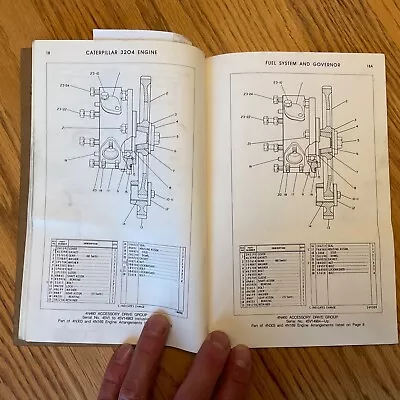
In this section, we will delve into the structure and layout of various mechanical assemblies commonly found in heavy-duty machinery. Understanding the individual elements and their interactions is crucial for maintaining and optimizing performance in industrial environments.
By examining the configuration and positioning of the key elements, operators and technicians can better assess the system’s functionality and ensure smooth operation. This knowledge aids in identifying potential areas that may require attention or replacement.
Furthermore, a detailed look at the interconnected elements provides insights into how they collectively contribute to the overall efficiency of the machinery. Proper maintenance and timely interventions can significantly extend the lifespan of these systems.
Overview of Key Components in the 4-Cylinder Diesel Power Unit

The internal structure of this 4-cylinder diesel power system is designed to ensure efficiency and durability. This section will outline the primary elements that contribute to its overall functionality, focusing on essential mechanical and operational features.
- Cylinder Block: The core frame that supports various mechanical parts and houses the pistons.
- Pistons: Integral to converting pressure into mechanical movement, the pistons play a crucial role in the system’s combustion process.
- Crankshaft: This rotating shaft transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational energy, driving other machinery parts.
- Fuel Injection System: A precise system responsible for delivering fuel into the combustion chambers, ensuring optimal performance.
- Main Parts of the Cat 3204 Engine
The structure of this machinery is composed of various essential elements that work together to ensure its reliable operation. Each component is designed to fulfill a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency and durability of the system. Understanding the primary components is crucial for maintaining and repairing the device efficiently.
Core Components Overview
The central unit includes vital sections that handle fuel combustion, mechanical motion, and heat management. These include mechanisms responsible for powering the system, along with parts that support air intake, fuel distribution, and temperature control.
Supporting Mechanisms
Alongside the primary components, several secondary systems assist in optimizing performance. These mechanisms help in lubrication, cooling, and minimizing wear and tear, ensuring that the machine runs smoothly under various conditions.
Understanding the Engine’s Fuel System
The fuel system plays a vital role in ensuring efficient performance and smooth operation. It is designed to deliver the right amount of fuel at the correct time, maintaining balance between power and efficiency. A deeper understanding of how fuel is processed and distributed can help identify potential issues and enhance overall maintenance practices.
Key Components of the Fuel System
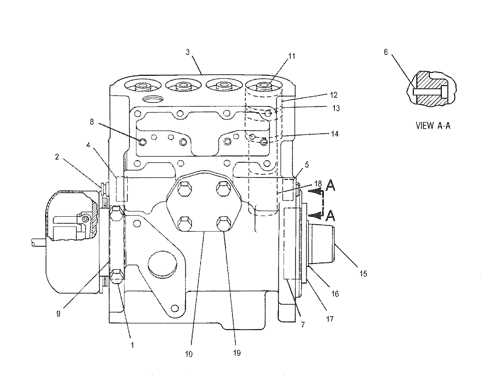
The fuel system is composed of various elements, each responsible for specific tasks. Fuel injectors play a crucial role in delivering fuel to the combustion chambers, while fuel pumps ensure the proper pressure is maintained. Additionally, fuel filters keep impurities from entering the system, protecting the components from damage.
Fuel Delivery Process
The process starts with the pump drawing fuel from the tank. The filtered fuel is then
Key Features of the Power Unit
The model under discussion is recognized for its efficiency, durability, and reliability. It is widely used in various heavy-duty applications, offering robust performance in demanding environments. This section will highlight the most notable characteristics that set this unit apart from others in its class.
- Fuel Efficiency: Designed to optimize fuel consumption, this unit ensures that operations can be carried out cost-effectively without compromising power.
- Durable Construction: Built with high-quality materials, the internal components are engineered to withstand wear and tear over prolonged use, making it a long-lasting choice.
- Compact Design: Despite its power, the unit maintains a compact form, making it suitable for a range of installations where space is limited.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: Its design allows for minimal maintenance intervals, reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency
Diagram of the Engine’s Cooling System
The cooling system plays a vital role in ensuring the proper functioning and temperature regulation of machinery. It operates by managing the heat produced during operation, maintaining optimal performance while preventing overheating. Understanding the layout and components of this system is key to maintaining longevity and reliability.
Key Components of the Cooling Mechanism
The cooling system includes several critical elements that work together to disperse excess heat. These elements consist of a radiator, hoses, a thermostat, and a water pump. Each of these parts contributes to efficient heat transfer, circulating coolant throughout the system to maintain stable temperatures.
Flow of Coolant Through the System
The coolant moves through a network designed to absorb heat and transport it
Function of the Lubrication System
The lubrication system plays a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of a mechanical unit. Its primary purpose is to reduce friction between moving components, ensuring smooth operation and preventing wear and tear. By providing a consistent supply of lubricating fluid, the system helps to minimize heat generation and protects against corrosion.
One of the key functions of the lubrication system is to transport oil to various parts, forming a protective film that separates surfaces. This film not only aids in reducing friction but also assists in cooling the components by dissipating heat. Moreover, it helps to carry away contaminants and debris that may accumulate over time.
Regular maintenance of the lubrication system is essential to ensure optimal performance. Checking the oil levels and replacing the lubricant at specified intervals can significantly extend the lifespan of the mechanical unit. Neglecting this aspect can lead to increased wear, overheating, and ultimately, costly repairs.
Understanding the Exhaust System Layout
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in managing the gases produced during combustion. It ensures that harmful emissions are effectively directed away from the vehicle, minimizing their impact on the environment and enhancing overall performance. This section will delve into the components and configuration of the exhaust system, providing insight into its functionality.
Main Components of the Exhaust System
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects gases from the combustion chamber and channels them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: This device transforms harmful pollutants into less harmful emissions through chemical reactions.
- Muffler: It reduces the noise produced by the exhaust gases as they exit the system.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes transport gases from the engine to the outside atmosphere.
Importance of Proper Layout

A well-designed exhaust layout is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance. It aids in reducing back pressure, which can adversely affect efficiency and power output. Furthermore, an effective configuration contributes to sound attenuation and helps meet regulatory emissions standards.
Detailed View of the Engine Block
The block serves as the heart of a machine, housing critical components that ensure optimal performance and efficiency. A thorough understanding of its structure and functions is essential for maintenance and repair, as it directly influences the overall operation of the system. This section delves into the intricate design and significance of the block, highlighting its various features and their roles in the machinery.
Key Features and Components

Within the block, several key elements work in harmony to facilitate the mechanical processes. The cylinder bores are precision-engineered to accommodate the pistons, while the coolant passages ensure temperature regulation. Additionally, the crankshaft supports rotational motion, contributing to power generation. Each feature plays a vital role in the overall functionality of the machinery, making the block a central focus for technicians and engineers alike.
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection and maintenance of the block are crucial to prevent premature wear and ensure longevity. Attention should be paid to signs of cracking, warping, or corrosion, which can compromise performance. Utilizing appropriate lubricants and following recommended service intervals can significantly enhance the reliability of the assembly. Understanding the structure and functions of the block is paramount for effective upkeep and optimal operation.
Cylinder Head Components
The cylinder head plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a combustion system. It houses several vital components that contribute to the efficiency and performance of the machinery. Understanding these elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Valves: Responsible for regulating the intake of air and the exhaust of gases, these elements are essential for the engine’s breathing process.
- Springs: These components ensure that the valves close properly after opening, maintaining optimal pressure within the combustion chamber.
- Cylinder Head Gasket: This critical part seals the cylinder head to the block, preventing leaks of fluids and gases.
- Camshaft: The camshaft operates the valves and is crucial for timing, directly impacting the performance of the machinery.
- Studs and Bolts: These fasteners secure the cylinder head to the block, providing stability and structural integrity.
Each of these components must be properly maintained to ensure reliable operation and longevity of the machinery. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent significant issues and enhance performance.
Exploring the Turbocharger Mechanism
The turbocharger plays a vital role in enhancing the performance and efficiency of internal combustion systems. This component harnesses exhaust gases to boost air intake, thereby increasing power output without significantly raising fuel consumption. Understanding its operation is crucial for optimizing performance and addressing potential issues.
How Turbocharging Works
The turbocharging process involves several key stages:
- Exhaust Gas Flow: Exhaust gases produced during combustion are directed into the turbocharger.
- Turbine Rotation: The force of the exhaust gases spins the turbine, which is connected to the compressor.
- Air Compression: As the turbine rotates, the compressor draws in ambient air, compressing it to a higher density.
- Boosted Air Delivery: The compressed air is then delivered into the combustion chamber, enhancing the air-fuel mixture.
Benefits of Turbocharging
Utilizing a turbocharger offers numerous advantages, including:
- Improved power output for a given engine size.
- Enhanced fuel efficiency due to better combustion.
- Reduced emissions as a result of optimized fuel usage.
- Increased responsiveness and acceleration.
Transmission and Power Output Details
The effectiveness of a machine largely depends on its ability to transmit power efficiently and reliably. This section explores the components and mechanisms involved in the transmission system, focusing on how power is generated and delivered to various applications. Understanding these elements is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring longevity.
Key Transmission Components
- Gearbox: This essential unit alters the torque and speed, allowing for adaptability in various operating conditions.
- Clutch: Serves to engage and disengage the power flow, facilitating smooth operation and control.
- Drive Shafts: These components transmit power from the gearbox to the final drive system, ensuring efficient movement.
- Torque Converter: It enhances performance by allowing for automatic adjustments in power delivery without manual intervention.
Power Output Characteristics
The output characteristics are critical for determining how effectively a machine can perform its tasks. Various factors influence these characteristics, including:
- Torque Ratings: Indicate the rotational force available at different speeds, impacting overall performance.
- Horsepower Output: Represents the engine’s ability to do work over time, vital for understanding capability in heavy-duty applications.
- Operational Efficiency: Influences fuel consumption and performance metrics, essential for long-term operational costs.
Parts Involved in Engine Timing

The timing mechanism of a vehicle’s power unit plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding the various components that contribute to this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element has a specific function that, when synchronized correctly, allows the power unit to operate smoothly.
Key Components
- Timing Belt/Chain: Connects the crankshaft to the camshaft, ensuring coordinated rotation.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of valves, influencing the intake and exhaust cycles.
- Crankshaft: Converts linear motion into rotational motion, driving the timing mechanism.
- Tensioner: Maintains proper tension in the timing belt or chain to prevent slippage.
- Guide Pulleys: Assist in directing the timing belt or chain along its designated path.
Importance of Synchronization
Proper alignment and timing of these components are vital for the harmonious operation of the power unit. Misalignment can lead to significant issues, including reduced performance and potential damage. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn components can enhance reliability and longevity.
Identifying Key Bearings and Se
Understanding the crucial components that facilitate smooth movement within machinery is essential for efficient operation. Bearings and seals play a vital role in reducing friction, supporting loads, and preventing contaminants from entering sensitive areas. Recognizing these elements and their functions can significantly enhance maintenance practices and prolong the lifespan of equipment.
Types of Bearings
- Ball Bearings: These are versatile components that handle both radial and axial loads, providing reliable performance in various applications.
- Cylindrical Bearings: Designed to support high radial loads, these bearings excel in applications with limited axial displacement.
- Tapered Bearings: Ideal for handling combined loads, tapered designs are commonly used in wheel hubs and transmission systems.
Seals Overview
- Oil Seals: These components prevent the leakage of lubricants and protect against dust and dirt, ensuring optimal performance.
- Gaskets: Used to create a tight seal between two surfaces, gaskets are crucial for maintaining pressure and preventing fluid loss.
- O-Rings: These circular seals are effective in creating a barrier against leakage in static and dynamic applications.
Proper identification and selection of these essential components can lead to improved reliability and reduced maintenance costs. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn or damaged bearings and seals are critical to maintaining optimal machinery performance.