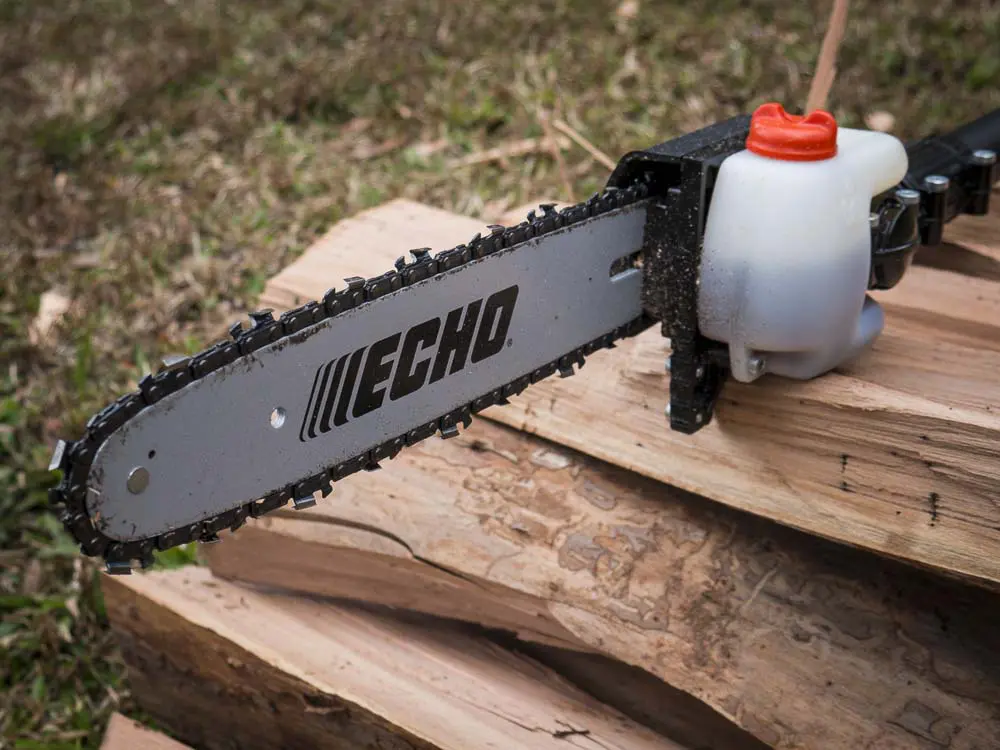

The intricate design of machinery often requires a detailed exploration of its individual elements. Analyzing the configuration of these components allows users to gain insights into the functionality and maintenance of the equipment. This examination is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
In this section, we will delve into the arrangement and roles of various elements within the system. By understanding how each part interacts and contributes to the overall operation, users can troubleshoot issues more effectively and implement necessary repairs.
Through a comprehensive breakdown, we aim to equip users with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of their equipment. This understanding fosters confidence in handling maintenance tasks, ultimately leading to improved reliability and efficiency.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential components that make up the specified model. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective maintenance, troubleshooting, and ensuring optimal performance. Each component plays a vital role in the functionality of the device, and recognizing them will enhance the user’s experience.
Key Components Overview
In order to gain insight into the internal structure, the following key elements should be examined:
- Engine: The heart of the system, responsible for generating power.
- Fuel System: Comprising the fuel tank, lines, and filters, it ensures a steady supply of energy.
- Ignition System: Vital for initiating combustion, this includes spark plugs and ignition coils.
- Cooling System: Prevents overheating, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Exhaust System: Facilitates the expulsion of combustion gases, critical for performance.
Functionality of Each Element
Understanding how each component functions is essential for effective operation:
- Engine: Converts fuel into mechanical energy, driving the entire system.
- Fuel System: Filters and delivers fuel to the engine, affecting efficiency.
- Ignition System: Creates the spark necessary for combustion, influencing power output.
- Cooling System: Regulates temperature to prevent damage, ensuring reliability.
- Exhaust System: Manages the release of gases, impacting performance and environmental compliance.
Maintenance Tips

Regular upkeep of the essential components can enhance performance and longevity:
- Check and replace filters regularly to maintain fuel efficiency.
- Inspect ignition components for wear to ensure reliable starting.
- Monitor the cooling system for leaks or blockages.
- Keep the exhaust system clear of obstructions to prevent back pressure.
By understanding the various elements and their functions, users can make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repairs, ultimately leading to improved performance and reliability.
Overview of Components and Functions

This section provides a comprehensive look at the various elements and their respective roles within the equipment. Understanding these components is crucial for effective operation and maintenance, as each element contributes to the overall functionality and efficiency of the machine.
Key components include:
- Engine: The power source that drives the entire system, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Throttle Control: A mechanism that regulates the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine, affecting speed and power.
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores fuel needed for operation, designed for easy access and refueling.
- Starter System: The electrical components responsible for initiating engine operation, including the battery and ignition coil.
- Cooling System: A series of parts designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating.
- Exhaust System: Components that direct and manage emissions from the engine, ensuring efficient expulsion of gases.
In addition to these main elements, other features enhance performance:
- Air Filter: Keeps debris from entering the engine, promoting longevity and efficiency.
- Vibration Dampers: Minimize mechanical vibrations, contributing to user comfort and equipment stability.
- Handle Assembly: Provides a means for the operator to maneuver the equipment safely and comfortably.
Each component plays a significant role, and understanding their functions is essential for troubleshooting and effective use.
Detailed Parts Breakdown
This section provides a comprehensive analysis of the various components that make up the equipment. Understanding the individual elements is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. Each segment plays a vital role in the overall functionality, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Component Overview

The following table outlines the key elements of the device, including their descriptions and functions. Familiarizing yourself with these components can aid in troubleshooting and enhancing the equipment’s longevity.
| Component Name | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | The outer shell that protects internal parts. | Provides structural integrity and safety. |
| Motor | Electric engine that powers the tool. | Generates the necessary force for operation. |
| Fuel Tank | Container for storing fuel. | Supplies energy to the engine for functioning. |
| Air Filter | Filter that cleans incoming air. | Prevents debris from entering the motor. |
| Blade Assembly | Cutting mechanism located at the front. | Performs the primary task of cutting through materials. |
Maintenance Tips
Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance performance and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Ensure that each part is clean and functioning correctly to avoid operational issues.
How to Read the Diagram

Understanding a visual representation of components is crucial for effective maintenance and repair. This section will guide you through essential techniques for interpreting such illustrations, making it easier to identify and address issues.
Familiarize with Symbols and Labels
Before diving into the details, take a moment to recognize the various symbols and annotations used in the illustration. Each symbol represents a specific part or function. Common elements include:
- Shapes: Circles may indicate connection points, while squares often represent fixed components.
- Lines: Solid lines typically denote physical connections, whereas dashed lines might suggest optional paths or relationships.
- Labels: Text descriptions alongside symbols provide vital information regarding specifications or configurations.
Follow the Flow of Information
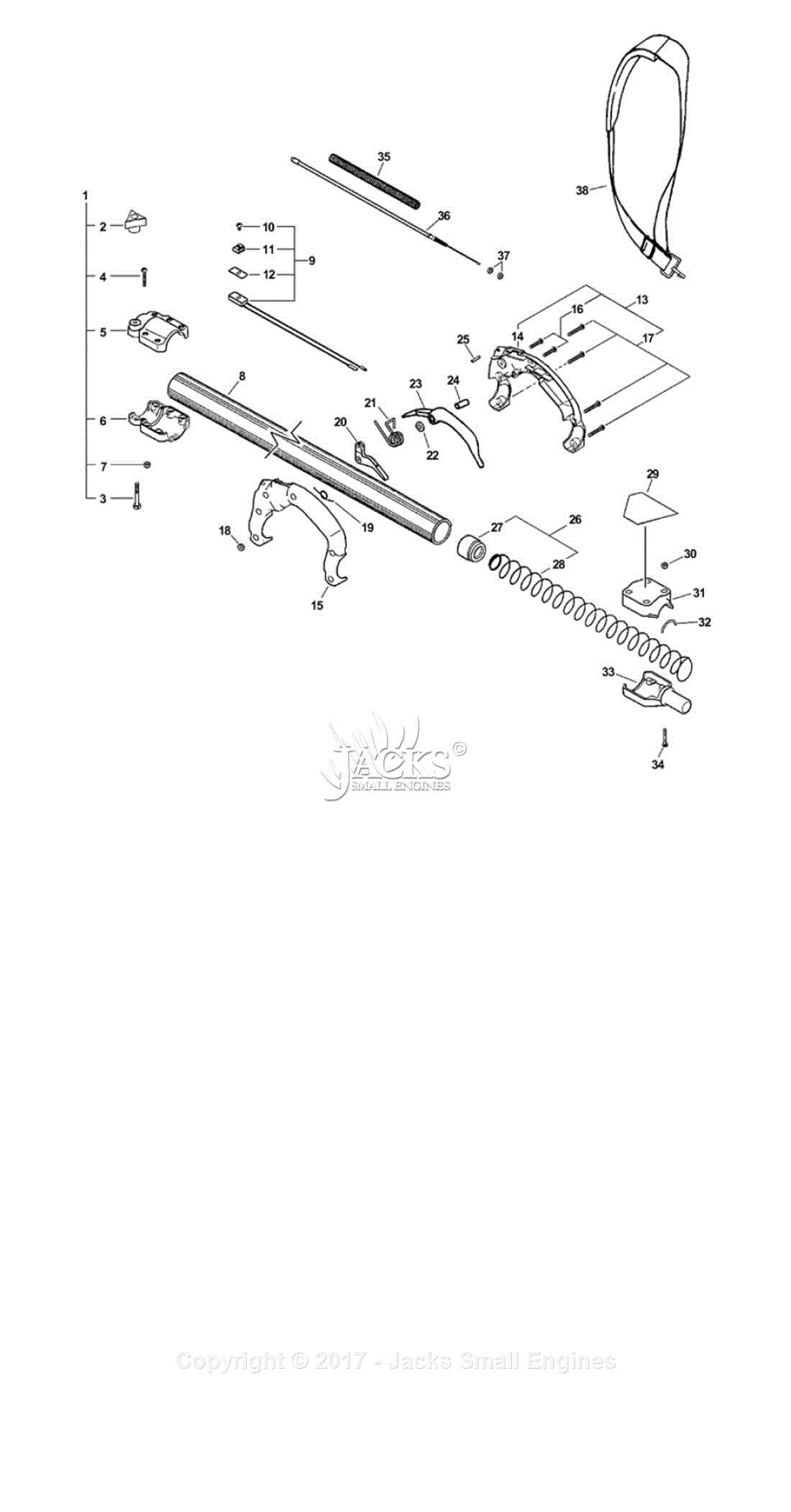
Once you are familiar with the symbols, focus on the flow of information. This will help you understand how components interact with each other:
- Identify the starting point, often marked by a power source or control unit.
- Trace the connections to see how energy or signals move between parts.
- Note any junctions or branching points, as these can indicate where decisions or diversions occur in the system.
By applying these strategies, you can effectively navigate through the complex relationships depicted, leading to more successful troubleshooting and repairs.
Common Replacement Parts
When maintaining outdoor power equipment, certain components often require replacement due to wear and tear. Understanding the most frequently needed items can help ensure optimal performance and longevity of the device.
Frequently Replaced Components
- Filters: Regularly replacing air and fuel filters is essential for proper airflow and fuel efficiency.
- Blades: Dull or damaged blades can significantly affect cutting performance; replacing them ensures a clean cut.
- Spark Plugs: Worn spark plugs can lead to poor ignition and reduced engine efficiency.
- Fuel Lines: Cracked or leaking fuel lines can cause operational issues; replacement helps maintain fuel delivery.
- Drive Belts: Worn or frayed drive belts may lead to power transfer problems, impacting the overall functionality.
Essential Maintenance Tips
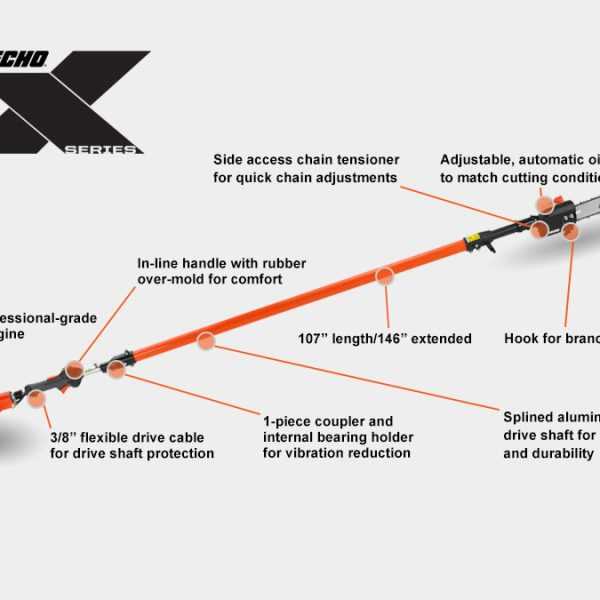
- Regularly check and replace filters to keep the engine running smoothly.
- Inspect blades for damage and sharpen or replace them as needed.
- Ensure spark plugs are cleaned or replaced to maintain optimal ignition.
- Examine fuel lines for signs of wear and replace them to prevent leaks.
- Monitor drive belts for any signs of deterioration and replace them promptly.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and performance of your equipment requires regular attention and care. By following a few essential practices, you can significantly extend its lifespan and maintain optimal functionality. These maintenance strategies not only improve performance but also prevent potential issues before they arise.
Regular Cleaning is crucial for the upkeep of any machinery. Accumulated dirt and debris can impede functionality and cause wear over time. Make it a habit to clean your device after each use, focusing on all accessible areas.
Routine Inspections help identify any signs of wear or damage early on. Check for loose screws, frayed wires, or any other abnormalities that could affect operation. Timely detection allows for prompt repairs, preventing more significant problems in the future.
Lubrication is another vital aspect of maintenance. Applying appropriate lubricants to moving parts reduces friction and minimizes wear, contributing to smoother operation and extending the lifespan of components.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines for maintenance schedules and practices. These recommendations are designed to optimize performance and ensure safety. Adhering to these guidelines helps you understand the specific needs of your equipment.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can enhance the durability and efficiency of your machinery, ensuring it remains reliable for years to come.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing frequent problems requires a systematic approach to identify and rectify faults in machinery. By understanding typical symptoms and their underlying causes, users can efficiently restore functionality and ensure optimal performance.
When faced with operational difficulties, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve issues effectively:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Device won’t start | Battery failure or disconnection | Check battery charge and connections; replace battery if necessary. |
| Inconsistent performance | Clogged air filter or damaged components | Inspect and clean air filters; examine for any physical damage. |
| Unusual noises | Loose parts or worn bearings | Tighten any loose screws; lubricate moving parts as needed. |
| Overheating | Poor ventilation or excessive load | Ensure adequate airflow; reduce workload and allow cooling periods. |
Finding Authentic Replacement Parts

When maintaining outdoor equipment, sourcing genuine components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Identifying authentic substitutes ensures that the machinery operates as intended, minimizing risks of malfunction and enhancing efficiency. This section provides guidance on how to effectively locate these essential elements.
Where to Look
Several avenues can be explored to find reliable replacements:
- Official Retailers: Authorized dealers often stock verified products that meet quality standards.
- Manufacturer Websites: Visiting the original manufacturer’s site can provide access to the latest offerings and specifications.
- Reputable Online Marketplaces: E-commerce platforms with positive reviews can be excellent resources for genuine components.
Verification Tips
To ensure the authenticity of the items, consider the following recommendations:
- Check for Certification: Authentic parts typically have specific markings or certifications from the manufacturer.
- Read Customer Reviews: Previous buyers’ experiences can reveal the reliability of both the product and the seller.
- Compare Prices: If a deal seems too good to be true, it may be a sign of counterfeit goods. Always verify against standard pricing.
Tools Needed for Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing outdoor equipment, having the right instruments is essential. Proper tools not only facilitate efficient repairs but also ensure safety and effectiveness during the process. Below is a guide to the essential tools required for successful repairs.
Essential Hand Tools
- Screwdrivers: A set of both flathead and Phillips screwdrivers in various sizes.
- Wrenches: Adjustable and socket wrenches for tightening or loosening nuts and bolts.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and slip-joint pliers for gripping and manipulating small parts.
- Cutting Tools: A utility knife or wire cutters for precise cuts.
Power Tools
- Drill: A cordless drill for making holes or driving screws efficiently.
- Angle Grinder: For cutting and grinding materials when necessary.
- Impact Wrench: Useful for loosening stubborn bolts with high torque.
Having these tools at hand will greatly assist in conducting repairs and maintaining the longevity of your equipment.
Assembly and Disassembly Guidelines

This section provides essential instructions for the proper assembly and disassembly of the equipment. Following these guidelines ensures the longevity and efficient operation of the machine while preventing potential damage during maintenance procedures.
Before beginning the assembly or disassembly process, it is crucial to prepare adequately. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Gather all necessary tools and components required for the task.
- Ensure a clean and organized workspace to facilitate efficient work.
- Refer to the user manual for specific guidelines related to the model.
During disassembly, it is advisable to:
- Turn off the equipment and disconnect from any power source to ensure safety.
- Carefully remove any covers or panels using appropriate tools.
- Keep track of all screws and small parts, placing them in labeled containers for easy reassembly.
- Take notes or photos during the process to aid in reassembly.
For assembly, follow these steps:
- Begin by placing the components in their designated positions according to the layout.
- Secure all parts gently, ensuring not to overtighten and risk damage.
- Double-check connections and fittings before reattaching covers or panels.
- Conduct a thorough inspection once assembled to confirm everything is in order.
By adhering to these guidelines, the assembly and disassembly processes can be executed smoothly and effectively, enhancing the overall functionality of the equipment.
Resources for Further Information
For those seeking to deepen their understanding of equipment maintenance and component identification, numerous resources are available. These materials can provide insights into troubleshooting, maintenance procedures, and parts identification for various models.
Online Guides and Manuals
- Manufacturer websites often offer downloadable manuals and guides that cover operational details and maintenance tips.
- Specialized forums and online communities frequently discuss troubleshooting techniques and share personal experiences.
- YouTube channels dedicated to equipment repair provide visual tutorials that can enhance comprehension of complex processes.
Books and Publications
- Technical manuals and repair books provide comprehensive information about equipment care and maintenance best practices.
- Industry magazines often feature articles on new technologies and maintenance strategies.
- Library resources may include historical references and guides that discuss various tools and their functions.