Power Steering Pump
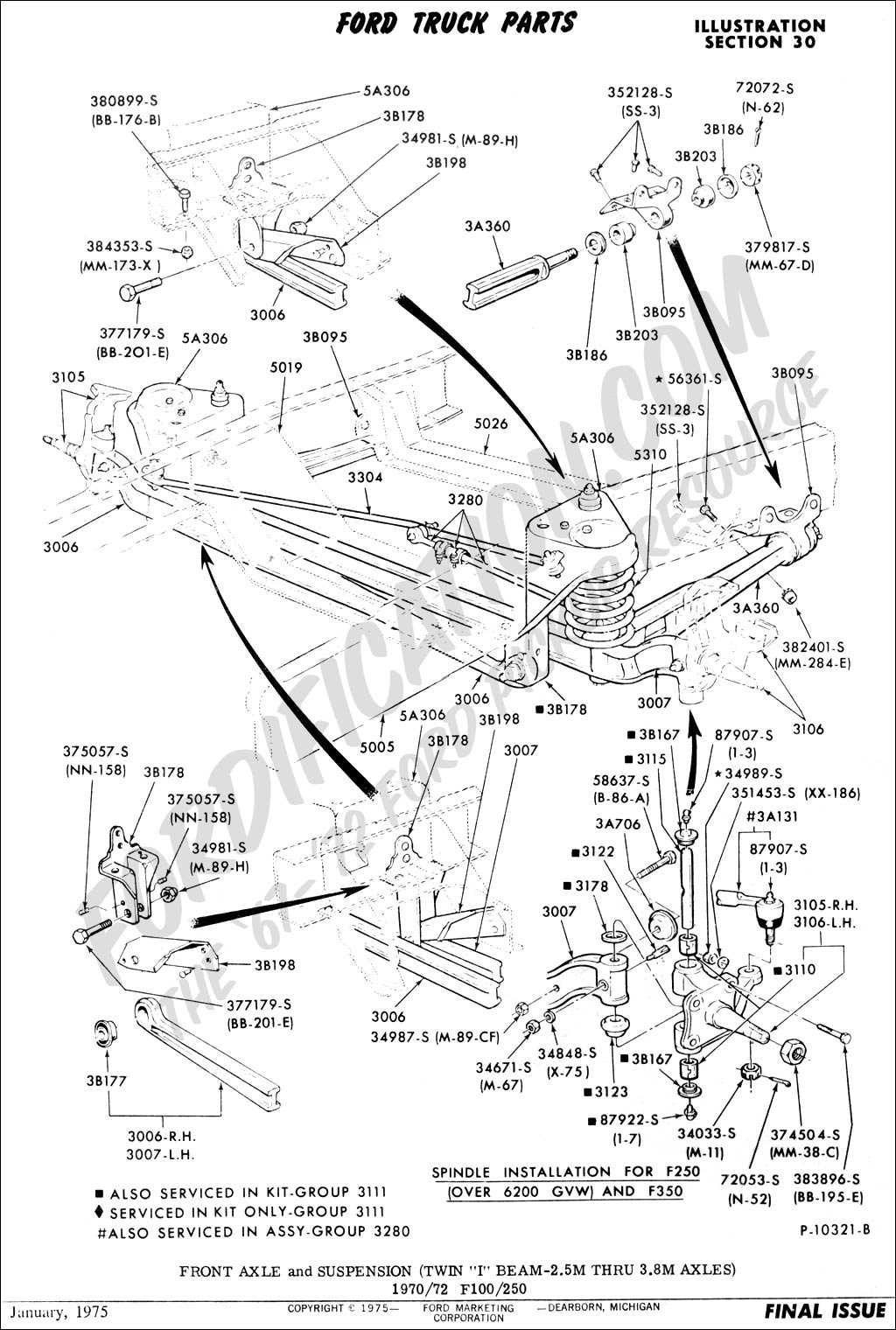
Axle Components and Their Roles
The axle system plays a critical role in the operation of vehicles, ensuring smooth and stable movement. It consists of various interconnected elements that work together to support the vehicle’s weight, provide torque transfer, and maintain control during driving. Each component has a specific function that contributes to overall safety and performance.
Main Structural Elements
- Axle shaft: This element transfers the engine’s power to the wheels, enabling motion. Its durability and strength are vital for handling various load conditions.
- Differential: A crucial part that allows wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds, especially when turning, helping with traction and stability.
- Bearings: These components reduce friction between moving parts, ensuring smooth rotation and reducing wear over time.
Sup
Suspension Elements and Compatibility
The structure supporting a vehicle’s weight and absorbing road irregularities is critical for a smooth and controlled ride. The components involved ensure stability during movement, helping the vehicle adapt to various terrains while maintaining comfort and safety. This system plays a significant role in minimizing the impact of vibrations and enhancing maneuverability.
Key Components of the Suspension System
The suspension mechanism consists of various elements, including springs, shock absorbers, and control arms. Springs manage the distribution of weight and absorb vertical forces, while shock absorbers reduce the oscillations caused by road bumps. Control arms connect the system to the vehicle’s frame, allowing smooth pivoting movements.
Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring compatibility between suspension elements and the vehicle model is essential for proper performance. Factors like weight distribution, size, and material strength should be taken into account to avoid premature wear or inefficiency. Proper alignment and fitting also contribute to the longevity
Front Brake System Breakdown
The braking mechanism is crucial for ensuring safe and effective stopping power. This section provides an overview of how the components work together to bring the vehicle to a halt, focusing on the main elements involved in the process without going into brand-specific details.
Main Components Overview
- Brake Caliper: A critical element that houses the brake pads and applies pressure to them.
- Brake Pads: These create the friction necessary to slow down the vehicle when pressed against the rotor.
- Brake Rotor: A disc that rotates with the wheels and receives pressure from the pads, allowing the vehicle to decelerate.
Process of Stopping
- The brake pedal is pressed, initiating hydraulic pressure in the system.
- Fluid is pushed through lines to the caliper, causing the brake pads to engage with the rotor.
- The resulting friction between the pads and rotor slows down the wheels, effectively reducing speed and stopping the vehicle.
This
Shock Absorber and Spring Mechanism
The shock absorber and spring system play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. This combination is designed to absorb and dampen the impacts and vibrations caused by uneven terrain, enhancing both comfort and control.
Typically, the spring mechanism supports the vehicle’s weight, while the shock absorber controls the oscillation of the springs, preventing excessive bouncing. Together, they work to maintain tire contact with the ground, which is essential for optimal handling and safety.
Key Components
- Coil Springs: These provide the primary support and help maintain the vehicle’s height.
- Shock Absorbers: These dampen the spring’s movements, ensuring a controlled response to road conditions.
- Mounting Hardware: Various brackets and bolts secure the components to the chassis and suspension system.
Functionality
The shock absorber and spring assembly works in the following manner:
- As the vehicle encounters bumps, the springs compress, absorbing the energy.
- The shock absorbers then restrict the spring’s rebound, controlling the rate at which the vehicle returns to its normal position.
- This process minimizes body roll and enhances stability during turns and braking.
Overall, the synergy between the shock absorber and spring mechanism is vital for delivering a comfortable and safe driving experience.
Ball Joint Types and Maintenance
Ball joints are crucial components in a vehicle’s suspension system, allowing for smooth movement between various parts. They connect the control arms to the steering knuckles, facilitating the vehicle’s ability to navigate turns and maintain stability. Understanding the different varieties and their upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety.
There are primarily two types of ball joints: the threaded type and the press-in type. The threaded variant is adjustable, allowing for easier alignment of the suspension system, while the press-in type is typically more robust but less adjustable. Each type has its own unique installation process and maintenance requirements.
Regular inspection and maintenance of ball joints can prevent premature wear and potential failure. It is advisable to check for any signs of damage or excessive play, which could indicate that a replacement is necessary. Greasing the joints regularly helps maintain lubrication and prolongs their lifespan. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance is key to ensuring these components function effectively.
Front Hub and Bearing Assembly
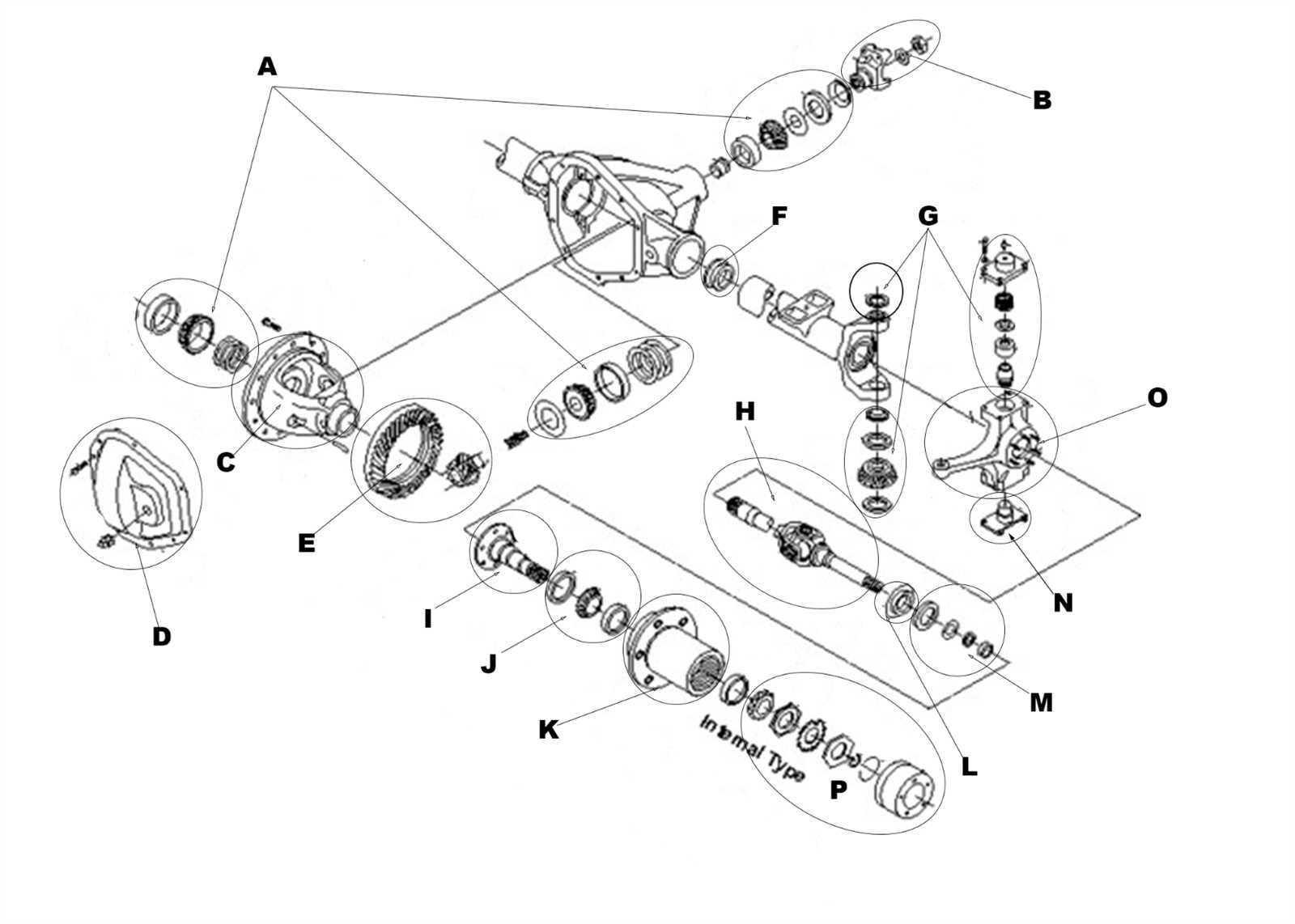
The assembly of the wheel hub and bearing plays a crucial role in the overall performance and safety of a vehicle. This component is responsible for supporting the wheel, enabling smooth rotation, and maintaining proper alignment during operation. Understanding its structure and function is essential for effective maintenance and repair.
Components Overview
The assembly consists of several key elements, each contributing to its efficiency and reliability:
- Hub: The central part that houses the wheel and connects it to the axle.
- Bearing: A set of smooth rollers or balls that reduce friction between the hub and the axle.
- Seals: Protect the bearings from dirt and moisture, ensuring longevity.
- Spindle: The shaft that provides a mounting point for the hub and allows for rotation.
Maintenance Tips
Proper upkeep of the hub and bearing assembly is vital for safe driving. Here are some recommendations:
- Regularly check for signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure that the seals are intact to prevent contaminants from entering.
- Grease the bearings according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Replace worn components promptly to avoid further issues.
Track Bar and Stabilizer Details
The track bar and stabilizer are crucial components that contribute to the vehicle’s handling and stability. These elements work in tandem to ensure that the wheels maintain proper alignment, which is essential for a smooth and controlled driving experience. Understanding their functions and the specifics of their design can greatly enhance the performance of the suspension system.
Functionality of the Track Bar
The track bar, often referred to as a lateral link, serves to keep the axle centered under the chassis. By limiting lateral movement, it prevents the vehicle from swaying during cornering and enhances steering responsiveness. A well-maintained track bar is vital for ensuring that the alignment of the wheels remains consistent, promoting even tire wear and improving overall safety.
Stabilizer Role in Suspension
The stabilizer, commonly known as the sway bar, helps reduce body roll during turns. It connects the left and right sides of the suspension, distributing weight evenly across the vehicle. This component is particularly important in maintaining stability, especially when navigating curves or uneven surfaces. An effective stabilizer setup can significantly enhance the overall driving dynamics, providing a more balanced and enjoyable ride.
Leaf Spring Structure and Performance
Leaf springs are essential components in vehicle suspension systems, designed to support weight and absorb shock during movement. Their structure typically consists of multiple layers of flexible material, which are layered together to form a robust and resilient assembly. This design allows them to efficiently manage both vertical loads and lateral forces, contributing to overall vehicle stability.
The performance of leaf springs greatly influences ride quality and handling characteristics. A well-engineered leaf spring system can provide optimal load distribution while maintaining a comfortable driving experience. Various factors, such as the number of leaves, their thickness, and the material used, play a critical role in determining the effectiveness and durability of the suspension system. Proper tuning of these elements ensures that the spring can adapt to varying road conditions while minimizing wear and enhancing longevity.
In addition to their structural benefits, leaf springs offer significant advantages in terms of maintenance and repair. Their simple design allows for straightforward replacement or adjustment, making them a popular choice for heavy-duty applications. Understanding the nuances of leaf spring construction can help vehicle owners make informed decisions about upgrades and replacements, ultimately enhancing the performance and reliability of their suspension systems.
Control Arm and Linkage Setup
The control arm and linkage assembly plays a crucial role in the suspension system of a vehicle, providing stability and facilitating smooth movement during various driving conditions. This setup is essential for maintaining proper wheel alignment and ensuring optimal handling characteristics.
Typically, the control arm connects the vehicle’s chassis to the wheels, allowing for vertical movement while maintaining lateral stability. The linkage components work in conjunction with the control arm to transmit forces effectively and to absorb shocks encountered on the road.
| Component |
Description |
| Control Arm |
Links the chassis to the wheel assembly, enabling vertical movement. |
| Ball Joint |
Facilitates pivoting movement between the control arm and the steering knuckle. |
| Bushings |
Provide cushioning and absorb vibrations between the control arm and the chassis. |
| Linkage Rod |
Connects various suspension elements, allowing coordinated movement. |
| Sway Bar |
Reduces body roll during cornering by linking opposite wheels. |
Spindle and Knuckle Interaction
The relationship between the spindle and knuckle is crucial for the effective functioning of the steering mechanism in vehicles. These components work together to enable smooth rotation and stability while navigating various terrains. Understanding their interaction can help in diagnosing issues related to handling and alignment.
Functionality of Components
The spindle serves as a pivotal element that connects the wheel assembly to the suspension system. It allows for vertical movement while also maintaining the proper orientation of the wheel. The knuckle, on the other hand, supports the spindle and houses the wheel bearing, playing a vital role in transferring forces during turning and braking. Their collaboration ensures optimal performance.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent wear and tear in these parts. Common issues may include:
- Worn bearings leading to play in the wheel assembly
- Corrosion affecting the connection between the spindle and knuckle
- Improper alignment causing uneven tire wear
Addressing these problems promptly can enhance the longevity of the suspension system and improve overall vehicle safety.
Replacement Tips for Worn Out Parts
When it comes to maintaining a vehicle, addressing degraded components is essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Recognizing the signs of wear and knowing how to approach replacements can significantly enhance your driving experience.
Identifying Worn Components
Regular inspections can help identify which elements require attention. Common indicators include unusual noises, vibrations, and poor handling. It’s crucial to check for visual signs of damage or excessive play in the mechanisms.
Replacement Process
Replacing worn components typically involves a systematic approach:
| Step |
Description |
| 1 |
Gather necessary tools and parts. |
| 2 |
Lift the vehicle safely using jack stands. |
| 3 |
Remove the damaged component carefully. |
| 4 |
Install the new part, ensuring proper alignment. |
| 5 |
Test the system to confirm functionality. |
|