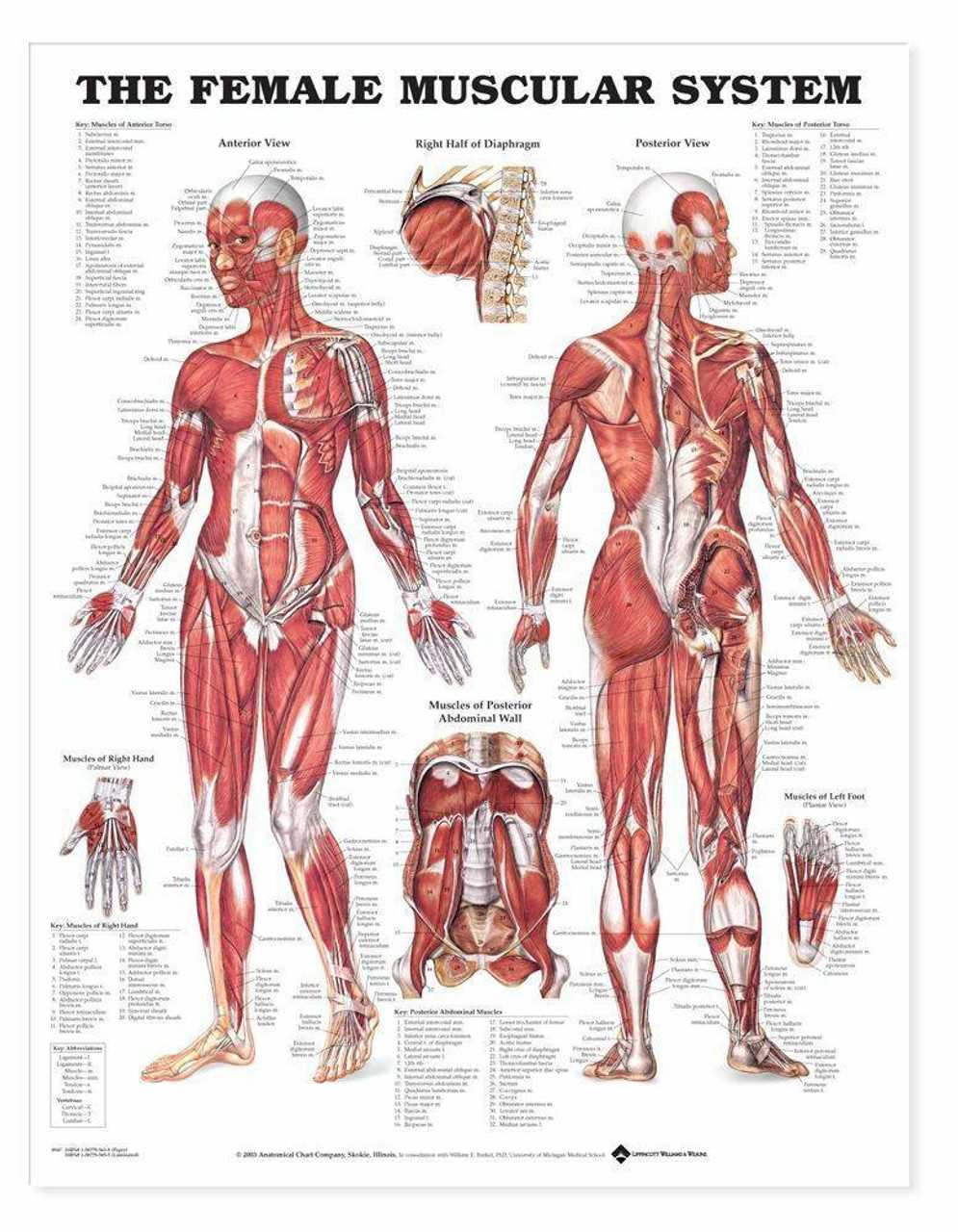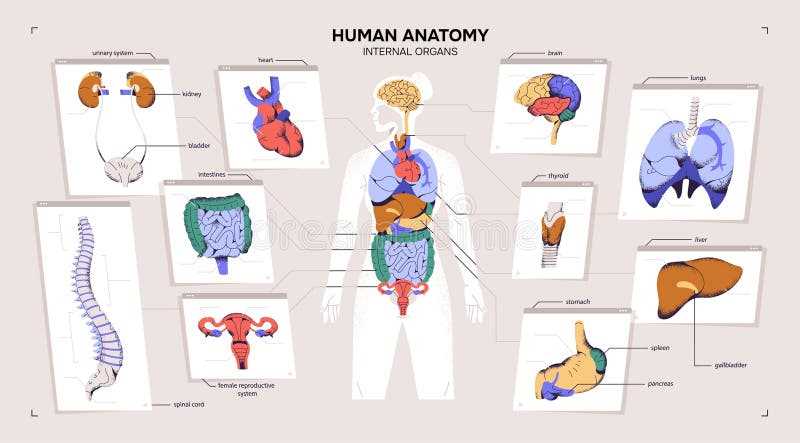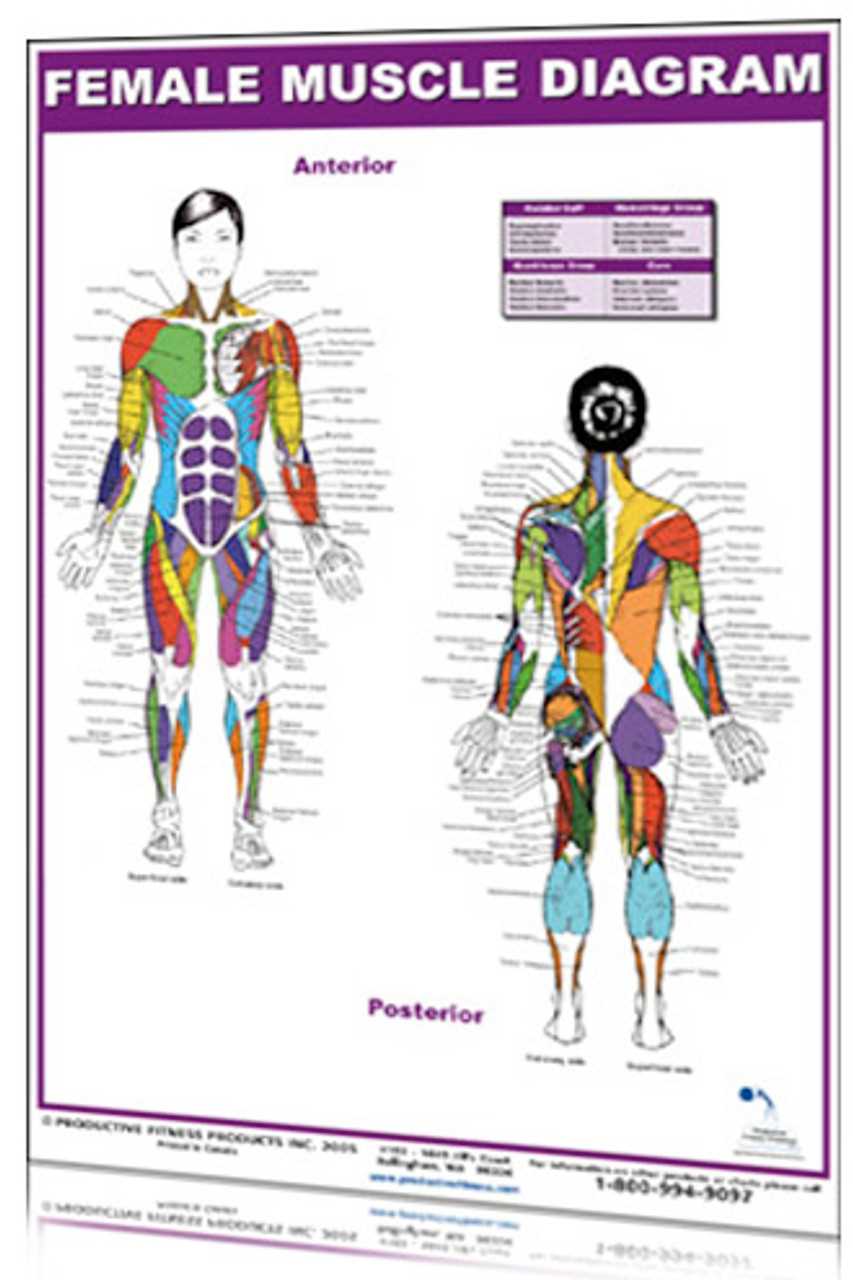
The human form is a complex and remarkable structure, made up of various systems that work together to maintain overall health and function. Understanding how these systems interact provides valuable insights into wellness, development, and medical care. Exploring the different regions and features of this structure allows for a clearer comprehension of its essential functions and the interrelated mechanisms that support life.
Delving deeper into these regions reveals a multitude of intricate components, each with a unique role. From supportive frameworks to intricate networks of organs and tissues, the architecture of this design reflects both strength and delicacy. This exploration helps to appreciate the sophistication of the physical structure and the harmony between its various elements.
By focusing on individual sections of this design, one can learn how various components contribute to key processes such as circulation, respiration, and reproduction. This understanding forms the foundation for further studies in health sciences and helps in identifying how different aspects of thi
Anatomy of the Female Body
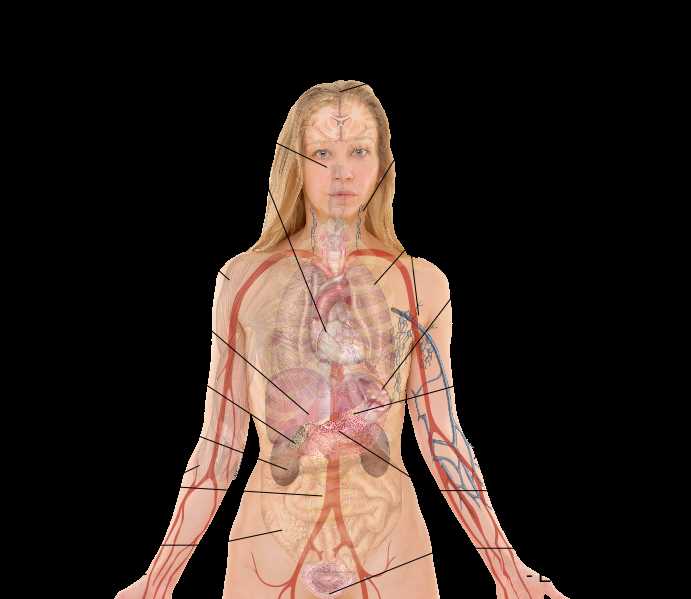
The intricate structure of the human form reflects a complex system designed to perform various functions. Each region plays a vital role in maintaining overall health, contributing to both internal and external processes essential for life. Understanding this structure provides insight into the harmonious interaction of different regions and their specific purposes.
Within this structure, there are various systems that work together to support functions such as reproduction, nourishment, and movement. These systems include vital organs, connective tissues, and muscles, all interacting in a delicate balance. By exploring each of these systems, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and efficiency of the human form.
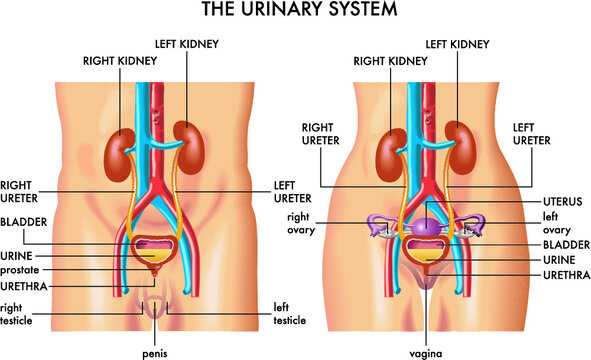
Understanding the Human Reproductive System
The reproductive system plays a critical role in the continuation of life, encompassing complex structures and functions. Its various components work together to ensure the possibility of new life, with intricate processes that are essential for the generation and development of offspring. Understanding how these components interact can provide valuable insight into the processes of conception, growth, and nurturing new life.
Main Structures and Functions
The core of the reproductive system is built around a set of essential structures, each contributing to the process in different ways. Hormonal regulation is a key factor, ensuring that each stage, from ovulation to potential fertilization, follows a precise order. The coordinated interaction between these structures allows for the preparation of necessary conditions for reproduction.
The Process of Reproduction
Reproduction involves several steps, starting with the release of cells, followed by their transportation and the possibility of union. When these cells combine, a new life can begin to develop. This process is driven by
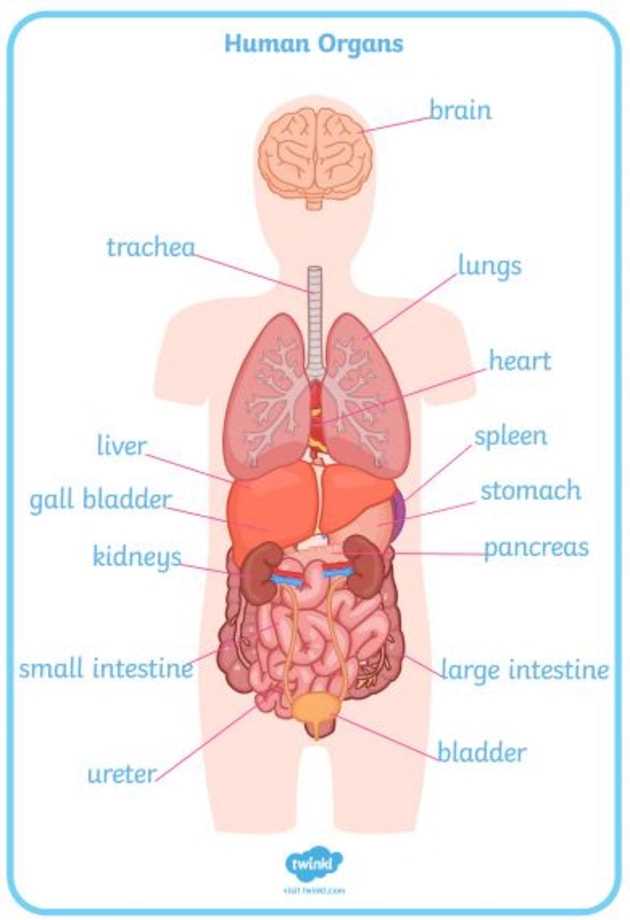
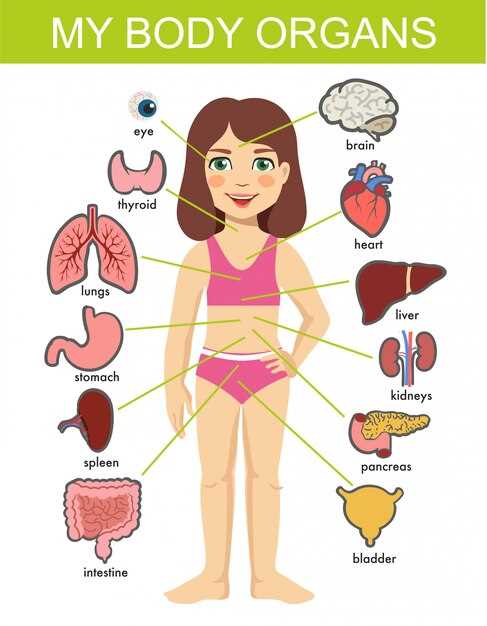
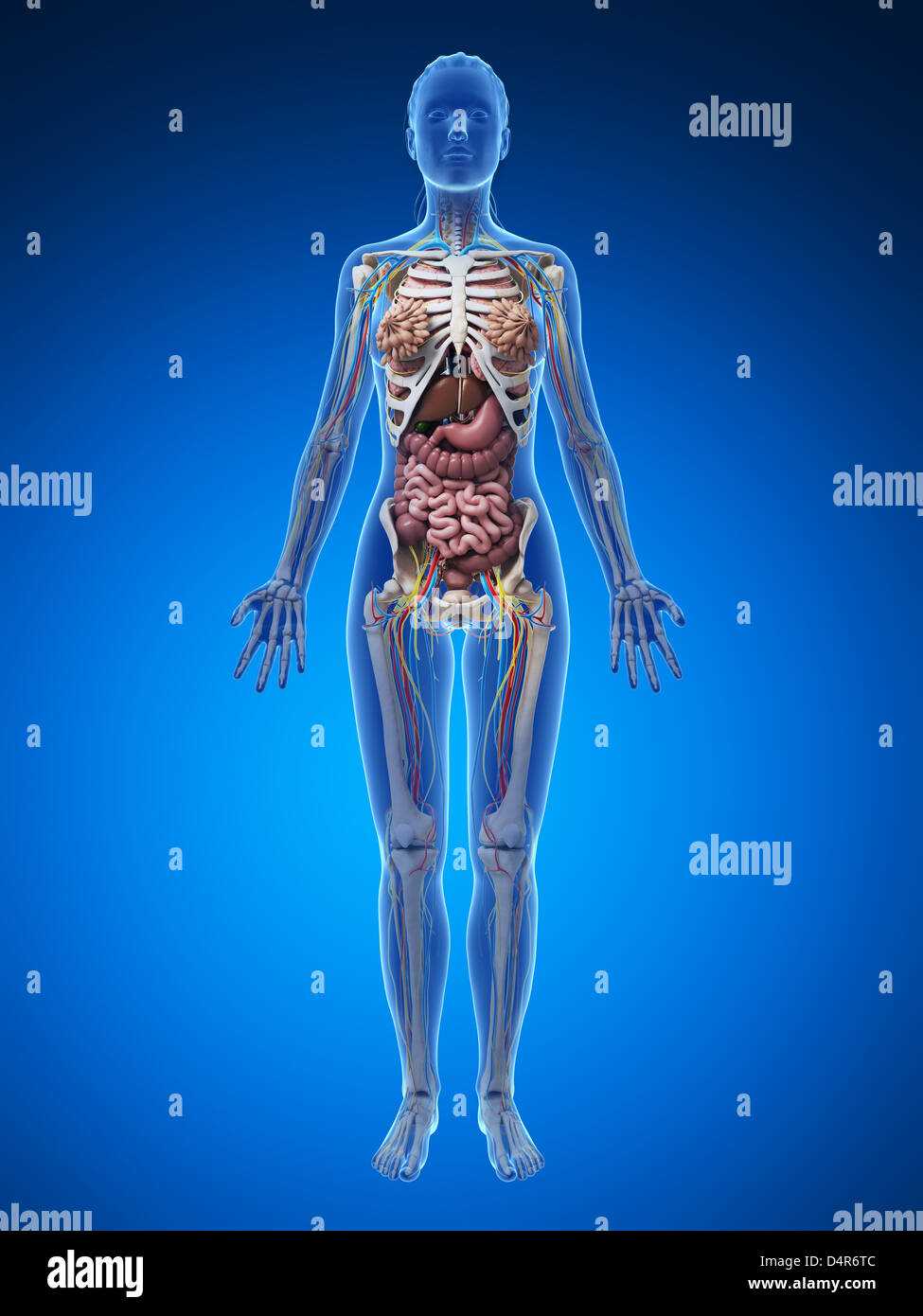
Major Organs in the Female Torso
The central section of the human anatomy contains a variety of essential structures responsible for vital functions. Each of these components plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and ensuring the seamless operation of various systems within the body.
| Organ | Function |
|---|---|
| Heart | Pumps blood throughout the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. |
| Lungs | Facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during the breathing process. |
| Stomach | Breaks down food with digestive enzymes, preparing nutrients for absorption in the intestines. |
| Liver | Processes nutrients from food, detoxifies harmful substances, and produces bile for digestion. |
| Kidneys | Filter blood
Exploring the Female Skeletal StructureThe framework of the human anatomy is supported by a complex arrangement of interconnected elements. This intricate system provides stability, flexibility, and protection to vital systems while enabling various movements. Each section within the skeletal framework is uniquely adapted to perform specific functions, maintaining a balance between strength and dexterity. Main Sections of the FrameworkThe upper region includes the cranium, responsible for protecting the control center of the body, while the lower section, comprised of the pelvis, ensures balance and support. Connecting these are the vertebral columns, which offer both flexibility and protection for the central nerve pathway. Limbs, both upper and lower, are structured for movement, precision, and strength, forming the essential components for mobility. Unique Characteristics of the FrameworkWhile the skeletal composition follows a general pattern, subtle variations can be observed in different structural elements, contributing to differences in shape and size. The adaptation of certain regions ensures an optimized structure for activities such as walking, lifting, and maintaining balance. These modifications are designed to accommodate various physiological needs, reflecting an evolutionary balance between function and form. Hormonal Glands and Their FunctionsThe endocrine system is a vital network of glands responsible for releasing chemical messengers that regulate various processes within the body. These secretions help coordinate functions such as growth, metabolism, and stress response, ensuring the body’s internal environment remains balanced. Main Endocrine Glands
Functions of Hormonal Secret
|