The inner workings of a modern automobile rely on various interconnected elements that ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding the structure and function of these core elements can greatly assist in maintaining and troubleshooting your vehicle.
Within the heart of the vehicle, several vital elements play a crucial role in ensuring efficient power generation and smooth functioning. Knowing how these elements interact and support one another can help you enhance both reliability and longevity.
Whether you’re a technician or simply a vehicle owner interested in the mechanics behind your car’s functionality, having a clear understanding of how the primary systems are organized is essential. This section will guide you through the key elements, offering valuable insights into how they contribute to the overall performance of your automobile.
Mazda 6 Engine Components Overview
The power system in this vehicle is designed with precision and attention to detail. Various mechanical elements work together to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Each unit has a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system. Understanding the layout of these components can help with maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key assemblies include several crucial mechanisms that manage fuel delivery, airflow, and temperature control. The harmonious interaction between these units is what allows the vehicle to perform reliably in a variety of conditions.
Comprehending the structure of these elements and their relationships provides valuable insights for enhancing the longevity and reliability of the vehicle’s power source.
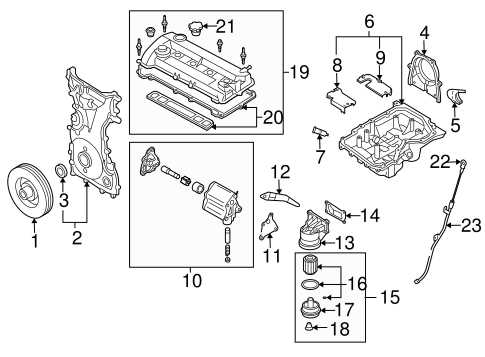
Key Elements of the Engine Block
The central component of a vehicle’s power unit consists of various crucial parts that work together to ensure smooth operation and performance. Understanding the essential features of this structure allows for better maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
The main framework serves as the foundation, housing multiple systems that are responsible for power generation and distribution. Within this core, several critical areas manage the flow of energy, contributing to overall functionality and efficiency.
Another important aspect is the cooling system, which regulates temperature and prevents overheating. Together with the lubrication system, these elements ensure that all moving components operate smoothly without excessive wear or damage.
Pistons and Their Function in Power Generation
Pistons play a crucial role in converting energy within the system into mechanical motion. Their movement is fundamental to the entire operation of a combustion process, as they help transform energy produced from fuel combustion into useful power.
How Pistons Work
As the combustion process occurs, pistons move within the cylinders. This movement is driven by the expansion of gases, which forces the piston to travel. The up-and-down motion is then converted into rotational motion, driving other components of the system.
Key Elements of Piston Functionality
- Compression: Pistons compress the air-fuel mixture before ignition, ensuring optimal combustion efficiency.
- Sealing: Pistons create a seal within the chamber to prevent gas leakage, maintaining pressure and improving performance.
- The Role of the Crankshaft in the Engine

The crankshaft is a crucial mechanical component that converts linear motion into rotational force. Its operation is fundamental to the overall movement and function of the vehicle, as it directly impacts the power delivery system. By transforming energy from one form to another, it ensures smooth operation and enables the effective transmission of force to other key systems within the machinery.
How the Crankshaft Works

The crankshaft operates by receiving energy from pistons and converting that energy into rotational movement. This movement is transferred through a series of connected components, which ultimately drives the mechanical motion needed for propulsion. The process is highly precise, requiring a balanced and synchronized system to ma
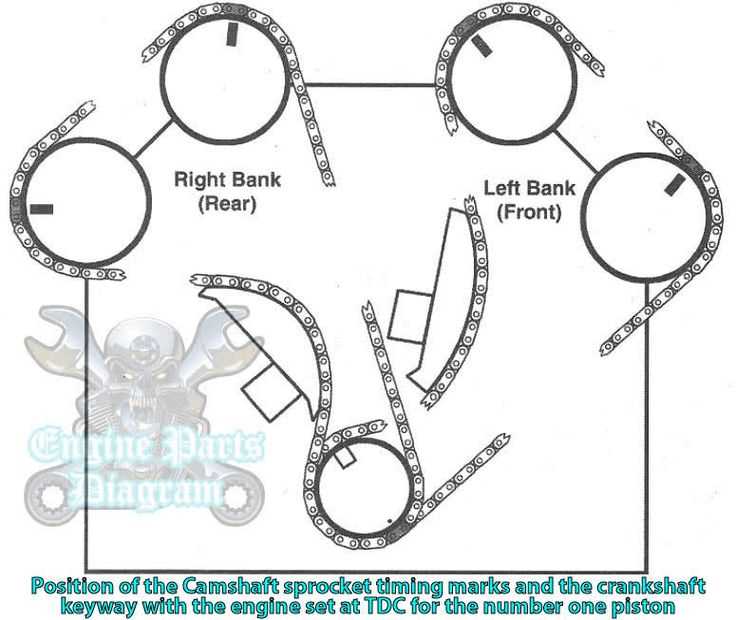
Understanding the Timing Belt System
The timing belt plays a crucial role in ensuring that various components within the motor work in harmony. It synchronizes key elements to guarantee smooth operation, preventing potential damage caused by improper timing. This system is essential for maintaining balance and efficiency in the vehicle’s overall performance.
Key Functions of the Timing Belt
One of the primary functions is to regulate the interaction between the rotating elements, ensuring they operate at precise intervals. This helps prevent mechanical conflicts and allows for optimal power distribution during the operation. If the belt is worn or damaged, it can lead to serious malfunctions, which may compromise the entire mechanism.
Components of the Timing Belt System
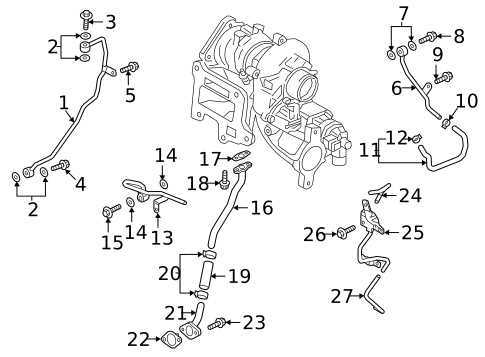
Component Function Exhaust System Parts and Their Importance
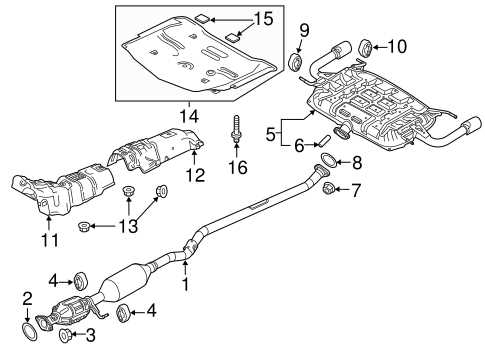
The exhaust system plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of a vehicle. It serves multiple functions, including the safe expulsion of gases produced during combustion, reduction of noise, and enhancement of overall driving experience. Understanding the components involved in this system can provide insight into its significance in maintaining vehicle health.
Key Components of the Exhaust System
Each element within the exhaust setup contributes to its functionality. For instance, the muffler helps to minimize noise levels, allowing for a more comfortable ride. Additionally, the catalytic converter plays a crucial role in converting harmful emissions into less harmful substances, thus reducing the environmental impact.
Benefits of a Well-Maintained Exhaust System
Maintaining the integrity of the exhaust system is essential for several reasons. A properly functioning system not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances engine performance. Regular inspections and timely repairs can prevent potential issues, ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly and adheres to emission regulations.
Fuel Injection System in Mazda 6
The fuel injection mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of the vehicle. This system is designed to deliver fuel to the combustion chamber in precise amounts, enhancing the power output while minimizing emissions. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for maintaining the overall health of the automobile.
Components of the Fuel Delivery System

The fuel delivery system consists of several key elements that work together to ensure efficient operation. These include the fuel pump, injectors, and pressure regulators. Each component contributes to the accurate timing and quantity of fuel injected into the combustion area.
Component Function Fuel Pump Delivers fuel from the tank to the injectors. Fuel Injectors Atomize fuel into a fine mist for optimal combustion. Pressure Regulator Maintains the correct fuel pressure in the system. Importance of Maintenance
Regular upkeep of the fuel injection system is vital for ensuring longevity and performance. Issues such as clogged injectors or faulty pumps can lead to decreased efficiency and increased emissions. Routine inspections and cleanings can help mitigate these problems, ensuring a smoother driving experience.
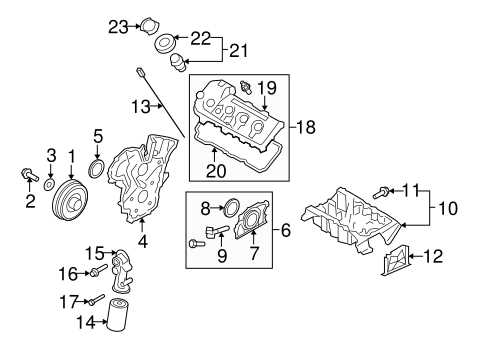
The Cooling System and Its Key Parts
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal temperature levels within a vehicle’s mechanism. It plays a critical role in preventing overheating, ensuring that all components function efficiently and effectively. A well-designed system helps dissipate excess heat generated during operation, thus prolonging the lifespan of various elements involved in the process.
Main Components of the Cooling System
How the Oil Pump Supports Engine Health

The oil pump plays a crucial role in maintaining the longevity and performance of a vehicle’s powertrain. By ensuring that the lubricant circulates effectively, it minimizes friction between moving components, thus enhancing overall functionality. This essential component not only promotes efficiency but also safeguards critical elements from wear and tear.
Lubrication and Friction Reduction
One of the primary functions of the oil pump is to deliver lubricant to various surfaces within the system. This flow reduces friction, allowing parts to operate smoothly. When the lubricant is circulated properly, it prevents overheating and helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, which is vital for preventing damage and ensuring reliable performance.
Contaminant Removal and System Health
In addition to lubrication, the oil pump aids in removing contaminants from the system. As lubricant circulates, it collects debris and other particles that could potentially harm components. The pump’s efficient design ensures that these impurities are directed to the filtration system, allowing for cleaner operation and extending the lifespan of the entire mechanism.
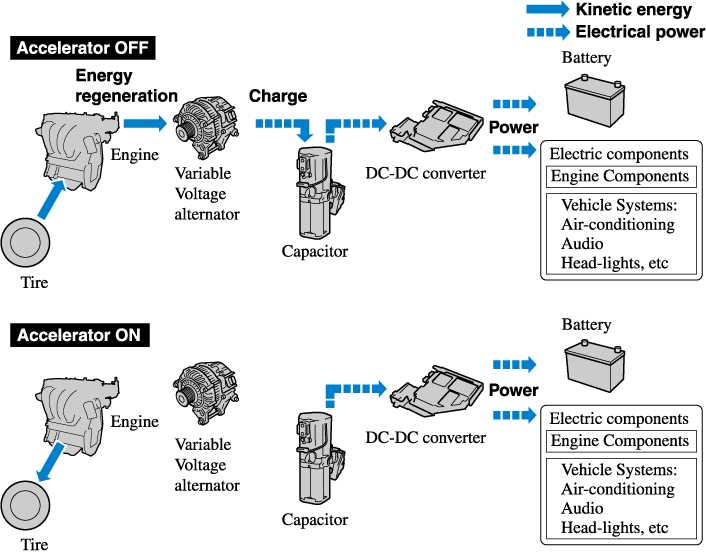
Alternator and Electrical System Overview
The alternator is a crucial component in the electrical system, responsible for generating and supplying power to various electrical accessories. It ensures that the battery remains charged and provides the necessary energy for the vehicle’s operation. A well-functioning electrical system is vital for the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle.
Functionality of the Alternator
The primary role of the alternator is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, which is then used to charge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical components. This process involves the generation of alternating current (AC) that is subsequently converted into direct current (DC) for use in the electrical system.
Key Components of the Electrical System
The electrical system consists of several key components that work together to ensure optimal performance. These include the alternator, battery, voltage regulator, and wiring harness. Each component plays a significant role in maintaining a stable electrical supply and ensuring the proper functioning of electrical accessories.
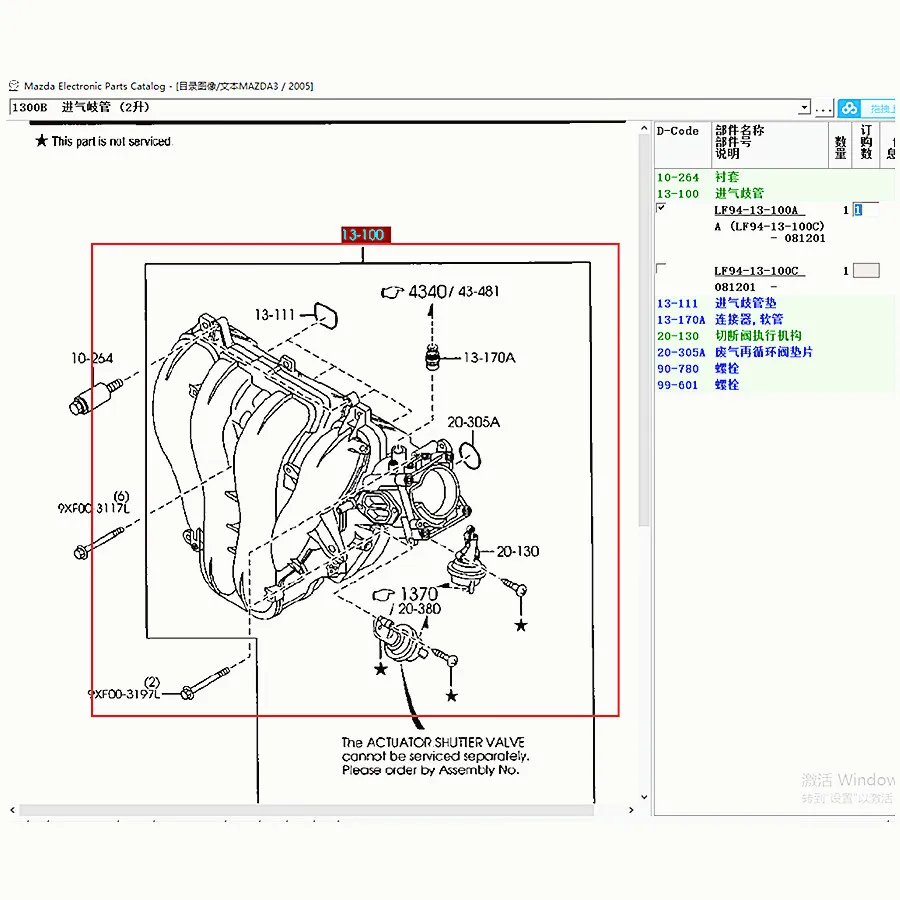
Component Function Alternator Generates electrical power and charges the battery Battery Stores electrical energy for starting and powering accessories Voltage Regulator Maintains a consistent voltage level within the system Wiring Harness Connects all electrical components and facilitates power distribution The Intake Manifold’s Impact on Performance
The intake manifold plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and efficiency of a vehicle’s propulsion system. It serves as the conduit for air entering the combustion chamber, influencing how effectively the mixture of air and fuel is delivered to the cylinders. A well-designed manifold optimizes airflow, enhancing the responsiveness and power output of the power unit.
Airflow Dynamics
The design of the intake manifold significantly affects the dynamics of airflow within the system. A manifold that promotes smooth and unobstructed airflow can reduce turbulence, which is vital for achieving optimal combustion conditions. By maintaining a consistent airflow pattern, the performance of the entire system can be improved, leading to enhanced acceleration and throttle response.
Material and Construction Considerations
The materials used in the construction of the intake manifold also contribute to its effectiveness. Lightweight materials can minimize weight while maintaining structural integrity, thus improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle. Additionally, the surface finish and internal geometry can further influence how air is distributed to each cylinder, ultimately affecting performance and fuel economy.
Common Mazda 6 Engine Part Issues
Many vehicle owners encounter various challenges related to essential components over time. These concerns can arise from wear and tear, manufacturing defects, or environmental factors. Understanding common issues can aid in early detection and timely repairs, ensuring optimal performance.
Component Common Issues Symptoms Recommended Action Fuel Pump Failure to deliver fuel Difficulty starting, engine sputtering Replace the fuel pump Alternator Inconsistent charging Battery warning light, dimming lights Inspect and replace if necessary Cooling System Leaks or overheating Temperature gauge rising, coolant puddles Check for leaks and flush system Timing Belt Wear and potential snapping Unusual noises, engine misfiring Replace as per maintenance schedule