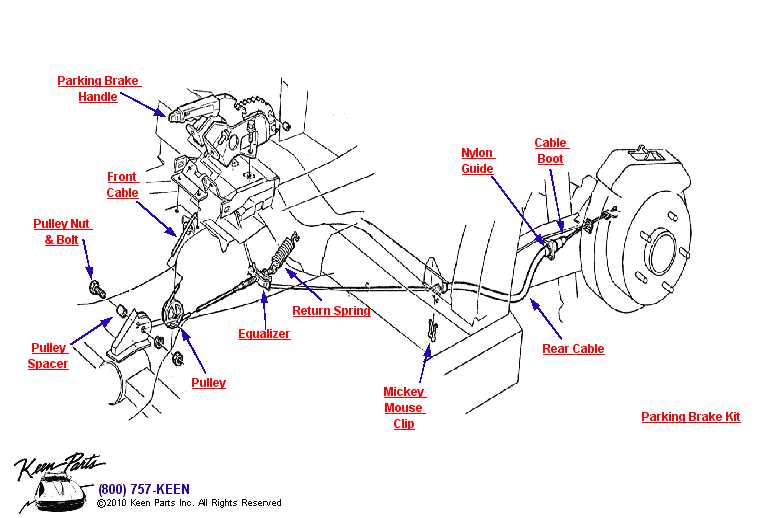
When it comes to ensuring the safety and stability of a vehicle during stationary periods, certain components play a critical role in securing the system. These elements work together to provide drivers with confidence that their vehicle will remain in place on an incline or flat surface. A well-maintained and properly functioning system is essential for overall vehicle performance and reliability.
Within this complex mechanism, a range of interconnected elements must operate smoothly. Each piece has a specific role in enhancing security and control, ensuring the vehicle remains immobilized when needed. Recognizing the key components and their interactions can help in both the maintenance and repair of this system.
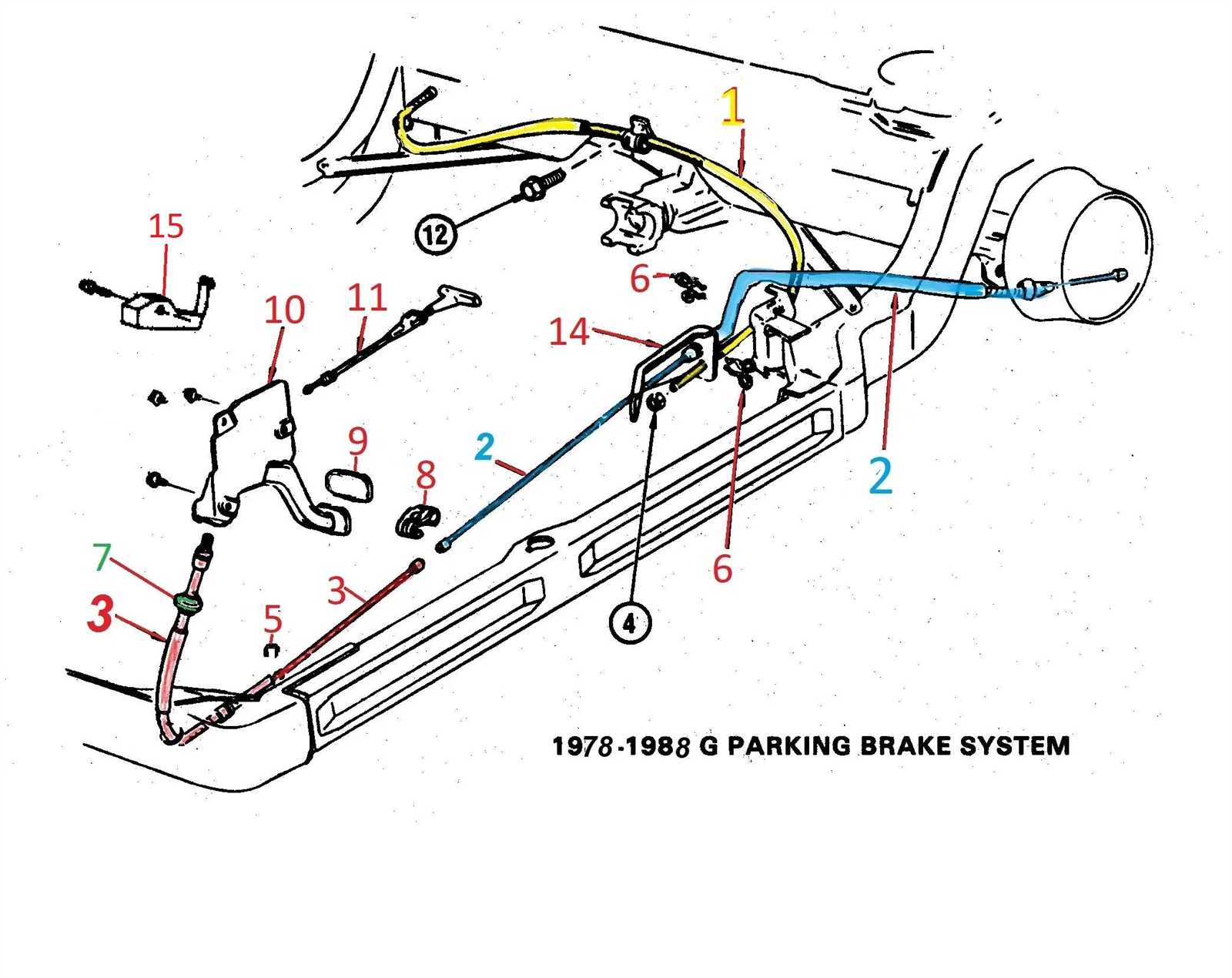
Parking Brake Components Overview
When it comes to maintaining vehicle stability during stationary periods, a specialized system of mechanical and hydraulic elements ensures effective performance. These components work together to prevent unintended movement by securely locking the vehicle in place.
Key Mechanical Elements
- Levers and Cables – A network of levers and steel wires that transmit force from the driver’s action to engage the system.
- Retaining Springs – Designed to keep tension and ensure the locking mechanism remains activated until released.
- Linkage Assembly – Connects various elements to enable smooth operation of the entire setup.
Hydraulic and Electrical Support
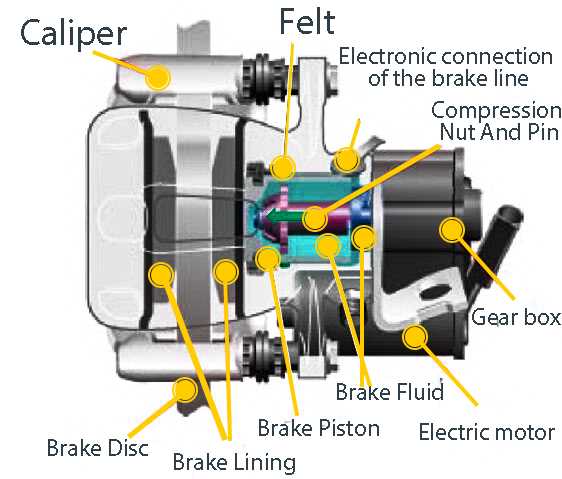
- Actuators – Components that apply force to engage the locking mechanism, often using hydraulic or electrical assistance.
- Sensors – Provide feedback to the control system, ensuring correct positioning and engagement of the locking system.
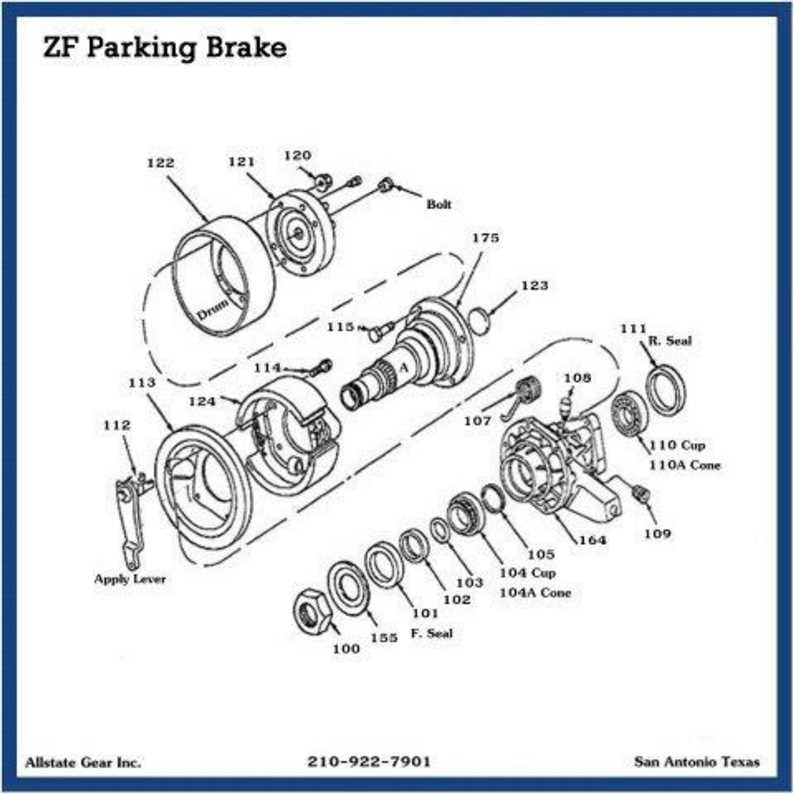
Key Elements of Brake Mechanism
Mechanical systems that control the halting of a vehicle are complex and involve several critical components. Each part plays a unique role in ensuring that motion is effectively restrained, and safety is maintained during operations.
Core Components of the System
The main structure includes devices that convert applied pressure into force, which then acts on the vehicle’s wheels. These elements work in unison to slow down or hold the vehicle in place when necessary. Key devices include those that facilitate pressure modulation and force distribution.
Supporting Features and Functions

Additional features complement the core system, providing balance, adjustment, and efficiency. These include components that regulate the interaction between various parts, ensuring smooth performance and long-term durability. Proper maintenance of these elements is crucial for optimal function.
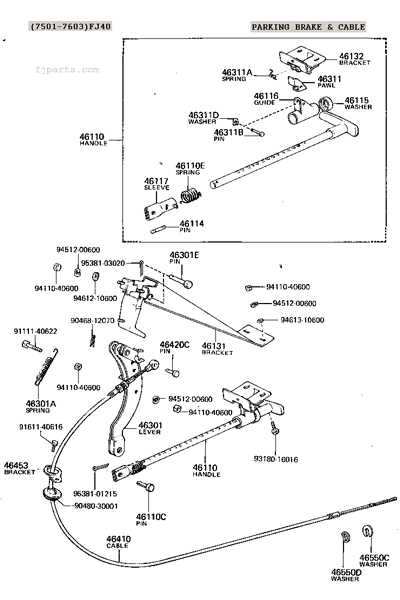
Understanding Cable and Lever Assembly
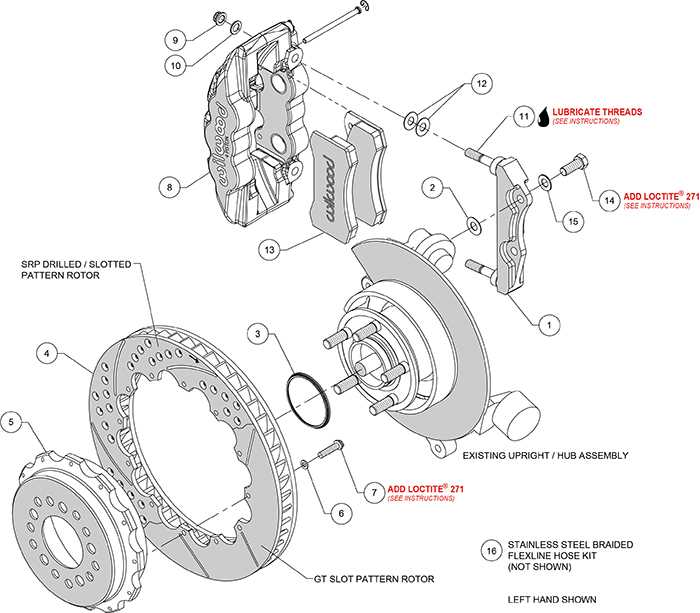
The cable and lever mechanism is a critical component of many vehicle systems, enabling precise control and operation of specific functions. This assembly works by transmitting motion between two points, allowing for manual or automatic adjustments.
The system consists of interconnected elements that ensure smooth performance and durability. Key factors in its design include flexibility, strength, and the ability to withstand constant use.
- Cable: A flexible line designed to transfer motion or force from one point to another.
- Lever: A pivotal arm that helps amplify force, making it easier to perform the desired action.
- Adjustments: Ensuring proper tension and alignment in the assembly to maintain efficiency.
- Inspect the cable regularly for wear or damage.
- Ensure the lever moves smoothly without resistance.
- Make
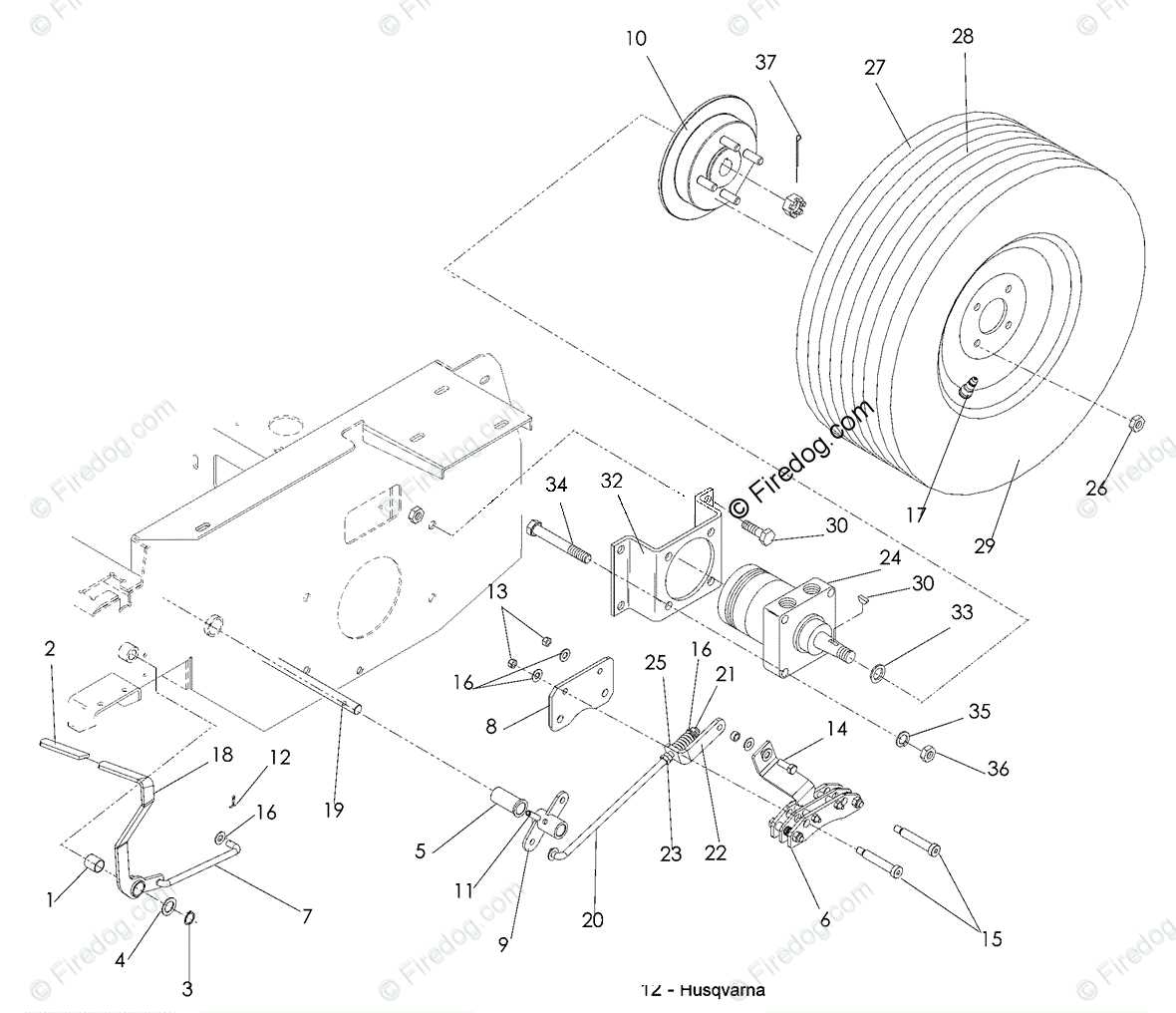
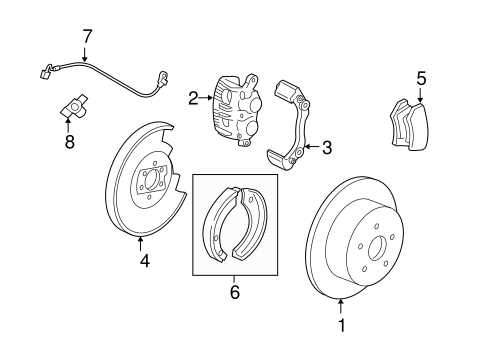
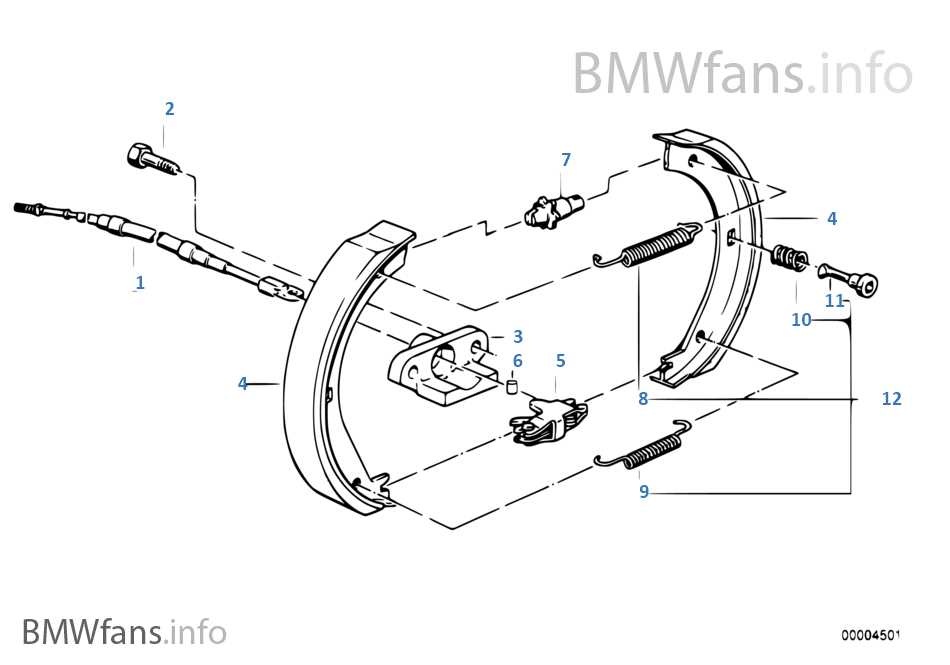
Exploring Rear Brake Shoe Setup

The assembly of rear friction components is crucial for ensuring smooth and effective deceleration in a vehicle. Understanding how the various elements are positioned and how they interact with each other helps maintain optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Main Components of the Setup
The key elements in this assembly include a set of friction linings and mechanisms designed to engage with rotating parts. These components must be installed in precise locations to allow the right amount of contact and resistance during operation.
Typical Arrangement Overview
Component Function Friction Lining Provides surface area for deceleration force. Return Spring Pulls the components back after release. Guide to Adjusting Brake Tension
Ensuring the correct tension in your vehicle’s stopping system is essential for optimal performance and safety. Properly adjusted mechanisms contribute to smooth operation and prevent premature wear. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to fine-tuning these components for reliable control.
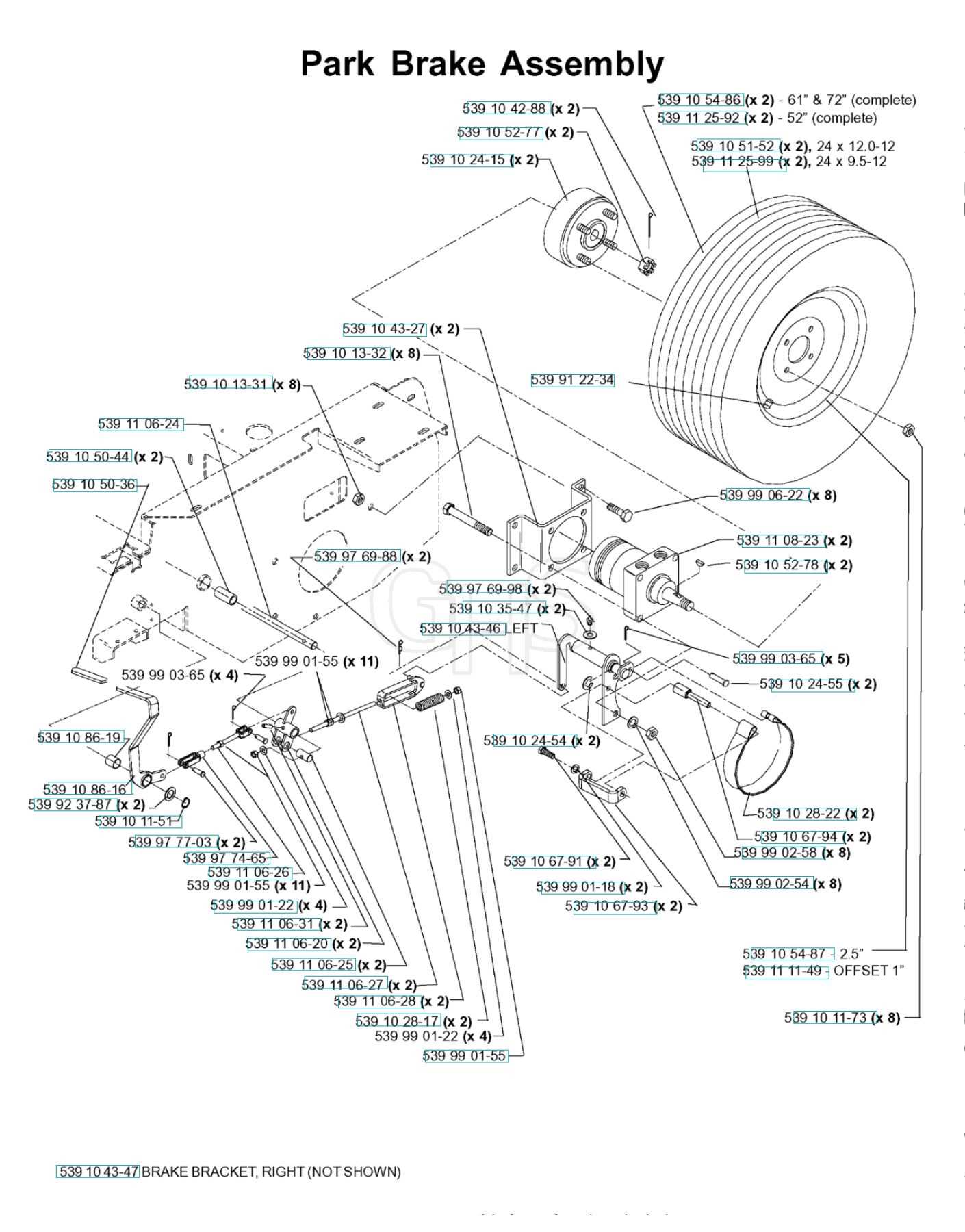
Steps to Achieve Proper Tension
Start by locating the adjustment mechanism, which can typically be found near the control lever or under the vehicle. Tighten or loosen the necessary components using the designated tool to achieve the right level of tension. Avoid overtightening, as it can cause excessive strain on the system.
Monitoring and Fine-Tuning
Once the tension has been set, test the system by gradually applying force and ensuring smooth and responsive feedback. If needed, make further adjustments to guarantee consistent operation under different conditions.
Adjustment Point Hydraulic vs Mechanical Brake Systems
Understanding the differences between two primary types of stopping mechanisms is essential for optimal performance and safety. Each system operates on distinct principles, utilizing various components to achieve effective vehicle control. While both have their advantages, they also present unique challenges that users should consider.
The following points outline the key characteristics of hydraulic and mechanical systems:
- Hydraulic Systems:
- Utilize fluid pressure to activate the stopping mechanism.
- Provide smoother and more responsive operation.
- Require regular maintenance to prevent leaks.
- Often found in modern vehicles due to efficiency.
- Mechanical Systems:
- Depend on physical components, such as cables and levers, for operation.
- Generally simpler in design and easier to repair.
- May exhibit less sensitivity compared to hydraulic alternatives.
- Commonly used in older models and certain specialized applications.
In conclusion, choosing between these systems involves evaluating individual needs, vehicle types, and performance expectations. Each offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for different driving conditions and user preferences.
Inspecting the Drum and Rotor Interface
Regular examination of the components that facilitate the interaction between the drum and rotor is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in the vehicle’s stopping mechanism. This interface plays a significant role in the overall functionality, and any wear or damage can lead to compromised effectiveness.
Begin the assessment by removing the wheel to gain access to the assembly. Look for signs of excessive wear, rust, or contamination that could hinder proper function. Ensure that the surfaces are clean and free from debris, as this can affect the connection between the two elements. It’s also important to check for any irregularities in shape or alignment, which might indicate underlying issues that need to be addressed.
How Brake Actuation Works
The mechanism that engages and disengages the stopping system in vehicles is essential for ensuring safety and control. This process relies on a series of components that work in harmony to translate the driver’s input into effective motion reduction. Understanding how this system operates can enhance knowledge of vehicle performance and maintenance.
Key Components of Actuation
Several crucial elements come together to facilitate the actuation process:
- Actuator: Converts mechanical force into hydraulic pressure.
- Fluid Reservoir: Stores the hydraulic fluid necessary for operation.
- Hoses: Transmit hydraulic fluid to various parts of the system.
- Calipers: Press pads against the rotating elements to create friction.
Process Overview
The sequence of actions involved in actuation includes:
- The driver applies force to the control mechanism.
- This force moves the actuator, generating hydraulic pressure.
- Hydraulic fluid travels through hoses to the calipers.
- Calipers engage the friction elements, slowing the vehicle.
Understanding these steps is vital for diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal performance of the stopping mechanism in vehicles.
Common Issues with Parking Brakes
Understanding the frequent problems associated with vehicle hold mechanisms is essential for maintaining safety and functionality. Drivers may encounter a range of issues that can hinder the effectiveness of these systems, leading to potential hazards on the road.
Inconsistent Engagement
Intermittent activation can be a common frustration, where the hold mechanism fails to engage or release properly. This inconsistency can stem from various factors, including worn components or insufficient adjustment. Regular inspection can help identify these issues early, preventing further complications.
Strange Noises During Operation
Unusual sounds, such as grinding or squeaking, often indicate that there is a problem within the hold system. These noises can be caused by debris accumulation or damaged components, requiring prompt attention to avoid more significant damage and ensure smooth operation.
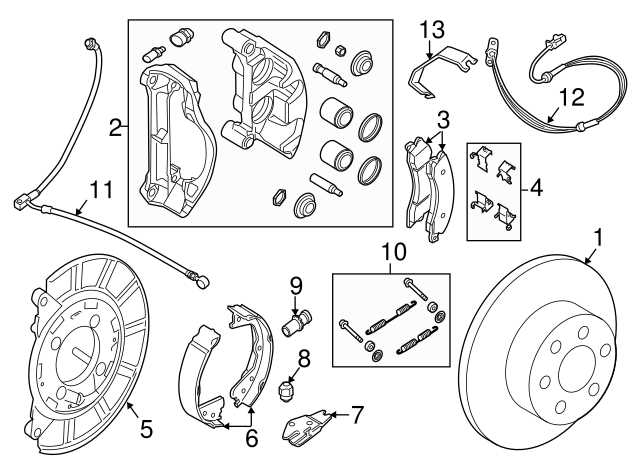
Choosing Replacement Brake Parts
When it comes to maintaining vehicle safety, selecting the right components for the stopping system is crucial. The quality and compatibility of these elements directly impact overall performance and reliability. Understanding the different options available can help ensure a safe driving experience.
Factors to Consider
Several factors should be taken into account when choosing new components. Compatibility with the vehicle model is paramount, as is the quality of the materials used. Additionally, understanding the driving conditions and personal driving habits can aid in making an informed decision.
Quality Over Cost
While budget constraints are a reality, prioritizing quality can prevent future issues and additional expenses. Investing in high-quality elements may lead to better performance and longevity, making it a worthwhile consideration.
Component Type Features Recommended Brands Rotors Heat resistance, durability Brand A, Brand B Pads Noise reduction, wear indicators Brand C, Brand D Calipers Sealing design, corrosion resistance Brand E, Brand F Maintaining Brake Efficiency and Safety
Ensuring optimal performance and reliability of a vehicle’s stopping mechanism is crucial for both safety and functionality. Regular upkeep is essential to prevent malfunctions and guarantee that the system responds effectively when required. This section explores key practices for sustaining operational integrity and enhancing safety standards.
Regular Inspections
Conducting frequent assessments is vital to identify wear and tear before they escalate into serious issues. Technicians should examine the entire system for signs of damage or deterioration. Timely detection allows for proactive measures, ensuring that components function correctly and reducing the risk of failure.
Quality Components and Fluids
Utilizing high-quality materials and fluids significantly contributes to the longevity of the system. Subpar products can lead to inefficiencies and increased wear. Investing in superior components not only enhances performance but also promotes overall safety during operation, providing peace of mind for the driver.
- Hydraulic Systems: