Lips: Flexible and precise, these are essential for grasping food and are
Essential Components of Horse’s Torso
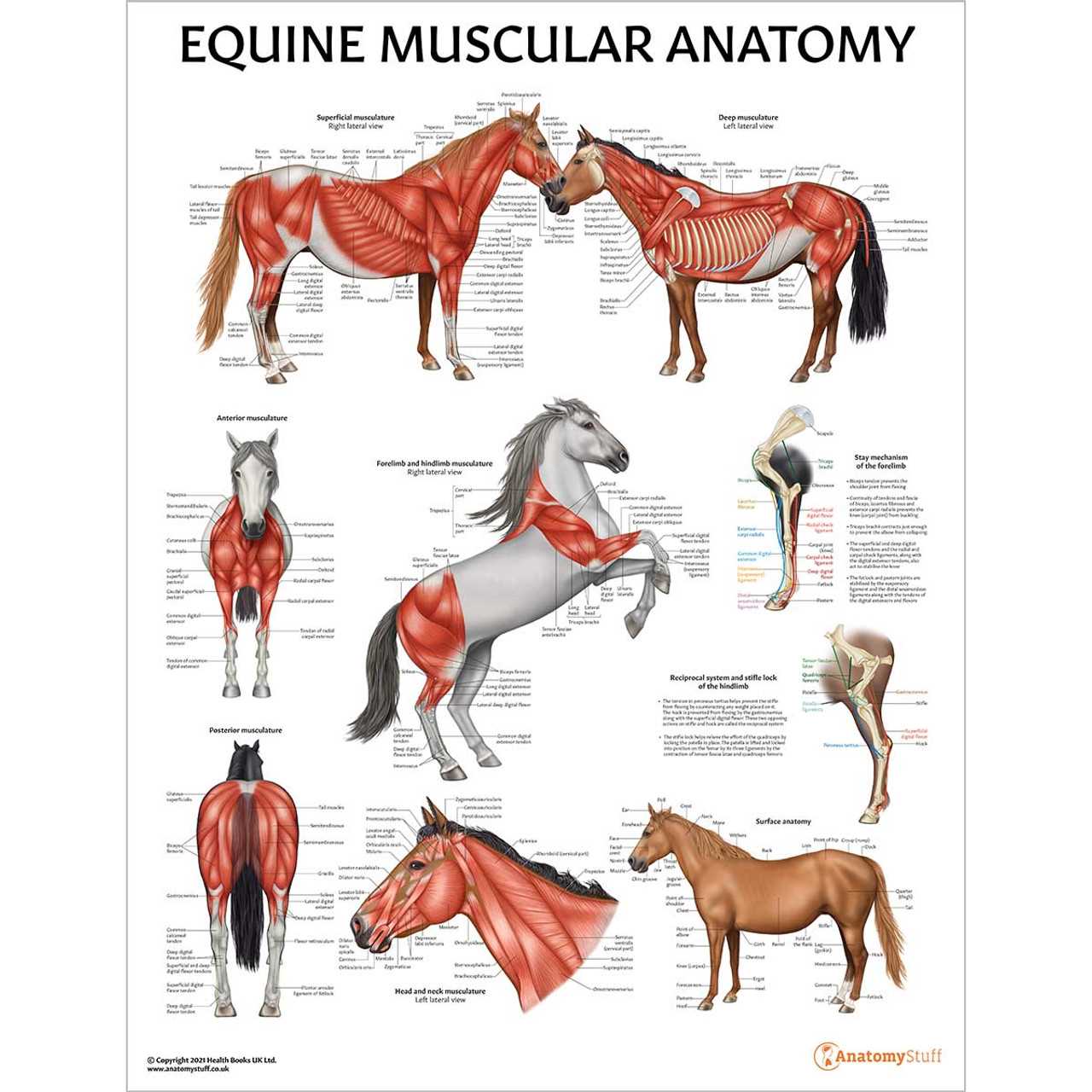
Understanding the central structure of this majestic animal helps in recognizing its movement and posture dynamics. The core of this area plays a significant role in supporting motion, providing balance, and ensuring agility. Exploring the details of this section reveals how it contributes to overall well-being and performance.
Main Structure and Support
The upper section is anchored by a strong and flexible spine, extending from the neck down to the lower back. This framework not only provides stability but also allows for a range of motion during various activities. Alongside this, the rib cage offers protection for vital organs, ensuring safety during both rest and action.
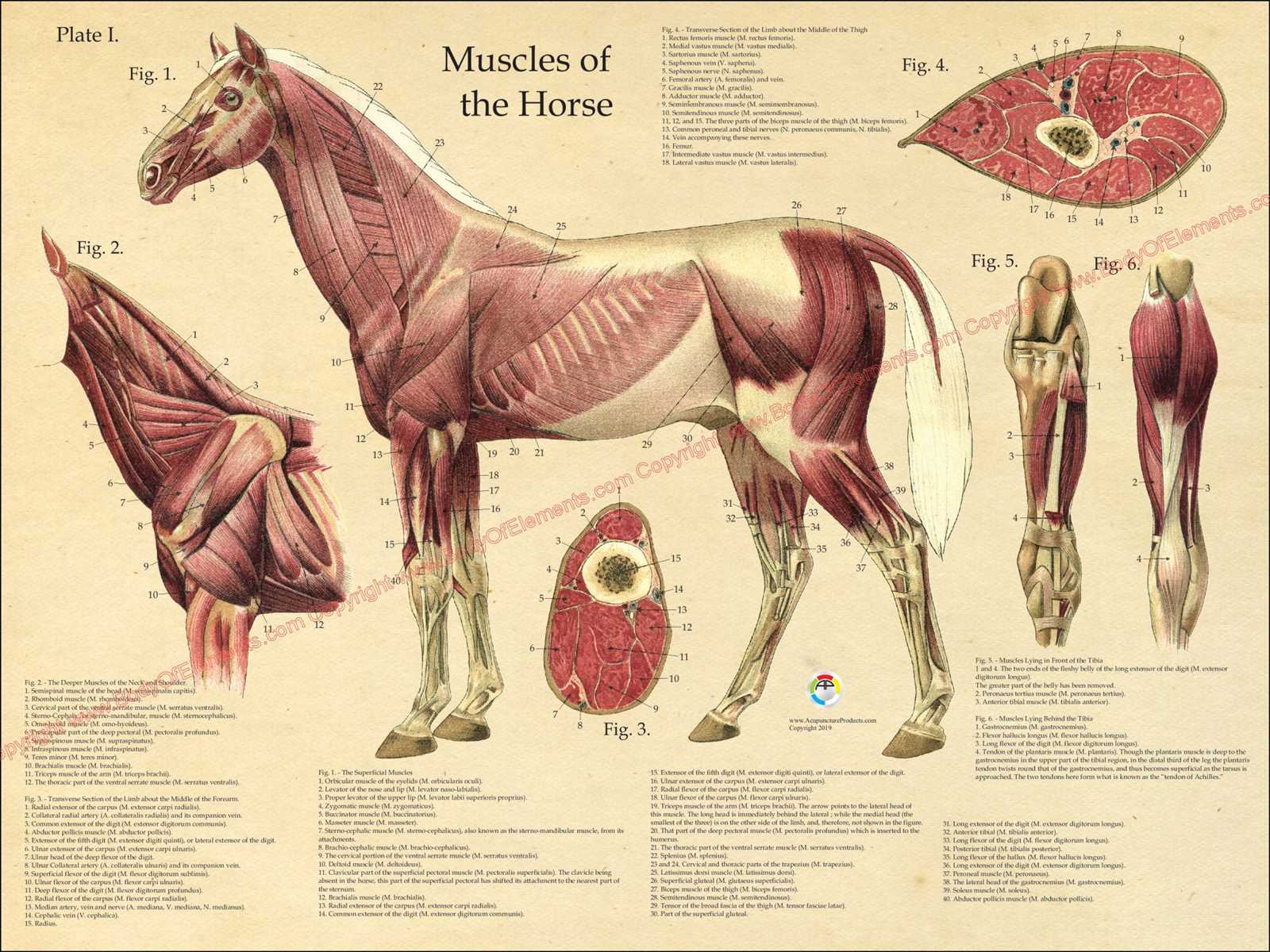
Key Musculature and Functionality
The muscular system around this area contributes significantly to strength and flexibility. Groups of muscles work together to enable fluid movement,
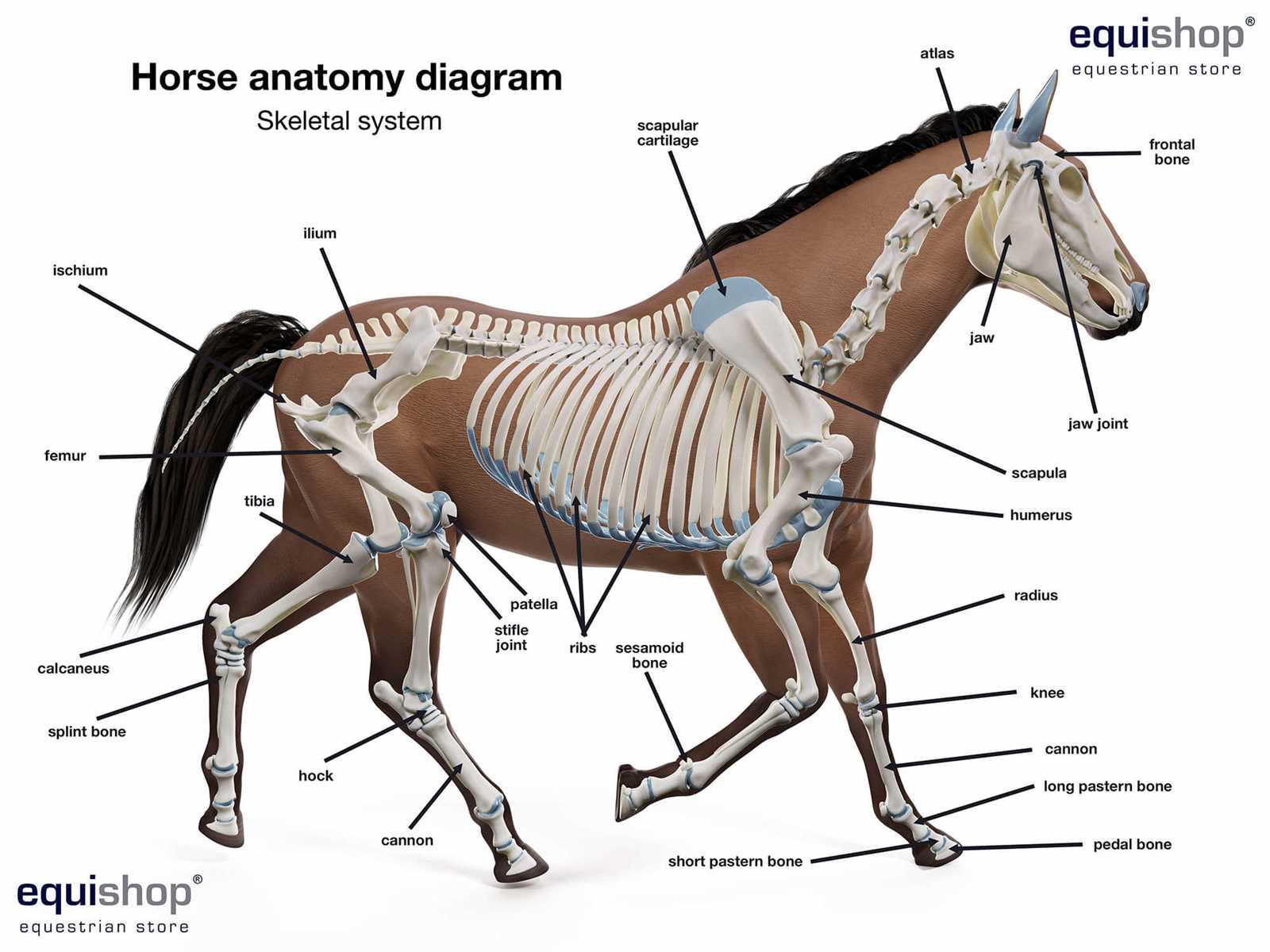
Detailed Guide to Equine Leg Anatomy
The limbs of equines are crucial for their movement, agility, and overall health. Understanding the structure and function of these extremities can enhance management practices, training methods, and injury prevention. This section delves into the intricacies of equine limb structure, exploring each segment’s roles and interrelations.
The anatomy of equine limbs can be categorized into several key components, each contributing to the overall functionality and stability of the animal. Below is a detailed overview of these components:
| Component |
Description |
| Fetlock |
Junction between the metacarpus/metatarsus and the proximal phalanx, allowing for flexion and extension. |
| Carpus |
Commonly known as the knee; consists of several small bones that provide flexibility and support during movement. |
| Radius |
Long bone located in the front limb, playing a vital role in supporting weight and facilitating motion. |
| Metacarpus/Metatarsus |
Long bones between the carpus and the fetlock, essential for shock absorption and load bearing. |
| Phalanges |
Three bones that make up each digit, critical for balance and propulsion. |
By grasping the complexities of these structures, equine caretakers can ensure optimal care, enhancing both performance and well-being.
Insights into Hoof Structure
The foundation of any equine creature is its specialized extremity, which plays a crucial role in overall functionality and health. This unique structure is engineered to absorb impact, provide traction, and support the weight of the animal. Understanding its anatomy can greatly enhance care and management practices, ensuring optimal performance and well-being.
Anatomical Overview

The hoof consists of several key components, each serving a distinct purpose in maintaining balance and facilitating movement. Key elements include the outer wall, sole, frog, and digital cushion. Each of these components works synergistically to protect internal structures while allowing for flexibility and shock absorption.
Importance of Care
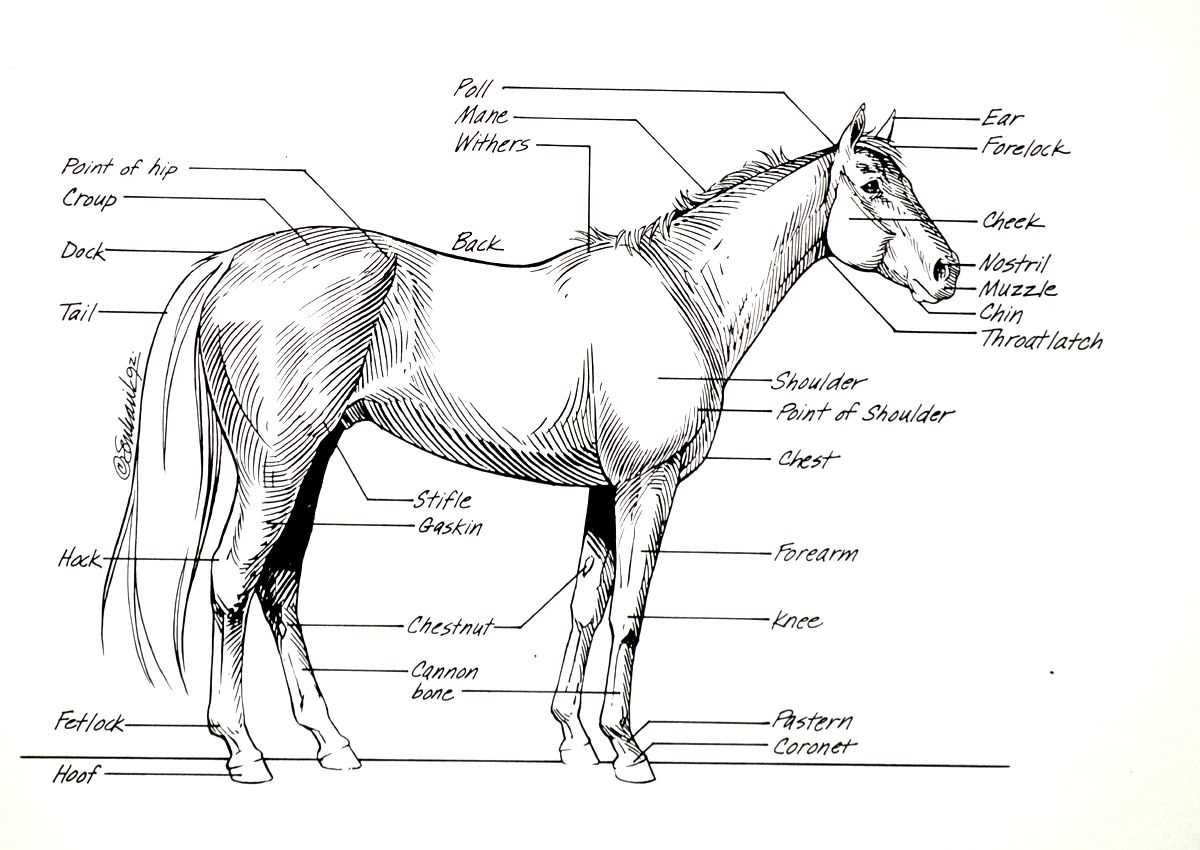
Regular maintenance is essential for preserving the integrity of the hoof. Neglecting care can lead to various conditions, such as laminitis and thrush, which can severely affect an equine’s mobility and overall health. Routine inspections and appropriate trimming are critical in preventing these issues.
| Component |
Description |
| Outer Wall |
The hard exterior that protects the inner structures and provides shape. |
| Sole |
The bottom surface that offers protection while allowing some flexibility. |
| Frog |
A wedge-shaped structure that aids in shock absorption and traction. |
| Digital Cushion |
A fibrous pad that absorbs impact and helps in blood circulation. |
Functions of a Horse’s Neck
The neck serves various essential roles that contribute to the overall well-being and performance of equines. This region not only supports head movements but also plays a vital part in communication and balance.
Key Functions
- Mobility: The neck allows for a wide range of motion, enabling the animal to reach for food, drink water, and respond to environmental stimuli.
- Balance: A well-developed neck aids in maintaining stability while moving, jumping, or engaging in other activities.
- Communication: Equines utilize their necks to express emotions and intentions through various gestures and movements.
- Support: The neck supports the head, which is crucial for coordination during physical exertion and daily tasks.
Muscle Functionality
The musculature in this area is vital for executing different gaits and activities. Strong, flexible muscles enhance performance in various disciplines, such as racing or dressage.
- Flexibility: A flexible neck contributes to agility, allowing for quick turns and transitions.
- Strength: Well-developed muscles help in controlling head movements, essential for proper navigation and safety.
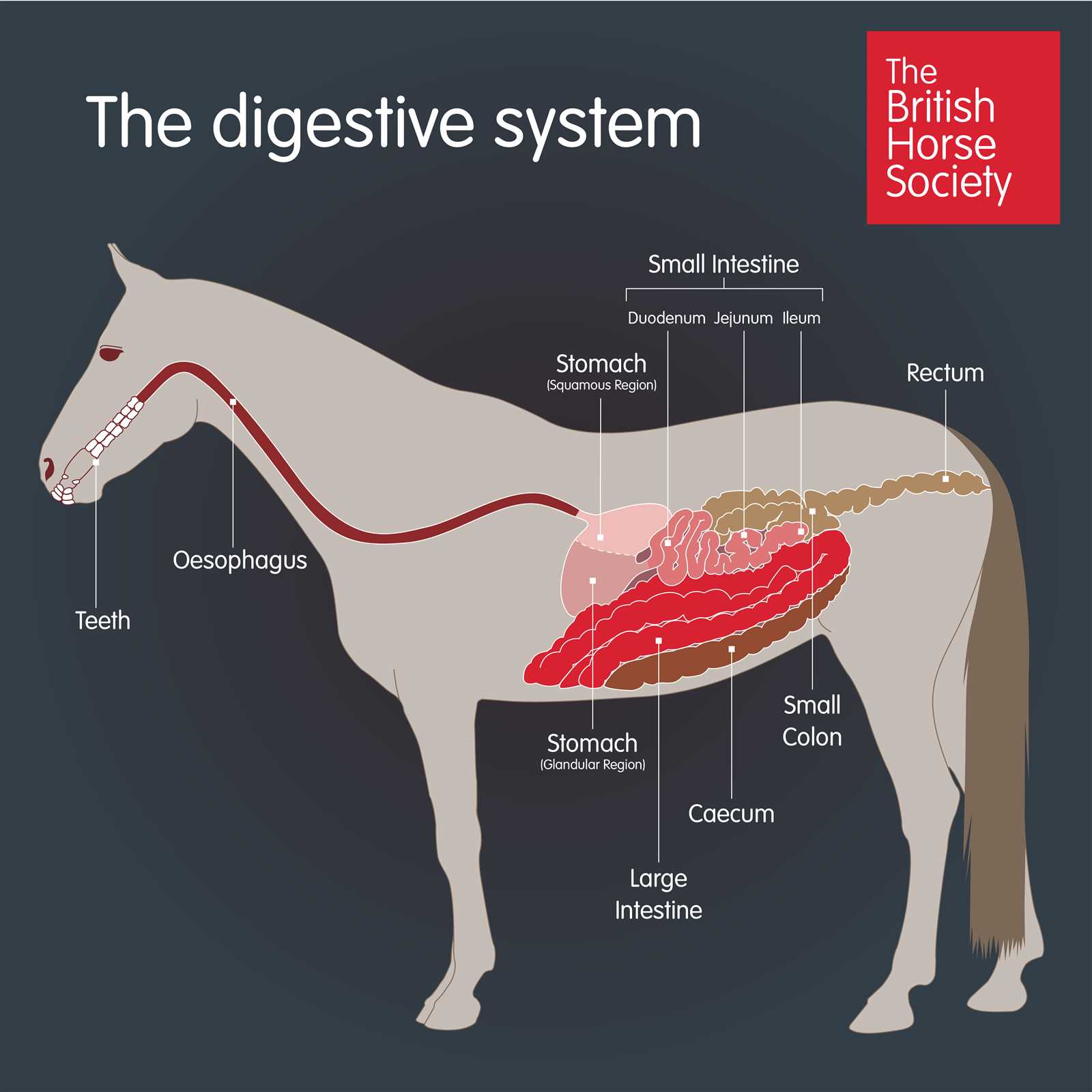
Critical Features of Equine Digestive System
The digestive system of these majestic animals is a remarkable and complex network that plays a vital role in their overall health and performance. Understanding its key components and functions is essential for ensuring optimal nutrition and well-being.
One of the most distinctive characteristics is the presence of a large cecum, which acts as a fermentation chamber. This unique feature allows for the efficient breakdown of fibrous materials, enabling the absorption of essential nutrients from plant-based diets. Additionally, the structure of the stomach is relatively small compared to the size of the animal, which necessitates frequent feeding to maintain energy levels.
Another critical aspect is the continuous flow of saliva, which aids in the digestion process by breaking down food particles and neutralizing stomach acid. This highlights the importance of providing a diet that promotes chewing and saliva production, ensuring effective digestion.
Furthermore, the equine digestive tract is designed for a grazing lifestyle, with a rapid transit time that facilitates quick digestion of grass and other forage. This adaptation underscores the need for a balanced diet rich in fiber to support gastrointestinal health.
Respiratory System Explained in Horses
The respiratory mechanism in equines plays a crucial role in their overall health and performance. It is responsible for the exchange of gases, allowing the animal to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. Understanding how this system functions can provide valuable insights into the well-being of these majestic creatures.
Anatomically, the structure involved in breathing includes various components that work harmoniously to ensure efficient airflow. The nasal passages, trachea, and lungs are interconnected, facilitating the movement of air during inhalation and exhalation. Additionally, the presence of specialized tissues aids in filtering and humidifying the incoming air, enhancing its quality before it reaches the lungs.
Importance of Equine Circulatory Network
The circulatory system plays a vital role in sustaining life by facilitating the transport of essential nutrients and oxygen throughout the organism. Its intricate network ensures that all organs and tissues receive adequate support for optimal functioning, which is crucial for maintaining health and performance.
Key Functions of the Circulatory System
- Nutrient Delivery: Efficient distribution of vital substances such as vitamins, minerals, and energy sources.
- Oxygen Transport: Essential for cellular respiration, this system ensures that oxygen is delivered to all tissues.
- Waste Removal: It aids in the elimination of metabolic byproducts, contributing to overall well-being.
- Thermoregulation: Helps maintain a stable internal temperature through blood flow adjustments.
Health Implications
A robust circulatory network is crucial for overall vitality and can significantly impact athletic performance. Compromise in this system may lead to various health issues, including:
- Reduced stamina and endurance
- Increased susceptibility to diseases
- Poor recovery from exertion
Understanding the significance of this system underscores the need for proper care, nutrition, and exercise, ensuring optimal functionality and longevity.
Role of Tail in Horse Physiology
The tail serves as a vital component in the overall function and health of equines. This unique appendage contributes significantly to various physiological processes, enhancing the creature’s adaptability and well-being in different environments.
One of the primary functions of this extension is to aid in communication. Through a range of movements, it conveys emotions and intentions to other individuals, playing a crucial role in social interactions. Additionally, the tail assists in maintaining balance and coordination during movement. By shifting its position, it helps stabilize the equine’s posture, particularly during activities such as running or jumping.
Moreover, this structure acts as a natural defense mechanism against pests and insects. The ability to swat away bothersome creatures protects the skin and overall health of the animal, allowing it to remain comfortable and focused on its surroundings. In this way, the tail is not merely an aesthetic feature but an essential element for survival and adaptation.
In summary, this appendage embodies multiple functions that are indispensable for the overall physiology of equines. Its role in communication, balance, and protection underscores its importance in the life of these magnificent creatures.