Ball Joints: Allow for smooth rotation and pivoting of the control arms
Brake Assembly and Related Components
The brake system is an essential part of a vehicle’s safety mechanism, responsible for ensuring effective stopping power. A well-maintained set of components within this system is crucial for optimal performance, and regular inspection of these elements can help prevent wear and potential failure. Understanding the different parts that make up this system is key to maintaining the overall efficiency of the vehicle.
Main Components of the Brake System
Within the braking assembly, there are several crucial elements that work together to ensure the proper function of the system. These include the disc, pads, calipers, and other supporting hardware. Each of these components plays a role in applying friction and pressure to bring the vehicle to a safe stop. Monitoring their condition is essential to prolong the life of the system.
Additional Components and Their Role

Beyond the primary elements, several auxiliary components contribute to the efficiency of the braking system. These include hydraulic lines, the master cylinder, and the brake booster. Each of these elements aids in amplifying the pressure applied by the driver to the brakes, making the system more responsive and effective. Ensuring their proper function is necessary for maintaining overall control during braking.
Transmission and Drivetrain Overview
This section provides an insightful examination of the mechanisms responsible for power transfer in vehicles. Understanding these components is essential for appreciating how motion is generated and controlled, impacting performance and driving experience.
The assembly responsible for the seamless connection between the engine and wheels is critical. It encompasses various elements that work in harmony to ensure optimal functionality, reliability, and efficiency.
| Component |
Description |
| Transmission |
Responsible for changing gears, adjusting torque and speed for different driving conditions. |
| Driveshaft |
Transmits power from the transmission to the wheels, facilitating movement. |
| Differential |
Allows for varying wheel speeds during turns, enhancing stability and control. |
| Axles |
Connect the wheels to the vehicle, supporting weight and transmitting power. |
Electrical System and Wiring Diagram
The electrical architecture of modern vehicles is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and reliability. It encompasses a complex network of components that facilitate communication and power distribution throughout the automobile. Understanding this framework can help in diagnosing issues and performing effective repairs.
Within this intricate setup, each segment plays a significant role. From the power supply unit to various sensors and actuators, every element is interconnected. The wiring schematic provides a clear representation of these connections, illustrating how electricity flows and how components interact.
Moreover, the electrical layout aids in troubleshooting potential faults. By analyzing the configuration, technicians can identify problematic areas, ensuring efficient repairs and maintenance. Knowledge of this system not only enhances the vehicle’s performance but also contributes to its longevity.
Cooling System: Radiator and Hoses
The efficiency of an engine relies heavily on its ability to manage heat, and a crucial component in this process is the mechanism responsible for transferring and dissipating thermal energy. This system comprises several vital elements that work in unison to maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring the longevity and performance of the power unit.
At the heart of this arrangement is the cooling apparatus, which plays a significant role in regulating the temperature of the engine. Alongside it, flexible conduits facilitate the movement of coolant, enabling a continuous flow that absorbs heat from the engine block and releases it to the environment. Understanding the layout and function of these components is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
| Component |
Function |
| Radiator |
Acts as a heat exchanger, dissipating heat from the coolant into the surrounding air. |
| Upper Hose |
Transports heated coolant from the engine to the radiator for cooling. |
| Lower Hose |
Returns cooled coolant from the radiator back to the engine to continue the cycle. |
| Expansion Tank |
Holds excess coolant and allows for pressure regulation in the system. |
Body Panels and Exterior Parts Guide

This section offers a comprehensive overview of the various components that make up the outer shell of a vehicle. Understanding the different elements is essential for maintenance, repair, or customization. Each piece plays a vital role in both aesthetics and functionality, ensuring that the vehicle not only looks good but also performs effectively on the road.
Overview of Exterior Components
Exterior components include items such as the hood, fenders, and doors, each contributing to the overall structure and design. These elements are engineered to protect the interior while also enhancing the vehicle’s style. Regular inspections can help identify any wear or damage that may require attention.
Importance of Quality Materials

When considering replacements or upgrades, it’s crucial to choose high-quality materials. Durable materials not only improve the longevity of the components but also contribute to the vehicle’s safety. Whether opting for OEM or aftermarket options, understanding the benefits of each can aid in making informed decisions.
Fuel System Components and Configuration
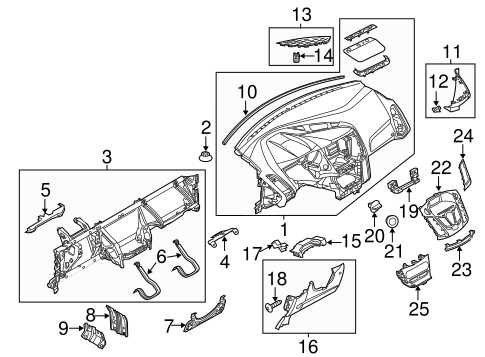
The fuel system in an automobile plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. It comprises various elements that work together to deliver the necessary fuel mixture to the engine, maintaining the desired operation under different conditions.
Key Components

- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel until it is needed by the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transferring fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Dispense the precise amount of fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains the correct fuel pressure for optimal performance.
Configuration Overview
The configuration of the fuel system is designed to maximize efficiency and minimize emissions. Typically, the layout includes a direct pathway from the fuel tank through the pump, filter, and injectors. The pressure regulator ensures that fuel flows at a consistent rate, adapting to engine demands.
- The fuel is drawn from the tank by the fuel pump.
- It then passes through the fuel filter to remove contaminants.
- The clean fuel is injected into the engine by the fuel injectors.
Understanding the components and configuration of the fuel delivery system is essential for diagnosing performance issues and ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly.
Exhaust System: Parts and Diagram

The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in managing emissions and optimizing engine performance. It consists of various components working together to redirect harmful gases away from the engine and out of the vehicle, ensuring a smooth operation and compliance with environmental regulations.
Key Components of the Exhaust Assembly
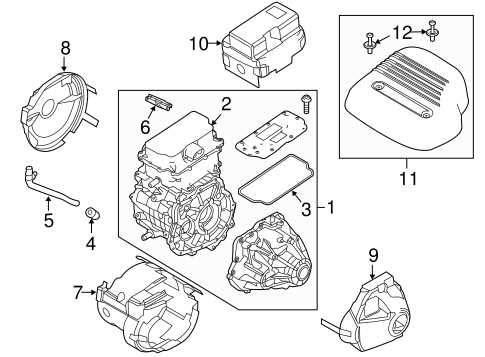
This assembly typically includes a manifold, catalytic converter, resonator, and muffler. Each element serves a specific purpose, from collecting exhaust gases to reducing noise and harmful emissions. Understanding the function of each component is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
Visual Representation
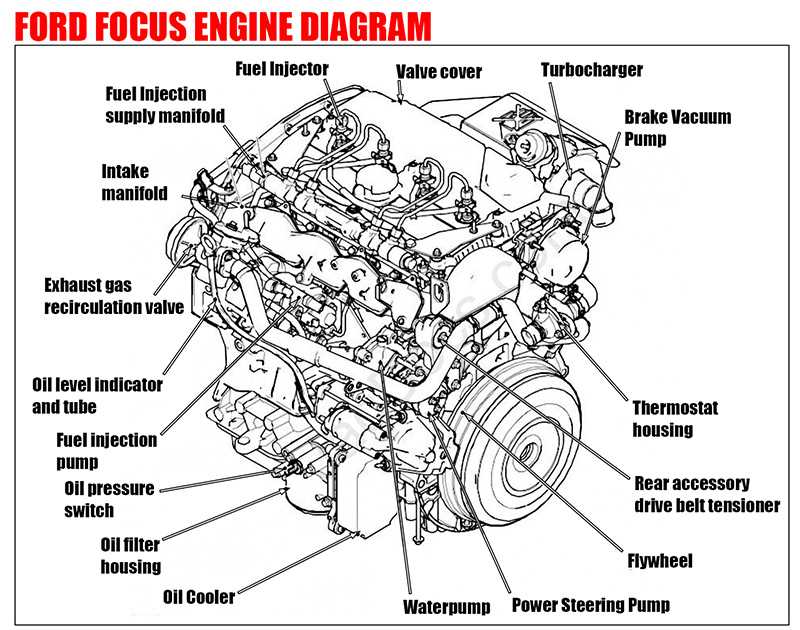
A visual representation of this assembly highlights the interconnected nature of its components. Diagrams often illustrate how gases flow through the system, showcasing the pathway from the engine to the exit point. This insight aids in diagnosing issues and planning modifications or replacements.