The world of human-powered transport devices offers a fascinating combination of engineering and design. With every turn of the pedal, these marvels of mechanics showcase their carefully constructed components, working together in perfect harmony to ensure smooth motion and control. Understanding the various elements involved in these systems opens up a new appreciation for how they function and maintain balance on the road.
From the frame that provides structure to the chains that drive propulsion, each element has its own crucial role. Whether focusing on comfort, speed, or durability, every section is designed with a specific purpose, contributing to the overall performance and reliability. The intricate connections between these elements highlight the precision needed to create an efficient, streamlined ride.
By gaining insight into the individual aspects of this mechanical system, one can better grasp how each component plays a vital role in the seamless operation of the entire structure. This deeper understanding can also assist in maintenance and upgrades, ensuring longevity and optimal performance over time.
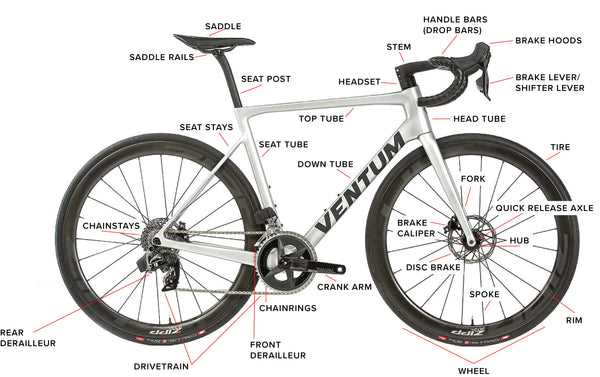
Diagram of Bike Parts
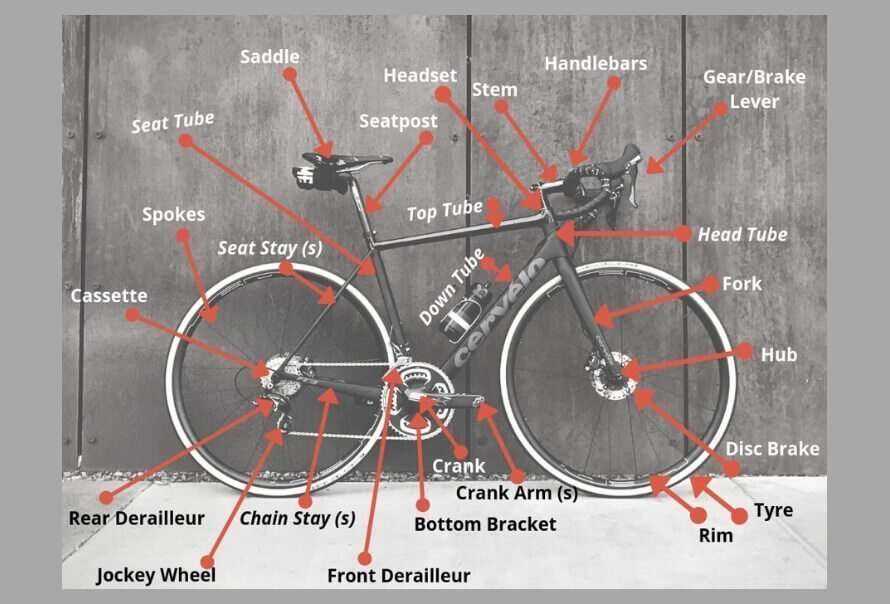
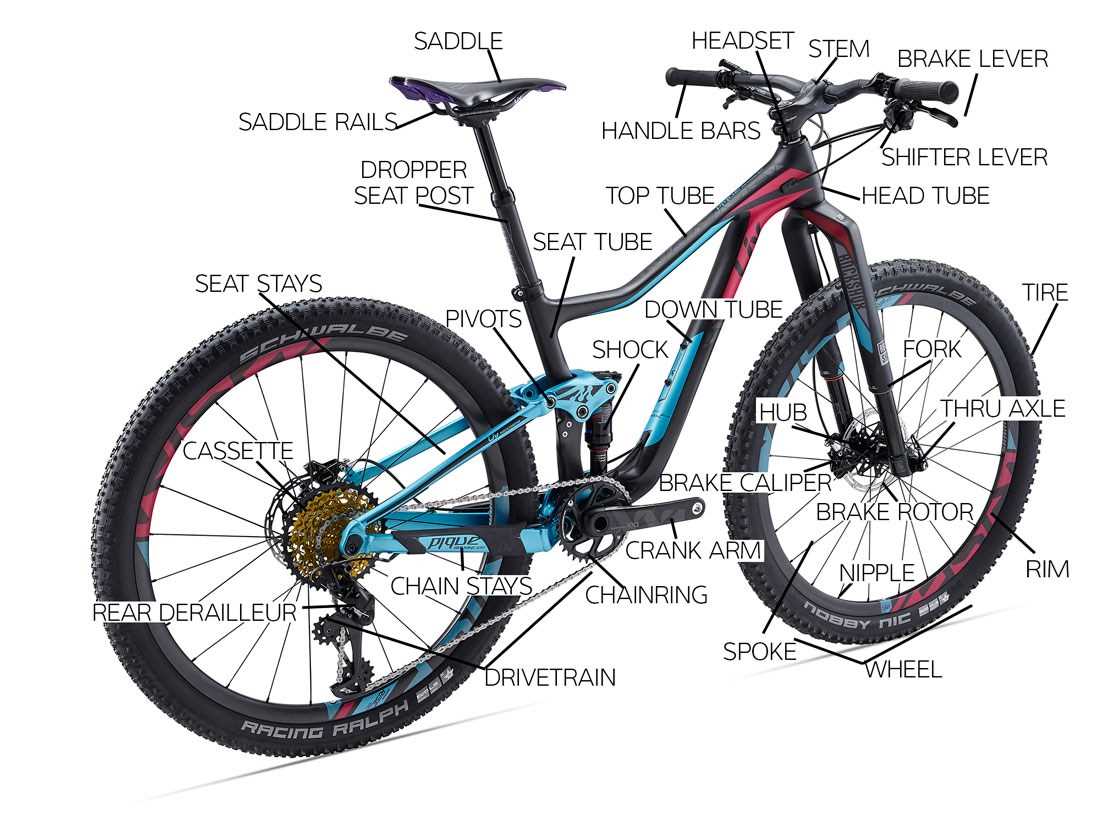
The structure of a two-wheeled vehicle consists of numerous interconnected elements, each serving a specific function. Understanding these components is essential for ensuring proper operation and maintenance. Every segment plays a role in the overall efficiency and comfort of the ride, contributing to both the rider’s experience and the longevity of the machine.
Key Components

The primary elements of this vehicle work together to create a smooth and safe journey. These parts can be categorized based on their role in movement, control, and support. Below is a list of the essential elements that are found in most models.
- Frame: The central structure that supports all other parts.
- Wheels: Provide movement and stability, connecting the structure to the ground.
- Handlebars: Enable the rider to steer and control direction.
- Pedals: Allow the rider to transfer power to the wheels.
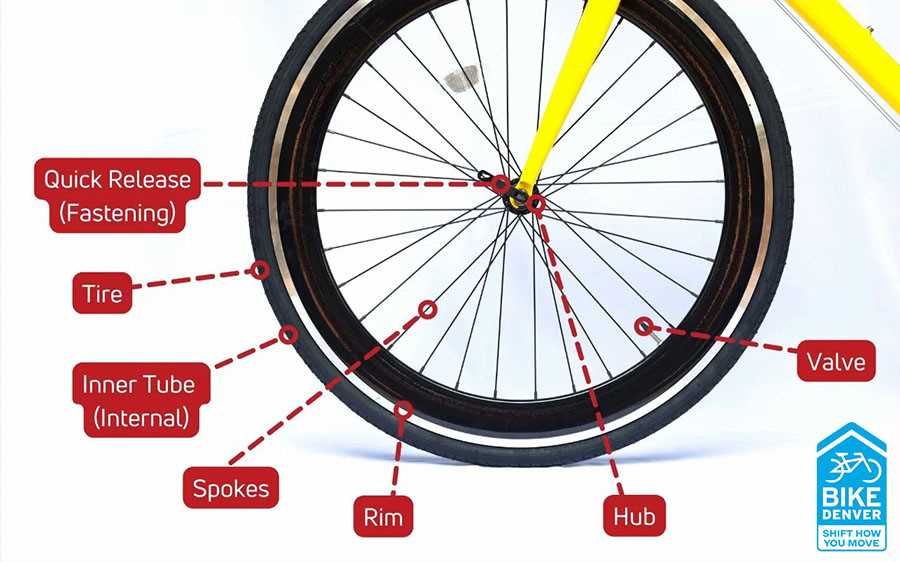
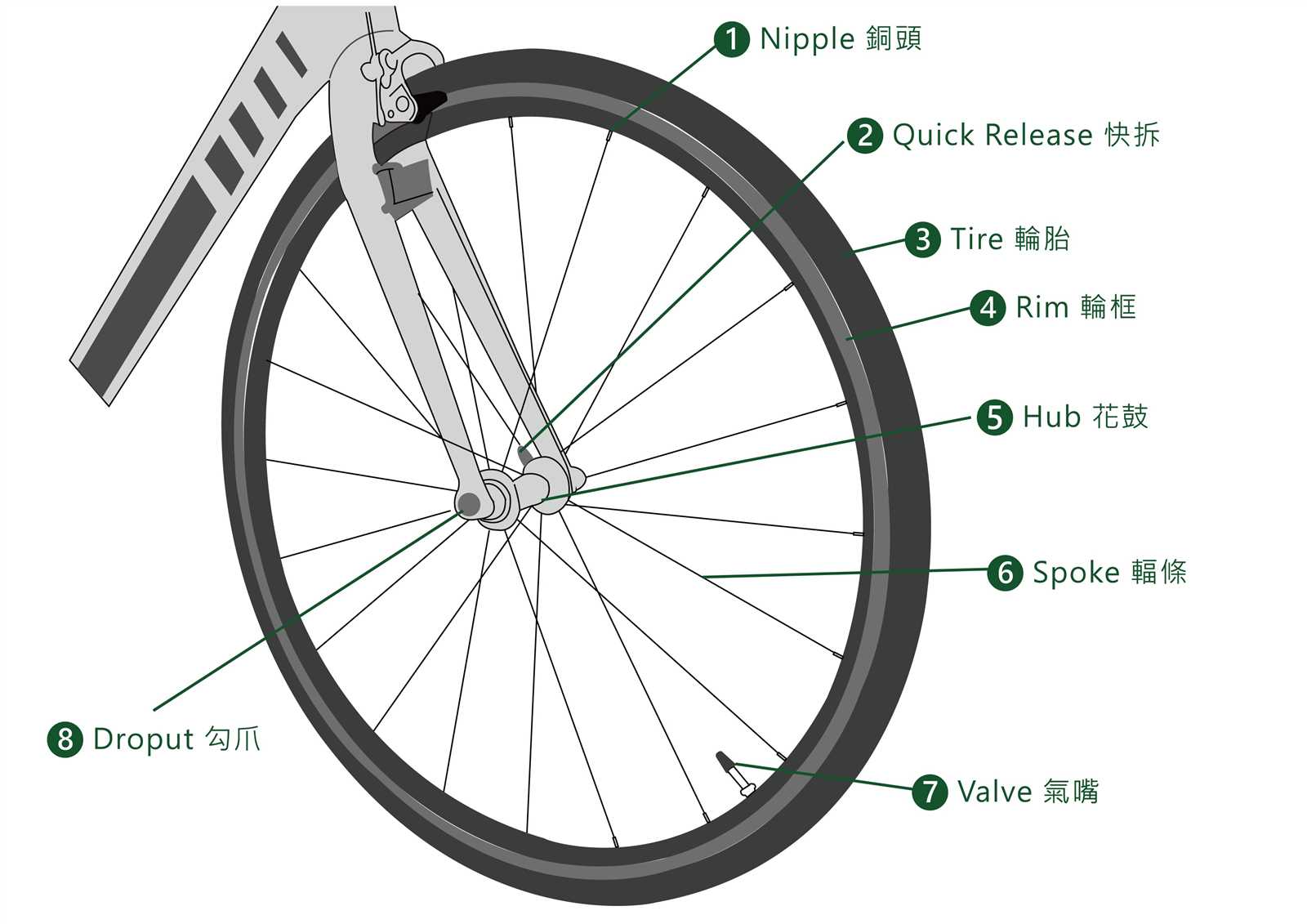
- Rim: The outer edge provides a surface for the tire to mount. It must be strong enough to handle impacts and maintain shape under pressure.
- Spokes: These thin rods connect the hub to the rim, distributing weight evenly while providing necessary tension and stability.
- Hub: Located at the center, the hub houses the axle and enables the rotation of the wheel.
The Role of Handlebars in Control

Seat and Saddle Adjustments for Comfort

Finding the perfect position for your seating surface can significantly enhance your riding experience. Adjusting this component ensures proper alignment with your body, allowing for optimal comfort and efficiency during your travels. The right setup minimizes strain and fatigue, promoting a more enjoyable journey.
To achieve an ideal fit, consider the following adjustments:
Adjustment Type Description Recommended Range Height Position the seating surface so that your leg is slightly bent at the lowest point of the stroke. 1-2 inches below hip height Fore-Aft Position Align the seating surface with your pedals to ensure proper leg extension and prevent knee strain. Vertical alignment with the ball of your foot Angle Adjust the tilt of the seating surface to enhance comfort and reduce pressure on sensitive areas. Level or slight downward angle Regularly revisiting these adjustments can help maintain comfort and prevent discomfort during extended rides.
Brake Systems and Their Varieties
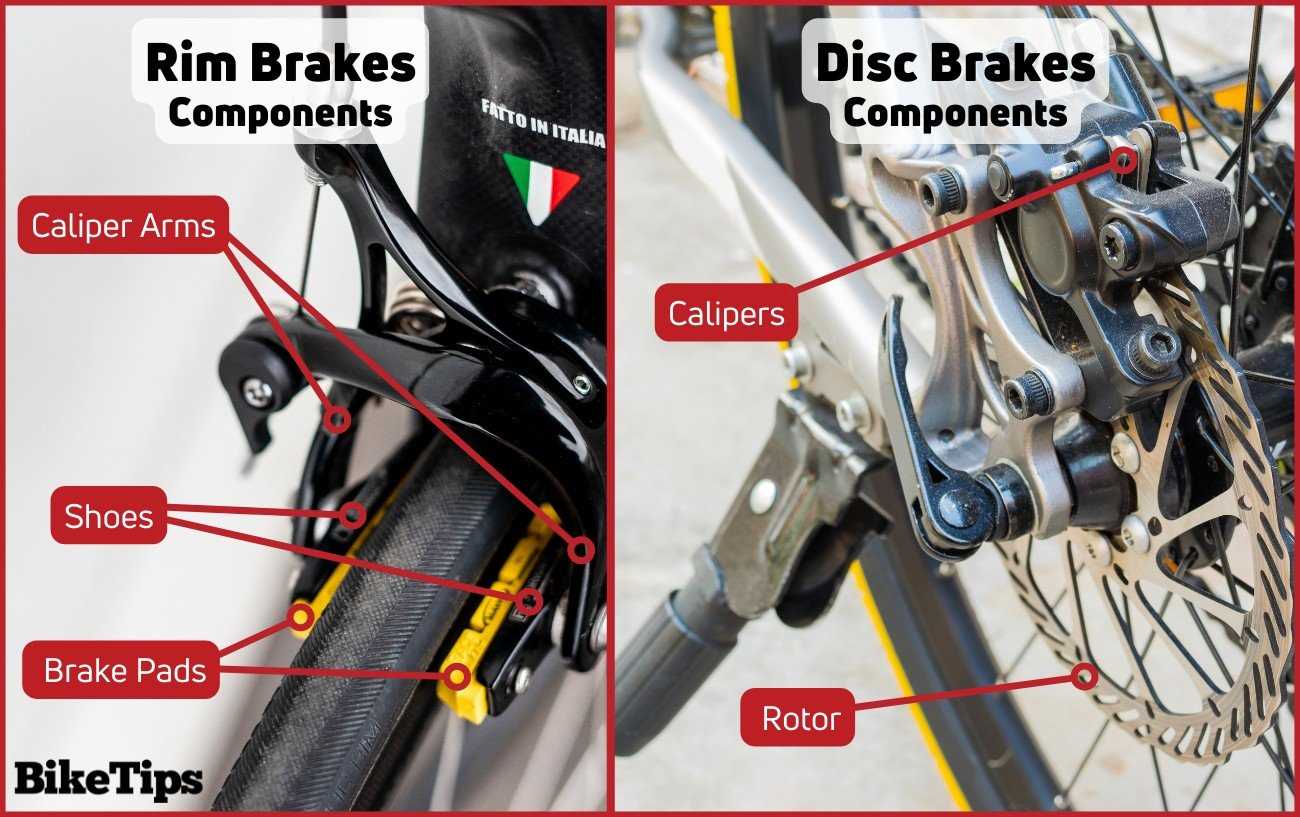
The braking mechanism is essential for ensuring safety and control in any two-wheeled vehicle. Various types of braking systems are designed to meet different riding styles, conditions, and performance requirements. Understanding these systems allows riders to choose the most suitable option for their needs.
There are primarily two categories of braking systems: rim brakes and disc brakes. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing factors like weight, stopping power, and maintenance needs. Below is a comparison of these systems.
Braking System Type Advantages Disadvantages Rim Brakes Lightweight, easier to maintain, lower cost Less effective in wet conditions, wear on the wheel rim Disc Brakes Superior stopping power, consistent performance in various conditions, less rim wear Heavier, more complex installation, higher cost In addition to these main categories, specialized systems like hydraulic and mechanical variants also exist. Hydraulic brakes offer more powerful performance with less effort, while mechanical brakes are simpler and often easier to service.
Choosing the right braking mechanism depends on the rider’s preferences, the terrain, and the intended use. By understanding the varieties of braking systems available, cyclists can make informed decisions to enhance their riding experience.
Gearing Mechanisms for Smooth Riding
The efficiency of propulsion and the overall comfort of movement rely heavily on the systems that enable seamless transitions between different levels of resistance. These mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring that the user can navigate various terrains effortlessly, adapting to both inclines and declines with ease. Understanding these components is vital for optimizing performance and enhancing the experience on any journey.
At the core of these systems lies the interplay between different components, each designed to facilitate smooth operation. By selecting appropriate ratios and configurations, riders can achieve the desired balance between speed and control. Below is a table outlining the primary elements involved in these mechanisms:
Component Function Chainring Transfers power from the pedals to the chain. Rear Cogs Engage with the chain to provide different gear ratios. Derailleur Shifts the chain between different gears for smooth transitions. Shifters Allow the user to control gear changes efficiently. Chain Connects the chainring and rear cogs, transmitting power. By comprehensively understanding these elements and their interactions, users can enhance their riding experience, achieving a more enjoyable and efficient journey across diverse landscapes.
Tire Types and Their Performance
The selection of suitable rubber components significantly influences the overall handling, stability, and efficiency of a vehicle. Various designs and materials are tailored to specific environments and riding styles, impacting everything from speed to traction. Understanding these variations allows enthusiasts to optimize their experience, whether on smooth pavement or rugged terrain.
Road Tires

These are engineered for smooth surfaces, offering minimal rolling resistance and enhanced speed. Their narrow profile and hard compounds maximize efficiency on asphalt, making them ideal for racing and long-distance riding. However, they may sacrifice grip on uneven or wet conditions, which can affect safety and performance.
Off-Road Tires
Constructed for rugged landscapes, these tires feature a wider profile and deeper treads to enhance traction on loose surfaces like dirt and gravel. Their robust design absorbs shocks from rough terrain, providing a more stable ride. While they excel in off-road conditions, they often compromise speed and efficiency on smooth roads.
Pedals and Their Functionality in Cycling
Pedals serve as a crucial interface between the cyclist and the vehicle, enabling the transfer of energy from the rider’s legs to the wheels. Their design and mechanics play a significant role in enhancing performance, comfort, and efficiency during rides. Understanding how these components function can improve the overall experience and effectiveness of any journey.
Types of Pedals
There are various designs available, each catering to different riding styles and preferences. The choice of pedals can significantly impact the cycling experience, affecting everything from power transfer to ease of use.
Type Description Advantages Flat Pedals These pedals offer a large surface area for the foot, allowing for easy entry and exit. Easy to use, versatile for casual riding and commuting. Clipless Pedals These require specialized shoes that clip into the pedal, providing a secure connection. Improved energy transfer and control during rides. Cage Pedals These have a cage that surrounds the foot, offering some grip without requiring specialized footwear. Good compromise between flat and clipless for various riding styles. Functionality in Motion

The primary function of pedals is to convert the cyclist’s leg movements into forward motion. This is achieved through a combination of rotational force and body weight, allowing for a seamless propulsion mechanism. Proper technique and pedal selection can enhance efficiency, leading to longer rides with less fatigue.
Chain Maintenance and Its Impact
Proper upkeep of the connecting mechanism in a two-wheeled vehicle is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular care not only enhances the efficiency of the system but also contributes to a smoother riding experience and can prevent costly repairs in the long run.
Neglecting maintenance can lead to several issues, including increased wear, poor functionality, and even safety risks. Therefore, understanding the significance of routine checks and the application of appropriate lubricants is essential for every user.
Maintenance Task Frequency Impact Cleaning Every 2-4 weeks Reduces friction and wear Lubrication After cleaning Improves smoothness and efficiency Tension Adjustment Monthly Ensures proper alignment and function Visual Inspection Weekly Identifies wear and potential failures By adhering to a consistent maintenance schedule, users can significantly enhance the overall experience, ensuring reliability and safety during rides. Investing time in this essential practice pays off through improved performance and reduced risk of breakdowns.
Suspension Systems for Rough Terrain
Riding over challenging landscapes requires specialized mechanisms designed to absorb shocks and enhance stability. These systems are crucial for maintaining control and comfort while navigating uneven surfaces. Their ability to adapt to various conditions significantly impacts the overall performance and rider experience.
One prevalent type of system utilizes springs and dampers to manage the energy generated by bumps and dips. By compressing and expanding, these components effectively cushion the impact, providing a smoother ride. The quality of these elements can determine how well they respond to different terrains, from rocky paths to muddy trails.
Another approach involves adjustable settings, allowing riders to modify the stiffness and travel based on personal preference and environmental factors. This adaptability can be particularly beneficial for those who frequently switch between urban roads and off-road tracks, ensuring optimal performance in each setting.
In addition to functionality, the design of these systems often emphasizes weight reduction and durability. Lightweight materials are commonly employed to enhance efficiency without compromising strength. This balance is essential for maintaining agility and responsiveness during intense rides.
Ultimately, effective shock absorption and handling are fundamental for overcoming rough terrains. Investing in a quality suspension system not only improves ride quality but also enhances safety and enjoyment in adventurous explorations.
Understanding the Bicycle Frame Structure
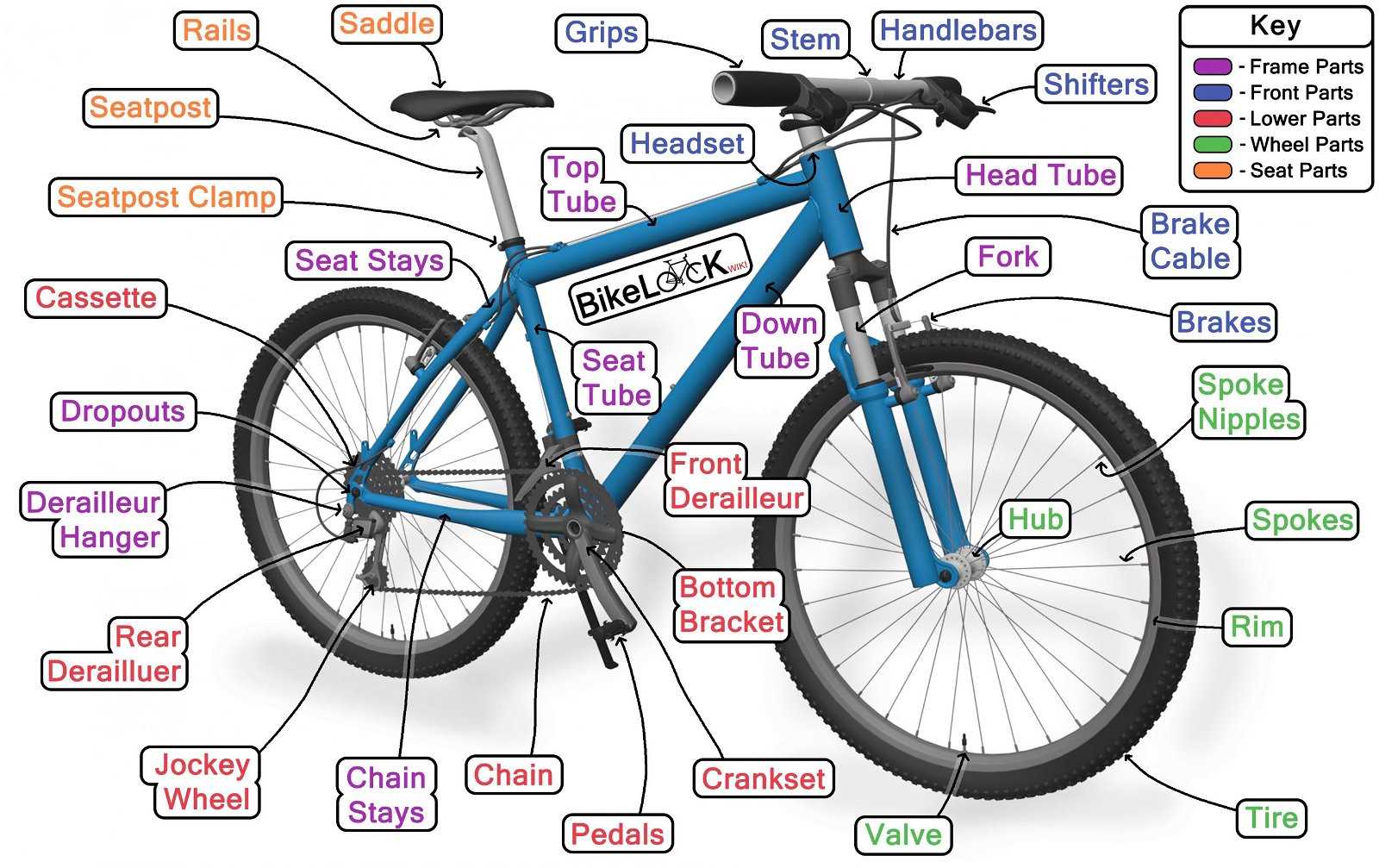
The foundation of every two-wheeled vehicle lies in its frame, which serves as the central element connecting all other components. This essential structure provides stability, ensures proper weight distribution, and offers a secure platform for various elements to function efficiently. The design and material of the frame significantly influence both the performance and durability of the vehicle.
Key Elements of the Frame
The frame is typically composed of two main triangles: the main and rear. Each section works together to maintain the overall shape and balance. The positioning and geometry of these sections are crucial for optimizing riding comfort and handling, making them a vital consideration for different riding styles and terrain types.
Material Considerations

The choice of material plays a major role in determining the overall strength, weight, and flexibility of the frame. Common materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and steel are selected based on factors like durability, weight, and cost. Each material offers distinct advantages, affecting how the vehicle handles on the road.
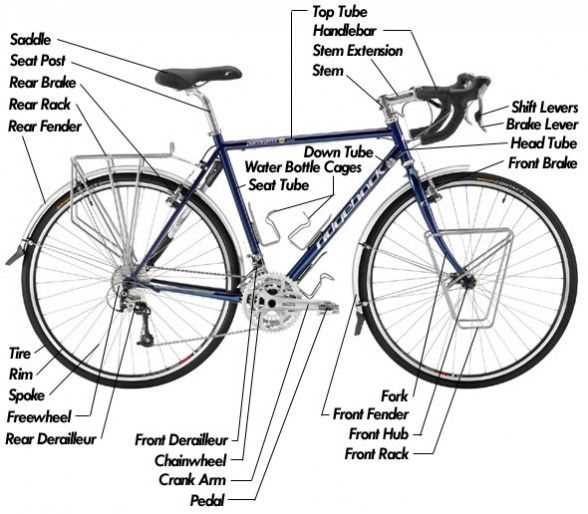
Key Components of the Drivetrain System
The drivetrain system is crucial for converting human energy into forward movement. It consists of interconnected elements that work together to transfer power from the pedals to the wheels, ensuring smooth and efficient propulsion. Each element has a specific role in this process, contributing to the overall performance and handling of the vehicle.
Crankset serves as the central mechanism that connects the pedals and transfers power through rotation. It works in conjunction with the chain, which links the various components, creating a continuous cycle of motion.
The derailleur is responsible for managing gear changes, allowing for an adaptable riding experience. It ensures that the rider can easily shift between different speeds, optimizing efficiency on different terrains.
Finally, the cassette
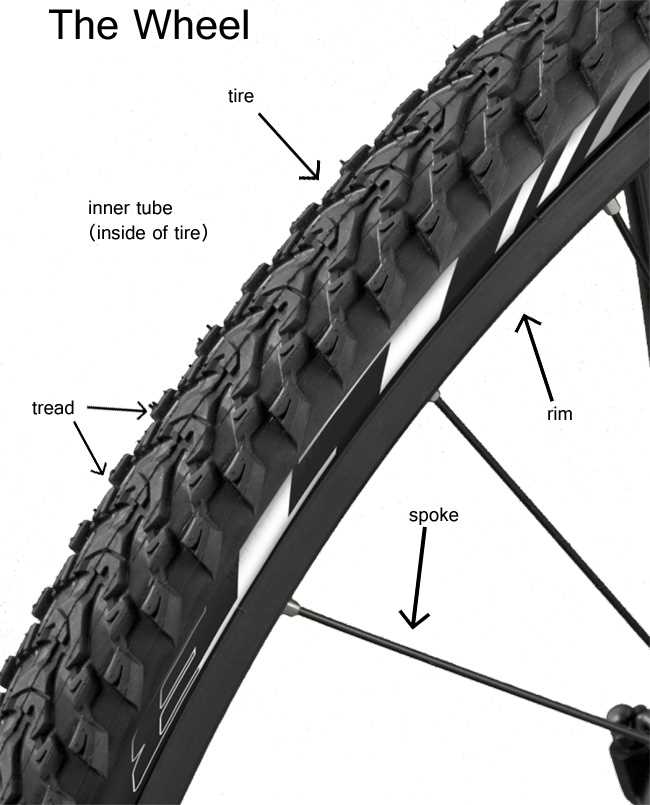
Wheel Anatomy and Its Importance
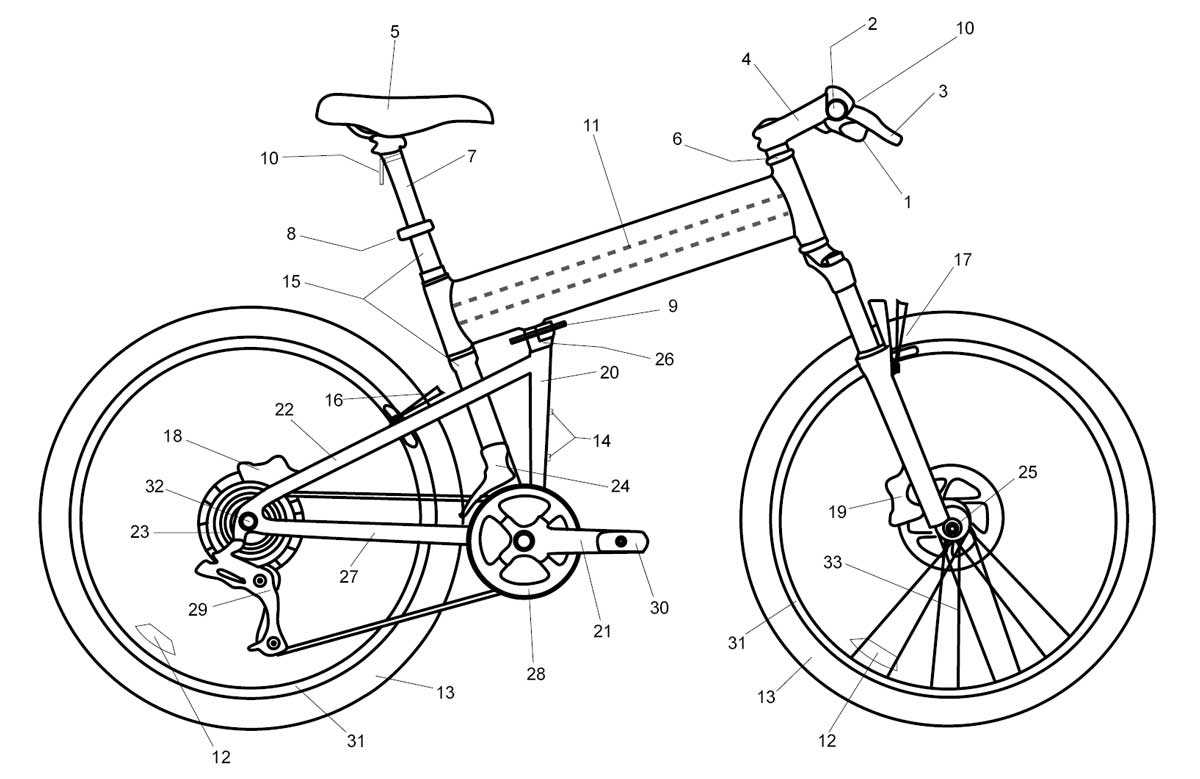
The structure of a wheel plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and efficient ride. Understanding the key components that make up this essential element helps highlight its impact on overall performance and safety. The balance, strength, and design of the wheel influence the way a vehicle moves, turns, and withstands various forces during use.
A wheel consists of multiple interconnected elements that contribute to its functionality: