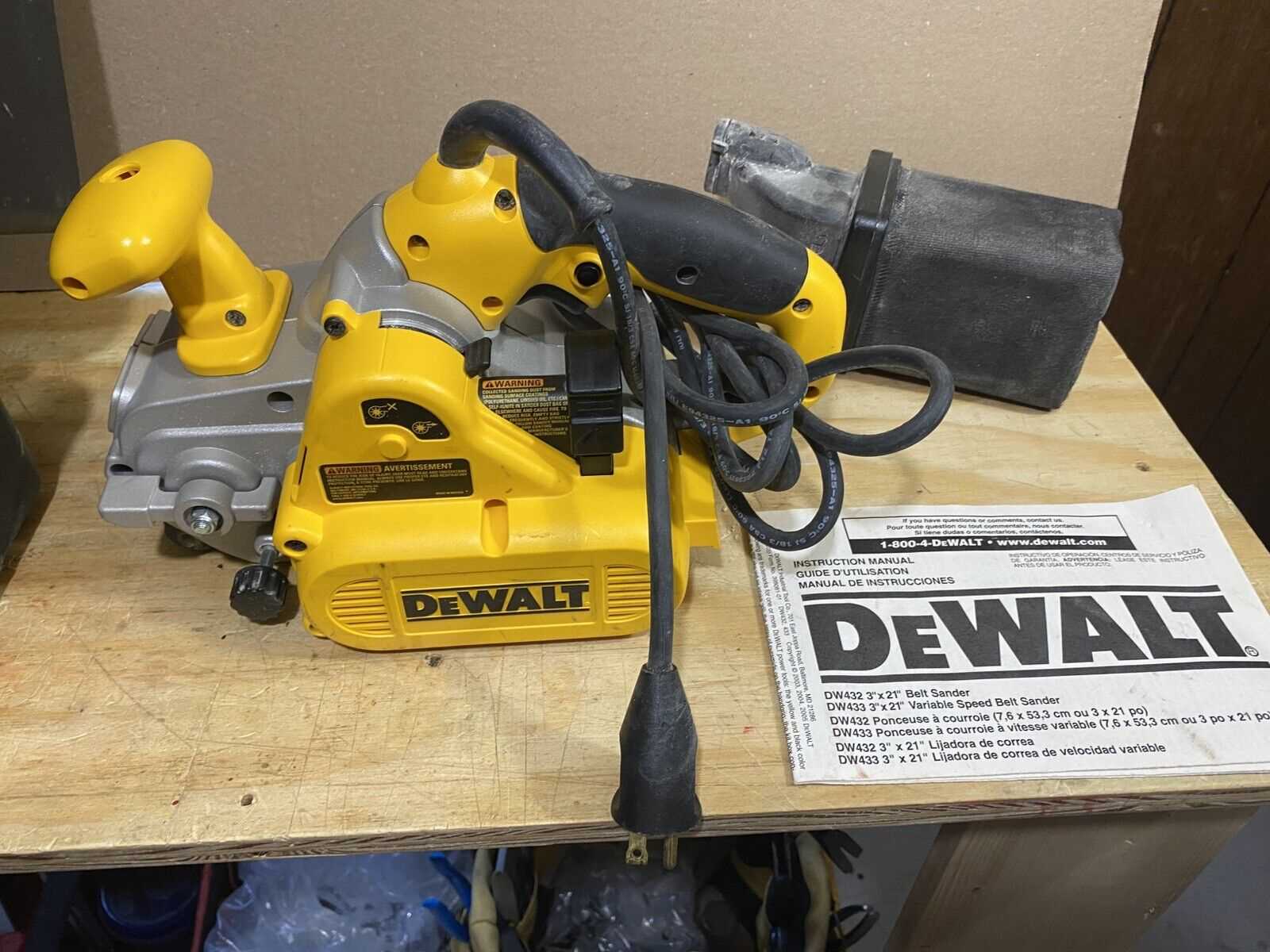
Understanding the DW433 Belt Sander
The belt sander is a powerful and versatile tool designed for smoothing large surfaces with efficiency. It’s ideal for projects requiring precision and durability, providing consistent results on wood, metal, and other materials. The key to understanding this tool lies in its ability to remove material quickly and its adaptability to various tasks.
Several important features make it a standout in its category:
- High-speed operation for faster material removal
- Adjustable tracking for stable belt alignment
- Ergonomic design for comfortable use during extended periods
- Reliable motor performance that maintains speed under load
By familiarizing yourself with these characteristics, you can maximize the tool’s efficiency in different applications. It’s essential to regularly maintain and check its components to ensure optimal performance.
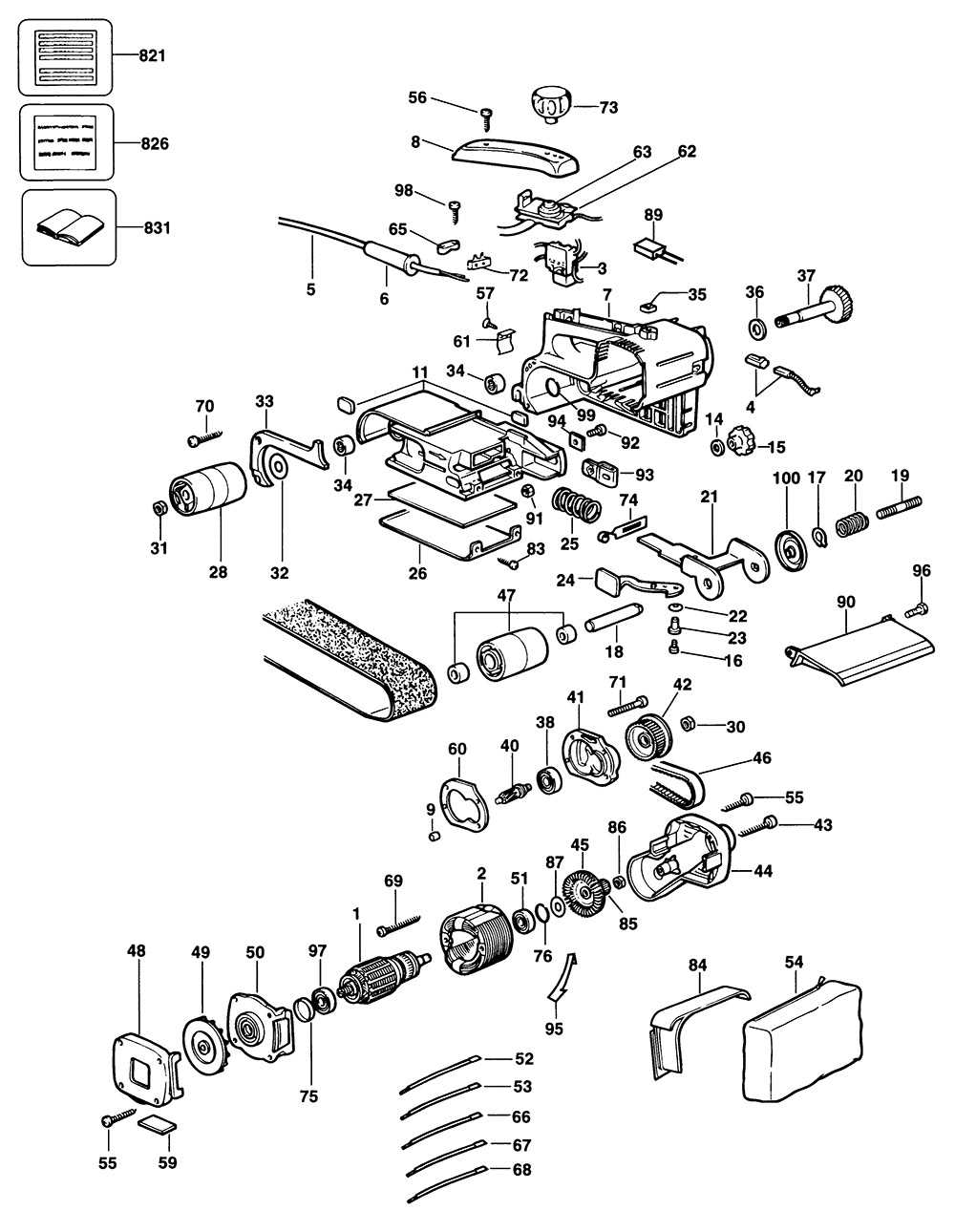
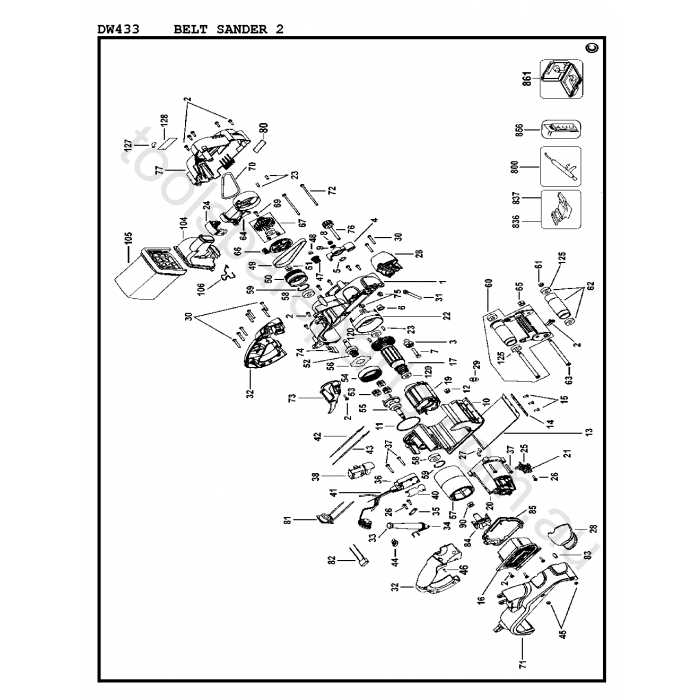
Main Components of the Dewalt DW433
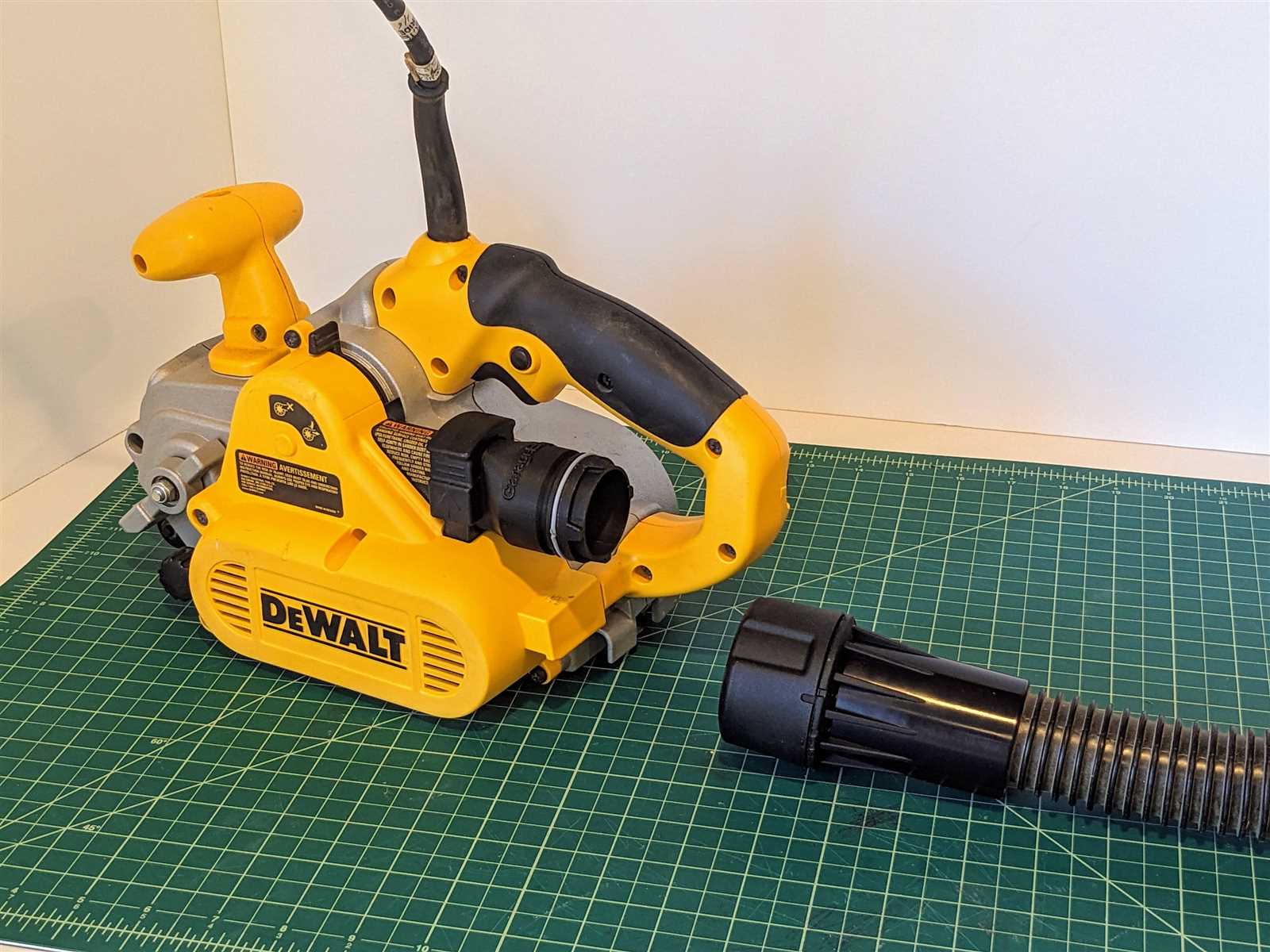

This tool consists of several critical elements that ensure its smooth operation and functionality. Each component plays a unique role in delivering efficiency and durability, working together to perform tasks efficiently. Understanding these parts helps in better maintenance and performance.
- Motor Assembly: The engine that drives the device, providing the power required for continuous performance.
- Drive Belt: A crucial part that transfers motion between different sections, allowing coordinated movement during use.
- Roller System: This set of rollers ensures smooth surface contact and consistent operation while moving the belt.
- Tracking Knob: This element adjusts the alignment of the belt, ensuring stability during use.
- Dust Collection Port: Designed to channel debris away, keeping the workspace cleaner and enhancing visibility.
Replacing the Sanding Belt
Changing the sanding belt is an essential maintenance step to keep your tool operating smoothly. Over time, the belt can wear out or become damaged, affecting performance. By regularly replacing it, you ensure optimal efficiency and finish quality during sanding tasks.
Steps to Replace the Belt
- Unplug the sander to ensure safety during the process.
- Locate the tension release lever on the side of the tool.
- Pull the lever to release the tension, allowing the old belt to slide off.
- Carefully place the new sanding belt, ensuring it aligns properly with the rollers.
- Push the tension lever back into place to secure the new belt.
- Plug the sander back in and test to ensure the belt moves smoothly.
Maintenance Tips
- Inspect the belt for wear before each use.
- Always ensure the belt is properly aligned to avoid uneven sanding.
- Store the tool in a dry place to prevent moisture damage to the belt.
Exploring the Motor Assembly

The motor assembly is a vital component in any handheld tool, ensuring smooth operation and consistent power delivery. It drives the belt mechanism, converting electrical energy into mechanical movement, which in turn allows for efficient cutting, sanding, or other tasks. Understanding how this assembly is structured can help users maintain optimal performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
The motor is composed of several interconnected elements that work together. Below are the key parts involved in this process:
- Rotor and Stator: These elements work together to generate the magnetic field that powers the motor, causing rotational movement.
- Brushes: Responsible for transferring electrical current to the motor’s moving components, these wear out over time and may need replacement.
- Bearings: Positioned on both ends of the motor shaft, bearings ensure smooth, low-friction rotation, reducing wear and tear on the system.
- Cooling Fan: Mounted near the motor, this helps prevent overheating by keeping the system cool during prolonged use.
By keeping these components in good condition, the overall motor assembly remains efficient, allowing for longer tool life and better performance.
Guide to the Dust Collection System
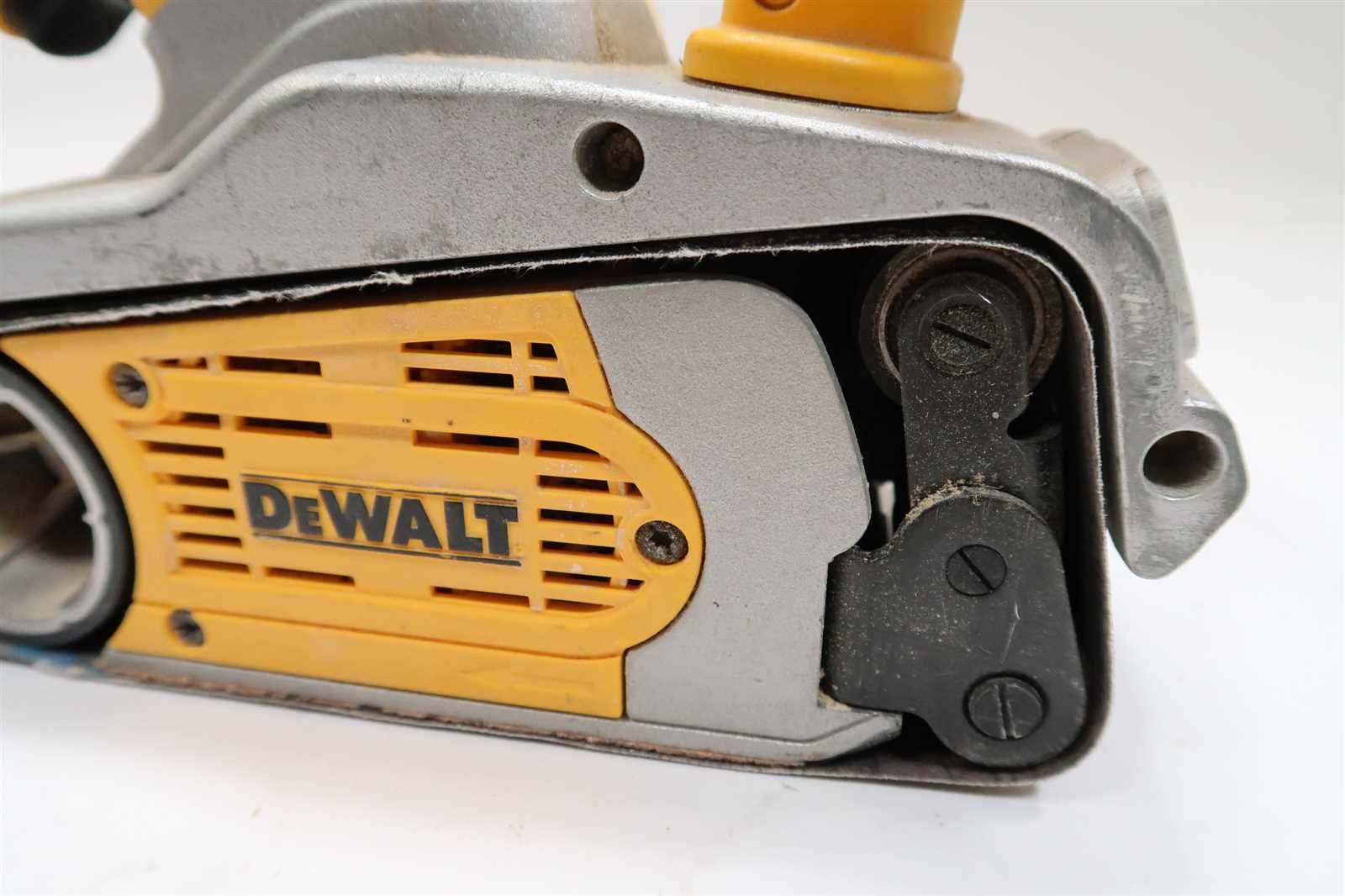

The dust collection system is a crucial component in any woodworking setup, ensuring a clean and safe working environment. This system effectively captures and removes airborne particles generated during various tasks, preventing dust accumulation that can lead to health issues and equipment damage.
Understanding the components and functionality of the dust collection system allows users to optimize its performance. Key elements include the vacuum mechanism, filters, and collection bags. Each part plays a significant role in maintaining efficient airflow and trapping fine debris.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep the dust collection system operating smoothly. This involves cleaning or replacing filters, checking for clogs, and ensuring that all connections are secure. Proper upkeep enhances the system’s efficiency and extends its lifespan.
For optimal performance, users should also consider the size and layout of their workspace. Positioning the collection system strategically can maximize its effectiveness, minimizing the spread of dust and enhancing the overall cleanliness of the area.
Handle and Grip Parts Breakdown
The handle and grip components play a crucial role in ensuring a secure and comfortable hold during operation. These elements are designed to enhance user control and stability while using the tool. Understanding the various elements that make up this section can aid in maintenance and replacement when necessary.
Key components of the handle include the main grip, which is often ergonomically shaped for comfort, and the trigger area, which provides easy access for operation. Additional features may consist of textured surfaces that enhance grip security and reduce slippage, contributing to safer handling. Proper inspection and upkeep of these elements are essential for optimal performance.
Tensioning and Tracking System Components
The tensioning and tracking mechanism plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. This system is designed to maintain appropriate tension on the belt, allowing for efficient operation while minimizing wear and tear. Understanding the various elements involved in this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Adjustable Tensioner: This component allows users to modify the tension applied to the belt. A correctly adjusted tensioner prevents slippage and prolongs the lifespan of the belt.
Tracking Roller: The tracking roller guides the belt along its intended path. Proper alignment of this component ensures that the belt remains centered, reducing the risk of damage and enhancing operational efficiency.
Tension Indicator: This feature provides visual feedback on the tension level of the belt. By monitoring this indicator, users can easily determine when adjustments are necessary, helping to maintain peak performance.
Mounting Brackets: These structures secure the tensioning and tracking components in place. Sturdy brackets are essential for maintaining the integrity of the system, preventing any movement that could lead to misalignment.
Spring Mechanism: Often integrated within the tensioning system, the spring ensures consistent pressure is applied to the belt. This component compensates for any slack, ensuring reliable operation under varying load conditions.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are crucial for the smooth operation of the equipment. By ensuring that each part is functioning optimally, users can enhance performance and extend the lifespan of the machine.
Commonly Replaced Parts for Maintenance

Regular upkeep of power tools is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Certain components are frequently exchanged to ensure machines run smoothly and efficiently. Understanding these key elements can assist users in maintaining their equipment effectively.
Essential Components to Consider
- Blades: Over time, cutting edges can dull or become damaged, necessitating replacement for effective operation.
- Brushes: Worn brushes can lead to reduced power and efficiency; regular checks and replacements are advisable.
- Filters: Air and dust filters accumulate debris, impacting airflow and tool performance, making periodic changes important.
- Gaskets: Seals can wear out, leading to leaks or decreased efficiency, highlighting the need for timely replacements.
- Switches: Faulty switches can interrupt power supply, so ensuring they are in good condition is crucial.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect all components for wear and tear.
- Keep a maintenance log to track replacements and service intervals.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for replacement intervals.
- Purchase quality replacements to ensure compatibility and performance.
Exploded View of Internal Mechanisms

The exploded representation of internal components offers a detailed insight into the intricate assembly and functioning of the device. This visualization helps in understanding how different elements interact and contribute to the overall performance.
Each part plays a crucial role in the operation, and recognizing their positions and connections is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting. Here are some key elements typically illustrated in such views:
- Motor Assembly: The heart of the device, responsible for providing power.
- Gear System: Transfers motion and adjusts speed for various applications.
- Control Switch: Allows users to manage power and speed settings effectively.
- Housing: Protects internal components and ensures user safety.
- Cooling Mechanism: Prevents overheating during extended use.
Understanding these components is essential for effective repair and enhancement of the device’s capabilities. An exploded view not only simplifies the identification of each part but also aids in visualizing the assembly process.
Steps to Access the Roller Bearings
Accessing the roller components requires a systematic approach to ensure safety and efficiency. Proper handling and understanding of the assembly will facilitate a smoother process and help prevent damage to the unit.
1. Gather Necessary Tools: Before starting, collect all essential tools, such as screwdrivers, wrenches, and any specialized equipment needed for disassembly.
2. Disconnect Power Source: Ensure the device is unplugged or disconnected from any power supply to prevent accidental activation during maintenance.
3. Remove Housing or Cover: Carefully detach the outer casing or cover, which may be secured with screws or clips. Store these fasteners in a safe place for reassembly.
4. Locate the Bearings: Once the cover is removed, identify the roller bearings within the mechanism. Familiarize yourself with their position to facilitate easy access.
5. Detach Bearings: Using appropriate tools, gently remove the bearings from their seating. Be cautious not to apply excessive force, as this may cause damage.
6. Inspect Components: After removal, examine the roller bearings for wear or damage. This step is crucial for determining whether replacement or further maintenance is necessary.
Detailed View of the Power Switch
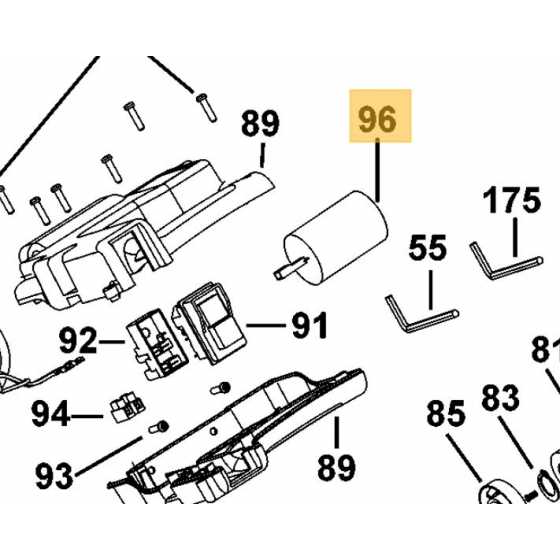
The power switch is a crucial component that facilitates the operation of various tools. Its design and functionality play a significant role in the user experience, ensuring that the device operates efficiently and safely. Understanding its structure helps in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Functionality and Operation
This element serves as the main control for activating and deactivating the tool. It typically includes a simple toggle mechanism that allows users to switch the device on or off easily. The reliability of this part is essential for optimal performance, as any malfunction can lead to operational failures.
Common Issues and Solutions
Users may encounter issues such as sticking or unresponsive switches over time. Regular cleaning and inspection can prevent dirt buildup that may affect its functionality. If problems persist, replacing the switch may be necessary to restore full operational capacity.
Troubleshooting Issues with DW433 Parts
When dealing with challenges related to tool components, it’s crucial to understand common problems and their solutions. This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving typical issues that users may encounter, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the equipment.
Common Problems and Symptoms
- Inconsistent performance during operation
- Unusual noises or vibrations while in use
- Overheating or excessive wear of specific components
- Difficulty in achieving the desired results
Steps to Resolve Issues
- Inspect all components for signs of damage or wear.
- Ensure that all connections are secure and free from debris.
- Lubricate moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Replace any worn or damaged items promptly to prevent further issues.