Understanding the intricacies of a vehicle’s assembly can significantly enhance the experience of ownership and maintenance. This section delves into the various elements that comprise a popular mid-size sedan, offering insights into their functionalities and interrelations. By examining these components, enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike can gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind modern automobiles.
The focus here will be on identifying key features and their roles within the automotive framework. From the engine to the suspension system, each part plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. By familiarizing oneself with these crucial aspects, individuals can better navigate the maintenance and repair processes that arise over time.
In the following sections, detailed illustrations and descriptions will provide clarity on the arrangement and purpose of each component. Whether you are looking to troubleshoot an issue or simply wish to understand your vehicle more thoroughly, this exploration promises to be both informative and engaging. Prepare to uncover the essentials that keep your sedan running smoothly.
Understanding the 2010 Ford Fusion Design

The design of this mid-size automobile showcases a blend of style and functionality, reflecting the automotive advancements of its time. The exterior features sleek lines and a modern silhouette, while the interior emphasizes comfort and user-friendly technology. This vehicle stands out in its class, offering a combination of aesthetics and practicality.
Exterior Features
The outer shell is characterized by its aerodynamic profile, which not only enhances visual appeal but also improves fuel efficiency. Noteworthy elements include refined headlights, a bold grille, and alloy wheels that contribute to its sporty look. The use of high-quality materials ensures durability while maintaining a lightweight structure.
Interior Layout
Inside, the cabin prioritizes passenger comfort and convenience. Spacious seating, thoughtful ergonomics, and an intuitive dashboard layout are prominent. Technology integrations, such as infotainment systems and advanced climate control, elevate the driving experience. Safety features are seamlessly incorporated, providing peace of mind for both the driver and passengers.
Key Components of the Ford Fusion
This section highlights essential elements found in a mid-size sedan, focusing on their roles and functionalities within the vehicle. Understanding these crucial components helps in appreciating the vehicle’s performance, safety, and overall design.
Engine and Transmission
The powertrain is vital for any automobile, comprising the engine and transmission. The engine converts fuel into motion, while the transmission manages the power transfer to the wheels, ensuring smooth acceleration and efficient fuel use.
Chassis and Suspension
The chassis serves as the vehicle’s foundation, housing essential systems and components. The suspension system works in tandem with the chassis, providing stability, comfort, and control while driving.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Engine | Converts fuel into mechanical energy |
| Transmission | Transfers power from the engine to the wheels |
| Chassis | Supports all vehicle components |
| Suspension | Ensures comfort and handling |
Engine Specifications and Variants
This section delves into the various powertrains and their specifications found in a specific midsize vehicle model. Understanding these engine options is essential for enthusiasts and technicians alike, as they influence performance, efficiency, and overall driving experience.
The vehicle features multiple engine configurations, catering to different driving preferences and requirements. Below is a summary of the engine specifications and their variants:
| Engine Type | Cylinders | Displacement (L) | Horsepower | Torque (lb-ft) | Transmission Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inline-4 | 4 | 2.5 | 175 | 172 | 6-Speed Manual, 6-Speed Automatic |
| V6 | 6 | 3.0 | 240 | 228 | 6-Speed Automatic |
| V6 | 6 | 3.5 | 263 | 249 | 6-Speed Automatic |
Each engine variant provides distinct advantages, enabling consumers to select the option that best aligns with their driving style and needs.
Transmission System Overview
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a vehicle, serving as the bridge between the engine and the wheels. This intricate assembly is responsible for transferring power, allowing for the efficient conversion of energy into motion. Understanding the components and their interactions within this system is essential for anyone looking to appreciate the engineering behind modern automobiles.
At its core, the transmission comprises several key elements, including gears, clutches, and hydraulic systems. Gears facilitate the adjustment of torque and speed, enabling the vehicle to operate effectively under various driving conditions. Meanwhile, clutches engage and disengage the engine’s power from the transmission, allowing for smooth transitions between gears.
The hydraulic system is vital for controlling these components, utilizing fluid pressure to activate the clutches and shift gears automatically in modern vehicles. This combination of mechanical and hydraulic engineering ensures that the vehicle can accelerate smoothly, respond quickly to driver inputs, and maintain optimal performance.
Overall, a well-functioning transmission system is essential for a vehicle’s reliability and efficiency, influencing everything from fuel economy to driving comfort. Understanding its design and function can greatly enhance one’s knowledge of automotive technology.
Brake System Details and Parts
The braking mechanism of a vehicle is crucial for ensuring safety and performance. This system is composed of various components that work together to halt motion effectively. Understanding the intricate relationships between these elements is essential for proper maintenance and repairs.
Key Components of the Braking Mechanism
The primary components include brake pads, rotors, calipers, and hydraulic lines. Brake pads are the friction materials that press against the rotors to create stopping power. Rotors are circular discs attached to the wheels, serving as the surface for the brake pads to clamp down on. Calipers house the brake pads and utilize hydraulic pressure to apply the necessary force for braking.
Maintenance and Common Issues
Regular inspections of the braking system are vital for optimal performance. Common issues include worn brake pads and warped rotors, which can lead to reduced braking efficiency. Timely replacement of these elements not only enhances safety but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire braking assembly.
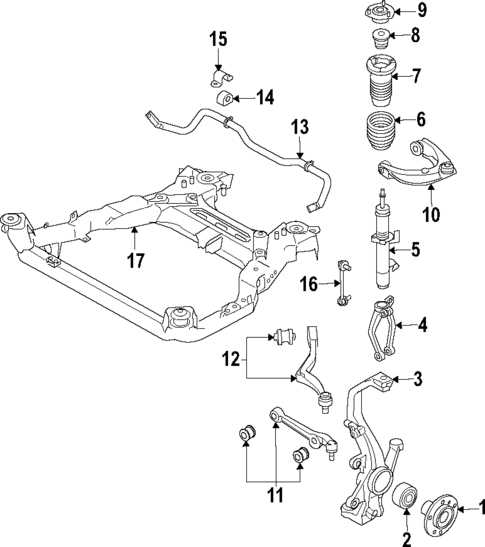
Suspension and Steering Mechanisms
This section delves into the crucial systems responsible for providing stability, control, and comfort in vehicles. These assemblies are engineered to absorb shocks from the road and facilitate smooth handling, ensuring an optimal driving experience. Understanding the configuration and function of these components is essential for maintaining vehicle performance and safety.
Components of the Suspension System
The suspension system is composed of various elements that work together to support the vehicle’s weight and enhance ride quality. Key components include:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorbers | Dampen the impact of road irregularities, improving ride comfort. |
| Coil Springs | Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb shocks during travel. |
| Control Arms | Connect the suspension to the vehicle’s frame, allowing for controlled movement. |
Steering System Overview
The steering system is integral to navigating the vehicle with precision and ease. It comprises various mechanisms that enable smooth directional changes, ensuring safety and responsiveness. Key elements include:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | Provides the driver with control to guide the vehicle. |
| Steering Column | Transmits the driver’s input from the wheel to the steering mechanism. |
| Rack and Pinion | Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion for the wheels. |
Electrical System Layout
The electrical architecture of a vehicle is crucial for its operation and functionality. It encompasses various components that work together to ensure efficient energy distribution, control, and communication between different systems. Understanding this framework is essential for troubleshooting issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key Components
Central to the electrical network are several vital elements, including the battery, alternator, and fuse box. The battery serves as the primary energy source, providing the necessary power to start the engine and operate various accessories. The alternator plays a critical role by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, replenishing the battery while the vehicle is in motion. Meanwhile, the fuse box protects the circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity in case of overloads, ensuring safety and preventing damage.
Wiring and Connections
The layout of wiring and connections is meticulously designed to facilitate seamless interaction among components. Wires are color-coded and routed strategically to minimize interference and ensure reliable performance. Connectors are also essential, allowing for easy disconnection and reconnection during repairs or upgrades. Understanding the routing and placement of these connections can significantly aid in diagnosing electrical issues.
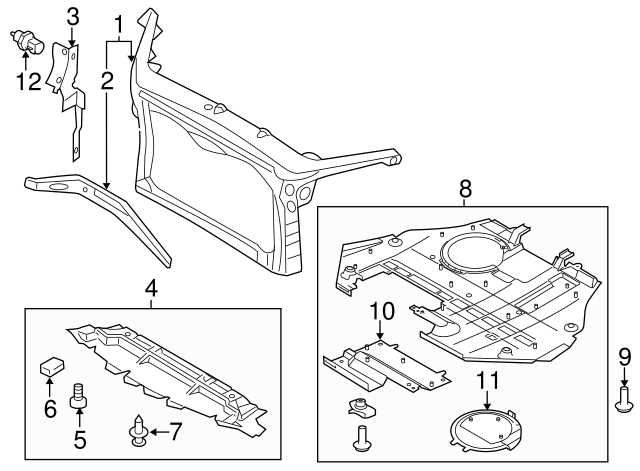
Body and Frame Assembly Insights
The integrity of a vehicle’s structure is crucial for both performance and safety. Understanding the elements that contribute to the chassis and outer shell is essential for effective maintenance and repairs. This section delves into the various components involved in the construction and assembly of the vehicle’s body and framework.
- Chassis: The backbone of the vehicle, providing structural support and housing critical systems.
- Body Panels: These include doors, fenders, and hoods, which are essential for both aesthetics and aerodynamics.
- Subframes: Reinforced sections that add rigidity and help in absorbing impact during collisions.
- Mounting Points: Critical locations where various components attach to the body and frame, ensuring stability and alignment.
When examining the assembly process, several factors come into play:
- Material Selection: The choice of materials affects weight, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Welding Techniques: Different methods are employed to ensure strong and secure joints between parts.
- Alignment and Fitment: Proper alignment during assembly is crucial for the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the body and frame assembly is vital for anyone involved in vehicle maintenance or repair. Recognizing how these components interact can lead to better service and enhanced vehicle longevity.
Interior Features and Components
The interior of a vehicle plays a crucial role in providing comfort, convenience, and functionality for its occupants. A well-designed cabin enhances the driving experience by integrating various components that cater to the needs of passengers and drivers alike. This section explores the essential features and elements found within the interior, emphasizing their importance and functionality.
Key Features
- Seating Arrangements
- Dashboard Layout
- Control Interfaces
- Storage Solutions
Each of these features contributes significantly to the overall usability and comfort of the interior space. The arrangement of seats ensures adequate legroom and support for all passengers, while the dashboard layout offers easy access to vital controls.
Comfort and Convenience Elements
- Climate Control System
- Infotainment System
- Sound Insulation
- Ambient Lighting
Comfort elements, such as an efficient climate control system and advanced infotainment options, create a pleasant atmosphere within the cabin. Additionally, sound insulation enhances the serenity of the driving experience, making journeys more enjoyable.
Cooling System Diagram Analysis
The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining the operational temperature of a vehicle’s engine. By managing heat distribution and ensuring that excess warmth is dissipated effectively, this system helps prevent overheating and ensures optimal performance. Understanding its components and their interaction is essential for troubleshooting or maintenance.
Core Components
At the heart of the temperature control system are key elements that regulate fluid flow and manage heat exchange. The primary components include the radiator, which cools the liquid as it passes through, and the thermostat, responsible for controlling the flow of coolant based on engine temperature. Additionally, hoses and pumps circulate the fluid, ensuring that the entire system remains balanced under varying conditions.
Fluid Circulation Path
The movement of coolant throughout the system follows a deliberate path. Beginning in the engine, the heated liquid is transferred to the radiator, where it loses heat before returning. The process is aided by the thermostat, which ensures the temperature stays within the optimal range. This continuous circulation prevents the engine from overheating during operation.
Fuel System Functionality
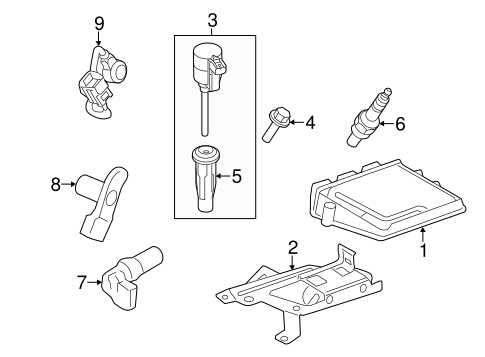
The primary function of a vehicle’s fuel system is to efficiently deliver energy to the engine, ensuring optimal performance. This process involves a series of components working together to transport, filter, and control the flow of liquid fuel, converting it into energy for propulsion. Every part of the system plays a crucial role in maintaining stability and fuel economy, while also reducing emissions.
The fuel system operates through several key stages:
- Fuel storage and delivery
- Regulation of fuel pressure
- Fuel filtration and cleanliness
- Combustion efficiency in the engine
By maintaining these stages, the system ensures that the engine receives a consistent and clean supply of energy, contributing to the vehicle’s overall efficiency and performance.
Exhaust System Design Elements
The design of an exhaust system is critical for the efficient operation of any vehicle. It serves to manage the gases produced by the engine, ensuring they are properly filtered and expelled. A well-constructed system helps improve engine performance, reduce emissions, and control noise levels. The structure includes various components that work in unison to optimize both the environmental and functional aspects of the vehicle’s operation.
Flow Efficiency
Flow efficiency plays a significant role in the overall performance of the system. The smoother the passage of exhaust gases, the less energy the engine needs to push them out. This improves fuel economy and enhances the vehicle’s responsiveness. Engineers carefully design the size and layout of pipes to minimize resistance and ensure that the gases are efficiently routed out of the engine.
Heat Management
Managing heat within the exhaust system is another essential aspect. Excessive heat can lead to damage and reduced performance, while a properly designed system dissipates it effectively. Heat shields and insulating materials are often integrated to protect other components and maintain a safe operating temperature.
Common Replacement Parts Guide
Vehicles require periodic maintenance, and over time, certain components become prone to wear and need to be replaced. Understanding which elements are most commonly substituted can help you keep your vehicle in optimal condition and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Below is a guide to frequently swapped-out elements that play critical roles in your car’s overall functionality.
- Brake Components: Essential for safety, elements such as brake pads, rotors, and calipers are often replaced due to regular use and exposure to high temperatures.
- Suspension Elements: Parts like shock absorbers and struts wear out over time, leading to a less comfortable ride and decreased handling performance.
- Filters: Air and fuel filters are key to maintaining engine health, and they need regular replacement to prevent clogs and ensure efficient operation.
- Belts and Hoses: Timing belts, serpentine belts, and various hoses degrade with age, and timely replacements are necessary to avoid more significant damage.
- Battery: A car’s battery will lose