
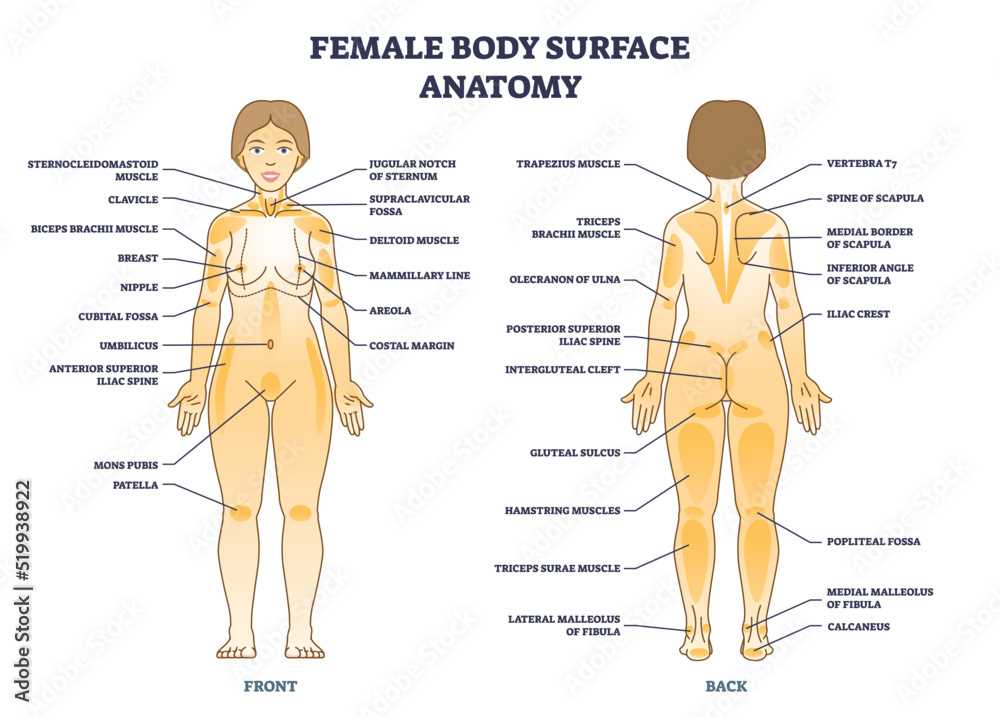
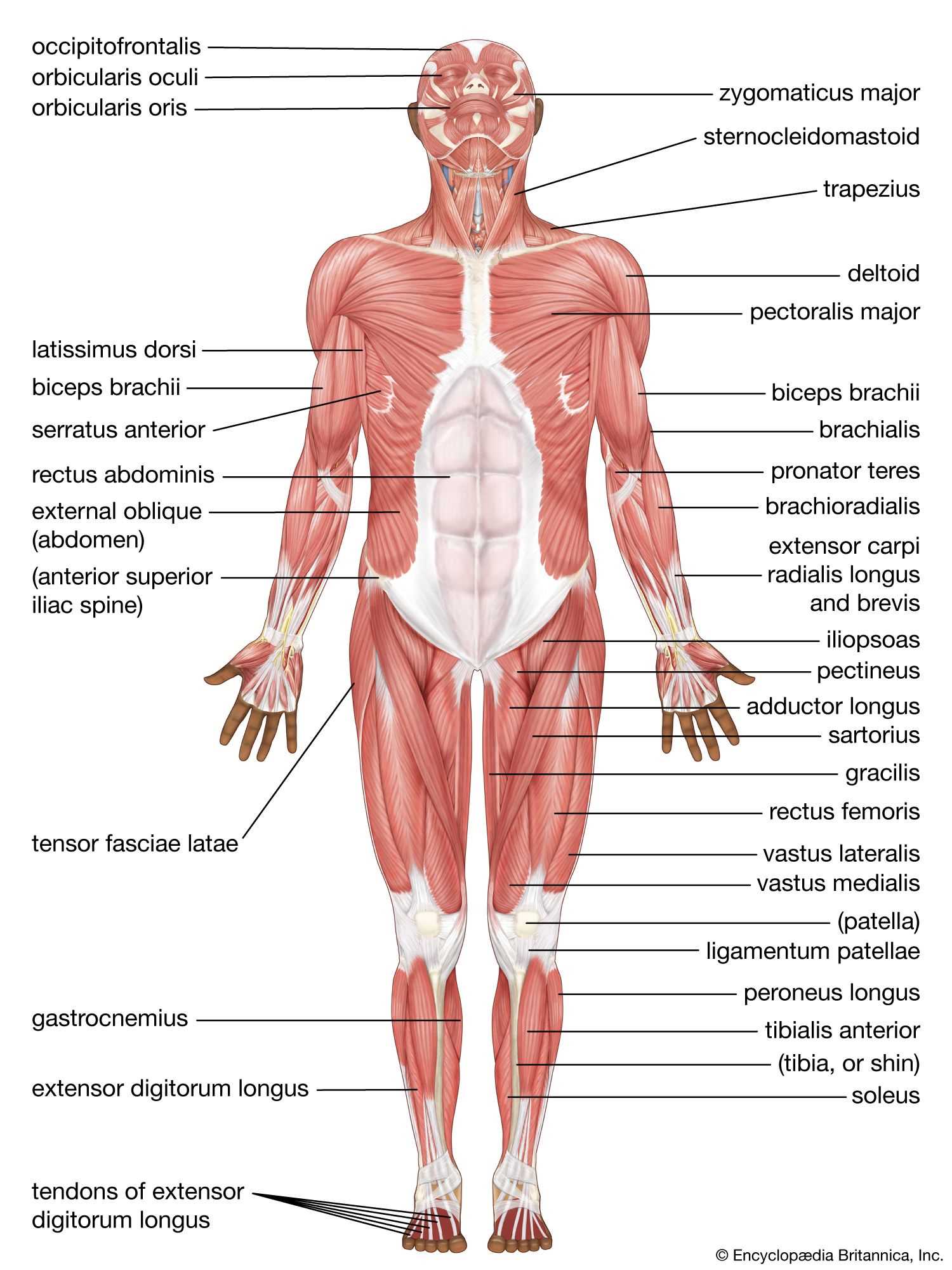
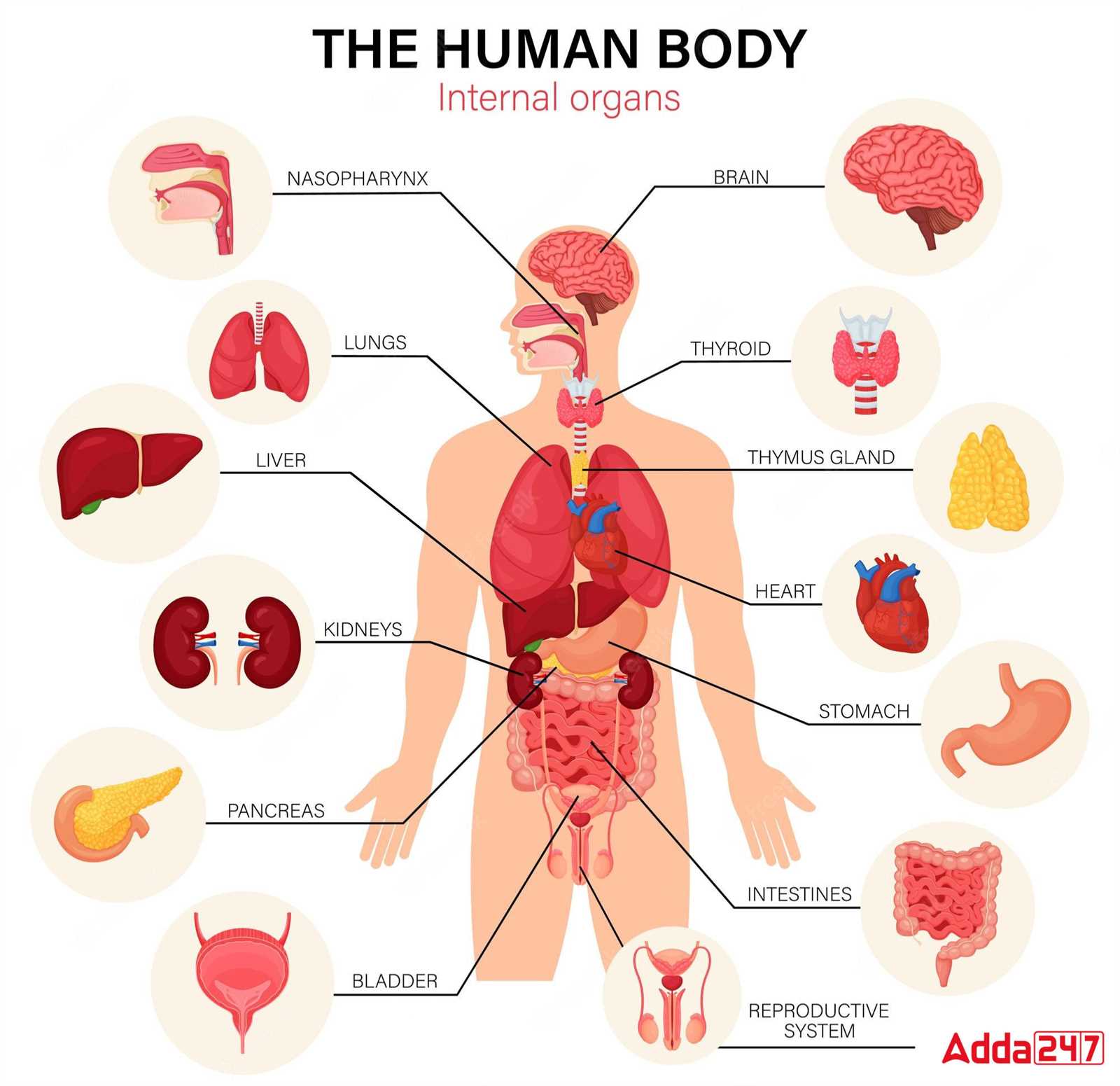
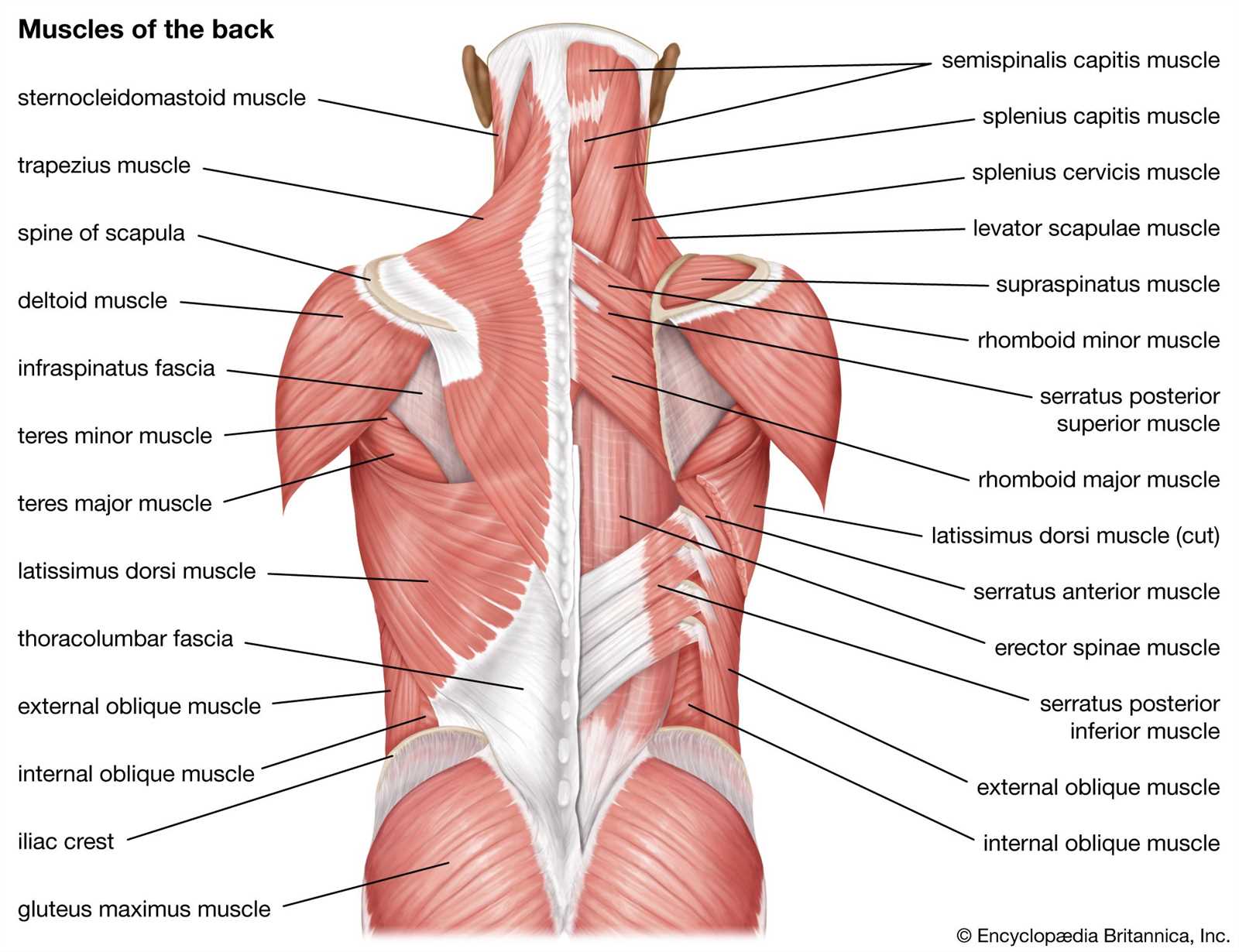
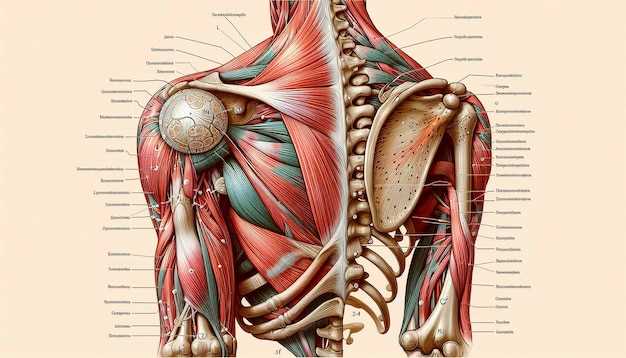
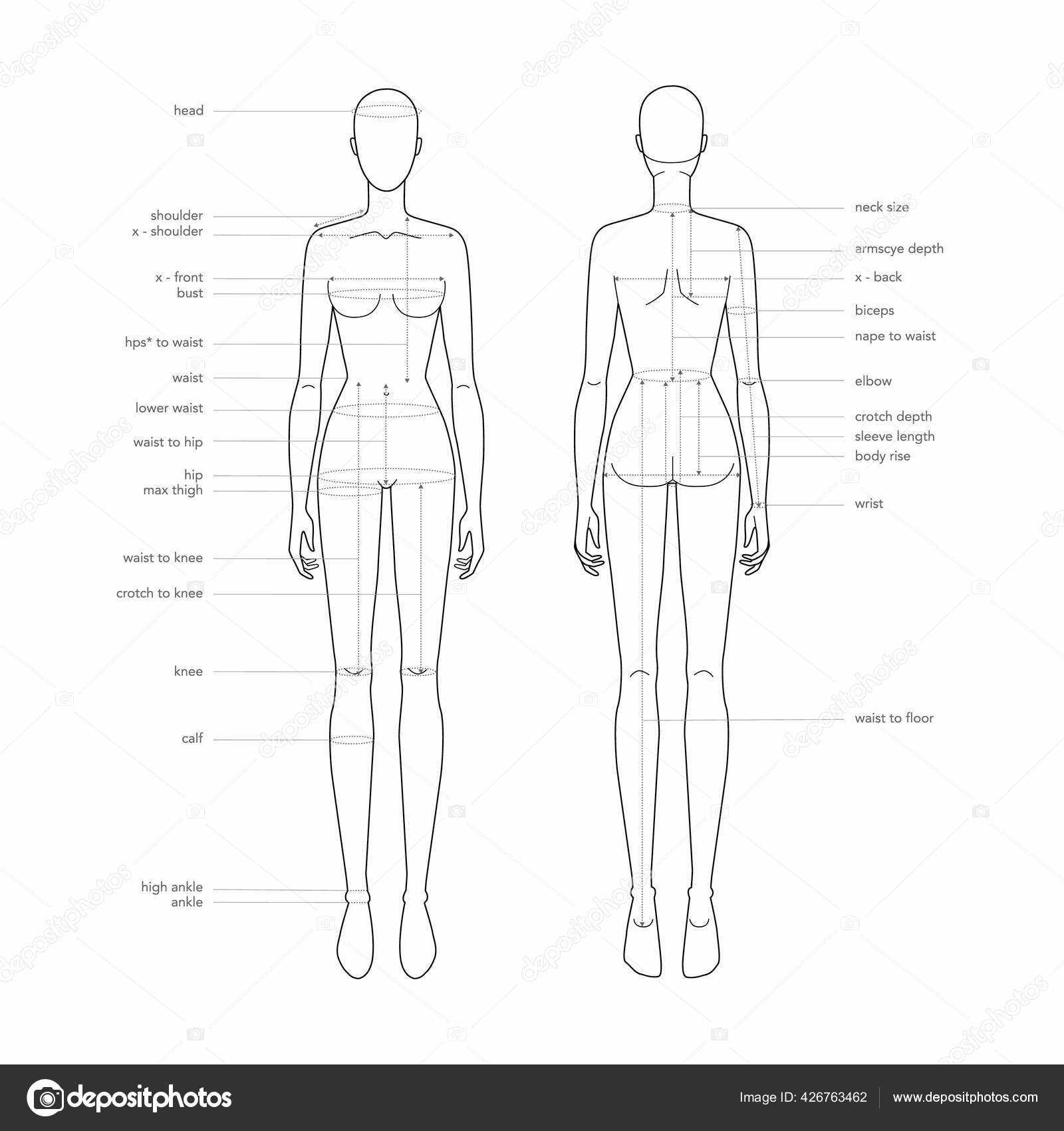
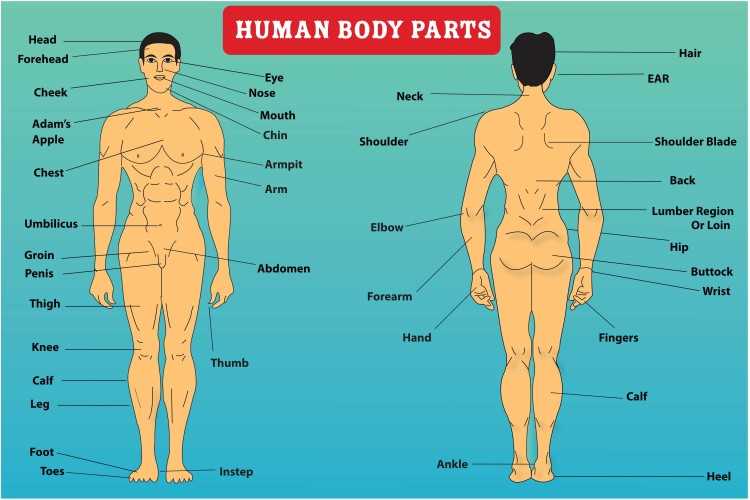
This section aims to explore the intricate layout of the posterior region, highlighting various elements and their functions. By delving into this subject, readers will gain insights into the complexities of human anatomy and how these structures contribute to overall well-being.
Visual representation plays a crucial role in understanding these components. Detailed illustrations allow for better comprehension of their locations and relationships, enhancing the learning experience.
Moreover, a thorough understanding of these features is essential for various fields, including healthcare and fitness. Knowledge of the anatomical layout can aid in injury prevention and rehabilitation, emphasizing the importance of proper care and maintenance.
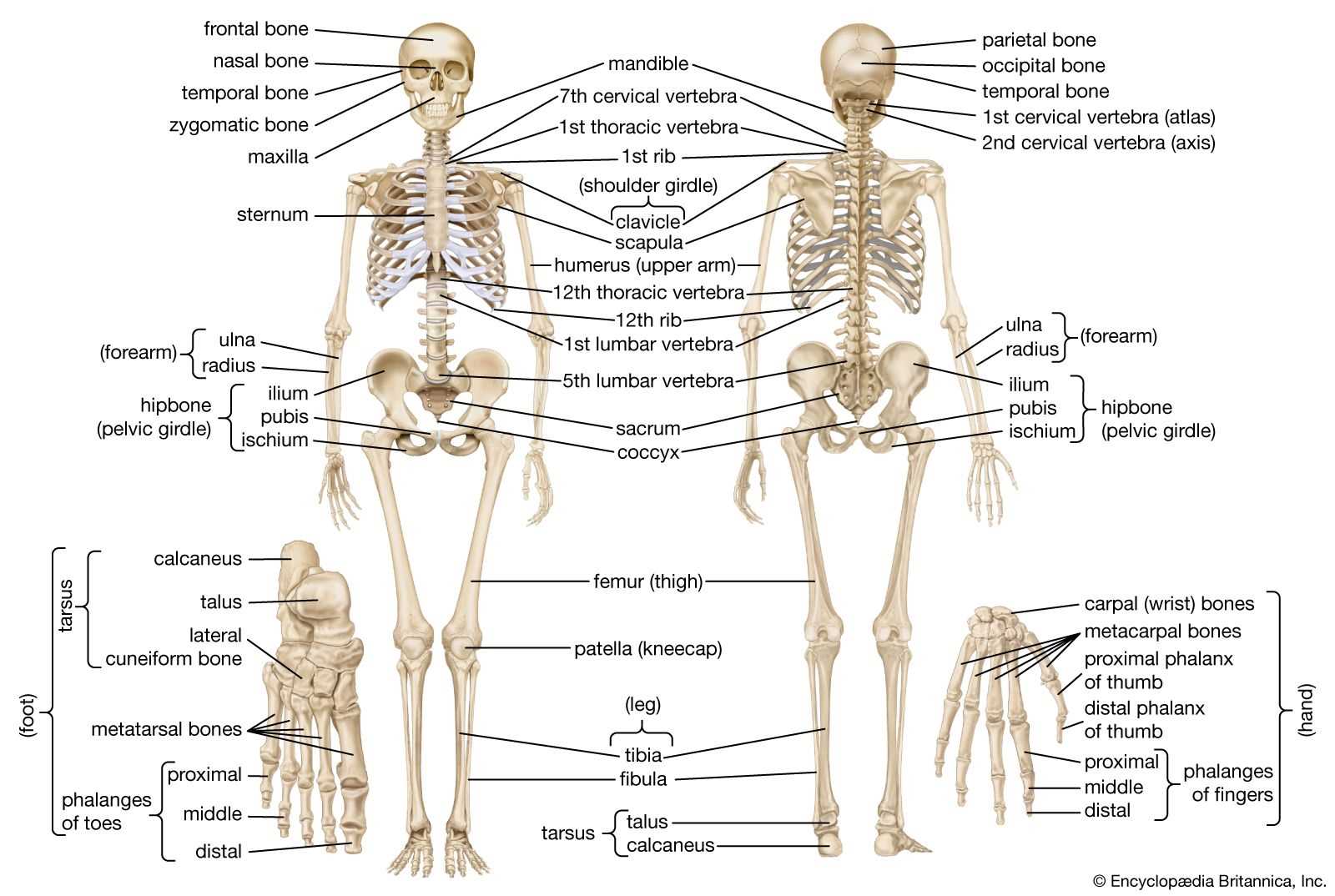
This section explores the significant skeletal structures located in the posterior region, crucial for providing support and facilitating movement. Understanding these components is essential for grasping their roles in maintaining overall stability and posture.
| Bone | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Vertebrae | Spinal column | Support and protect the spinal cord |
| Scapula | Shoulder area | Connects arm bones and aids in movement |
| Sacrum | Base of spine | Links spine to pelvis and bears weight |
| Ribs | Thoracic region | Protects vital organs and supports the chest |
Common Back Injuries
Various types of trauma can affect the rear region, leading to discomfort and impaired mobility. Understanding these issues is essential for effective prevention and treatment.
Types of Injuries
- Strains: Overstretching or tearing of muscles or tendons.
- Sprains: Damage to ligaments due to twisting or impact.
- Herniated Discs: Bulging discs pressing on nearby nerves.
- Fractures: Breaks in the vertebrae, often due to falls or accidents.
- Sciatica: Pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve due to nerve compression.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Pain that may be sharp or dull.
- Stiffness or reduced flexibility.
- Radiating discomfort in legs or arms.
- Muscle weakness or spasms.
- Numbness or tingling sensations.
Function of Spinal Column
The spinal column plays a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity and supporting various functions within the human framework. It serves as a central axis, providing both stability and flexibility.
Key functions include:
- Providing protection for the spinal cord, a vital component of the nervous system.
- Facilitating movement by allowing bending and twisting motions.
- Acting as a shock absorber to mitigate the impact of physical activities.
- Maintaining posture and alignment, contributing to overall balance.
In summary, this vital structure supports not only physical capabilities but also plays an essential role in overall health and well-being.
Role of Intervertebral Discs
Intervertebral discs serve a crucial function in maintaining the overall integrity and flexibility of the spinal column. These unique structures are positioned between the vertebrae, acting as natural shock absorbers that facilitate movement while ensuring stability.
The main responsibilities of these discs include:
- Shock Absorption: They cushion the forces exerted during various activities, reducing impact on adjacent vertebrae.
- Flexibility: Discs allow for a range of motion, enabling bending, twisting, and other movements without strain.
- Support: They help distribute weight evenly across the spine, contributing to overall postural alignment.
Additionally, the discs contain a gel-like center that helps in maintaining hydration and elasticity. Over time, factors such as aging and injury can affect the health of these vital components, leading to potential discomfort and mobility issues.
Understanding Nerve Pathways
The intricate system of neural connections plays a crucial role in how sensations and signals are transmitted throughout an organism. These pathways are essential for coordinating functions and responses, enabling communication between various regions.
Key Functions
- Transmission of sensory information
- Coordination of motor responses
- Regulation of reflex actions
Components of Neural Networks
- Neurons: The primary cells responsible for transmitting information.
- Synapses: Junctions that facilitate communication between neurons.
- Neurotransmitters: Chemicals that relay signals across synapses.
Posture and Its Impact
Proper alignment plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being. The way one holds themselves not only affects physical appearance but also has significant implications for comfort and functionality. Maintaining an appropriate stance can enhance performance and prevent various discomforts.
Physical Health Benefits
Good posture contributes to optimal organ function and aids in reducing strain on muscles and joints. By aligning the framework correctly, individuals can experience fewer aches and enhanced mobility, leading to a more active lifestyle.
Mental and Emotional Effects
Additionally, a confident stance can positively influence self-esteem and mood. Research suggests that maintaining an upright position can lead to increased feelings of empowerment and a more positive outlook on life.
Exercises for Back Strength
Enhancing the stability and resilience of the rear section is vital for overall physical health. Engaging in specific workouts can promote strength, improve posture, and reduce the risk of injuries. Below are some effective routines to build endurance and flexibility in this area.
Key Exercises
Incorporating a variety of movements into your training can yield optimal results. Here are some recommended exercises:
| Exercise | Description | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Deadlift | Focuses on lifting weights from the ground, engaging multiple muscle groups. | 3 sets of 8-10 |
| Rows | Pull weights towards the torso, targeting the muscles along the spine. | 3 sets of 10-12 |
| Plank | Maintain a stable position to strengthen core muscles and improve endurance. | 3 sets, hold for 30-60 seconds |
Incorporating Flexibility
In addition to strengthening exercises, flexibility routines can enhance mobility and prevent stiffness. Incorporate stretches like the cat-cow and child’s pose for comprehensive benefits.
Preventive Measures for Pain
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of discomfort and strain in various regions. Implementing effective strategies not only enhances overall well-being but also promotes longevity in daily activities.
Ergonomic Adjustments
- Use supportive seating that maintains natural posture.
- Adjust workstations to ensure proper alignment.
- Incorporate standing desks to alternate positions.
Regular Physical Activity
- Engage in stretching exercises to maintain flexibility.
- Participate in strength training to support muscle health.
- Practice low-impact activities like walking or swimming.