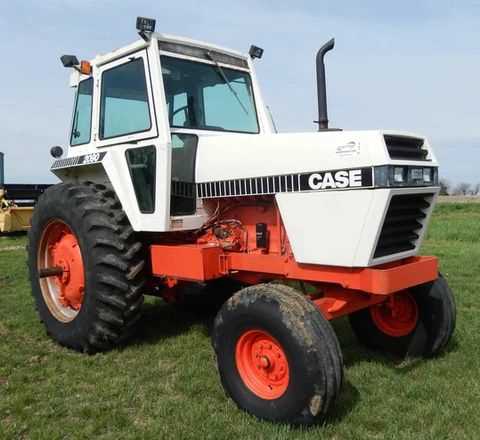

The importance of understanding how various mechanical elements fit together cannot be overstated. Whether you are maintaining agricultural machinery or handling routine inspections, a clear comprehension of how each section interacts is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and longevity. By recognizing the arrangement of different elements, you can significantly improve both performance and reliability.
In this guide, we will explore the internal structure and provide a detailed breakdown of the primary elements, helping you familiarize yourself with essential functions. This information is vital for those involved in repair work, maintenance, or who simply want to gain deeper insights into how these components contribute to overall machinery performance.
With this knowledge, you will be better equipped to manage the upkeep of your equipment, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency. By focusing on the core areas, you can enhance your understanding and ensure your machinery operates at peak performance throughout its lifecycle.
Overview of Case 2090 Tractor Components
In this section, we will provide a comprehensive breakdown of the various mechanical elements that form the structure and functionality of this agricultural machine. Understanding these elements is essential for both maintenance and optimal performance of the equipment.
- Engine Assembly: The heart of the machinery, ensuring power output and operational efficiency across all tasks.
- Transmission System: This mechanism is responsible for managing speed and torque, allowing the operator to adjust according to field conditions.
- Hydraulic Circuit: Provides necessary fluid power for lifting, steering, and other vital functions.
- Chassis and Frame: These structural elements offer support and durability, ensuring the machine can handle heavy workloads.
- Axles and Wheels: Designed to provide stability and mobility, even in tough terrain.
- Control and Steering: The operator’s interface for guiding and managing various systems efficiently.
Each of these systems plays a crucial role in ensuring the machine operates smoothly and reliably, with all components working in harmony to deliver optimal performance in agricultural environments.
Main Sections of the Case 2090
This section covers the essential components and systems found in this agricultural machinery. Each part is designed to perform a specific function, contributing to the overall operation and efficiency of the vehicle.
Engine and Transmission
The heart of this equipment lies in its power source, which ensures smooth performance and reliable operation. The transmission system works in tandem to manage speed and torque, optimizing power distribution across various working conditions.
- Power generation system
- Speed and torque control
- Fuel efficiency mechanisms
Hydraulic System
Another critical aspect is the hydraulic setup, which supports various lifting and movement operations. This system is vital for controlling different attachments and ensuring smooth operation during demanding tasks.
- Pumps and valves for fluid control
- Attachment handling mechanisms
- Pressure regulation components
Exploring the Hydraulic System Design
The hydraulic system is a key component responsible for delivering power through fluid pressure. It operates by utilizing a network of pumps, valves, and cylinders to control the movement of various mechanical elements. Understanding the configuration and functionality of these elements is crucial to maintain efficiency and ensure smooth operation.
Key Elements of the Hydraulic Circuit
- Pumps: Responsible for converting mechanical energy into hydraulic pressure.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of fluid, controlling the direction and force of movement.
- Cylinders: Execute the actual mechanical tasks by translating hydraulic pressure into motion.
Operational Efficiency and Maintenance
Regular inspection and proper maintenance of hydraulic systems help prevent malfunctions and extend their operational life. Monitoring fluid levels, checking for leaks, and ensuring all components are functioning optimally contribute to the overall performance and reliability of the machinery.
Detailed Engine Parts Layout
Understanding the arrangement of various components in the engine is essential for ensuring optimal performance and maintenance. This section provides a clear overview of how key elements are positioned within the machinery, offering a comprehensive look at their structure and organization.
Core Components and Their Placement
The central elements of the engine are meticulously arranged to work together seamlessly. From the combustion chamber to the crankshaft, each component is strategically placed to facilitate efficient energy conversion and smooth operation. Special attention is given to the alignment of the pistons, ensuring balance and stability during operation.
Peripheral Systems and Connections
The peripheral systems, including the fuel injectors and cooling mechanisms, are integrated around the main engine structure. These systems play a crucial role in maintaining the engine’s efficiency, ensuring that it operates under optimal conditions. The connections between these components are designed to maximize the flow of fluids and gases, enhancing overall performance.
| Component | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Piston | Converts energy from combustion | Inside the cylinder |
| Crankshaft | Transforms piston movement into rotation | Lower section of the engine |
| Fuel Injector | Supplies fuel into the combustion chamber | Near the cylinder head |
Transmission Assembly Structure
The transmission system plays a crucial role in converting engine power into controlled movement. It ensures that the engine operates at an optimal range while providing the necessary torque for various operational speeds. The assembly consists of multiple interconnected components that work in harmony to deliver smooth power shifts and enhance mechanical efficiency.
Gears and Shafts form the core of the transmission, transmitting rotational force through different speed ratios. Each gear set is strategically designed to provide the desired output under varying load conditions. Synchronizers ensure seamless gear engagement, preventing wear and tear while maintaining smooth operation.
Another essential component is the clutch system, which temporarily disengages the engine from the drivetrain, allowing for effortless shifting between gears. The combination of these elements ensures that the machine can handle diverse tasks while maintaining a balance between power and speed.
Front Axle and Steering Mechanism
The front axle and steering system play a critical role in maintaining vehicle stability and maneuverability. This section explores the key components involved in supporting the weight of the machinery and ensuring precise directional control, offering a clear understanding of their function and interaction.
Main Components of the Front Axle
The front axle assembly is composed of various elements designed to withstand stress and distribute weight evenly. These components contribute to the overall durability and performance of the machine during operation.
- Axle beam: The main structural element that supports the machine’s weight and connects both front wheels.
- Spindles: Attach to the wheels, allowing them to rotate freely while maintaining alignment with the axle beam.
- Bearings: Reduce friction between rotating parts, ensuring smooth operation and preventing wear.
Steering Mechanism Overview
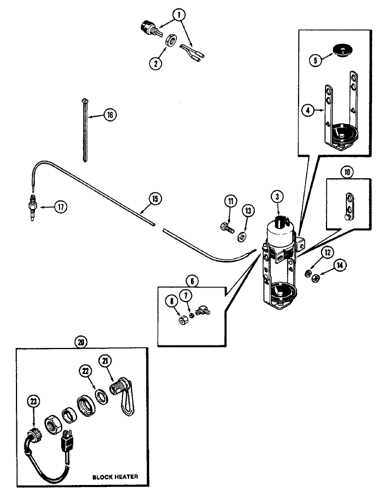
The steering system ensures precise control of the vehicle’s direction. It includes a range of interconnected parts that convert driver input into smooth, responsive turns.
- Steering linkage: Transfers motion from the steering wheel to the front wheels, enabling accurate direction changes.
- Hydraulic assist system: Enhances steering efficiency by reducing the effort required to turn the wheels, especially under load.
- Tie rods: Connect the steering gear to the spindles, ensuring consistent movement between the wheels and steering system.
Brake System Components and Diagram
The brake system is crucial for the safe operation of any machinery, ensuring effective stopping power and control. Understanding its various elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the primary components of the braking mechanism, offering insights into their functions and interactions.
Main Elements of the Braking Mechanism
Each component plays a vital role in the overall performance of the braking system. Key parts include the actuator, calipers, and friction materials. Together, they work to convert hydraulic pressure into the mechanical force needed to slow down or stop the vehicle.
Functional Overview
Regular inspection of these components can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring the reliability and safety of the equipment. Proper maintenance practices enhance the longevity and effectiveness of the braking system.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Actuator | Translates driver input into hydraulic pressure. |
| Caliper | Houses the friction materials and applies pressure to the discs. |
| Friction Material | Creates the necessary friction to slow or stop motion. |
| Disc | Rotates with the wheel and interacts with the caliper. |
| Hydraulic Lines | Transmits hydraulic fluid from the actuator to the calipers. |
Electrical Circuit and Wiring Layout
This section explores the intricate connections and arrangements that power various systems within the machinery. Understanding the electrical framework is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality and safety.
The layout includes a comprehensive network of wiring, switches, and connectors that facilitate the flow of electricity. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining operational efficiency and reliability, enabling seamless communication between different parts of the equipment.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of the electrical connections are essential for preventing malfunctions. Familiarity with the wiring configuration allows operators and technicians to identify potential issues swiftly, ensuring uninterrupted performance.
Fuel System Configuration and Parts
The fuel delivery mechanism is a crucial aspect of any agricultural machinery, influencing both efficiency and performance. Understanding the components that make up this system can aid in proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal operation over time.
Key Components of the Fuel Delivery System
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel required for engine operation.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Transports fuel from the tank to the engine at the correct pressure.
- Injector: Sprays the fuel into the combustion chamber for efficient ignition.
Understanding the Configuration
The arrangement of these elements is designed to optimize fuel flow and ensure that the engine receives a consistent supply. Proper alignment and connection between the fuel tank, pump, and injectors play a vital role in maintaining the system’s integrity. Regular checks can prevent common issues such as leaks or blockages, thereby enhancing overall performance.
Cooling System Parts Breakdown
The efficiency of any engine greatly depends on the functionality of its cooling mechanism. A well-designed cooling system ensures that the engine operates within optimal temperature ranges, preventing overheating and maintaining performance. Understanding the components involved in this system is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism
- Radiator: This unit dissipates heat from the coolant to the atmosphere, helping to regulate engine temperature.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating coolant throughout the system, ensuring a steady flow for effective heat transfer.
- Thermostat: A temperature-sensitive valve that regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, allowing for efficient operation.
- Coolant Reservoir: A container that holds excess coolant, maintaining the system’s pressure and preventing air from entering.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between the various components, ensuring a continuous flow throughout the system.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check coolant levels and top up as necessary.
- Inspect hoses for signs of wear or leaks and replace if needed.
- Flush the system periodically to remove any built-up debris or sediment.
- Monitor the radiator for any blockages that could hinder airflow.
Clutch and Drivetrain Assembly

The clutch and drivetrain assembly play a pivotal role in the effective transmission of power within a vehicle. This essential component facilitates the engagement and disengagement of the engine’s power to the wheels, allowing for smooth acceleration and deceleration.
Understanding the intricacies of this assembly involves examining its primary components, each contributing to the overall functionality:
- Clutch Plate: A crucial element that engages and disengages the engine from the transmission.
- Flywheel: Serves as a mechanical reservoir, providing rotational energy to maintain engine momentum.
- Pressure Plate: Applies force to the clutch disc, ensuring a secure connection between the engine and the transmission.
- Release Bearing: Facilitates the smooth disengagement of the clutch when the pedal is pressed.
- Driveshaft: Transfers torque from the transmission to the wheels, enabling movement.
Each of these components must function harmoniously to ensure optimal performance. Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to prevent wear and ensure the longevity of the drivetrain system.
Maintenance Guide for Key Components
Regular upkeep of essential elements in machinery is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section provides valuable insights into the best practices for maintaining critical components that play a significant role in the overall functionality of your equipment.
1. Engine Care: The heart of your machinery requires consistent attention. Regular oil changes, timely filter replacements, and proper cooling system maintenance are essential to prevent overheating and ensure smooth operation. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific intervals.
2. Hydraulics System: Maintaining the hydraulic system is vital for efficient movement and operation. Check fluid levels regularly and inspect hoses and connections for leaks or wear. Proper filtration and fluid replacement will enhance system performance and reduce the risk of breakdowns.
3. Electrical System: Regular checks on the electrical system help avoid unexpected failures. Inspect wiring for damage, ensure connections are tight, and replace worn-out components promptly. Keeping the battery charged and terminals clean will prevent electrical issues.
4. Transmission Maintenance: The transmission plays a crucial role in power delivery. Regularly check and replace transmission fluid as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. Pay attention to any unusual noises or shifting problems, as these could indicate underlying issues.
5. Tires and Tracks: Proper tire pressure and tread depth are essential for safe operation. Inspect tracks for wear and damage, ensuring they are properly aligned. Regularly rotating and balancing tires can enhance performance and extend their lifespan.
Implementing these maintenance practices will significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of your equipment, leading to reduced downtime and increased productivity.