
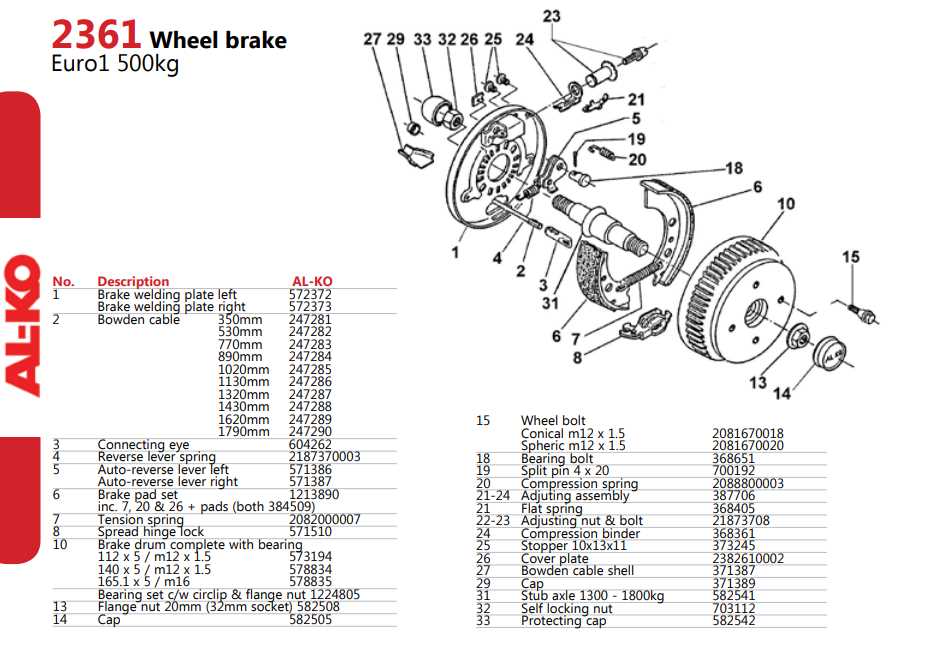
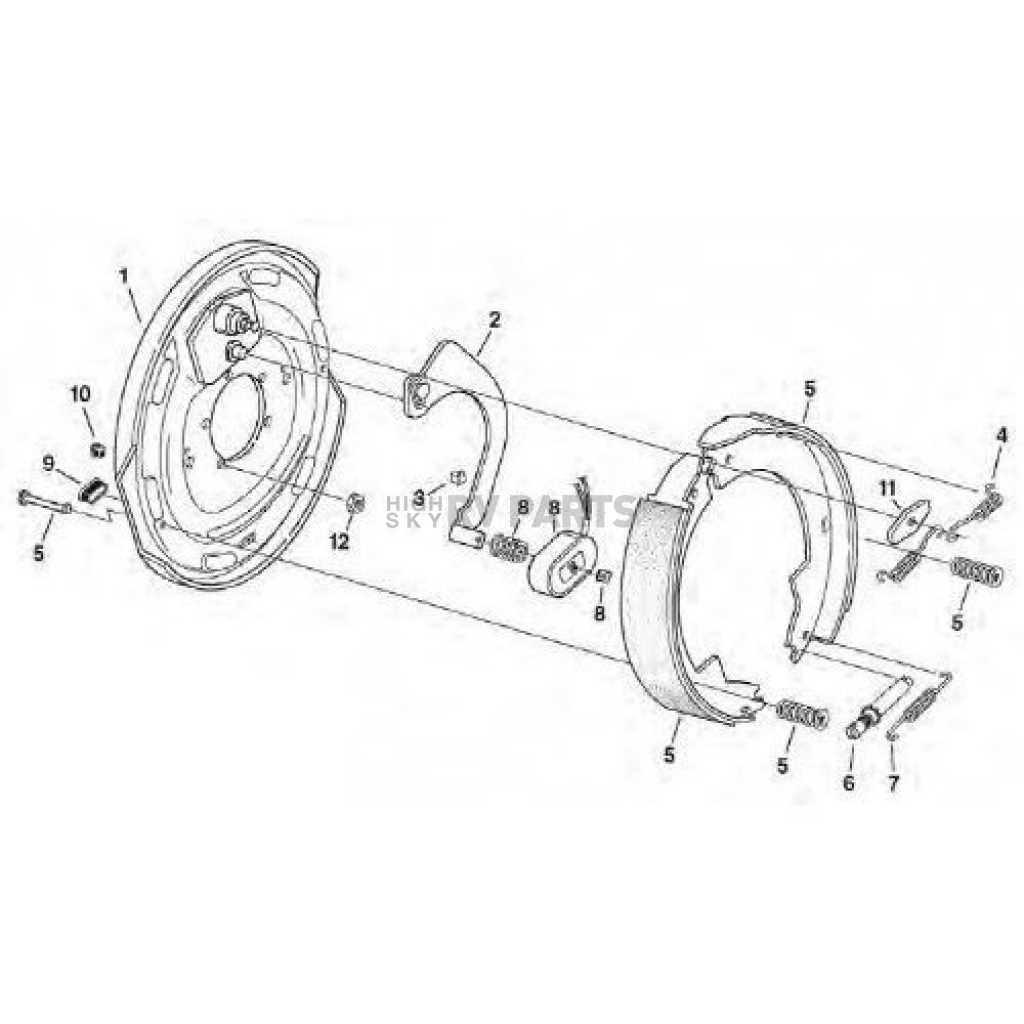
When it comes to ensuring safe transport for your vehicles and cargo, knowledge of the essential elements involved in the towing system is crucial. Proper functionality of these components significantly enhances overall performance and reliability during travel.
Every aspect, from the connection mechanism to the control systems, plays a pivotal role in managing the load. A well-structured overview of these elements helps users grasp their importance and interrelations, ultimately contributing to safer journeys.
In this section, we will delve into the intricate components involved, providing insights into their configuration and functionality. Understanding these elements not only aids in maintenance but also enhances the effectiveness of your towing experience.
Understanding Electric Trailer Brakes
The modern systems designed for controlling the stopping mechanisms of towed vehicles have become essential for safety and performance. These mechanisms utilize advanced technology to enhance responsiveness and reliability during operation, ensuring that the towed unit operates smoothly in conjunction with the towing vehicle.
At the heart of these systems lies a collection of components that work together to create an efficient stopping force. Each element plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to a seamless interaction between the vehicle and its load. Knowledge of how these components interact can aid in better maintenance and troubleshooting.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Controller | Regulates the force applied during stopping based on the vehicle’s dynamics. |
| Actuator | Converts electrical signals into mechanical movement to engage the stopping system. |
| Wiring Harness | Facilitates the electrical connections between components for proper communication. |
| Adjustment Mechanism | Allows for fine-tuning of the stopping force to match the load and towing conditions. |
| Mounting Bracket | Secures components in place, ensuring stability and optimal performance. |
Understanding these systems is essential for anyone involved in towing, as it directly impacts safety and efficiency. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components can prevent issues and enhance the overall experience of towing. Proper knowledge equips users with the ability to make informed decisions and undertake necessary repairs when required.
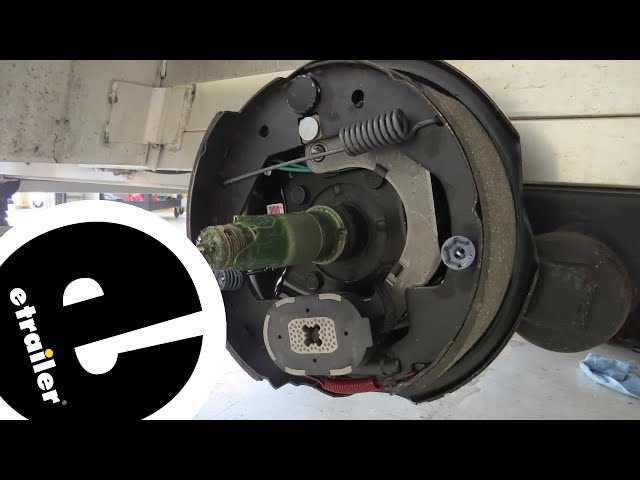
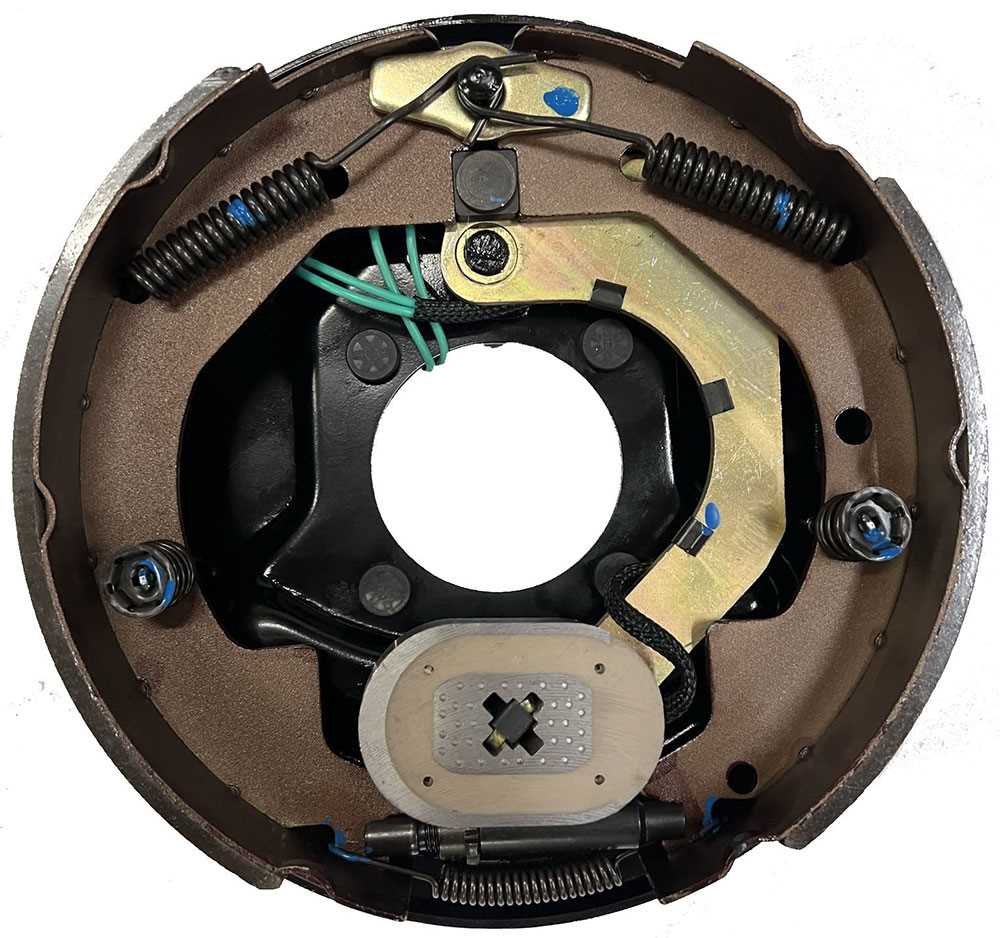
Components of Electric Brake Systems

The functionality of modern stopping systems relies on a variety of essential elements working in harmony. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency, contributing to the overall performance of the system. Understanding these elements provides insight into how they interact to deliver reliable operation.
One key element is the actuator, which converts electrical signals into mechanical force. This mechanism is vital for initiating the stopping action, responding promptly to driver inputs. Coupled with this is the controller, responsible for managing the flow of electricity and regulating the system’s performance under various conditions.
The assembly also includes various wiring harnesses and connectors, facilitating communication between components. These connections are designed to withstand environmental factors, ensuring durability and consistent operation. Additionally, various sensors monitor performance, providing feedback to optimize efficiency and responsiveness.
Furthermore, the friction elements are critical for converting kinetic energy into heat, effectively slowing down or stopping motion. These components are engineered for longevity and performance, ensuring that the system remains effective over time.
By understanding these fundamental elements, one can appreciate the complexity and reliability of modern stopping systems, which are designed to enhance safety and performance on the road.
How Electric Trailer Brakes Work

The functionality of a braking system in towed vehicles relies on a clever combination of mechanical and electrical components. When the towing vehicle slows down, the system engages to ensure that the additional weight does not compromise safety or stability during transit. This integration allows for smoother stops and better control, particularly in challenging driving conditions.
Key Components and Their Roles
At the heart of this mechanism are several essential elements that work together. The controller in the towing vehicle sends signals to the braking assemblies, activating them as needed. These assemblies, often located on the wheels of the towed unit, respond by applying pressure to the wheel components, creating friction that slows down the motion.
Benefits of This System
Utilizing a system that incorporates both electronic signals and physical force offers significant advantages. It enhances responsiveness, allowing for precise adjustments based on the load and terrain. Additionally, the design minimizes wear on the primary vehicle’s brakes, prolonging their lifespan and improving overall efficiency. With the integration of these elements, safety and performance are significantly elevated.
Key Benefits of Electric Braking
The adoption of advanced stopping mechanisms offers numerous advantages, enhancing safety and performance during towing. These systems not only improve control but also provide a seamless driving experience.
Enhanced Safety: One of the primary benefits is increased safety. These systems allow for smoother deceleration, reducing the risk of skidding or loss of control.
Improved Responsiveness: The mechanisms react more quickly to the driver’s inputs, ensuring timely stopping power. This responsiveness is crucial, especially in emergency situations.
Reduced Wear: With these systems, wear on both the vehicle and the load is minimized, leading to lower maintenance costs over time. This durability extends the lifespan of both components.
Easy Adjustability: Many systems offer customizable settings, allowing users to tailor the performance to their specific needs. This flexibility enhances usability across various conditions.
Environmentally Friendly: By optimizing energy use, these systems contribute to lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint, making them a more sustainable choice for modern transport.
Common Issues with Electric Brakes
Understanding frequent challenges associated with automated stopping systems can enhance safety and performance. These complications may arise from various components or user errors, necessitating careful attention and maintenance.
Wiring and Connection Problems
Faulty wiring or loose connections often lead to inconsistent functionality. Regular inspection can help identify any wear or corrosion that may disrupt power supply, ensuring reliable operation.
Controller Malfunctions
Inaccurate settings or damaged controllers can result in inadequate response when slowing down. Adjusting the sensitivity and verifying the calibration are crucial steps to prevent potential hazards on the road.
Identifying Brake Wiring Diagrams

Understanding the intricacies of wiring schematics is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance of braking systems. These visual representations provide clarity on how different components interact, allowing users to pinpoint issues with ease. Recognizing the various elements within these illustrations can enhance one’s ability to make informed repairs.
Color coding is often employed in these representations to differentiate between various wires and their functions. Familiarizing yourself with these color schemes is crucial, as it simplifies the process of tracing connections and identifying the source of potential problems.
Additionally, labels and symbols within the schematics serve as guides, indicating the role of each wire in the overall system. Paying close attention to these details can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that repairs are executed correctly, ultimately enhancing safety and functionality.
Tools for Electric Brake Maintenance

Maintaining the functionality of your towing equipment requires specific tools designed to ensure safety and performance. Proper upkeep not only prolongs the lifespan of components but also enhances overall reliability. This section explores essential implements needed for effective maintenance.
Essential Implements
Key tools include a multimeter for electrical diagnostics, wrenches for adjustments, and specialized pliers for securing connections. Lubricants play a crucial role in reducing friction and wear, while cleaning solutions help remove debris that can impede performance.
Safety Gear
Always prioritize safety with appropriate gear such as gloves and goggles. Using a sturdy jack stands can also prevent accidents while working underneath the vehicle. Keeping these tools and safety measures at hand will ensure a smoother maintenance process.
Choosing the Right Brake Controller
When it comes to ensuring optimal performance and safety during towing, selecting an appropriate controller is crucial. This device plays a vital role in managing the deceleration of the vehicle and the attached load, enhancing stability and control. Understanding the various options available will help in making an informed decision tailored to specific requirements.
There are several types of controllers on the market, each designed to cater to different towing scenarios. Time-based controllers operate on a preset delay, allowing the user to set how quickly the brakes engage. In contrast, proportional controllers automatically adjust the braking force based on the vehicle’s deceleration, offering a more responsive experience. Evaluating the towing capacity, load characteristics, and frequency of use will aid in determining the best fit.
Additionally, compatibility with the towing vehicle is essential. Some controllers require specific wiring or connections, while others offer plug-and-play convenience. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to ensure seamless integration. Ultimately, selecting the right controller not only enhances safety but also improves the overall towing experience.
Safety Features in Electric Brakes
The incorporation of various safety mechanisms is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in braking systems. These features work together to enhance the overall effectiveness and minimize potential hazards during operation.
Automatic Adjustment Mechanism: This feature allows the system to maintain consistent performance by self-adjusting to wear and tear over time. Such adaptability ensures that the stopping power remains effective, regardless of the condition of the components.
Proportional Response: A vital aspect of modern systems, this capability enables the braking force to be proportional to the pressure applied. This ensures smoother and more controlled deceleration, reducing the risk of skidding or loss of control.
Thermal Protection: The inclusion of thermal safeguards helps prevent overheating, which can lead to system failure. These protective measures ensure that the components operate within safe temperature limits, extending their lifespan and maintaining performance integrity.
Fail-Safe Mechanisms: In the event of a malfunction, these mechanisms activate to provide an additional layer of security. This feature allows the system to engage a backup stopping function, ensuring that the vehicle can be brought to a halt safely.
Incorporating these safety features not only enhances the reliability of braking systems but also instills confidence in users regarding the efficiency and security of their operations.
Installing Electric Trailer Brakes
Proper installation of braking systems is crucial for enhancing safety and control while transporting heavy loads. This section outlines essential steps and considerations for successfully equipping your vehicle with a reliable braking mechanism.
Preparation Steps
Before beginning the installation, ensure you have all the necessary tools and components at hand. Follow these preparatory steps:
- Gather tools such as wrenches, pliers, and a drill.
- Obtain all required components, including wiring, controllers, and mounting brackets.
- Review the vehicle’s manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
Installation Process
Follow these steps for a successful setup:
- Lift the vehicle and securely support it with jack stands.
- Remove the existing assembly if applicable, ensuring all electrical connections are detached.
- Attach the new components according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring proper alignment.
- Connect the wiring harness, following the color-coding system for accuracy.
- Test the system before lowering the vehicle to ensure all connections are secure and functional.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively enhance your vehicle’s stopping capabilities, ensuring safer journeys ahead.
Upgrading from Hydraulic to Electric
Transitioning from a fluid-based system to an electrically controlled mechanism can significantly enhance performance and reliability. This shift not only modernizes the setup but also introduces a range of advantages that contribute to improved functionality.
Key benefits of this upgrade include:
- Increased responsiveness: An electrically controlled system provides quicker reaction times, ensuring timely performance.
- Enhanced control: The ability to adjust settings easily allows for a more tailored experience.
- Reduced maintenance: Fewer components that can wear out lead to lower upkeep costs and less frequent repairs.
- Improved safety: Advanced features often include integrated safety mechanisms, providing greater peace of mind.
When considering this change, it is essential to assess compatibility with the existing framework. This may involve:
- Evaluating the power supply requirements to ensure adequate energy availability.
- Reviewing the compatibility of existing hardware with the new system.
- Consulting professionals for installation to ensure optimal performance and adherence to regulations.
Overall, upgrading to a more advanced mechanism not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to a more modern and dependable setup.
Best Practices for Brake Testing
Ensuring optimal functionality of the stopping mechanisms is crucial for safety and reliability. Regular assessment can prevent potential failures and enhance performance. Implementing the following practices will help achieve thorough evaluation and maintenance of these essential components.
- Conduct Routine Inspections: Regularly examine the system for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. Early detection of issues can prevent more serious problems.
- Test Under Realistic Conditions: Perform evaluations in conditions that closely mimic actual usage. This includes varying speeds, loads, and terrains.
- Check for Fluid Leaks: Inspect all connections and lines for any signs of leakage. Fluid integrity is vital for consistent operation.
- Monitor Response Times: Measure the time it takes for the system to engage and disengage. Quick response is essential for effective stopping power.
- Assess Wear Patterns: Pay attention to the wear patterns on components. Uneven wear may indicate alignment issues or improper installation.
Incorporating these best practices into a regular maintenance routine will help ensure the effective operation of the stopping systems. Consistent testing not only enhances performance but also contributes to overall safety on the road.
Regulatory Standards for Trailer Brakes
The safety and efficiency of vehicular systems that connect to heavy loads are paramount. To ensure optimal performance, various regulations and standards are established. These guidelines govern the functionality and design of braking mechanisms in transport solutions, ensuring they meet specific safety requirements. Compliance with these regulations is critical for preventing accidents and promoting safe transportation practices.
Importance of Compliance

Adhering to regulatory frameworks is essential for manufacturers and users alike. Compliance guarantees that systems are constructed to withstand the stresses of operation while providing reliable stopping power. Additionally, meeting these standards can lead to reduced liability and improved marketability for manufacturers.
Key Standards Overview
| Standard Name | Description | Applicable Region |
|---|---|---|
| FMVSS 105 | Regulates hydraulic brake systems for safety and performance. | United States |
| SAE J2944 | Specifies performance requirements for electric brake systems. | International |
| ISO 1726 | Covers the design and performance of braking mechanisms in transport vehicles. | International |