The efficient functioning of a bicycle’s stopping system is crucial for safety and performance. This section aims to explore the intricate elements that contribute to this essential mechanism, providing insights into their roles and interconnections.
By examining the various elements involved, one can appreciate how they work together to ensure reliable deceleration. Each component plays a vital role, impacting both the responsiveness and overall efficiency of the system.
As we delve deeper, we will highlight the ultimate features and characteristics of these components, offering a clearer understanding of their significance in the cycling experience. Whether for maintenance or enhancement, knowledge of these essentials is invaluable.
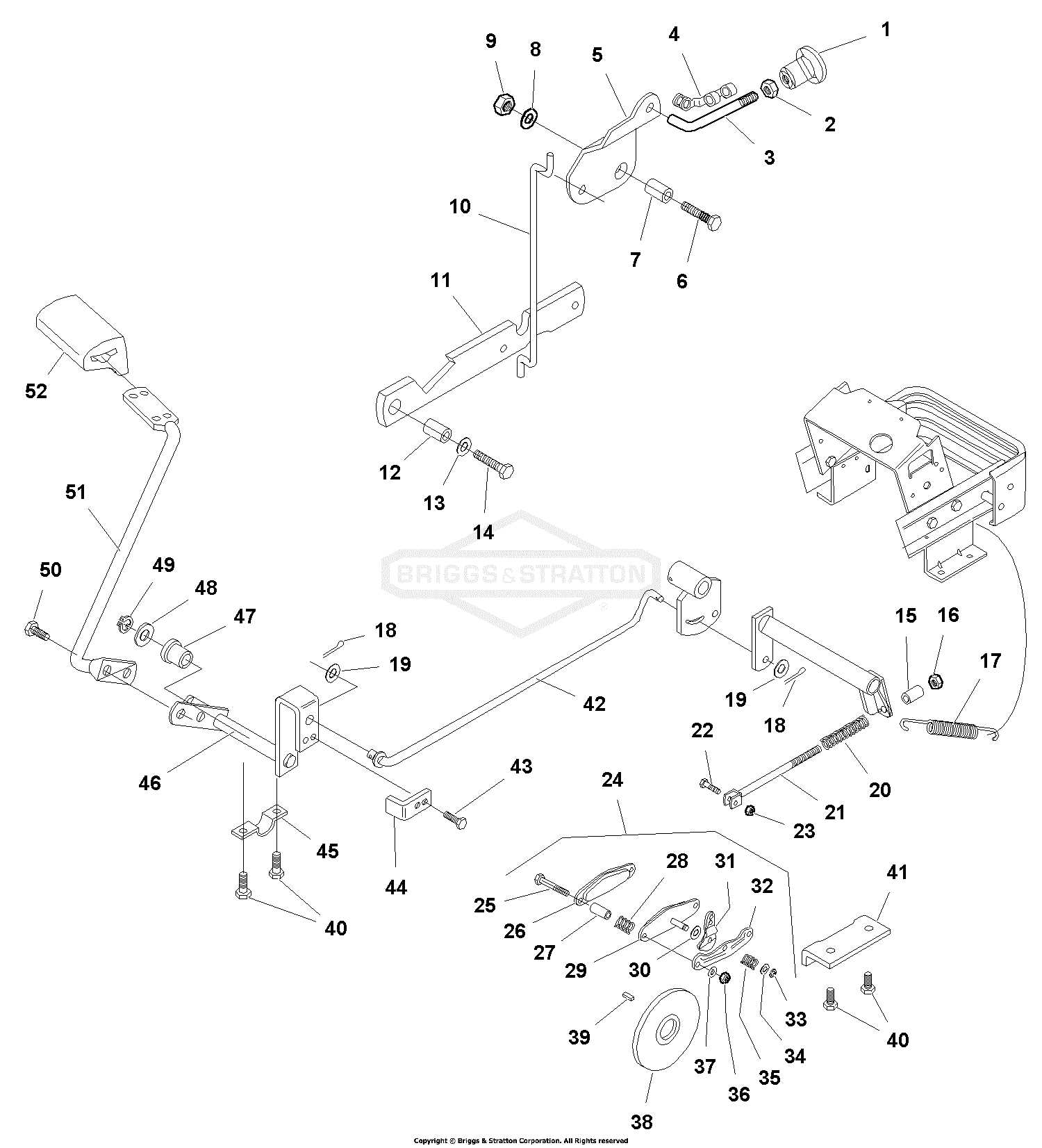
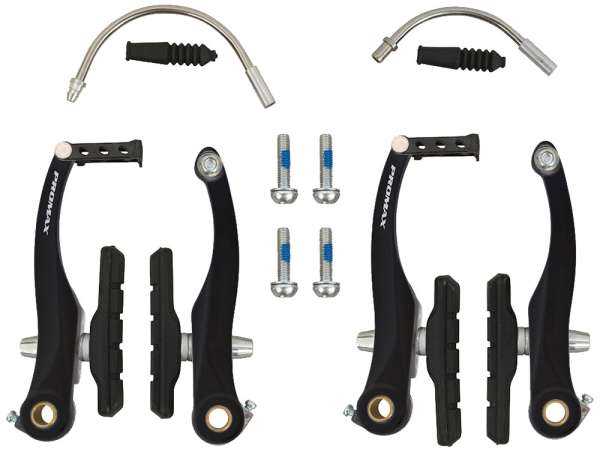
Understanding V Brake Components
When exploring the mechanics behind the stopping system of bicycles, it’s essential to grasp the various elements that come together to ensure effective deceleration. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and efficiency, contributing to a smooth and safe riding experience.
Key Elements of the System
The primary elements include the lever, which initiates the action, the arms that facilitate movement, and the pads that create friction against the rim. Together, these components work harmoniously to achieve reliable stopping power.
Maintenance and Performance
Diagram Overview of V Brakes
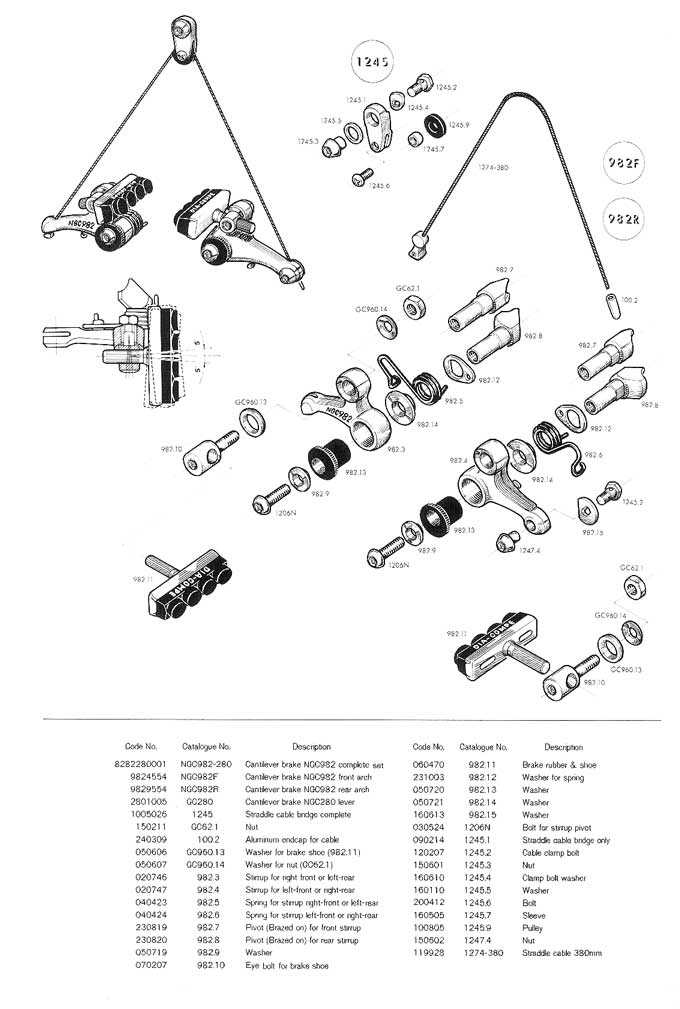
This section provides a comprehensive look at the essential components involved in the operation of a specific stopping mechanism commonly used in cycling. Understanding how each element interacts is crucial for maintenance and performance enhancement.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lever | The control mechanism that the rider engages to initiate stopping. |
| Cable | Connects the lever to the stopping system, transmitting force. |
| Pivot | Allows for movement and adjustment of the mechanism. |
| Shoes | The contact points that engage with the wheel surface to create friction. |
| Mounting Bracket | Secures the assembly to the bicycle frame, ensuring stability. |
Key Parts Explained
Understanding the essential components of the stopping system is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Each element plays a specific role, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the mechanism designed to halt movement.
Lever Mechanism
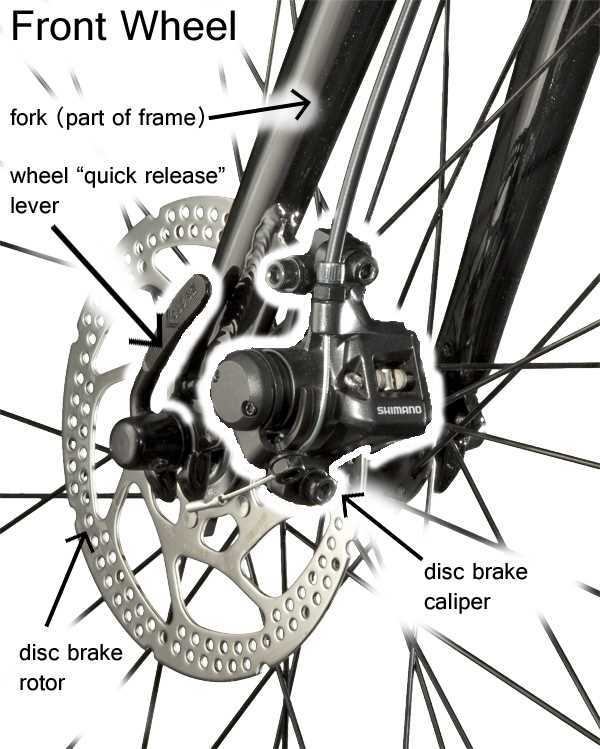
The lever mechanism acts as the initiator, allowing the rider to apply force with minimal effort. This component translates the user’s input into motion, making it a vital part of the assembly.
Pads and Contact Surface
Pads serve as the interface between the system and the wheel, generating friction to slow down the vehicle. Understanding the materials used for these surfaces can enhance performance and durability, ensuring efficient operation under various conditions.
Function of Brake Pads
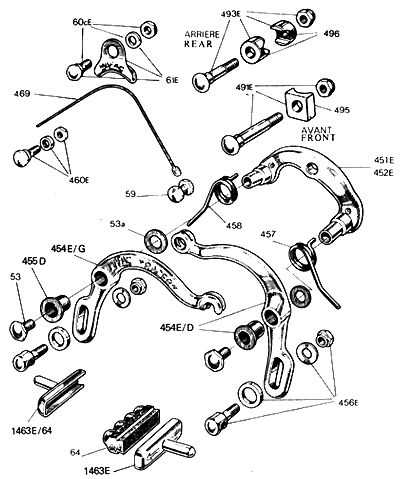
The elements responsible for creating friction in a stopping mechanism play a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency. They interact directly with the wheel’s system, transforming kinetic energy into heat, which ultimately slows down the vehicle. Understanding their function is essential for proper maintenance and optimal performance.
Friction Generation
The primary role of these components is to generate resistance when activated. This process involves pressing against a rotating surface, leading to effective deceleration. The material composition is designed to withstand high temperatures and provide consistent contact.
Heat Dissipation
Another important aspect is their ability to dissipate heat. As friction occurs, excessive heat is produced, which can affect performance if not managed properly. High-quality materials are essential to ensure durability and prevent fade during prolonged use.
Role of Brake Cables
The effectiveness of a stopping mechanism relies heavily on the functionality of various components, one of which is the cable system. These cables serve as a critical link between the controlling mechanism and the stopping devices, ensuring that commands are executed efficiently and promptly.
Functionality and Importance
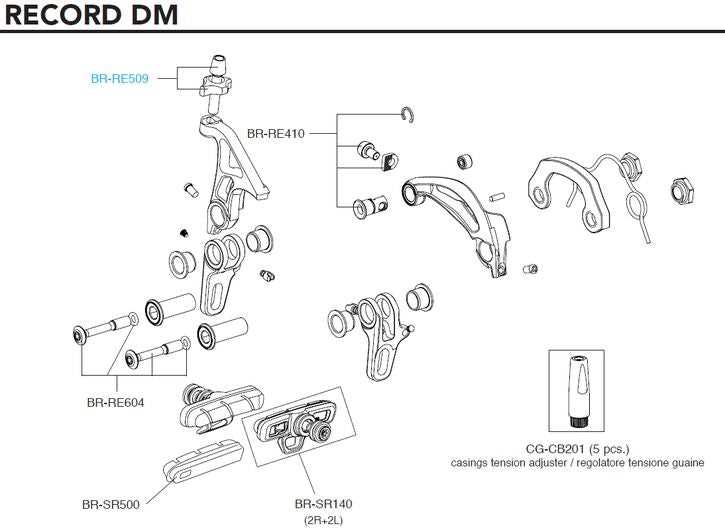
Cables are essential in transmitting force from the lever to the stopping mechanism. Their primary functions include:
- Providing a responsive connection between the control lever and the stopping device.
- Enabling smooth operation through the precise transfer of force.
- Maintaining consistent tension for reliable performance.
Maintenance Considerations

Regular upkeep of the cable system is vital for optimal performance. Key aspects to consider include:
- Inspecting for fraying or wear that can compromise functionality.
- Ensuring proper tension is maintained to prevent slippage.
- Lubricating the cables to reduce friction and enhance longevity.
By understanding the role of these essential components, users can appreciate the significance of maintaining their systems for improved safety and reliability.
Mounting Mechanism Details
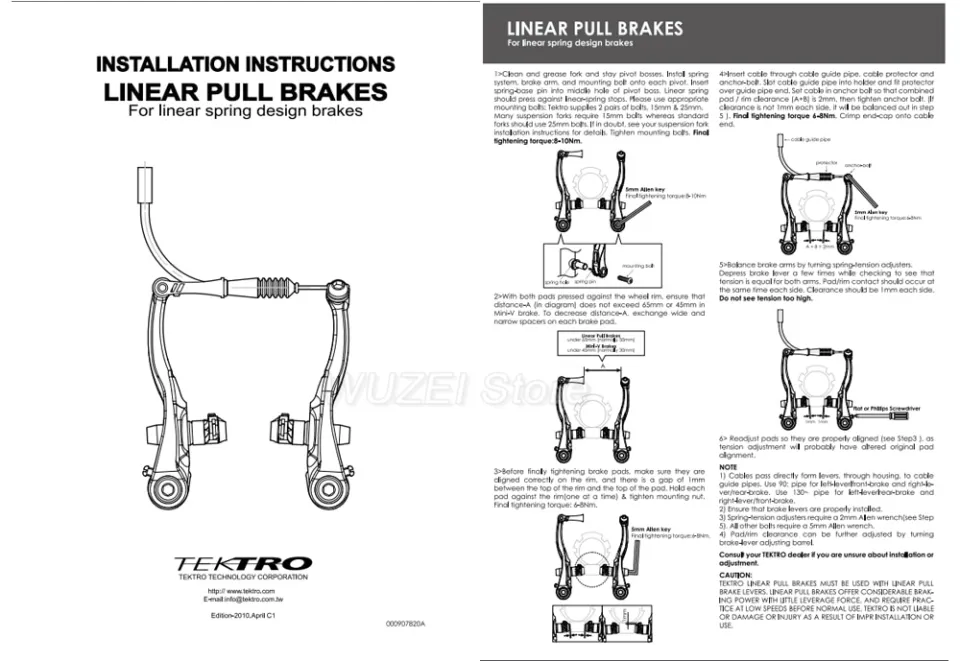
The assembly structure of the stopping system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding its components allows for better maintenance and enhancements, ultimately leading to improved functionality.
Components Overview
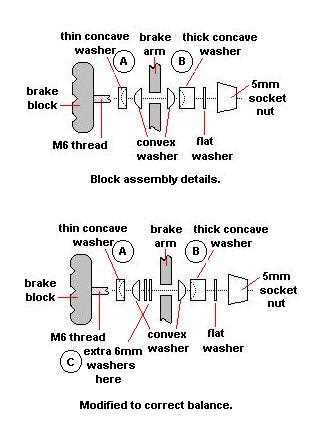
The key elements include anchors, levers, and adjustment screws, all designed to facilitate seamless interaction. Each component contributes to the overall stability and effectiveness, allowing for precise control during operation.
Installation Considerations
When setting up the mechanism, proper alignment and secure fastening are vital. Attention to detail during installation can prevent issues and enhance longevity. Regular checks on the connections and adjustments will ensure the ultimate performance of the system.
Adjusting the Brake System

Fine-tuning your stopping mechanism is essential for optimal performance and safety. Proper adjustments enhance responsiveness and ensure that your setup functions smoothly.
Here are key steps to achieve effective alignment:
- Inspect the alignment of the stopping elements to ensure they are positioned correctly.
- Check the tension of the cables, ensuring they are neither too loose nor too tight.
- Examine the wear on the stopping surfaces and replace if necessary.
- Adjust the angle and positioning to achieve even contact with the rim.
By following these steps, you can enhance the overall effectiveness and longevity of your system.
Common V Brake Issues
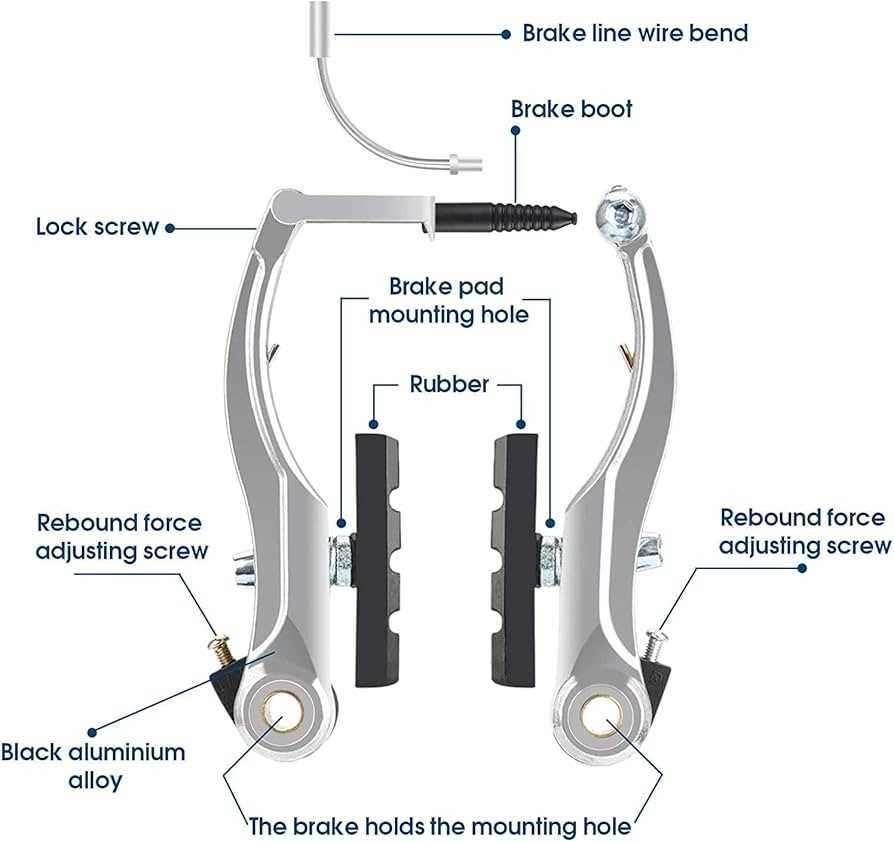
When it comes to stopping mechanisms, various challenges can arise that hinder performance and safety. Understanding these common problems is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring a smooth ride.
| Issue | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Responsiveness | Insufficient contact may lead to reduced stopping power. | Adjust alignment and check cable tension. |
| Uneven Wear | Uneven surfaces can cause irregular performance. | Inspect and replace worn components. |
| Noise | Unusual sounds during operation may indicate misalignment. | Re-align and lubricate necessary areas. |
| Debris Accumulation | Foreign materials can interfere with function. | Regular cleaning and maintenance are required. |
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the lasting performance of your cycling system requires consistent care and attention. Regular upkeep can significantly extend its life and efficiency, allowing for smoother rides and enhanced safety.
1. Clean Regularly: Keeping components free from dirt and grime is essential. Use a soft brush and mild soap to remove debris, which can cause wear over time.
2. Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply appropriate lubricant to hinges and pivot points. This reduces friction and prevents rust, ensuring optimal functionality.
3. Inspect for Wear: Regularly check for signs of deterioration. Identifying issues early can prevent more significant problems and ensure reliable performance.
4. Store Properly: When not in use, keep your equipment in a dry, sheltered location. This protects it from environmental damage and prolongs its lifespan.
5. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhering to maintenance schedules and recommendations can provide the ultimate assurance of durability and safety.
Comparison with Other Brake Types

This section explores the distinctions and similarities between various stopping mechanisms utilized in cycling. Understanding these differences can help enthusiasts select the most suitable option for their needs.
Key Differences
Each system presents unique characteristics that affect performance, maintenance, and user experience. The choice often depends on riding style, terrain, and personal preference.
Performance Overview
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Rim | Lightweight, simple maintenance | Less effective in wet conditions |
| Disc | Consistent performance, better modulation | Heavier, more complex setup |
| Cantilever | Good for off-road, easy to adjust | Less powerful than disc systems |
Choosing the Right Brake Pads

Selecting the appropriate components for stopping mechanisms is crucial for optimal performance and safety. The right materials and specifications can significantly enhance efficiency, longevity, and comfort during use.
Material Composition plays a vital role in effectiveness. Common options include organic, semi-metallic, and ceramic. Each type offers unique benefits regarding noise levels, heat resistance, and wear characteristics.
Compatibility with your specific system is essential. Ensuring the chosen items match your vehicle’s requirements helps prevent premature wear and improves overall functionality.
Performance Considerations should also be taken into account. Factors such as intended use, climate conditions, and riding style can influence the ideal selection, allowing for a more tailored experience.
Ultimately, making an informed choice will enhance both safety and enjoyment while navigating various terrains.
Upgrading Your V Brake System
Enhancing your stopping mechanism can significantly improve your riding experience. By focusing on key elements, you can achieve better control and performance.
- Evaluate Current Setup: Assess the condition and efficiency of your existing equipment.
- Select Quality Components: Choose high-performance items to boost reliability.
- Improve Leverage: Consider upgrading the lever for better modulation.
Additionally, integrating advanced materials can enhance overall functionality:
- Upgrade to aluminum or composite for lighter weight.
- Choose enhanced friction materials for superior stopping power.
- Consider adjusting cable housing for smoother operation.
By delving into these enhancements, you can achieve the ultimate riding experience with improved safety and efficiency.
Resources for Further Learning
For those eager to deepen their understanding of essential components in cycling mechanics, a variety of materials are available. These resources provide comprehensive insights into design, functionality, and maintenance practices that enhance both knowledge and skills.
Books and Manuals: Consider exploring specialized literature that covers technical aspects and troubleshooting techniques. Many authors provide detailed illustrations and step-by-step guides that can be invaluable for enthusiasts.
Online Courses: Various platforms offer structured courses focusing on cycling mechanics, including video tutorials that allow for interactive learning. These courses often include practical demonstrations to help solidify concepts.
Forums and Communities: Engaging with online communities can provide real-time advice and shared experiences. Participants often discuss common issues and solutions, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
Workshops: Look for local workshops or events where hands-on learning is emphasized. These gatherings often feature experts who share their knowledge and offer practical demonstrations.
Exploring these avenues can ultimately enhance your comprehension and proficiency in maintaining and improving cycling systems.