Understanding the intricate structure of the human form is essential for various fields, from medicine to fitness. By examining the key regions above the waist, we gain valuable insights into how these areas function and interact with one another. This knowledge not only enhances our grasp of physical health but also informs practices in rehabilitation and strength training.
In this exploration, we will uncover the essential components that make up the upper section of our physique. Through detailed visuals and informative descriptions, readers will be equipped to appreciate the complexity of these regions. Each element plays a vital role in movement and stability, making it crucial to understand their anatomy and functionality.
Join us as we delve into the specifics, providing an ultimate resource for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge of human structure. Whether for academic purposes or personal interest, this guide aims to illuminate the fascinating connections within our anatomy.
Understanding Upper Body Anatomy
Grasping the structure and function of the torso and its associated components is essential for various fields, including medicine, fitness, and art. A thorough comprehension of these elements facilitates better movement, enhances athletic performance, and aids in diagnosing potential issues.
Key Structures
The torso consists of several crucial components, each serving a specific function. Familiarity with these elements allows for improved engagement in physical activities and a deeper understanding of overall health.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Chest | Protects vital organs and supports respiratory function |
| Shoulders | Facilitates a wide range of arm movements |
| Back | Supports posture and enables bending and twisting |
| Arms | Allows for manipulation of objects and contributes to balance |
Importance of Awareness
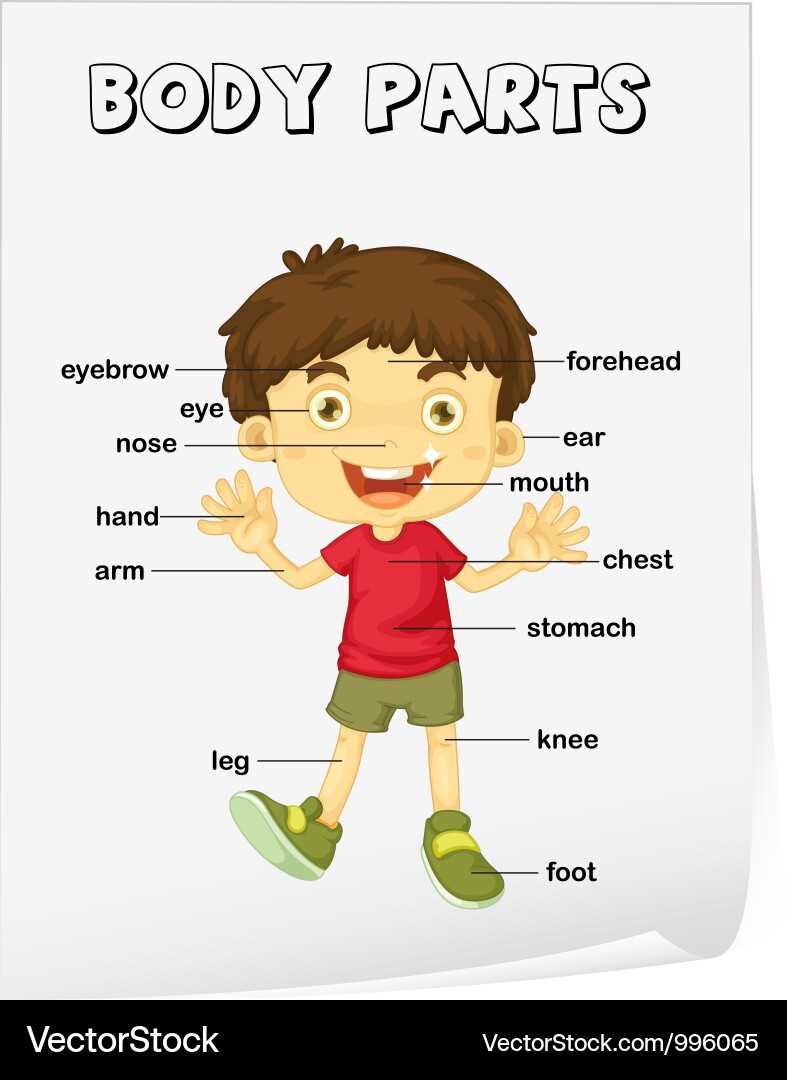
Understanding these essential structures not only promotes physical well-being but also fosters greater awareness of one’s own capabilities and limitations. This knowledge can lead to better training methods, injury prevention, and enhanced performance in various activities.
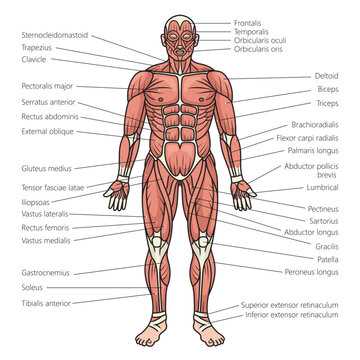
Key Muscles of the Upper Body
The anatomy of the torso and arms encompasses a range of vital muscle groups that facilitate movement and strength. Understanding these essential components is crucial for effective training and rehabilitation.
Deltoids play a pivotal role in shoulder mobility, allowing for a wide range of arm movements. Trapezius muscles support the neck and upper back, aiding in posture and head movement. The pectoralis major is integral for pushing actions, while the latissimus dorsi contributes to pulling motions, providing stability and strength.
Furthermore, the biceps brachii and triceps brachii are fundamental for flexion and extension of the elbow, respectively. Together, these muscle groups form a cohesive system essential for various physical activities.
Importance of Upper Body Strength
Developing strength in the top half of the physique is essential for overall physical performance. It influences numerous daily movements, supporting balance and enhancing endurance. Strength in this area also plays a crucial role in preventing injuries during various activities.
Key Benefits for Daily Life
A stronger upper area contributes to improved posture and flexibility. It allows individuals to perform tasks such as lifting and carrying with greater ease, reducing strain on other muscle groups. Moreover, it supports cardiovascular health and boosts energy levels, making everyday activities less tiring.
Impact on Athletic Performance

A well-conditioned top section of the torso is fundamental for athletes. It enhances speed, power, and precision in a wide range of sports, from swimming to climbing. By strengthening this area, athletes can achieve better results and reduce the risk of long-term injuries.
Upper Body Skeleton Overview
The framework of the human torso consists of several interconnected structures that form a supportive base for movement and stability. These elements work together to ensure balance, protect vital organs, and provide attachment points for muscles essential for function.
- The central column plays a pivotal role in maintaining posture and transferring weight during motion.
- Complex joints in this area allow for a wide range of motion while maintaining structural integrity.
- Protective layers encase sensitive tissues, shielding them from external impact.
The overall structure not only supports external movement but also serves as a protective shield for crucial internal systems.
Common Injuries in Upper Body
Injuries affecting the upper region can arise from various activities, whether from sports, daily tasks, or accidents. Understanding these injuries is essential for effective prevention and recovery. Common ailments in this area may result from repetitive motions, impact, or improper techniques.
Some frequently encountered injuries include:
- Shoulder Dislocation: Often caused by falls or direct hits, leading to severe pain and immobility.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons, commonly due to overuse, especially in athletes.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Occurs when the muscles or tendons surrounding the shoulder joint are damaged, causing pain and weakness.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones of the collarbone or upper arm, typically resulting from falls or accidents.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to numbness and tingling in the hand.
Recognizing the symptoms of these conditions can aid in early diagnosis and treatment, helping individuals return to their activities safely.
Exercises to Strengthen Your Upper Body
In this section, we focus on a variety of exercises aimed at enhancing the strength and endurance of your upper torso. These workouts target key muscle groups without relying on overly complex diagrams or detailed anatomical descriptions.
1. Push-ups

Push-ups are a fundamental exercise that engages your chest, shoulders, and triceps. They can be performed anywhere and are effective for building upper body strength.
2. Dumbbell Shoulder Press
Dumbbell shoulder presses help develop shoulder muscles, providing stability and strength. By adjusting the weight, you can tailor this exercise to your fitness level and goals.
Exploring these exercises will contribute to a well-rounded upper body workout routine, promoting overall fitness and functional strength.
Role of the Shoulder Girdle
The shoulder girdle plays a vital function in ensuring the movement and stability of the arm. It is responsible for connecting the arm to the rest of the skeleton, allowing for a wide range of motion while also providing the necessary support. This unique structure enables flexibility and strength, facilitating complex actions that involve lifting, pushing, or rotating.
Support and Mobility

The girdle’s structure provides both strength and freedom of motion. This balance allows the arm to perform precise movements while handling significant weight and force. Proper alignment of the girdle is essential for maintaining efficient movement and avoiding injury.
Coordination with Other Systems

The shoulder girdle works in close coordination with muscles and joints, ensuring smooth and controlled movements. It forms a key part of the body’s mechanical system, distributing forces across multiple areas to maximize efficiency and protect other regions from strain.
Anatomy of the Upper Arm
The structure of the arm above the elbow involves several important elements that work together to allow for movement and strength. This region contains muscles, bones, and connective tissues that support various motions, making it a vital part of everyday actions such as lifting, pushing, and pulling. Understanding the components located here helps in recognizing how they function harmoniously to maintain flexibility and stability.
Main Muscles
The arm’s primary muscles include strong tissues that control extension and flexion. These muscles are critical in moving the arm and forearm, allowing for a wide range of movements essential in many physical activities.
Key Components
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Bone | Provides structure and support for the muscles and joints. |
| Muscle | Enables movement by contracting and relaxing. |
| Nerves | Transmit signals from the brain to control muscle actions. |
| Function of the Chest Muscles
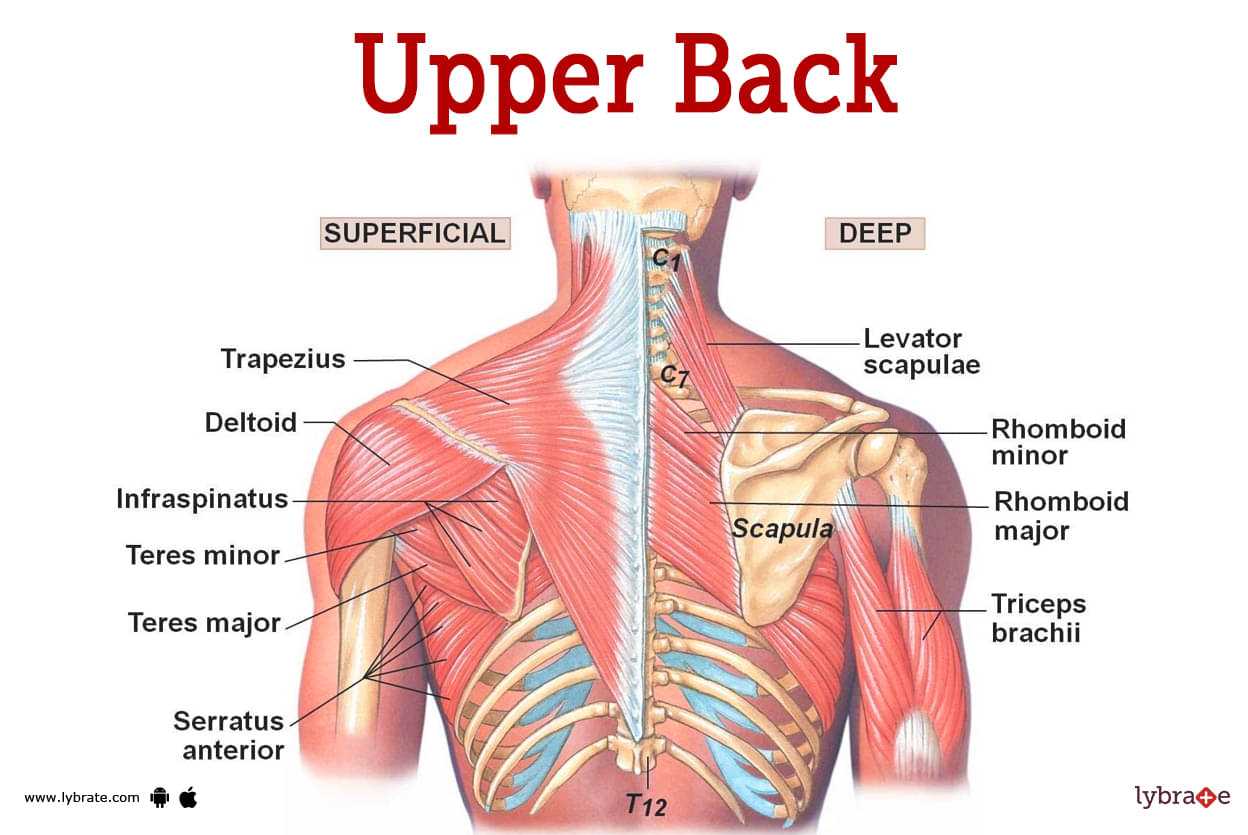
The muscles in the chest area play a pivotal role in various upper body movements and stability. They contribute significantly to actions involving the arms and shoulders, aiding in pushing, pulling, and lifting motions. These muscles are essential for maintaining posture and providing support during physical activities. Pectoralis Major: This prominent chest muscle is responsible for the primary movements of the shoulder joint, including flexion, adduction, and medial rotation of the arm. It assists in activities such as pushing heavy objects away from the body. Pectoralis Minor: Found beneath the pectoralis major, this muscle helps in stabilizing the shoulder blade (scapula) and aids in lifting the ribs during deep inhalation. It plays a crucial role in maintaining proper posture and supporting the upper body during overhead movements. Serratus Anterior: Positioned on the lateral aspect of the chest wall, this muscle contributes to the protraction of the scapula, allowing the arm to move forward and around the body. It stabilizes the scapula against the rib cage during pushing motions and overhead activities. Understanding the function of these chest muscles is essential for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and individuals engaging in physical therapy to optimize upper body strength and movement efficiency. Significance of Upper Back Health
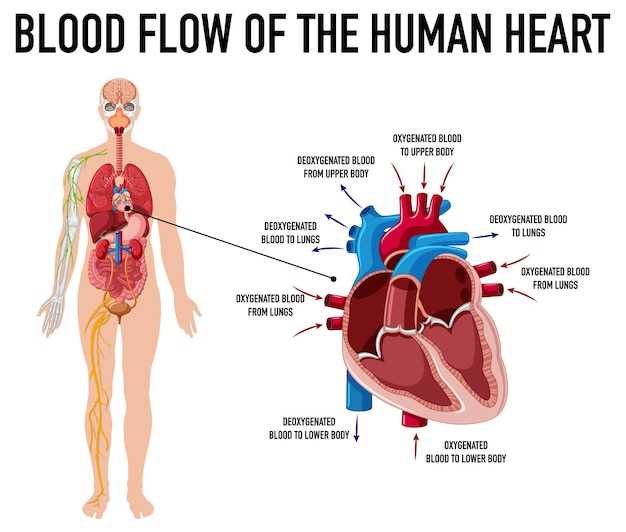
The well-being of the area around the spine plays a crucial role in maintaining overall physical comfort and mobility. It supports various daily activities, from simple tasks like sitting and standing to more strenuous movements. Ignoring the care of this region can lead to long-term discomfort, reduced range of motion, and even chronic conditions. Impact on PostureMaintaining good alignment is essential for preventing unnecessary strain. Poor posture can result in pain, especially in the shoulder and neck regions, as these areas compensate for the imbalance. Correcting this issue early can enhance comfort and reduce tension. Prevention of Chronic PainTaking preventive measures to care for the spinal region can significantly reduce the risk of developing long-lasting pain. Strengthening and flexibility exercises are key to avoiding stiffness and injury, promoting long-term wellness. Upper Body Mobility and FlexibilityMovement and suppleness in the torso and limbs play a crucial role in maintaining overall physical well-being. Enhancing range of motion in these areas helps prevent stiffness and supports daily activities, promoting better posture and ease of movement. Developing flexibility also minimizes the risk of injuries and increases efficiency in physical performance. Flexibility training for the shoulders, chest, and back is essential for ensuring that muscles and joints stay responsive and resilient. By regularly engaging in stretching and mobility exercises, individuals can improve their ability to move freely, ensuring long-term benefits for comfort and health. Practices such as dynamic stretching and controlled movements contribute significantly to boosting flexibility. These techniques target multiple muscle groups, encouraging coordinated and fluid movements, which are vital for overall functional strength and endurance. Upper Body Circulatory SystemThe circulatory mechanism within the upper half of the human anatomy plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. This network ensures the efficient transport of vital nutrients and oxygen to organs and tissues while also aiding in the removal of metabolic waste. By facilitating constant movement, it supports the proper functioning of various systems in the human frame. Main Vessels and Functions
Key components of this system include a series of vessels that distribute life-sustaining elements throughout the chest and surrounding areas. The primary artery carries oxygen-rich fluid away from the heart, while veins return deoxygenated fluid back to the heart for reoxygenation. This balanced cycle is fundamental for maintaining stability in the body’s physiological processes. Importance of Efficient Circulation
Efficient circulation is essential for sustaining energy levels, supporting immune function, and promoting overall well-being. If circulation is compromised, organs and tissues may suffer from insufficient oxygenation, leading to various health complications. Therefore, the circulatory system’s role is pivotal for maintaining vitality and ensuring the body’s resilience against external factors. Preventing Upper Body StrainMaintaining comfort in your daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of discomfort and tension in the muscles. Over time, small habits can lead to noticeable improvements in how you feel and move, helping to prevent unnecessary strain. Adopting Ergonomic PosturesTo minimize discomfort, it’s essential to focus on ergonomics. Correct posture during daily activities, such as working at a desk or lifting objects, helps reduce unnecessary pressure. Ensure that your environment is set up to support natural movements.
Regular Breaks and StretchingTaking frequent breaks from repetitive activities or prolonged sitting can prevent stiffness and improve circulation. Incorporating stretching exercises can also help alleviate tension.
|