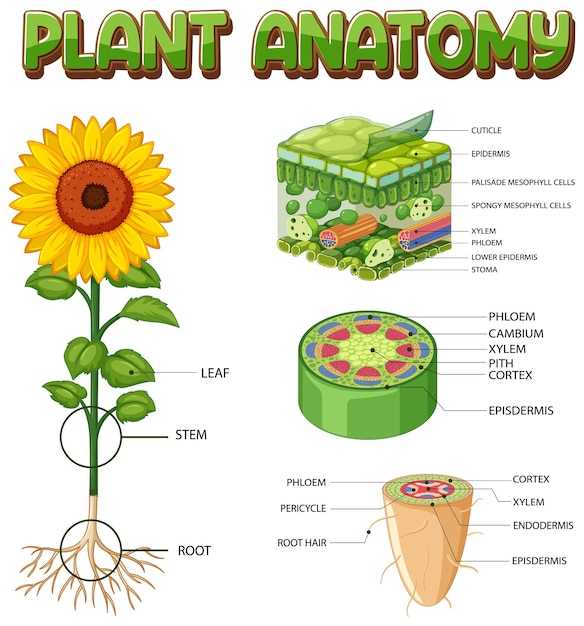
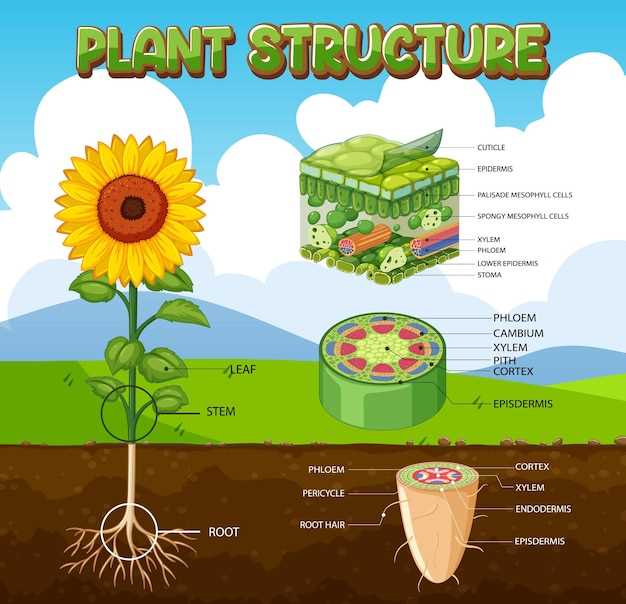
The intricate design of a flowering plant reveals a captivating world of biological complexity. Each element contributes to the overall function and beauty, playing specific roles that enhance growth and reproduction. Exploring these components offers a deeper appreciation of nature’s engineering.
From the vibrant blooms to the supporting structures, the anatomy showcases remarkable adaptations. These features not only attract pollinators but also ensure the plant’s survival in diverse environments. A closer look uncovers the relationships between these elements, emphasizing their importance in the ecosystem.
By examining the various components, one can truly delve into the ultimate purpose of this botanical marvel. Understanding how each part interacts enriches our knowledge and fosters a greater respect for the natural world that surrounds us.
Overview of Sunflower Anatomy
This section explores the intricate structure of a prominent flowering plant, highlighting its various components that contribute to its beauty and functionality. Understanding these elements provides insights into its life cycle and ecological significance.
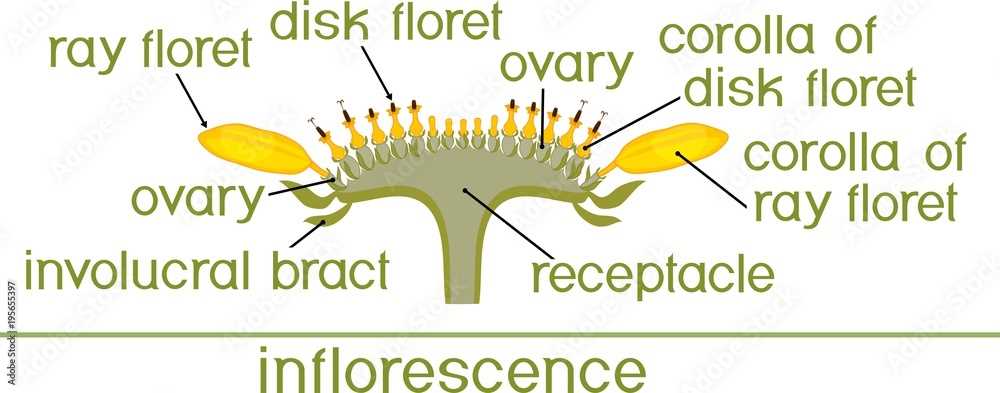
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Receptacle | The base that supports the floral arrangement, playing a crucial role in structure. |
| Pedicel | The stalk that connects the flower to the main stem, facilitating nutrient transfer. |
| Petals | Colorful structures that attract pollinators and enhance reproductive success. |
| Bracts | Modified leaves that provide protection and support to the flower head. |
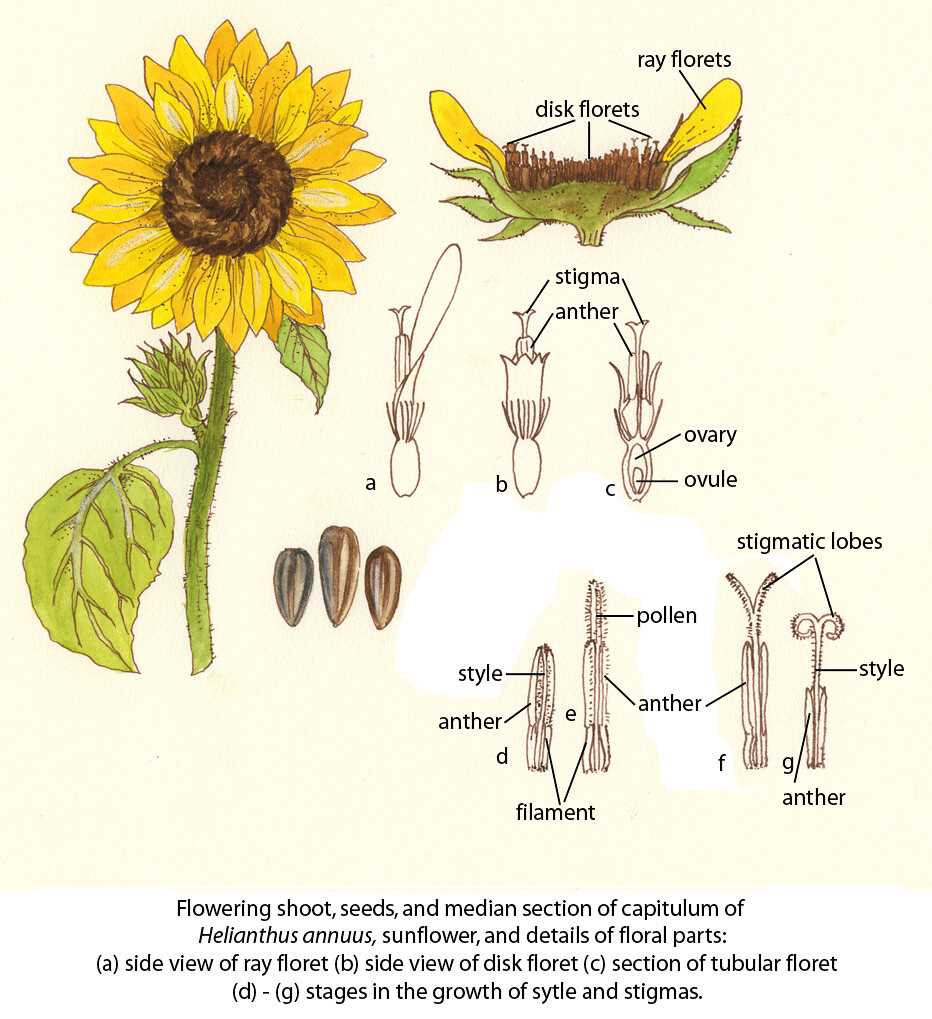
| Stamens | The male reproductive parts responsible for pollen production. |
| Pistil | The female reproductive structure that houses ovules and is essential for seed development. |
Key Functions of Sunflower Components

The various elements of this vibrant plant play crucial roles in its growth, reproduction, and overall health. Each component is intricately designed to contribute to the life cycle and ecological balance, ensuring survival and propagation in its environment.
Reproductive Structures
The reproductive organs are vital for the continuation of the species. They facilitate the process of pollination, which allows for the transfer of genetic material, leading to the formation of seeds. This process not only ensures the plant’s survival but also enhances genetic diversity within the population.
Photosynthetic Leaves
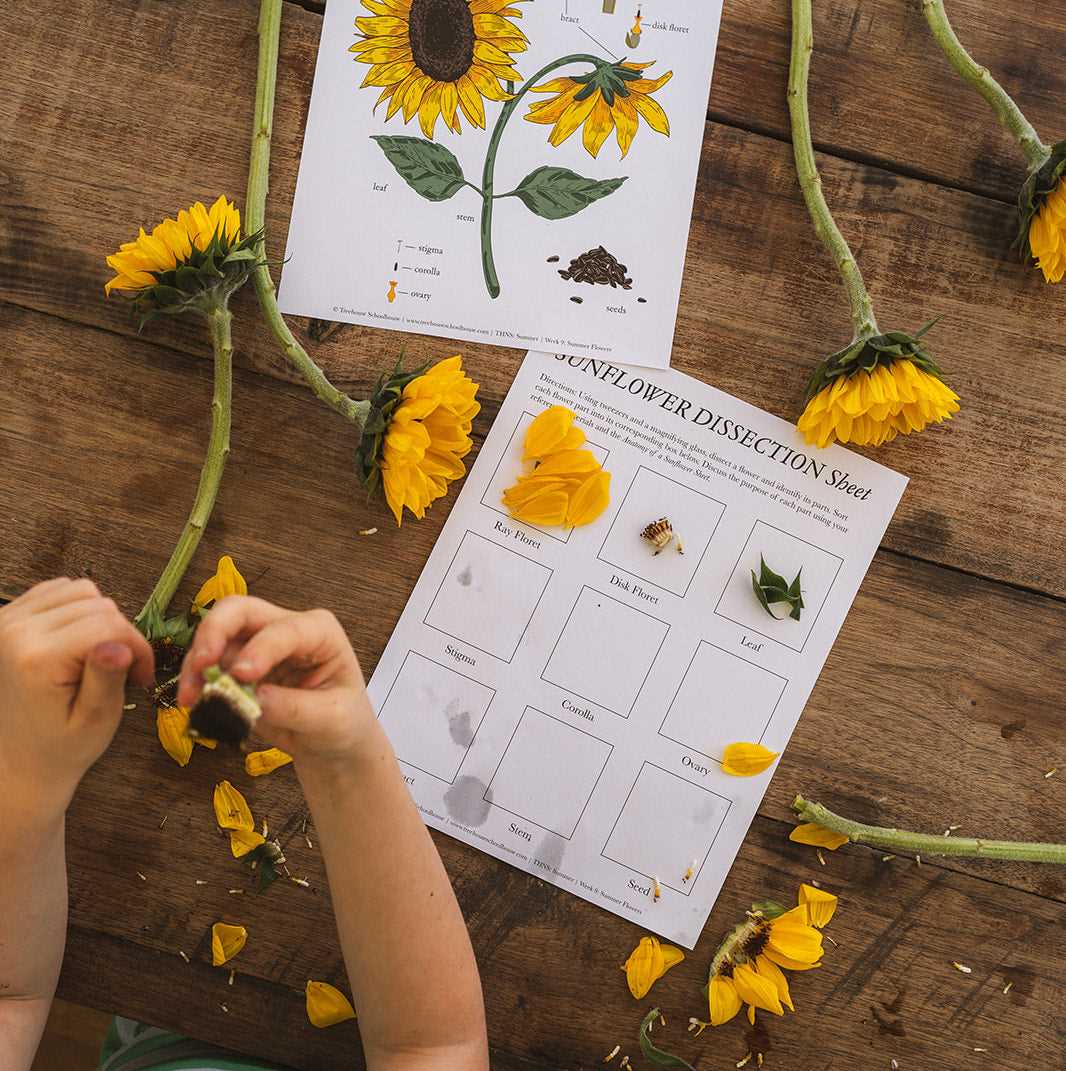

The foliage is essential for harnessing sunlight, converting it into energy through photosynthesis. This process sustains the plant and provides energy for growth and development. Additionally, the leaves play a role in transpiration, helping to regulate water and nutrient uptake.
Different Types of Sunflower Varieties

Exploring the diverse range of cultivated species reveals fascinating characteristics and uses that appeal to gardeners and farmers alike. Each type showcases unique traits that contribute to its popularity and functionality.
- Oilseed Varieties: Primarily grown for oil extraction, these types are known for their high oil content.
- Confectionery Varieties: These larger-seeded options are ideal for snacking and are often enjoyed roasted.
- Perennial Varieties: Unlike annuals, these plants can live for several years, offering long-term beauty in gardens.
- Dwarf Varieties: Compact and perfect for small spaces, these types bring vibrant colors without taking up much room.
Each variety serves a unique purpose, from ornamental uses to agricultural benefits, inviting enthusiasts to delve into their cultivation and care.
Importance of Sunflower Seeds
These tiny morsels are more than just a snack; they are a powerhouse of nutrition and versatility, playing a significant role in diets around the globe. Their rich composition makes them a valuable addition to various culinary applications, while their health benefits have garnered widespread attention.
- Nutritional Benefits:
- High in healthy fats, particularly polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats.
- Rich in protein, making them an excellent option for plant-based diets.
- Loaded with essential vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin E, magnesium, and selenium.
- Heart Health:
Their composition contributes to heart health by promoting healthy cholesterol levels and reducing inflammation.
- Weight Management:
Rich in fiber and protein, these seeds can help keep you full and satisfied, aiding in weight control.
- Culinary Uses:
They can be enjoyed raw, roasted, or added to salads, granola, and baked goods, enhancing flavor and texture.
Incorporating these seeds into your diet not only boosts nutritional intake but also supports overall well-being, making them a worthy choice for anyone looking to improve their health.
Pollination Process in Sunflowers

The journey of fertilization in these vibrant blooms is a fascinating interplay of nature’s elements. It involves the transfer of pollen from the male structures to the female reproductive parts, facilitating the creation of seeds and the continuation of the species. This intricate mechanism is essential for the development of new generations and the maintenance of biodiversity.
Sunflower Growth Stages Explained
Understanding the various phases of development for this vibrant plant reveals the intricate processes that contribute to its life cycle. Each stage represents a critical period of transformation, influencing overall health and productivity. Observing these stages helps enthusiasts appreciate the beauty and complexity inherent in nature’s designs.
The journey begins with germination, where the seed awakens and sprouts roots, establishing a foundation. Following this, the seedling stage showcases rapid growth, as the young plant develops its initial leaves, harnessing sunlight for energy. This is a crucial time for establishing strength and resilience.
As the plant matures, it enters the vegetative phase, characterized by leaf proliferation and height increase. This stage is vital for maximizing photosynthesis, which supports further development. The transition to the flowering phase marks a significant milestone, as buds form and prepare to unveil the stunning blooms that draw in pollinators.
Finally, the ripening stage sees the production of seeds, culminating in a process that ensures the continuation of the species. Each phase is interlinked, creating a harmonious cycle that reflects the resilience and beauty of life.
Role of Leaves in Sunflowers
The foliage of this vibrant plant plays a crucial role in its overall health and growth. Through a series of essential functions, these green structures contribute to the plant’s vitality and ability to thrive in its environment.
Photosynthesis and Energy Production
One of the primary functions of leaves is to capture sunlight and convert it into energy. This process is vital for the following reasons:
- Absorption of light through chlorophyll.
- Conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
- Release of oxygen as a byproduct.
Water Regulation and Nutrient Transport
In addition to energy production, foliage plays a significant role in regulating water and nutrients:
- Transpiration helps to maintain moisture levels within the plant.
- Leaf structures aid in nutrient absorption from the soil.
- Support for overall plant structure and stability.
Sunflower Stem Structure and Support
The upright component of this plant plays a vital role in its overall health and functionality. It provides not only stability but also serves as a conduit for essential nutrients and water, ensuring that the upper parts thrive. Understanding its composition and function is key to appreciating how these plants achieve their remarkable height and resilience.
This vertical support system is characterized by several distinct features:
- Strength: The core is composed of fibrous tissue, granting it the ability to withstand environmental pressures such as wind and rain.
- Vascular System: Internal channels facilitate the movement of fluids, delivering nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flowers.
- Growth Nodes: These segments allow for the development of leaves and branches, promoting a wider canopy for photosynthesis.
Moreover, the flexibility of the stalk allows it to bend without breaking, adapting to various conditions while maintaining its integrity. This adaptability is crucial for survival in diverse habitats.
In conclusion, the robust structure of the stem is integral to the plant’s growth and survival, providing essential support while allowing for the efficient transport of resources.
How Sunflowers Attract Pollinators
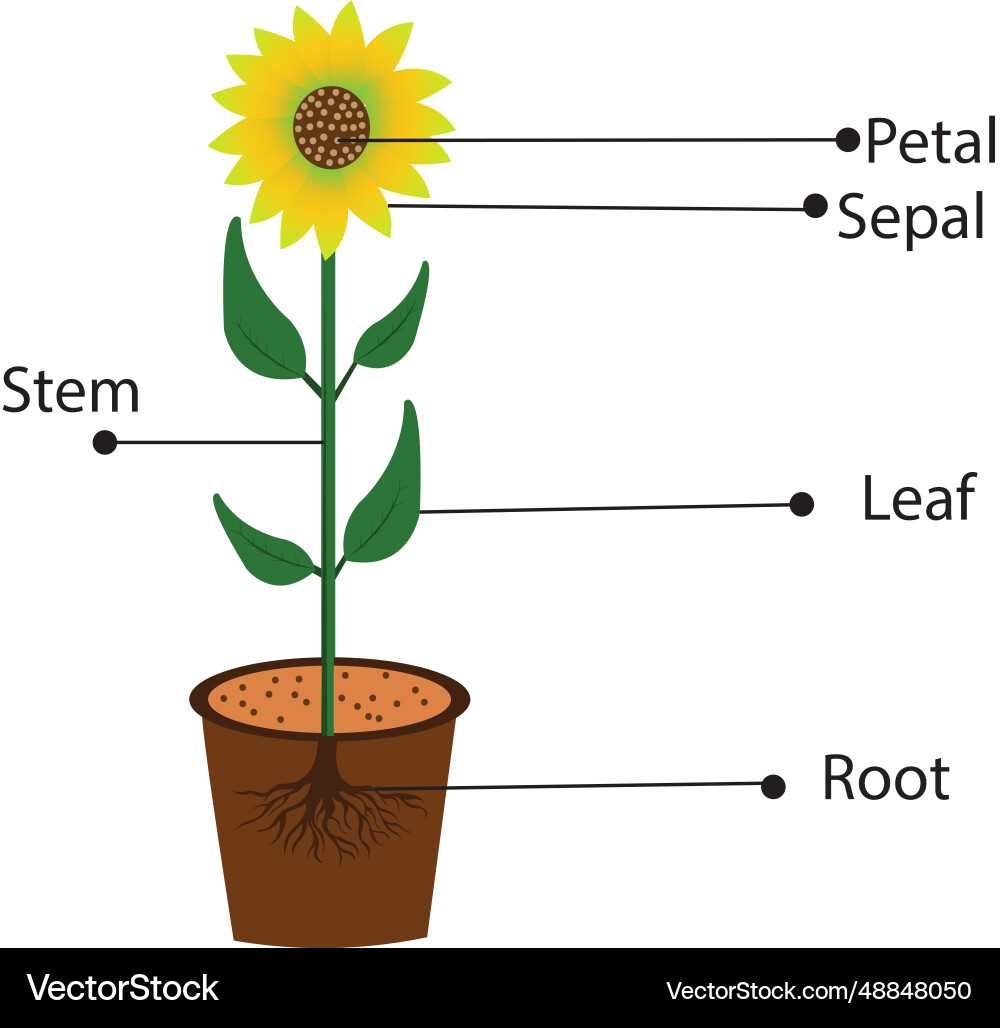
Bright, vibrant blooms play a crucial role in luring essential insects and other creatures that facilitate the process of reproduction in plants. The combination of visual appeal and olfactory signals makes these flora irresistible to various species, ensuring the continuation of their lifecycle.
Visual Attraction
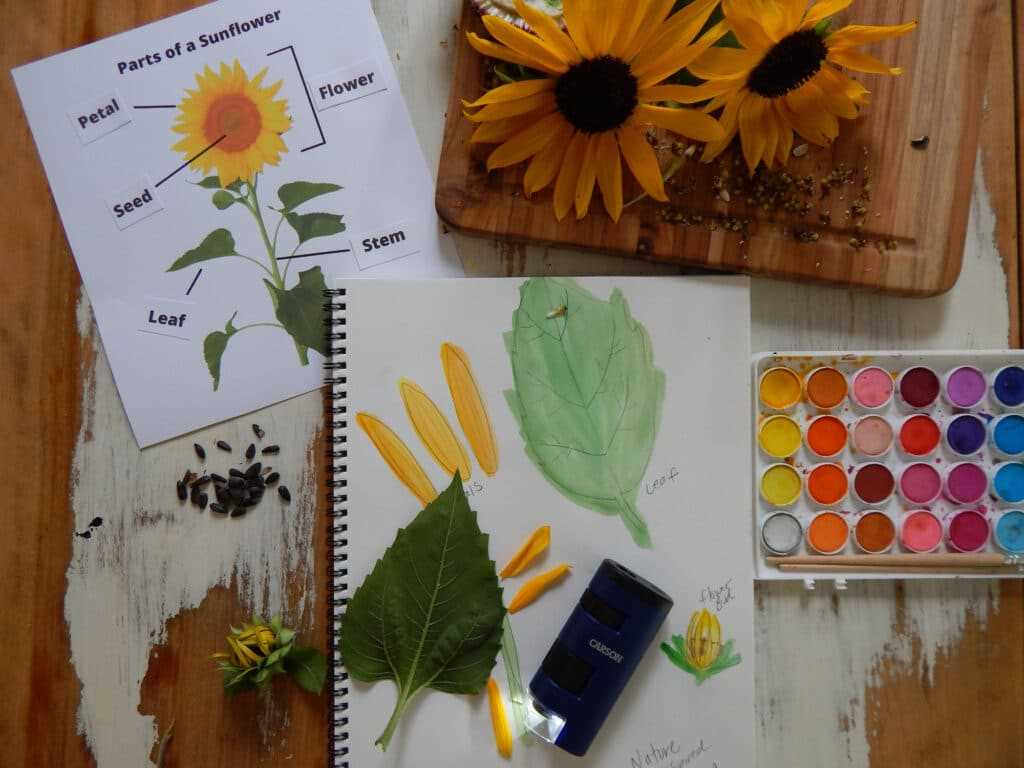

Colorful petals serve as a beacon for pollinators. The following features enhance their attractiveness:
- Color: Rich hues, particularly yellows and oranges, stand out against green foliage, guiding pollinators.
- Size: Large blossoms provide a substantial landing area, making it easier for insects to access nectar.
- Shape: A flat, open structure allows for easy access to reproductive parts.
Olfactory Signals
In addition to visual cues, many blooms emit specific scents that further entice visitors:
- Nectar: Sweet liquids attract a variety of species, rewarding them for their efforts.
- Fragrance: Distinct aromas can signal the presence of food sources, increasing the likelihood of visits.
- Timing: Certain species release scents during peak activity hours of their preferred pollinators.
Through a combination of visual and olfactory strategies, these flowering plants effectively engage their pollinator partners, facilitating successful reproduction and vibrant ecosystems.
Uses of Sunflowers in Agriculture

This versatile plant serves numerous functions within farming systems, contributing to both ecological balance and economic viability. Its cultivation can enhance soil health, attract beneficial insects, and provide a source of nutritious food and oil.
Primarily, the seeds are harvested for their oil, which is widely used in cooking and food production. Additionally, they are processed into meal for livestock, enriching animal diets. The oil extracted is also a popular ingredient in various industrial applications, including cosmetics and biodiesel.
Moreover, cultivating this plant can help improve soil structure and fertility through its deep root system, which reduces erosion and promotes water retention. The bright flowers attract pollinators, supporting the biodiversity necessary for healthy ecosystems.
In summary, this remarkable plant offers numerous agricultural benefits, from providing valuable resources to enhancing environmental sustainability, making it a vital component of modern farming practices.