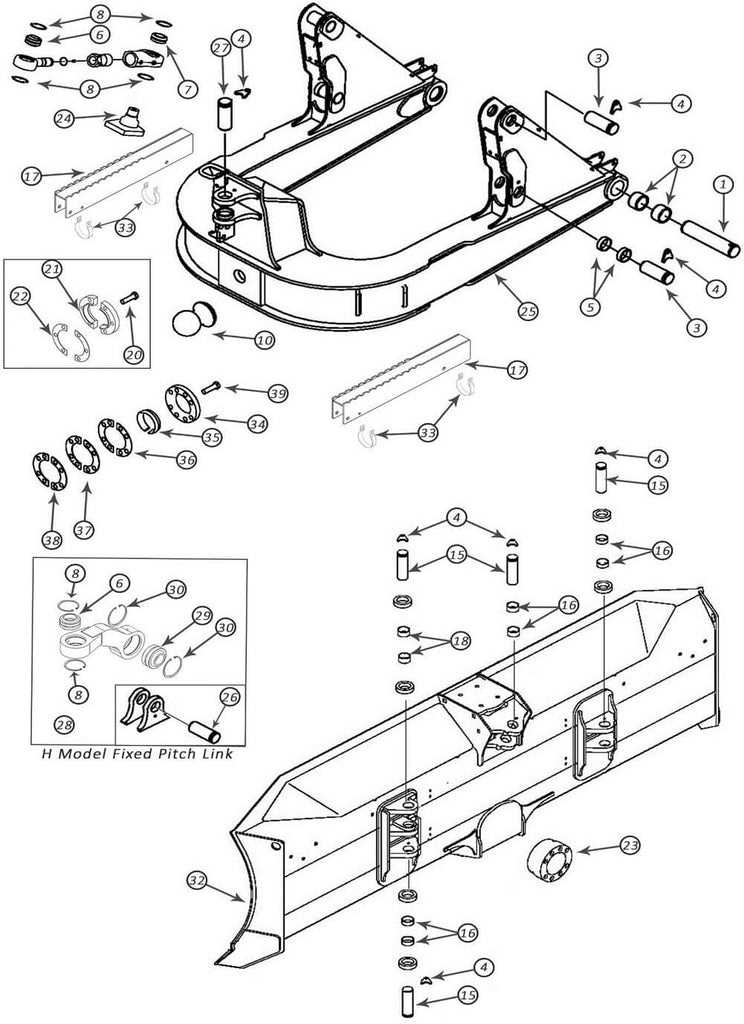
When maintaining or repairing agricultural machinery, understanding its internal structure is crucial for efficient operation. Knowing the arrangement and connections of various elements ensures smoother functioning, easier troubleshooting, and longer lifespan. This section provides a detailed look into how specific pieces come together to form a reliable, high-performance machine.
Exploring the assembly of these elements reveals how each piece is designed to work in harmony with others, ensuring seamless operation. Whether it’s regular upkeep or necessary repairs, having a clear overview of the setup makes it easier to address issues and maintain optimal performance. This guide is intended to help users visualize the connections and understand how everything fits together, improving overall efficiency.
For those looking to enhance their knowledge or perform hands-on work, this breakdown will serve as a useful tool. By delving deeper into the structure, users can more confidently approach any maintenance or repair tasks with the insight provided here.
Overview of John Deere 170 Components
The machine in question consists of several interconnected elements that work together to ensure efficient performance and smooth operation. Understanding the key structures and how they function will help users maintain and repair the equipment when necessary. Each element is engineered for durability and to fit seamlessly within the overall system.
| Component | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | A powerful mechanism designed to drive the machine’s operation, providing the necessary force to handle various tasks. | ||||||||
| Transmission | This system is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring controlled movement and speed. | ||||||||
| Chassis | The robust frame that supports the overall structure, giving it stability and strength during usage. | ||||||||
| Steering System | A set of components allowing precise directional control, providing ease of maneuverability. |
| Component | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | The foundation of the motor, housing the cylinders and other vital mechanisms for power generation. | ||||||||
| Pistons | Movable components within the cylinders, responsible for converting fuel combustion into mechanical movement. | ||||||||
| Crankshaft | A rotating mechanism that transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational force, driving the engine. | ||||||||
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of valves, regulating the intake of air
Transmission System OverviewThe transmission system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient power delivery from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth movement and control. It is responsible for managing gear changes and optimizing the performance of the vehicle, adapting to various terrains and workloads. Understanding the components involved in this process can help in maintaining and troubleshooting the system effectively. Key Functions: The transmission’s primary function is to modulate speed and torque, allowing the vehicle to operate efficiently under different conditions. It also works to prevent engine overload by adjusting the power output according to the load and driving situation. Components Overview: Various gears, linkages, and mechanisms are involved in the process, all working together to ensure precise operation. Regular maintenance of these parts can significantly extend the system’s lifespan and improve overall performance. Electrical Components and WiringThe electrical system plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functionality of various equipment, managing power distribution and connecting key features. A well-maintained wiring setup ensures smooth operation and prevents potential issues related to performance or safety. Main Electrical ConnectionsSeveral essential elements are involved in the electrical configuration, ranging from wiring to specific connectors. Ensuring that all cables are properly routed and securely attached helps in avoiding malfunctions and prolongs the system’s lifespan.
Wiring Maintenance TipsMaintaining the electrical components requires regular inspection and preventive care. Common areas to check include the condition of the cables, tightness of connections, and the integrity of the insulation.
Steering Mechanism LayoutThe steering system plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth and precise maneuvering of any vehicle. Understanding the structure of this system is essential for proper maintenance and efficient operation. Below is an overview of how various components work together to control the vehicle’s direction, ensuring responsive handling and stability during movement. Main Components Overview
How Steering Functions
|