When addressing the intricate structure of an automobile, it’s crucial to understand how the different elements are interconnected. The arrangement of these elements within the system plays a vital role in the overall performance and maintenance. Identifying the position and relationship of various mechanical sections ensures that repairs and replacements are handled with precision.
Exploring the detailed layout of the internal and external elements of your vehicle helps users and technicians alike. This understanding allows for more efficient servicing and the ability to pinpoint potential issues. Whether focusing on the engine, transmission, or other critical sections, having a clear view of the components involved is essential for long-term vehicle health.
With the correct knowledge of these mechanical structures, both maintenance and upgrades can be approached with confidence. Learning how each section is organized provides a strong foundation for anyone looking to enhance their understanding or troubleshoot specific issues effectively.
Chevy Cruze 2012 Component Layout Overview
The overall configuration of the vehicle’s mechanical and electronic systems is designed with efficiency and accessibility in mind. Key elements, including the engine bay, suspension system, and interior components, are arranged to optimize performance, safety, and ease of maintenance. Understanding the placement and interaction of these systems can assist in identifying potential issues and performing routine upkeep.
Engine Compartment Structure
The core of the system lies within the front section, where crucial components like the powertrain, cooling unit, and fuel delivery mechanisms are positioned. This area is structured to allow quick access for inspections, repairs, and adjustments, ensuring smooth operation of the vehicle.
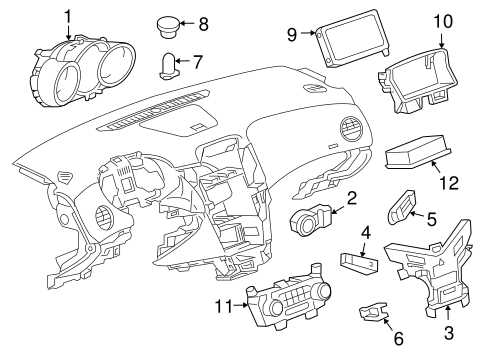
Interior and Electrical Layout
Internally, the electrical systems are distributed through a network of control units, sensors, and wiring, coordinating functions like climate regulation, infotainment, and lighting. These elements are embedded strategically to support both user comfort and system integration, all while remaining easily serviceable.
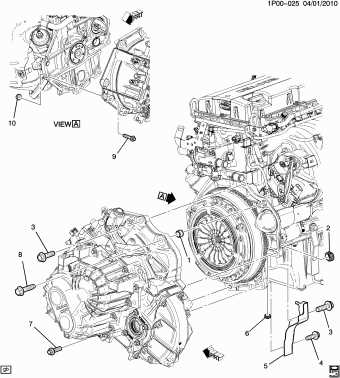
Engine Compartment Structure and Key Parts
The engine compartment houses numerous crucial elements that contribute to the efficient performance of a vehicle. This section provides an overview of the main components found under the hood and explains their significance in ensuring smooth operation. Each element is positioned strategically to maximize functionality and ease of maintenance.
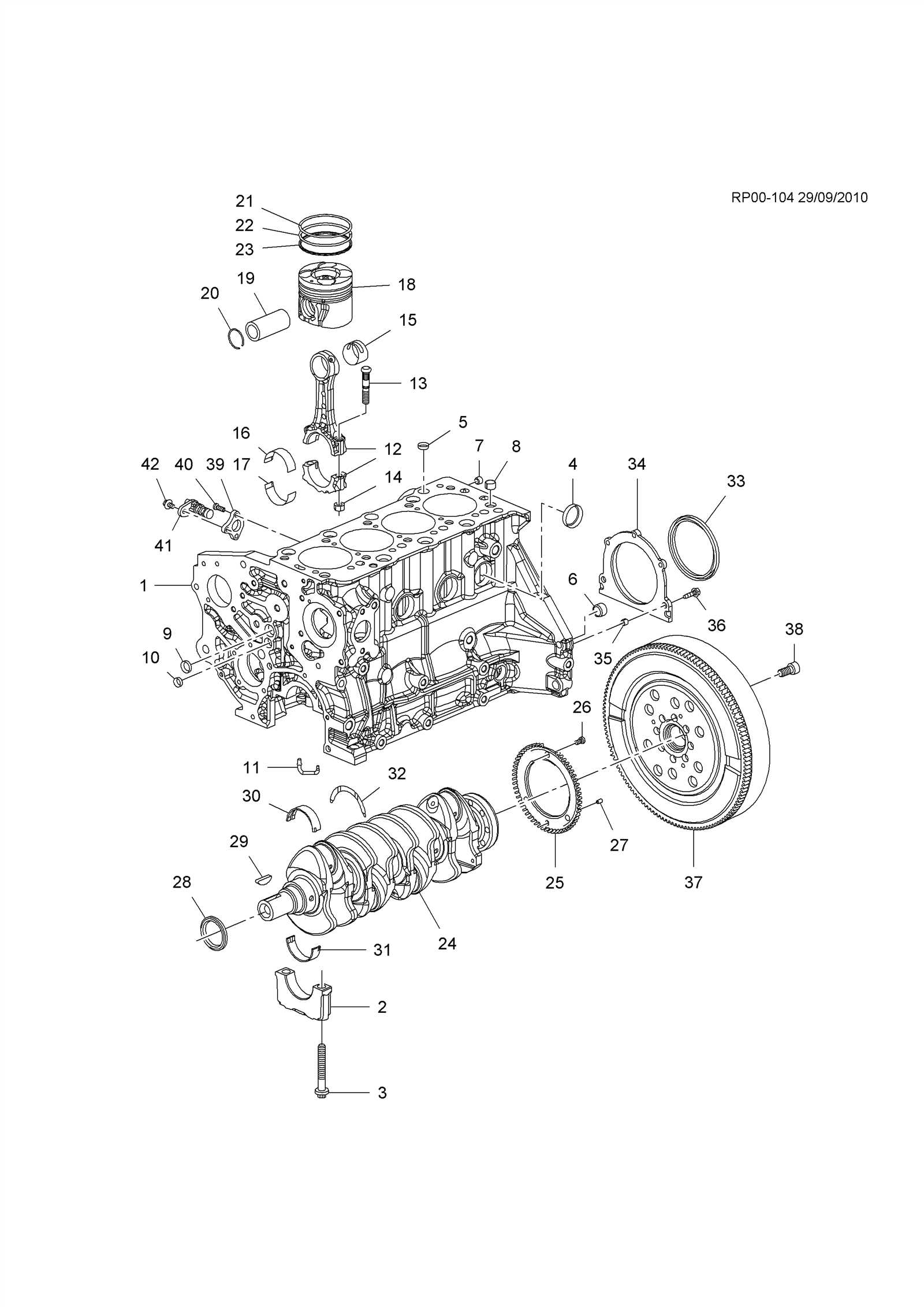
Main Structural Components
The engine block serves as the foundation of the entire system, holding critical elements such as the cylinders, pistons, and various mounts. Adjacent to it, the transmission is responsible for transferring power to the wheels. Additional structures like the radiator, cooling system, and intake manifold are situated to regulate temperature and air intake, helping the engine maintain optimal performance under different conditions.
Essential Functional Units
Key functional units include the altern
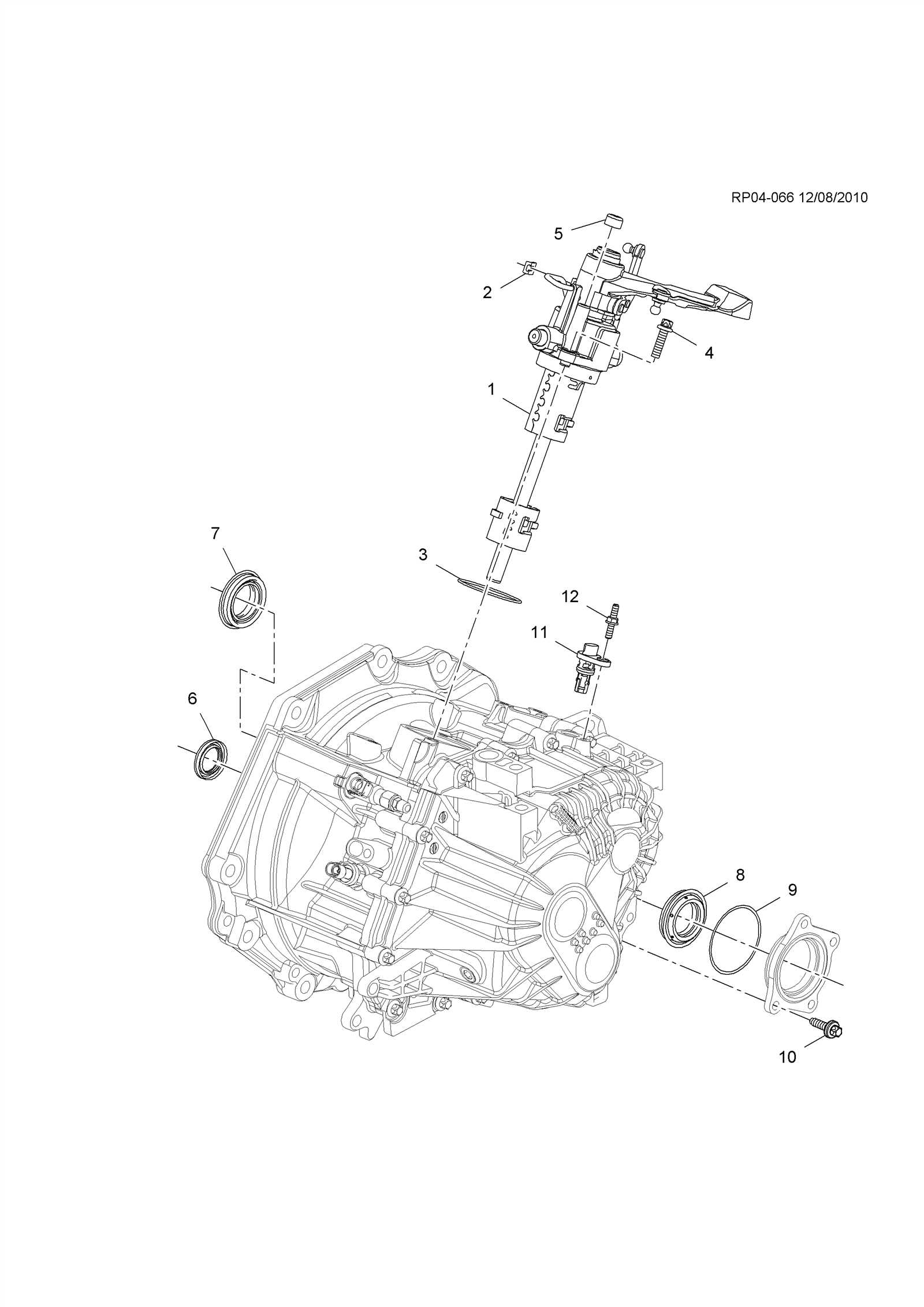
Transmission System: Key Elements and Placement
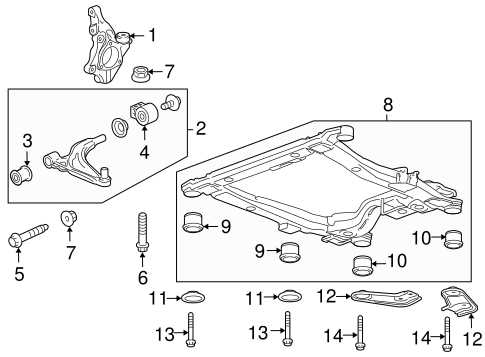
The transmission system plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move efficiently. This complex mechanism consists of various components, each working in harmony to ensure smooth gear shifts, torque control, and optimal performance. Understanding the key elements and how they are arranged within the system is essential for ensuring proper maintenance and functionality.
Main Components of the Transmission
The transmission consists of several primary elements. One of the core parts is the gearbox, which houses a set of gears responsible for adjusting the torque and speed. The clutch (or torque converter in automatic models) is another vital component, allowing the disengagement and engagement of power between the engine and the transmission. Additionally, the shift mechanism regulates gear
Suspension Parts and Their Diagram
The suspension system is an essential component responsible for ensuring a smooth and stable ride by absorbing shocks and maintaining control during various driving conditions. Understanding the key elements of this system helps in identifying potential issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Main Components of the Suspension
- Control Arms: These connect the vehicle’s chassis to the wheels, allowing for proper movement and alignment during travel.
- Shocks and Struts: Designed to absorb impact and maintain the vehicle’s stability by controlling the motion of the springs.
- Springs: Provide support by absorbing energy from road irregularities, ensuring the vehicle remains balanced and comfortable.
- Sway Bar: Helps reduce body roll during cornering by distributing forces across both sides of the vehicle.
- Bushings: Act as cushions between different me
Cooling System Components and Configuration
The cooling mechanism of any vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, ensuring efficient performance and preventing overheating. It is designed to circulate a specific fluid through various components, extracting heat and regulating thermal conditions during operation. This system is essential for sustaining the engine’s durability and overall health over time.
Main Elements of the Cooling System
The primary elements include a radiator, responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant, and a water pump that ensures fluid movement throughout the engine. Additionally, the thermostat monitors temperature levels, allowing the flow of coolant when necessary. Another vital part is the cooling fan, which aids in airflow through the radiator to enhance heat exchange.
System Configuration and Flow
Exhaust System Parts and Locations
The exhaust system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and ensuring optimal performance. Understanding the various elements of this system and their specific locations can greatly assist in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components of the exhaust system include:
- Exhaust Manifold: Located at the engine’s head, this part collects exhaust gases from multiple cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Positioned between the exhaust manifold and the muffler, it reduces harmful emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances.
- Oxygen Sensors: Typically found before and after the catalytic converter, these sensors monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases.
- Resonator: Located along the exhaust path, this component helps to modify sound and reduce noise levels.
- Muffler: Positioned towards the end of the exhaust system, it dampens sound produced by the engine and exhaust gases.
- Exhaust Pipes: These run from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, transporting exhaust gases through the system.
Each of these elements plays a vital role in ensuring that the exhaust system functions ef
Brake Assembly Layout for Chevy Cruze
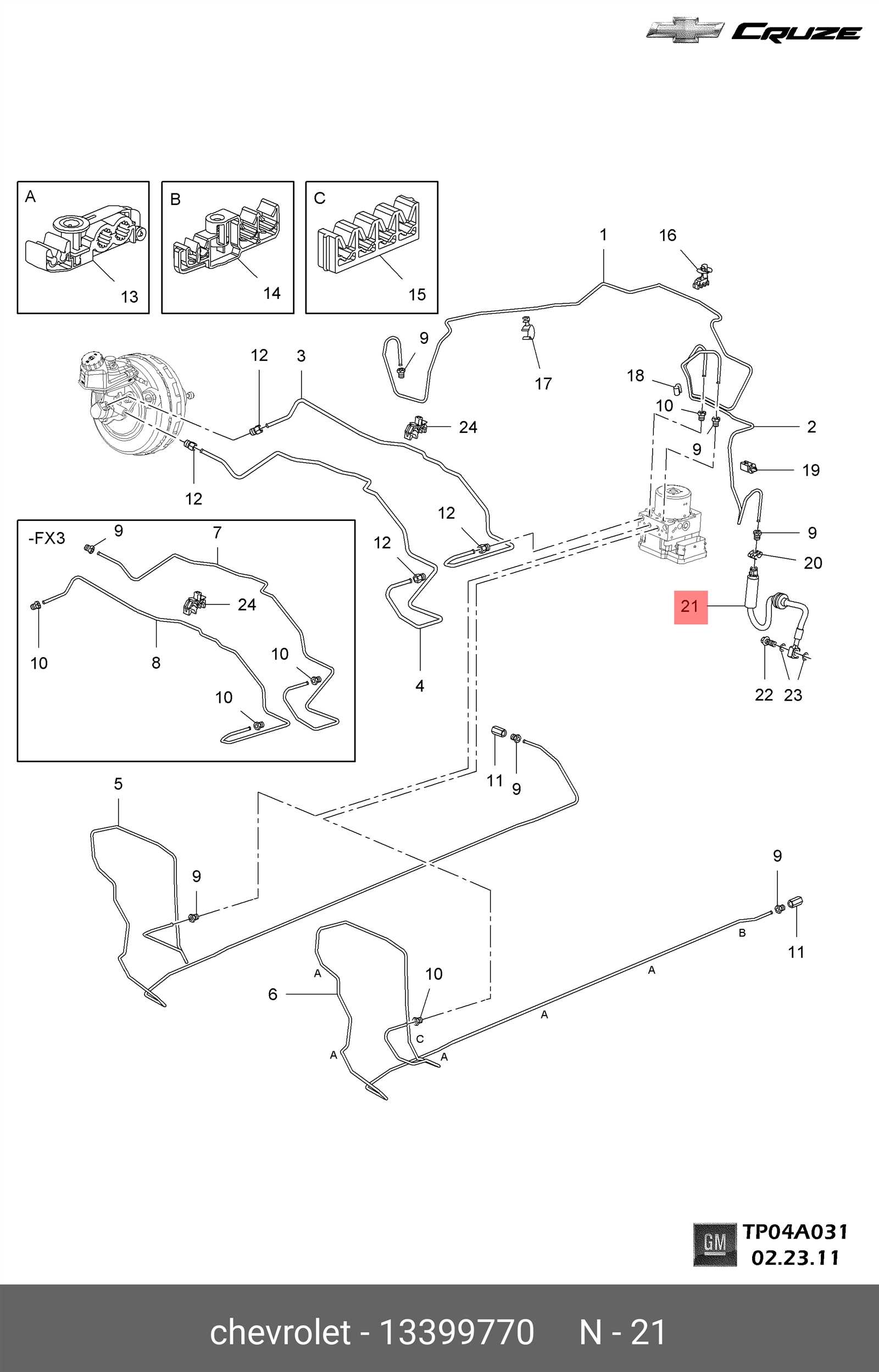
The brake system of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring safe operation. Understanding the configuration of the braking components can aid in maintenance and repairs, allowing for effective troubleshooting and replacement when necessary. This section provides an overview of the arrangement of essential braking elements, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Key Components of the Braking System
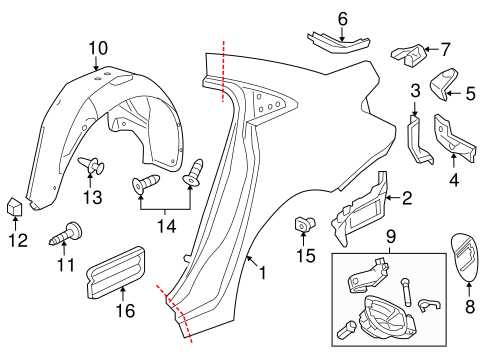
The primary elements involved in the braking assembly include the brake pads, rotors, calipers, and brake lines. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the system. Brake pads are responsible for creating friction against the rotors, while calipers house the pads and apply pressure to them. The rotors are the surfaces that the pads grip to slow down the vehicle, and brake lines transport hydraulic fluid to facilitate the braking action.
Understanding the Layout
In the layout of the braking system, components are strategically positioned to optimize performance and efficiency. Typically, the calipers are mounted on either side of the rotors, allowing for balanced pressure application. The hydraulic lines connect the calipers to the master cylinder, enabling smooth operation when the brake pedal is engaged. Familiarizing oneself with this arrangement can enhance the ability to identify issues and perform effective maintenance.
Steering Mechanism and Main Elements
The steering system is a crucial component of any vehicle, facilitating the driver’s control over the direction and movement of the automobile. This system comprises several key components that work in unison to ensure smooth maneuverability and responsiveness. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Primary Components: The steering assembly includes a steering wheel, column, gear mechanism, and connecting links. The steering wheel allows the driver to initiate the steering action, while the column transmits this motion to the gear mechanism, which converts rotational movement into lateral motion. This process ultimately directs the front wheels.
Key Features: Within the steering mechanism, various elements such as tie rods, control arms, and ball joints play vital roles. Tie rods connect the steering gear to the wheels, facilitating their movement. Control arms provide stability and support, allowing for precise handling. Meanwhile, ball joints act as pivot points, ensuring smooth transitions as the wheels turn.
Proper maintenance of the steering system is essential for optimal performance and safety. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn components can significantly enhance the vehicle’s handling capabilities and overall driving experience.
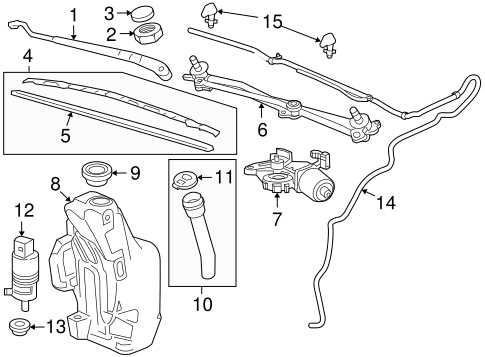
Fuel System Parts and Their Placement
The fuel delivery mechanism in a vehicle is crucial for optimal engine performance. It consists of various components that work harmoniously to ensure the proper supply of fuel to the engine. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting purposes.
Component Description Location Fuel Tank Stores the fuel until needed by the engine. Located at the rear of the vehicle. Fuel Pump Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine. Typically found inside the fuel tank. Fuel Filter Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Usually situated between the fuel tank and the engine. Fuel Injectors Atomize the fuel and deliver it into the combustion chamber. Located on the intake manifold. Fuel Rail Distributes fuel to the injectors. Connected to the fuel injectors along the engine. Interior Components: Key Diagrams
This section provides a comprehensive overview of essential internal elements, highlighting their arrangements and functions within the vehicle’s cabin. Understanding these components is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Interior Elements

Below is a summary of significant internal parts that contribute to the overall functionality and comfort of the vehicle’s interior.
Component Description Function Dashboard The panel located directly in front of the driver. Displays important information such as speed and fuel level. Center Console The area between the driver and passenger seats. Houses controls for the audio system and climate settings. Door Panels Sections that form the inner surface of the vehicle’s doors. Provide access to window controls and storage compartments. Seats Furniture designed for passenger seating. Ensures comfort and safety during travel. Maintenance Insights
Regular checks and maintenance of these internal features enhance the overall driving experience and longevity of the vehicle. Keeping these components in optimal condition is vital for both functionality and comfort.
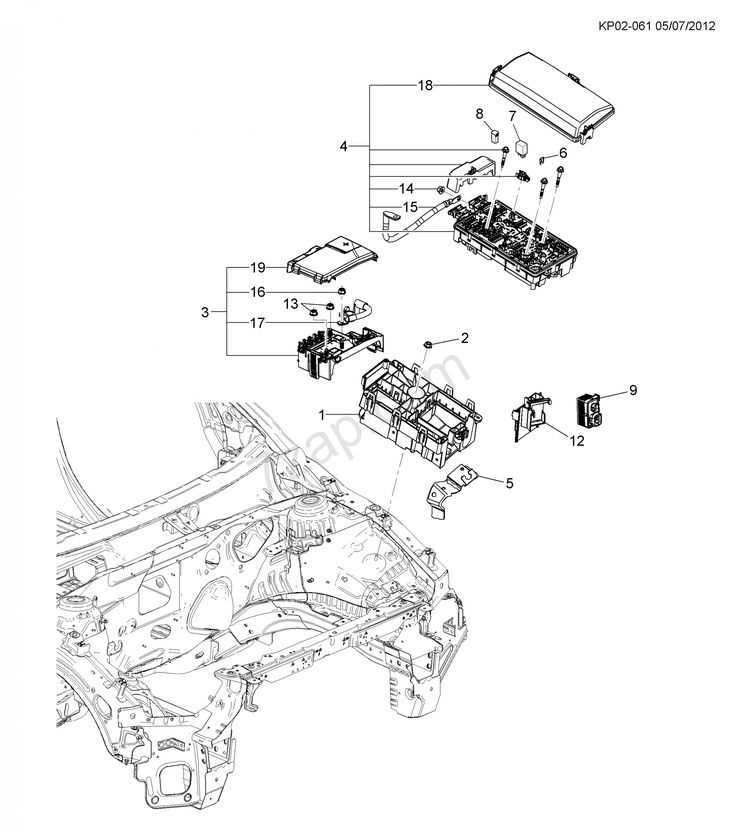
Electrical System Overview and Key Parts
The electrical framework of a vehicle is essential for its overall functionality and performance. This intricate network encompasses various components that work collaboratively to power critical systems, ensuring the smooth operation of both fundamental and advanced features. Understanding this system is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
At the core of the electrical system are the battery and the alternator, which provide the necessary energy for starting the engine and powering electrical accessories. The battery stores electrical energy, while the alternator generates power while the engine runs, ensuring a constant supply of electricity.
Another important aspect includes the wiring harness, which connects all electrical components, facilitating communication between them. Additionally, the fuse box protects the system from overloads by interrupting the circuit when necessary. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the vehicle’s electrical operations.
Furthermore, various sensors and control modules are integrated within the system to monitor performance and enhance functionality. These components work together to optimize energy consumption and provide feedback to the driver, contributing to a seamless driving experience.
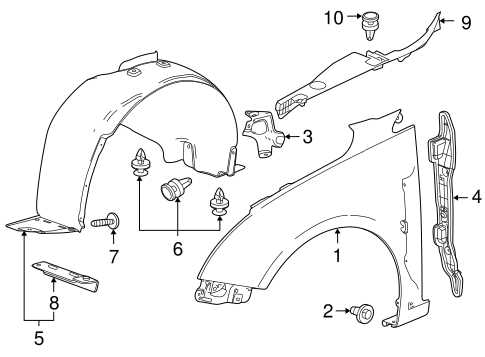
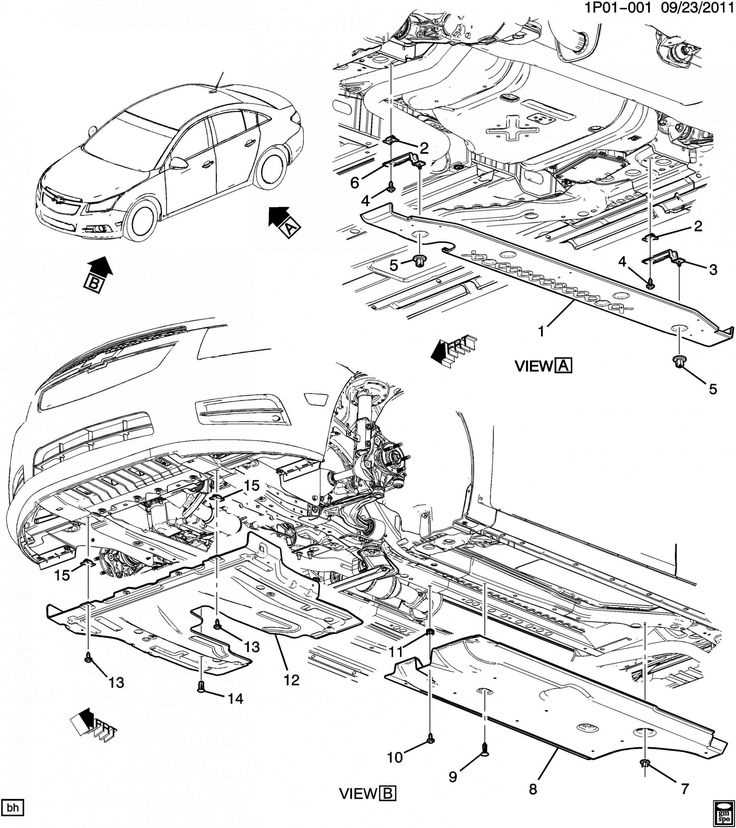
Body Panels and Exterior Component Layout
This section delves into the arrangement of outer structural elements and features of a compact vehicle, emphasizing their design and interrelationship. Understanding the positioning and functionality of these components is crucial for both aesthetic appeal and aerodynamic performance. The layout significantly influences the overall integrity and safety of the automobile.
Overview of Exterior Elements
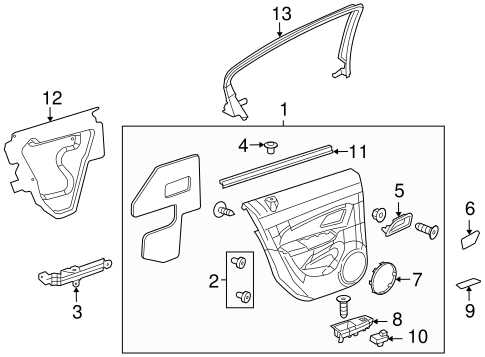
The outer panels serve as a protective layer, shielding internal mechanisms from environmental factors. They are designed not only for durability but also to enhance visual characteristics. Key elements include the front and rear fascias, fenders, and door assemblies, which contribute to the vehicle’s silhouette and style.
Component Interconnections
Each external element is interconnected, playing a pivotal role in the vehicle’s structural framework. For instance, the alignment of fenders with the body ensures seamless integration, while the precision of the door fits maintains security and ease of access. Proper installation and maintenance of these components are essential for optimal performance and longevity.
HVAC System: Main Parts and Position
The heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system is a crucial component in ensuring comfort within a vehicle’s interior. This system is designed to regulate temperature and air quality, providing a pleasant environment for passengers. Understanding the primary elements and their locations can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
The core components of the HVAC system include the blower motor, evaporator, heater core, and various ducts. The blower motor is responsible for circulating air throughout the cabin, while the evaporator cools the incoming air. Positioned within the engine compartment, the heater core warms the air before it enters the cabin. Additionally, an array of ducts directs airflow, ensuring even distribution throughout the vehicle.
Each element plays a specific role, and their strategic positioning allows for optimal performance. For instance, the evaporator is typically located near the firewall, while the blower motor is often situated behind the dashboard. Understanding these placements aids in troubleshooting and repairs, ensuring that the HVAC system functions efficiently.