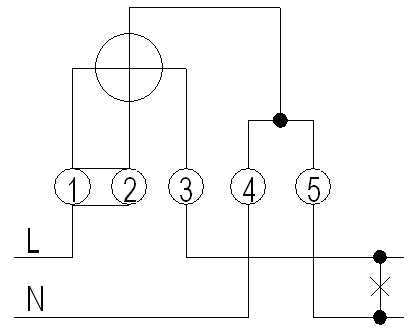
In the realm of energy consumption, the functionality and design of measuring devices play a crucial role. These instruments, which track and display usage, consist of various elements that work in harmony. Each component contributes to the overall accuracy and efficiency of the system.
Familiarity with these individual elements can enhance comprehension of how energy usage is calculated and recorded. From display interfaces to internal mechanisms, understanding these aspects can empower users to make informed decisions regarding their consumption patterns.
Moreover, a clear grasp of the different components can facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance. Recognizing the significance of each part ensures that users can respond effectively to any issues that may arise, leading to better performance and longevity of the device.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential elements found within a measuring device used to track consumption. Each component plays a vital role in the overall functionality and accuracy of the device, contributing to its efficiency in monitoring usage.
| Component Name | Function |
|---|---|
| Display Unit | Shows the readings and data visually to the user. |
| Measurement Sensor | Captures the flow or consumption of energy. |
| Control Circuit | Regulates and processes the input from the sensor. |
| Power Supply | Provides the necessary energy for the device to operate. |
| Enclosure | Protects internal components from environmental factors. |
Main Functional Elements Overview
This section explores the essential components that contribute to the operation of a measurement device, highlighting their roles and interactions. Each element plays a pivotal part in ensuring accurate readings and reliable performance, forming a cohesive system that functions seamlessly.
Core Components
The primary elements include sensing units that capture data, processing units that interpret the information, and display systems that present results. Together, they create a harmonious workflow, facilitating efficient monitoring and analysis.
Support Mechanisms
Additional mechanisms such as calibration systems and protective enclosures enhance the overall functionality. These elements ensure durability and accuracy, further refining the device’s capability to provide precise information over time.
How the Measurement Process Works
The process of quantifying energy consumption involves several critical components that work together seamlessly. Each element plays a unique role in ensuring accurate readings, allowing users to monitor usage effectively. Understanding how these components interact helps in appreciating the intricacies of energy tracking.
Key Components of the Measurement System
The system consists of various elements that contribute to the overall functionality. Each component has a specific purpose, from capturing energy flow to processing and displaying the results. Below is a summary of these essential parts:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensor | Detects the flow of energy |
| Processor | Interprets data from the sensor |
| Display | Shows the measurement results to the user |
Operational Workflow
The entire process begins with the detection of energy movement, where sensors capture relevant data. This information is then sent to a processing unit, which analyzes the inputs and converts them into comprehensible figures. Finally, the results are displayed for the user, allowing for informed decision-making regarding energy usage.
Types of Electric Meters Explained
Understanding the various categories of energy measurement devices is essential for grasping how they function and their applications in daily life. Each variant offers unique features and benefits tailored to specific needs, making it important to recognize their distinctions.
Analog Devices
These traditional tools utilize mechanical components to display usage through a rotating dial. They are known for their reliability and simplicity, making them suitable for many residential settings.
Digital Instruments
Modern counterparts use electronic displays to present data. They often include advanced functionalities such as real-time monitoring and data logging, which enhance user interaction and energy management.
Detailed Component Functions
This section explores the essential roles of various elements within a measurement device, highlighting their specific contributions to the overall functionality.
- Measurement Sensor: Captures the necessary data regarding consumption, ensuring accurate readings.
- Microcontroller: Processes incoming signals and translates them into readable information for users.
- Display Unit: Provides visual representation of the data, allowing for easy interpretation by the user.
- Communication Module: Enables the transmission of data to external systems for monitoring and analysis.
- Power Supply: Ensures all components receive the necessary energy to operate effectively.
Understanding these functions helps in grasping how each element interacts to provide reliable information about consumption levels.
Safety Features in Electric Meters
Devices used for monitoring energy consumption are equipped with various protective mechanisms to ensure user safety and prevent hazards. These features play a crucial role in safeguarding both the equipment and the individuals interacting with them.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Automatically disconnects the device to prevent damage from excessive current. |
| Surge Protection | Shields against voltage spikes that can cause malfunctions or failures. |
| Insulation | Prevents accidental contact with live components, reducing shock risks. |
| Automatic Shutoff | Turns off the device in case of abnormal operation or faults. |
Installation Process for Electric Meters
The process of setting up a measuring device involves several crucial steps that ensure proper functionality and safety. Initially, it is essential to prepare the site, ensuring that all necessary tools and equipment are readily available.
Next, one should carefully assess the location to confirm that it meets the required standards for installation. This includes checking for adequate space, accessibility, and compliance with local regulations. Proper positioning is vital for efficient operation and maintenance.
After confirming the site conditions, the next step involves securely mounting the device, ensuring it is stable and positioned correctly for accurate readings. Connections to power sources must be executed with precision, following all safety protocols to prevent hazards.
Finally, conducting tests to verify functionality is crucial. This includes checking the accuracy of readings and ensuring that all connections are secure. Following these steps helps guarantee a successful installation and reliable performance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your measurement device involves regular upkeep and attention. By following a few straightforward guidelines, you can enhance its performance and extend its lifespan significantly.
Regular Cleaning
- Dust and debris can accumulate and affect functionality.
- Use a soft cloth and mild cleaner to gently wipe surfaces.
Check Connections
- Inspect all connections periodically to ensure they are secure.
- Look for any signs of wear or damage that may need addressing.
By implementing these practices, you can contribute to the efficiency and longevity of your device, ensuring reliable readings for years to come.
Common Issues and Solutions
This section addresses frequent challenges encountered in the operation of measurement devices and provides practical remedies. Understanding these common problems can lead to improved performance and longevity of the equipment.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Inaccurate readings | Calibration error | Perform a recalibration using the manufacturer’s guidelines. |
| Device not responding | Power supply failure | Check connections and replace the power source if necessary. |
| Intermittent functionality | Loose connections | Inspect all wiring and secure any loose ends. |
| Display issues | Screen malfunction | Replace the display unit following the provided instructions. |
| Excessive wear | Overuse or environmental factors | Limit usage frequency and protect from harsh conditions. |
Innovations in Meter Technology
Recent advancements in measuring devices have transformed how we monitor and manage consumption. These developments aim to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and user experience, reflecting the growing demand for smarter solutions in various applications.
Smart Features and Connectivity
Modern devices now incorporate a range of intelligent functionalities that facilitate real-time monitoring and control. Key features include:
- Wireless communication for remote access and data transmission
- Integration with home automation systems
- Mobile applications for user-friendly interface and management
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Recent innovations have also focused on enhancing energy efficiency. This is achieved through:
- Advanced algorithms for precise consumption analysis
- Adaptive technologies that adjust to changing conditions
- Support for renewable energy sources and smart grid interactions
Future Trends in Metering Solutions
The landscape of energy measurement is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and growing demands for efficiency. As industries and households seek smarter options, innovative approaches are becoming central to the development of measurement devices. These enhancements are not only enhancing functionality but also promoting sustainability and user engagement.
One notable trend is the integration of smart technology, enabling devices to communicate in real-time with management systems. This connectivity facilitates immediate data analysis, allowing users to monitor consumption patterns and make informed decisions. Additionally, the rise of renewable energy sources is influencing the design of these tools, pushing for solutions that can seamlessly integrate with solar and wind technologies.
Another significant development is the emphasis on data security. With increasing reliance on digital platforms, safeguarding sensitive information is becoming paramount. Manufacturers are prioritizing secure communication protocols to ensure that user data remains protected against potential threats.
Moreover, user experience is being redefined. Intuitive interfaces and user-friendly applications are being developed to enhance interaction with measurement systems. This focus on accessibility empowers consumers, making them active participants in managing their energy use and promoting conservation efforts.