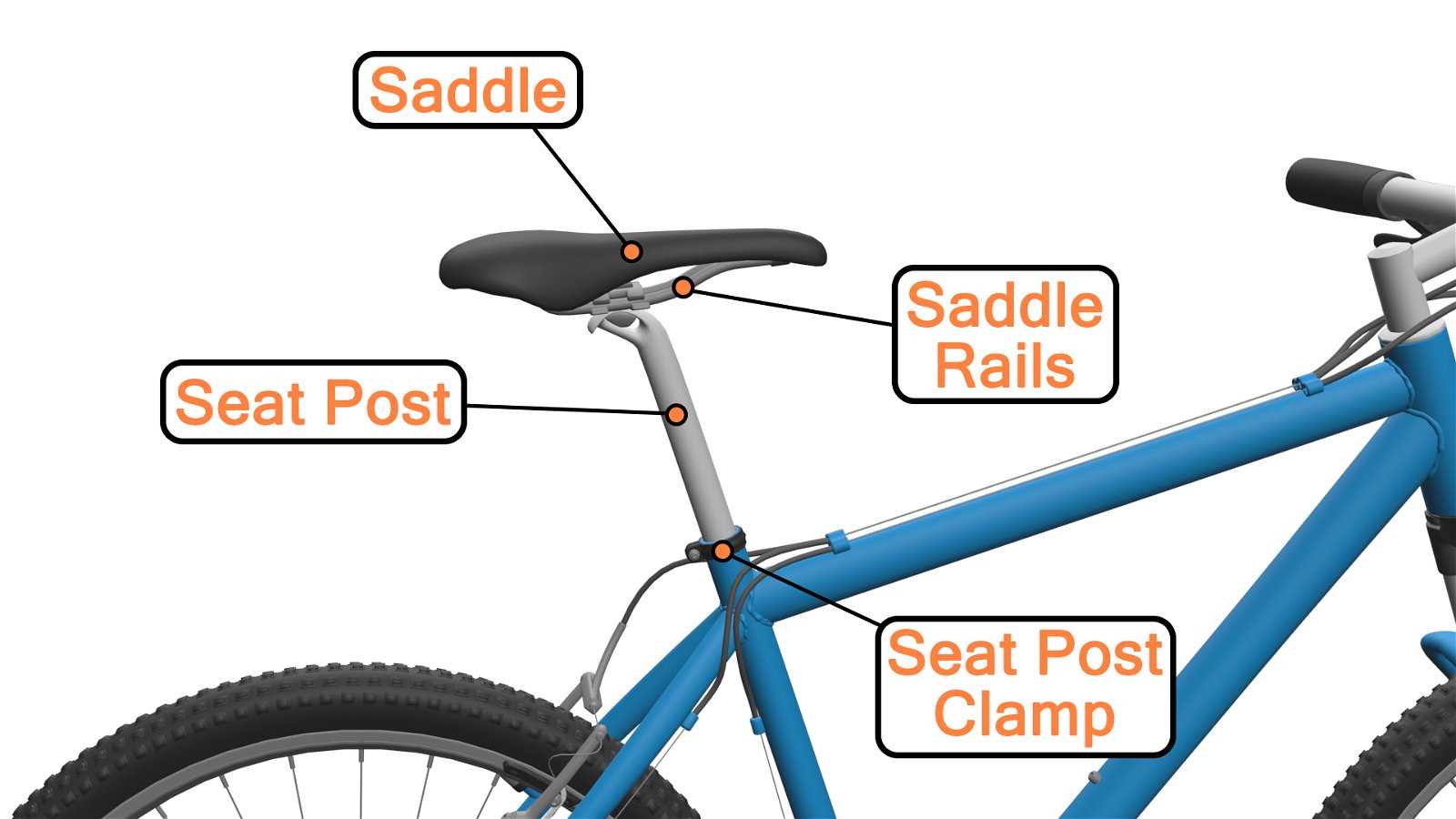
The size also affects maneuverability and responsiveness. A properly proportioned unit provides better control during turns and descents, which ultimately enhances the rider’s confidence and performance in various terrains.
Role of the Head Tube in Steering
The head tube serves a crucial function in the dynamics of steering, influencing the overall maneuverability and stability of the vehicle. Positioned at the front, it forms the connection between the front assembly and the main structure, allowing for efficient directional changes.
Strongly impacting the steering geometry, the angle and length of the head tube determine how responsive the handling will be. A steeper angle generally enhances agility, making it easier to navigate sharp turns, while a slacker angle provides increased stability at high speeds. This balance is essential for achieving the ultimate performance on various terrains.
Furthermore, the head tube accommodates the headset, which contains bearings that enable smooth rotation of the handlebars. This interplay ensures that the rider can maintain control, effectively translating their inputs into precise movements. Ultimately, the head tube is integral to creating a seamless riding experience, enhancing both comfort and safety.
Integrating the Bottom Bracket in Bike Design
The integration of a crucial component in two-wheeled vehicles significantly influences performance and rider experience. This element serves as a vital junction, connecting various mechanical systems and ensuring smooth operation. Its placement and design can impact stability, efficiency, and overall handling.
When considering the configuration of this essential unit, designers must account for factors such as material choice and geometry. A well-engineered connection enhances power transfer, allowing cyclists to harness their energy effectively. Moreover, innovation in manufacturing techniques can lead to lightweight solutions that do not compromise durability.
Ultimately, a thoughtfully integrated component contributes to the vehicle’s responsiveness and comfort. The ongoing evolution of design practices highlights the importance of this integration, ensuring that enthusiasts enjoy optimal performance on every ride.
How to Read a Bike Frame Diagram
Understanding the layout of a two-wheeled vehicle can significantly enhance your experience as an enthusiast. Familiarity with the components and their arrangement will empower you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades. This section will guide you through the essentials of interpreting a visual representation of these structures.
Identifying Key Elements
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the main components illustrated. Look for labels and symbols that denote different sections. Each part serves a unique function, contributing to the overall performance and stability of the vehicle. Recognizing these elements will help you grasp their interrelationships.
Understanding Measurements and Angles
Pay attention to numerical values and angular notations that provide critical specifications. These details are crucial for assessing compatibility with accessories or replacements. Knowing how to interpret these figures will allow you to make the ultimate choices for your riding needs.
Frame Types and Their Uses
When exploring the various structures that support two-wheeled vehicles, it’s essential to recognize the distinct forms available, each tailored for specific activities and preferences. Understanding these configurations aids in selecting the right option for diverse riding styles and conditions.
One popular style is the lightweight construction, favored for speed and agility on paved surfaces. These models are typically designed for racing or fitness, offering a streamlined profile that enhances performance. Conversely, sturdier designs excel in rugged environments, providing durability and stability on uneven terrains. Such constructions are ideal for adventurous riders seeking off-road experiences.
An additional type emphasizes versatility, suitable for commuting and casual outings. These frameworks often feature attachment points for accessories, making them practical for daily use. There are also specialized designs tailored for specific disciplines, such as touring or mountain riding, each offering unique characteristics that optimize the experience based on the intended use.
Ultimately, the choice of structure can significantly influence the riding experience, emphasizing the importance of selecting one that aligns with individual needs and preferences.
Maintaining Your Bike Frame for Longevity
Proper care and attention to the main structure of your two-wheeled vehicle are crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. Regular maintenance can prevent wear and tear, reduce the risk of damage, and keep the overall assembly in top condition for years to come. With just a few simple steps, you can enhance its durability and enjoy smoother rides on various terrains.
Cleaning and Inspection: Keeping the main body clean and free of debris is essential for preventing rust and corrosion. After every ride, make it a habit to wipe down the surface, paying special attention to areas where dirt and moisture accumulate. Regular inspections allow you to spot any potential issues, such as cracks or loose fittings, before they become serious problems.
Protective Coatings: Applying protective layers, such as wax or specialized sprays, can help shield the structure from environmental damage. These products create a barrier against water, dirt, and UV rays, preserving the material and maintaining its aesthetic appeal.
Tightening and Lubrication: Ensure all screws, bolts, and joints are secure and properly tightened. Loose components can lead to stress on the structure, causing premature wear. Additionally, lubricating moving parts, such as the handlebars and pedals, can reduce friction and enhance the overall riding experience.
Storage and Parking: Storing your vehicle in a dry, cool place will protect it from extreme weather conditions. Avoid leaving it exposed to direct sunlight for long periods, as this can cause fading and weakening of the material. When parking, ensure it’s placed on a stable surface to prevent accidental falls or impact damage.
By following these straightforward practices, you can ensure that your two-wheeled companion remains in excellent condition, ready to deliver a smooth, safe ride for many more adventures.