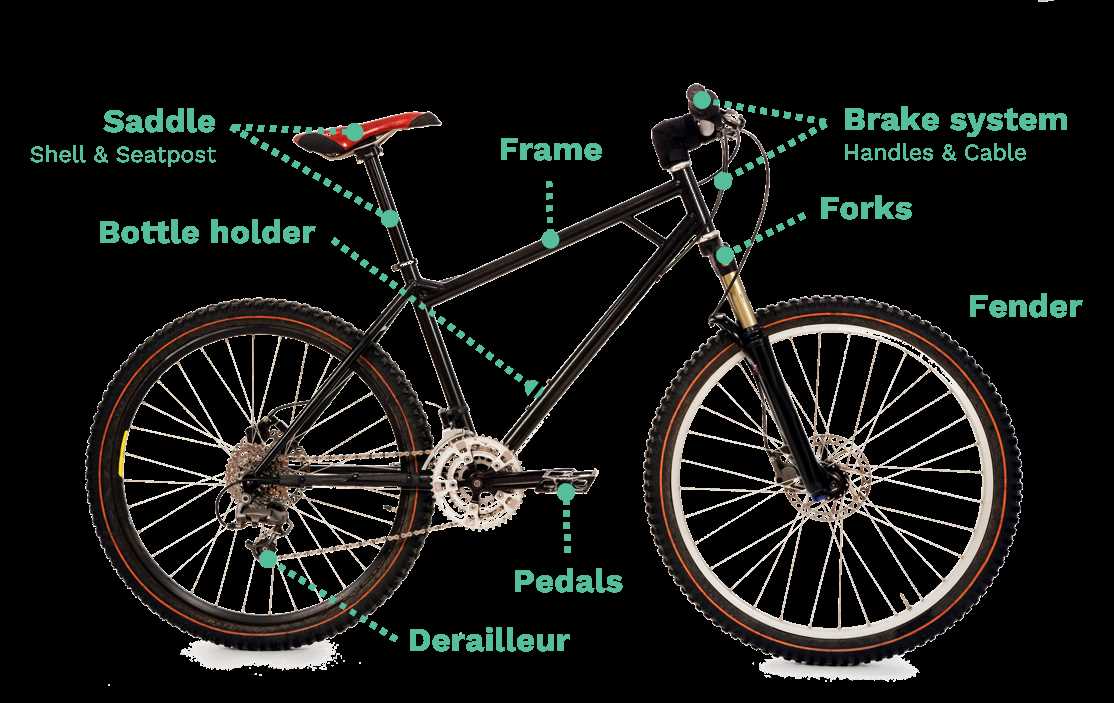
The world of two-wheeled vehicles encompasses a variety of elements that work harmoniously to enhance performance and rider experience. Understanding these essential components can significantly improve one’s ability to maintain and optimize the vehicle. Each element plays a vital role, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the ride.
From the frame to the wheels, every section has its unique purpose, designed to support different terrains and riding styles. Familiarizing oneself with these features not only aids in proper care but also empowers riders to make informed choices when customizing their equipment. Whether navigating rugged trails or cruising through urban environments, recognizing the significance of each aspect can lead to a more enjoyable journey.
Exploring the intricacies of this cycling machine reveals how various elements interact to create a seamless riding experience. By delving into these components, cyclists can better appreciate the engineering and design that enable their adventures on two wheels. Understanding these features is crucial for anyone looking to elevate their cycling endeavors.
Components of a Trail Bicycle
This section explores the essential elements that come together to create a reliable two-wheeled vehicle designed for off-road adventures. Understanding these components is crucial for enthusiasts looking to enhance their riding experience and ensure optimal performance.
Key Elements
Each element plays a significant role in the functionality and handling of the vehicle. From the frame’s design to the wheels’ construction, every detail contributes to the overall riding experience. Below is a table that highlights some of these vital components and their functions.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | Provides structural integrity and support. |
| Fork | Holds the front wheel and allows steering. |
| Wheels | Facilitates movement and absorbs shocks. |
| Brakes | Ensures safe stopping and control. |
| Gearing System | Adjusts the pedaling effort and speed. |
Conclusion
Grasping the significance of these elements enhances riders’ understanding and appreciation of their vehicle. Proper knowledge aids in maintenance and upgrades, ultimately leading to improved performance on rugged terrains.
Understanding the Frame Structure
The framework of a two-wheeled vehicle plays a crucial role in determining its overall performance, stability, and durability. It serves as the core foundation that connects various elements, providing a robust structure that supports both the rider and the components attached to it. A well-designed frame not only enhances the aesthetics but also contributes significantly to the riding experience.
Furthermore, the frame acts as a central hub for the integration of additional components, such as gears and brakes, ensuring that all parts work harmoniously. Understanding the intricacies of this structure allows riders to make informed choices when selecting or customizing their vehicle, tailoring it to their specific riding preferences and conditions.
Types of Suspension Systems Explained
Suspension systems play a crucial role in enhancing the riding experience by improving comfort and control. These mechanisms allow for better handling of various terrains and obstacles, ensuring that the rider maintains stability and safety during their journey. Understanding the different types of suspension systems can help enthusiasts choose the right setup for their specific needs.
1. Hardtail Suspension
Hardtail systems feature a rigid rear end, providing simplicity and efficiency. This design is often lighter and requires less maintenance compared to other types. Riders benefit from improved power transfer, making it ideal for climbing and smooth trails. However, it may not absorb impacts as effectively as other systems.
2. Full Suspension
Full suspension setups incorporate both front and rear shock absorbers, offering enhanced comfort and traction. This design allows for better absorption of bumps and dips, making it suitable for rougher terrains. Riders often find that this type improves control during descents, allowing for a more confident ride.
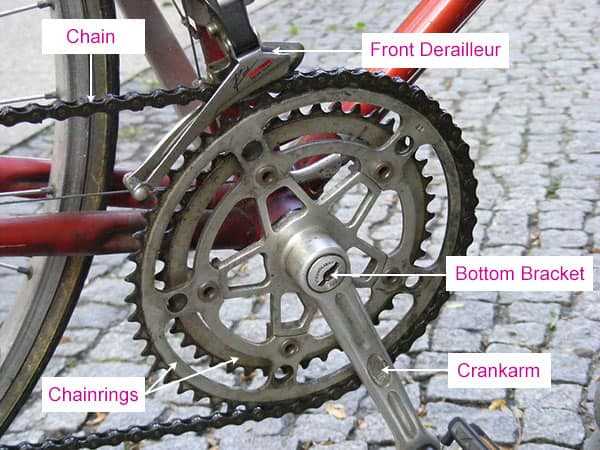
Components of the Drivetrain Assembly
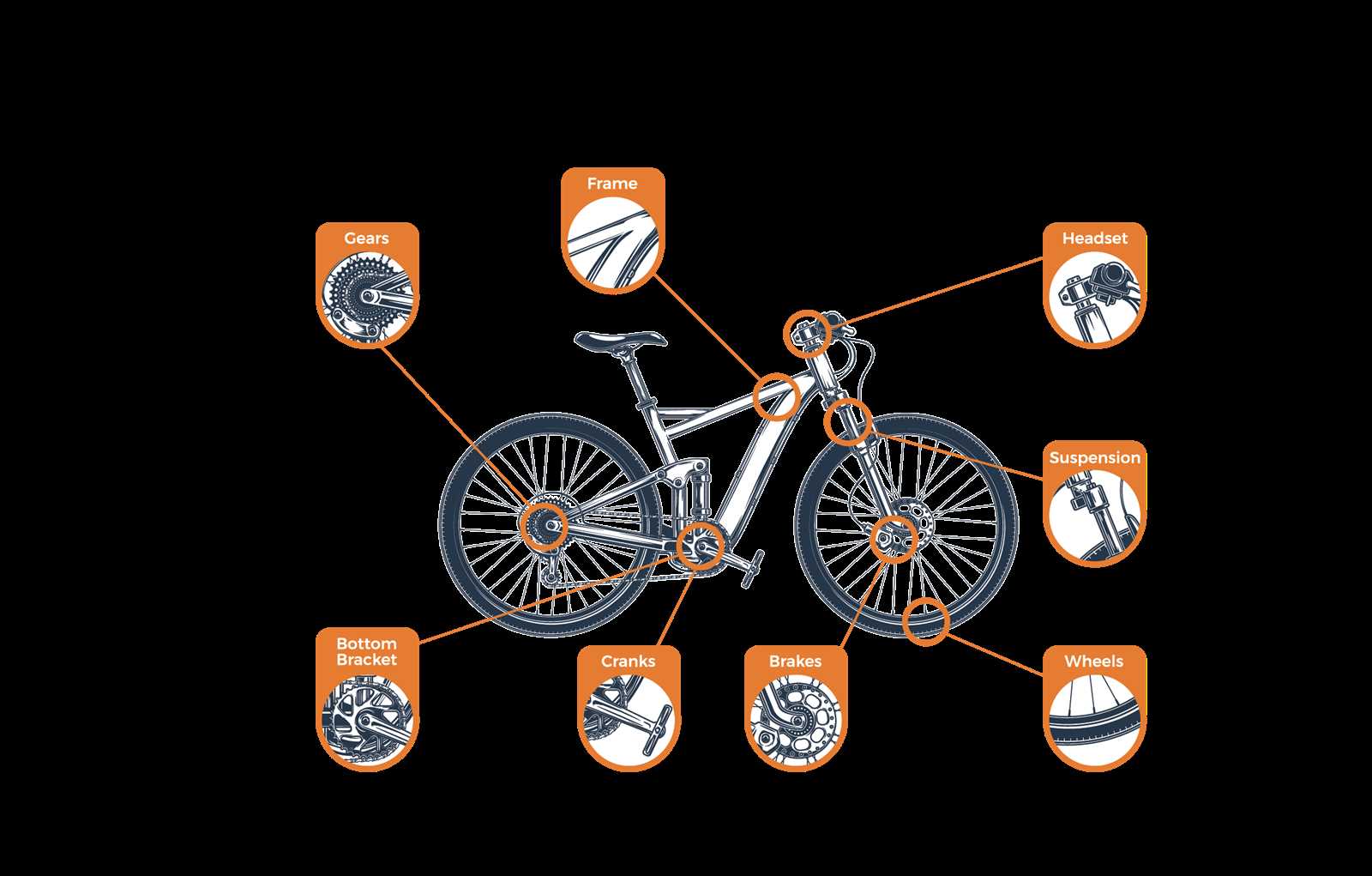
The drivetrain assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a two-wheeled vehicle, enabling efficient transfer of power from the rider to the wheels. Understanding its structure is essential for enthusiasts and riders alike, as it directly influences performance, speed, and responsiveness.
At the heart of the drivetrain lies the crankset, which connects the pedals to the bike and converts the rider’s leg movement into rotational energy. This energy is then transmitted through the chain, a vital link that ensures smooth and effective power delivery to the rear wheel.
The rear derailleur is another key component, responsible for shifting the chain between different gears on the rear cassette, allowing the rider to adjust their speed and climbing ability. Complementing this is the front derailleur, which manages shifts between chainrings at the front, providing a broader range of gearing options.
Furthermore, the cassette consists of multiple sprockets of varying sizes, enabling the rider to select the appropriate gear for different terrains. Lastly, the bottom bracket connects the crankset to the frame, ensuring smooth rotation while maintaining structural integrity.
Importance of Wheel Specifications
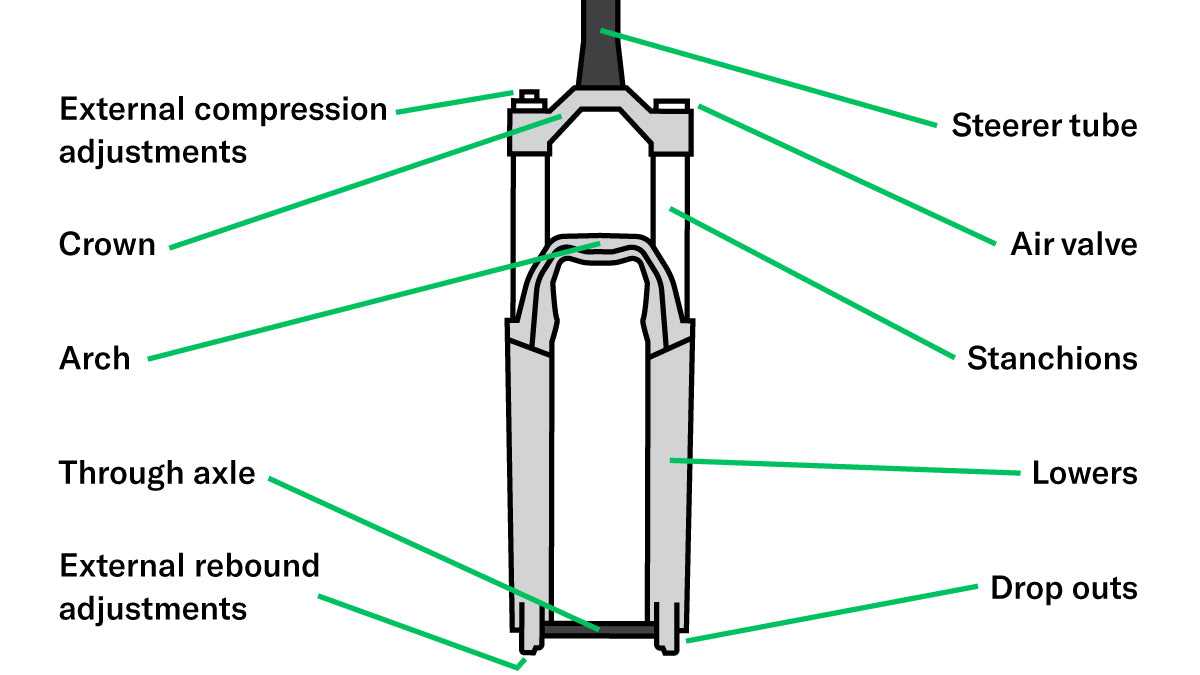
The specifications of the wheels play a crucial role in determining the overall performance and experience of riding. Properly chosen dimensions and features can significantly impact factors such as handling, speed, and stability, affecting how effectively a rider can navigate various terrains.
Influence on Performance
Wheel specifications directly affect acceleration, grip, and maneuverability. Wider rims can provide better traction, especially on uneven surfaces, while lighter materials may enhance speed. The choice of tire size also influences the ability to absorb shocks, providing a smoother ride over obstacles.
Impact on Durability
Choosing the right wheel specifications is essential for ensuring long-lasting performance. High-quality materials and appropriate design can withstand rough conditions, reducing the likelihood of damage and enhancing the lifespan of the entire setup. This is particularly important for those who frequently ride in challenging environments.
Role of Handlebars in Control
Handlebars play a crucial role in steering and maneuvering a two-wheeled vehicle, allowing riders to maintain balance and direction. Their design influences the overall handling characteristics, which can significantly affect the riding experience. Proper control over the handlebars enables the cyclist to navigate various terrains and obstacles with ease.
Importance of Grip and Comfort
The grip on the handlebars is vital for ensuring comfort and stability. Ergonomically designed handlebars allow for a natural hand position, reducing fatigue during long rides. Comfortable grips enhance control, enabling the rider to react quickly to changes in the environment.
Steering Precision and Responsiveness
Handlebars also provide the necessary leverage for precise steering. The angle and width of the handlebars can affect how responsive the vehicle is to inputs from the rider. Effective steering allows for better control over the trajectory and speed, enhancing overall performance. A well-designed handlebar setup can significantly improve the rider’s confidence and safety.
Functionality of Brake Mechanisms
The efficiency of braking systems is crucial for ensuring safety and control during cycling adventures. These mechanisms are designed to slow down or stop the movement of the bicycle, providing riders with the ability to navigate diverse terrains effectively. Understanding how these systems operate can enhance the overall cycling experience.
Types of Braking Systems
- Rim Brakes: These brakes function by applying friction to the wheel’s rim, allowing for quick stopping power.
- Disc Brakes: Utilizing a rotor and caliper, these systems offer superior stopping force and perform well in various weather conditions.
- Coaster Brakes: Engaged by pedaling backward, this type provides a simple and reliable braking solution.
Components of Brake Systems
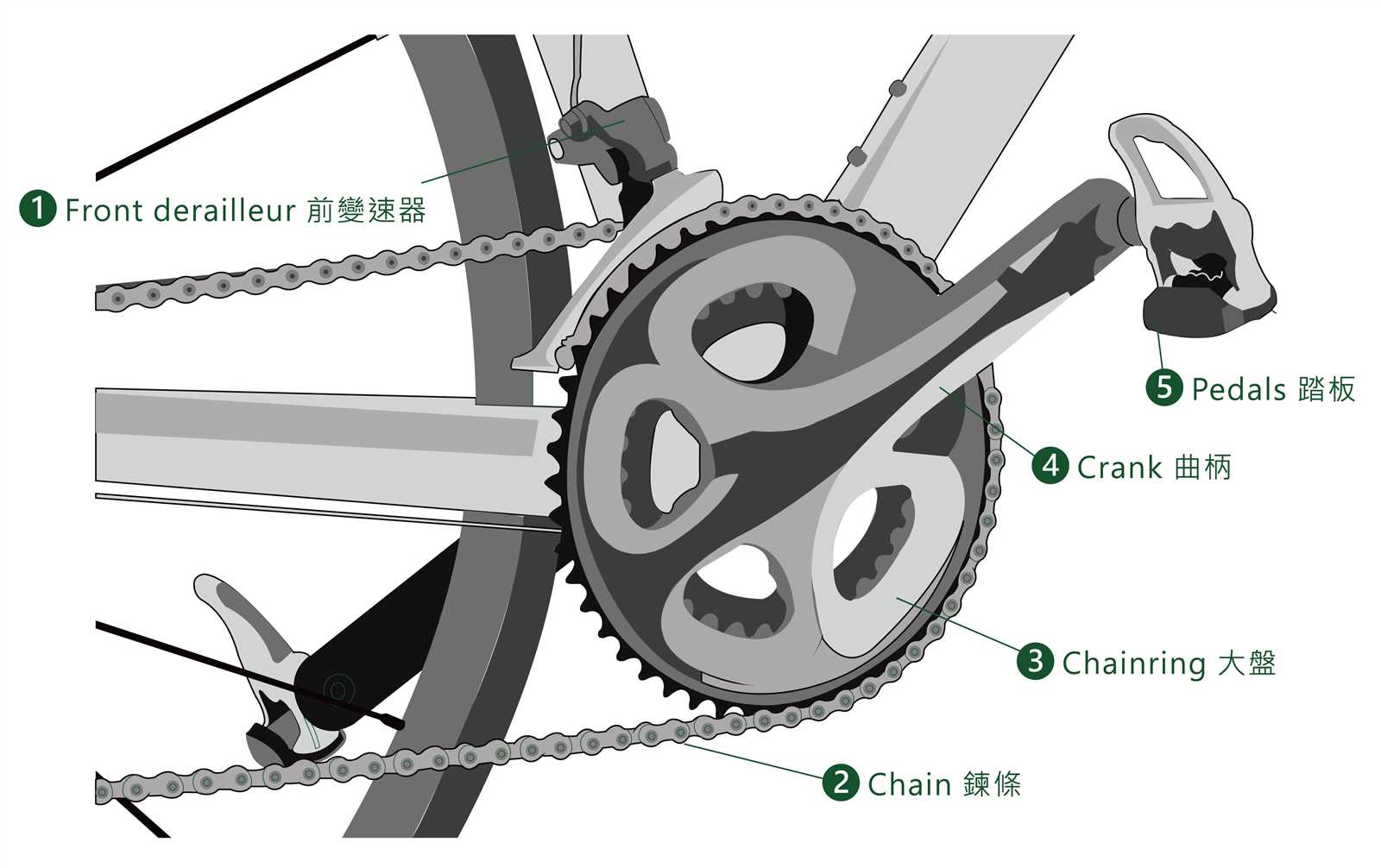
- Brake Levers: Located on the handlebars, they allow riders to activate the braking system.
- Cables or Hoses: These connect the levers to the braking components, transmitting the rider’s input.
- Brake Pads: Made from materials designed to create friction, they come into contact with the wheel or rotor.
- Rotors or Rims: The surface against which the brake pads press, crucial for effective stopping.
Each element works in unison to provide reliable stopping power, enhancing the rider’s ability to control their speed and direction.
Gear Shifting Mechanisms Overview
Understanding the various systems that facilitate gear changes is crucial for optimizing performance and enhancing the riding experience. These mechanisms enable smooth transitions between different gear ratios, allowing for better control and efficiency on diverse terrains.
Several types of shifting systems are commonly utilized in cycling. Each type serves a distinct purpose and offers unique advantages, catering to the needs of different riders.
| Type | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Shifting | Utilizes cables and levers for gear changes. | Reliable and easier to maintain. |
| Electronic Shifting | Employs electronic components for precise shifting. | Offers faster and more accurate gear changes. |
| Automatic Shifting | Adjusts gears automatically based on terrain. | Provides a hands-free experience for riders. |
These systems play a vital role in enhancing the overall cycling experience, allowing riders to adapt to varying conditions effortlessly.
Material Choices for Bike Components
When it comes to the construction of cycling equipment, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in performance, durability, and weight. Various materials offer unique benefits and drawbacks, influencing the overall functionality and user experience. Understanding these options helps cyclists make informed decisions tailored to their specific riding needs.
Aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. It offers a good balance between strength and weight, making it ideal for those who prioritize agility without sacrificing durability.
Carbon fiber is another advanced option, renowned for its exceptional stiffness and low weight. This material allows for precise engineering, enabling the design of components that enhance aerodynamics and responsiveness. However, it often comes at a higher price point.
Steel is favored for its strength and shock absorption qualities. While it may be heavier than aluminum or carbon fiber, many riders appreciate its reliability and the comfortable ride it provides over rough terrain.
Each of these materials contributes differently to the overall performance and ride experience, highlighting the importance of choosing components that align with individual preferences and riding styles.
Significance of Tire Types
The choice of tire variety plays a crucial role in determining the performance and handling characteristics of a two-wheeled vehicle. Different designs cater to specific terrains and riding conditions, influencing factors such as grip, speed, and comfort. Understanding the significance of these variations allows riders to make informed decisions that enhance their overall experience.
In particular, the tread pattern, width, and compound of tires significantly impact traction and control. Selecting the appropriate type based on the intended use is essential for optimizing ride quality and safety.
| Tire Type | Tread Pattern | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Knobby | Deep and spaced-out knobs | Off-road and rugged trails |
| Slick | Smooth surface | Paved roads and urban environments |
| Intermediate | Combination of knobs and smooth sections | Mixed terrain |
Pedals and Their Varieties
Pedals serve as a crucial interface between the rider and the cycling machine, facilitating efficient energy transfer from the legs to the wheels. The diversity in designs and functionalities allows cyclists to choose options that best suit their riding style and preferences.
Types of Pedals
Understanding the various types of pedals can help in making an informed decision. Here are the most common varieties:
- Platform Pedals:
- Wide and flat design for easy foot placement.
- Ideal for casual riding and tricks.
- Cage Pedals:
- Include a cage or clip that holds the foot securely.
- Enhances grip and reduces slippage.
- Clipless Pedals:
- Require special shoes with cleats that attach to the pedal.
- Offers improved power transfer and stability.
- Toe Clip Pedals:
- Feature a strap or clip to secure the foot in place.
- Provides some advantages of clipless pedals without full commitment.
Choosing the Right Pedals
Selecting the appropriate pedals depends on various factors, including:
- Riding style and discipline.
- Comfort and fit with cycling shoes.
- Personal preferences regarding security and ease of use.
Ultimately, the right choice can enhance the overall cycling experience, making each ride more enjoyable and efficient.
Effects of Weight Distribution
Weight placement on a two-wheeled vehicle significantly impacts its handling, stability, and overall performance. Properly managing where the mass is situated can enhance control during various maneuvers, making it essential for riders to understand how distribution affects their experience.
Impact on Handling
When the load is centered, riders often experience improved balance, allowing for sharper turns and greater responsiveness. Conversely, if the weight is too far forward or backward, it can lead to difficulties in steering and instability, particularly on uneven terrain.
Influence on Traction
Distribution also plays a critical role in traction. When weight is correctly aligned over the wheels, it maximizes contact with the ground, enhancing grip and control. This is especially important during climbs or descents, where maintaining a solid grip can determine success or failure.
Understanding how to adjust weight placement according to riding conditions can help enthusiasts achieve optimal performance and enhance their overall enjoyment of the ride.
Maintenance Tips for Key Parts
Proper upkeep of essential components is vital for optimal performance and longevity of your ride. Regular attention to specific areas can prevent issues and ensure a smooth experience. Here are some valuable recommendations to maintain these crucial elements.
1. Regular Cleaning: Keeping surfaces free from dirt and grime is essential. Use a gentle cleanser and a soft brush to eliminate debris without causing damage.
2. Lubrication: Applying appropriate lubricant to moving elements reduces friction and wear. Focus on areas like chains and pivots, ensuring they operate smoothly.
3. Tire Pressure Checks: Maintaining the correct air pressure enhances stability and performance. Regularly inspect tires and inflate them to the recommended levels.
4. Brake Adjustments: Ensure braking systems are functioning properly. Check alignment and pad wear frequently, making necessary adjustments to guarantee reliable stopping power.
5. Periodic Inspections: Conduct thorough examinations of all key components to identify any signs of wear or damage. Promptly address issues to avoid further complications.
6. Professional Servicing: Seek assistance from professionals for in-depth maintenance when needed. They can provide expertise and perform complex repairs, ensuring everything is in top condition.