The design and functionality of a mid-size sedan’s mechanical and electrical elements are critical to its performance and reliability. Understanding the various systems and how they interact can help in identifying and maintaining each part effectively. This exploration delves into the intricate details of the vehicle’s essential structures, offering insights into its composition.
Whether it’s the engine components or the sophisticated electrical systems, each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation. The layout of these systems is thoughtfully designed to optimize efficiency and longevity, contributing to a well-rounded driving experience.
From the suspension to the transmission system, every aspect has been crafted to deliver comfort, stability, and performance. This article provides an in-depth look at the vital structures, helping drivers and enthusiasts alike navigate through the complexities of vehicle maintenance and upgrades.
2013 Ford Fusion Parts Overview
The following section provides a concise guide to the various components that make up a popular mid-sized sedan from its generation. These elements work together to ensure smooth operation and reliable performance over time. Understanding the layout and function of each component can help owners maintain and repair their vehicles effectively.
Key Mechanical Systems
- Engine Assembly: Central to the vehicle’s function, this includes critical parts such as the block, pistons, and intake system, all working together to power the car.
- Transmission: Responsible for shifting gears, ensuring the car adjusts its speed efficiently. Automatic and manual options offer different configurations.
- Suspension: Provides comfort and stability, with struts, shocks, and control arms managing the vehicle’s response to road conditions.
Electrical and Interior Components
- Engine Components of the 2013 Fusion

The power unit of this vehicle consists of various essential elements that work in unison to ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. These components are intricately designed to handle various tasks, from fuel combustion to energy distribution. Understanding how each piece functions together provides a comprehensive view of what makes the engine both reliable and efficient.
Key elements include systems responsible for air intake, fuel delivery, and exhaust management. Each of these areas plays a crucial role in maximizing efficiency, power output, and overall vehicle longevity. Proper maintenance and knowledge of these parts are vital to keeping the engine running effectively.
Transmission System Breakdown
The transmission system is responsible for managing the power generated by the engine and transferring it to the wheels, ensuring smooth transitions between speeds. Understanding its structure is essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and handling. This system comprises various interconnected elements that work together to regulate torque and speed, allowing the vehicle to adapt to different driving conditions.
- Clutch assembly: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, enabling the driver to shift gears smoothly.
- Gearbox: Contains different sets of gears that control the speed and torque of the vehicle. The driver selects the appropriate gear for different road conditions and speeds.
- Driveshaft: Transfers rotational power from the gearbox to the differential, which then distributes power to the wheels.
- Differential: Balances the speed between the wheels, allowing smooth turning while maintaining power to both sides.
- Torque converter (for automatic systems):
Suspension and Steering Elements
The components responsible for smooth handling and control play a key role in the vehicle’s overall performance. These interconnected systems allow for balanced movement, stability, and comfort, especially when navigating various road conditions. The assembly of parts ensures precise maneuverability, maintaining both safety and ride quality.
Key Suspension Components
The suspension system includes several elements designed to absorb shocks, enhance ride comfort, and maintain tire contact with the road. Each piece works together to balance weight distribution and minimize vibrations, providing a smoother driving experience.
Steering Mechanism Overview
The steering mechanism is essential for controlling direction and ensuring responsive handling. With various linkages and gears, the system allows for accurate turns and adjustments. It ensures that the vehicle responds promptly to the driver’s input, offering ease of control even at high speeds.
Component Function Shock Absorbers Reduce impact from road irregularities Control Arms Connect wheels to the chassis, allowing up and down motion Tie Rods Transmit force from the steering wheel to the wheels Ball Joints Enable free movement of suspension and steering parts Interior Electrical System Diagram
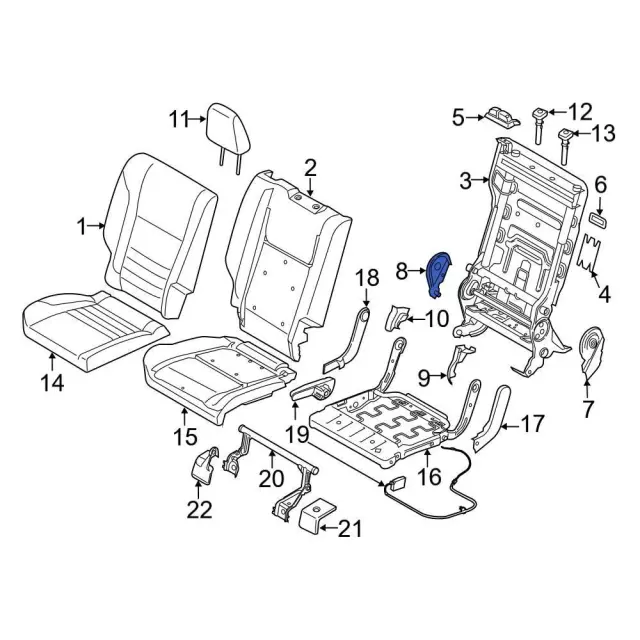
The interior electrical setup plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of a vehicle’s internal systems. Various components work together to manage functions like lighting, dashboard instruments, and climate control. Understanding how these elements are connected and operate is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality.
Key Components of the Electrical Network
The electrical network within the cabin includes circuits that control the lights, sensors, and entertainment systems. Wiring harnesses connect these components, ensuring power is distributed efficiently. Regular inspection of these circuits can prevent malfunctions and keep the overall system in good working order.
Control Modules and Wiring
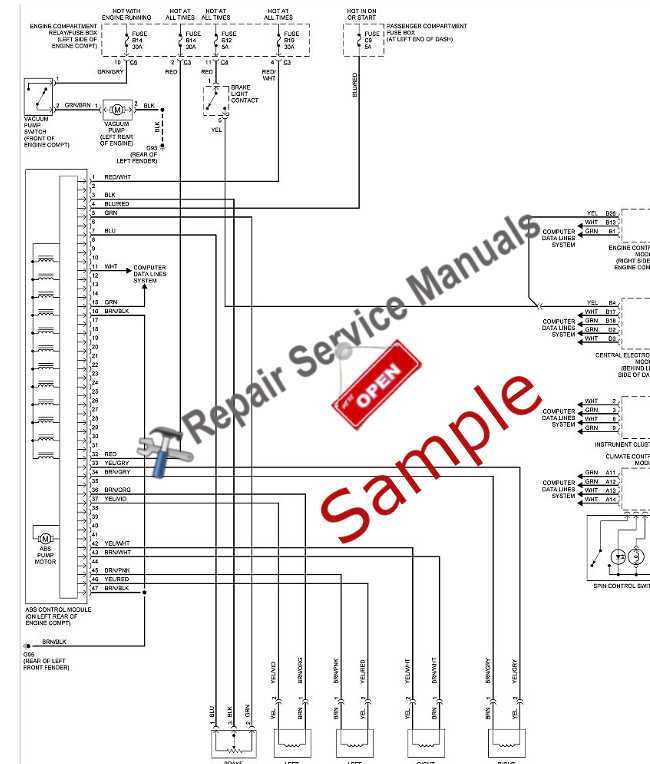
The control modules are responsible for managing various operations within the cabin, such as seat adjustments and window controls. These modules rely on a complex web
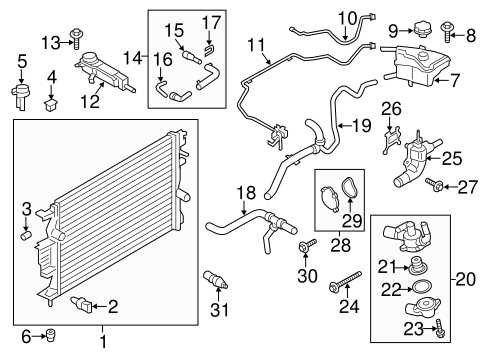
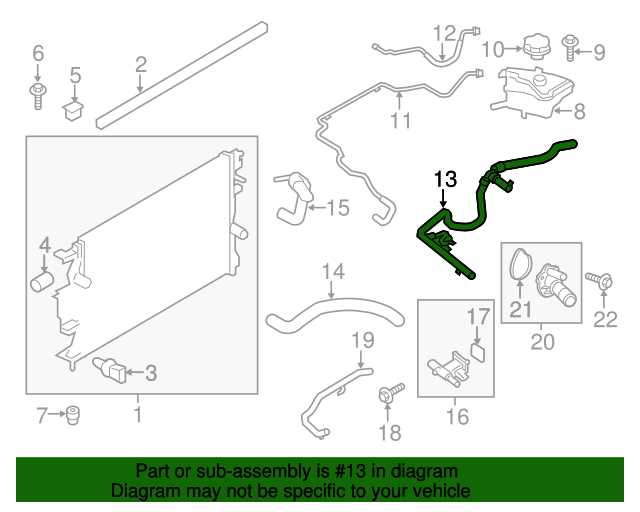
Cooling and Heating System Parts
The cooling and heating system plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable environment inside the vehicle. This complex setup ensures that the temperature can be regulated effectively, providing both warmth during cold weather and a refreshing atmosphere in warmer conditions.
Key components within this system include the radiator, which dissipates heat from the engine, and the heater core, responsible for distributing warm air into the cabin. Additionally, the thermostat regulates coolant flow to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Another essential element is the blower motor, which facilitates the circulation of air through the system, ensuring that temperature adjustments are felt promptly. Other important features include various hoses and valves that facilitate fluid movement and control within the system.
Braking System Components

The braking system is a crucial element in vehicle safety, playing a vital role in ensuring effective stopping power and control. Understanding the various components involved helps in maintaining optimal performance and enhancing overall driving experience.
- Brake Pedal: The primary control mechanism for activating the braking system.
- Master Cylinder: Converts pedal pressure into hydraulic force, transmitting it to the brakes.
- Brake Lines: Tubes that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the brake components.
- Brake Calipers: Clamps that squeeze the brake pads against the rotor to create friction.
- Brake Pads: Friction materials that press against the rotors to slow down the vehicle.
- Rotors: Disc-shaped components that rotate with the wheels and are gripped by the brake pads.
- Brake Fluid: Hydraulic fluid that transfers force within the braking system.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are essential to ensure the system functions properly and safely. Awareness of each component’s role can aid in identifying potential issues early.
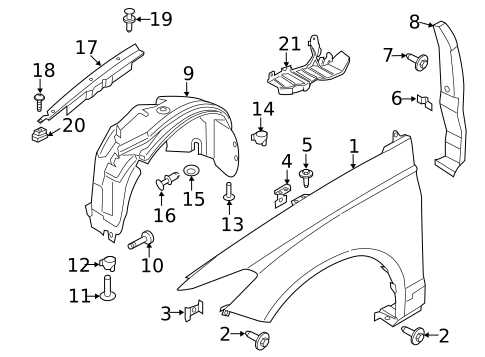
Body and Frame Structural Elements
The integrity and performance of a vehicle heavily rely on its body and frame components. These foundational elements provide the necessary support and stability, ensuring that the vehicle maintains its shape and durability under various conditions. Understanding the structure of these components is essential for maintenance and repair, as well as for enhancing overall safety and performance.
Key Components of the Structure
At the core of the vehicle’s architecture are the chassis and body panels. The chassis acts as the backbone, accommodating essential systems and supporting the weight of the vehicle. Meanwhile, the body panels protect internal systems and provide aesthetic appeal. Each element is designed with precision to optimize performance and safety.
Importance of Structural Integrity
Maintaining the integrity of the frame and body is crucial for a safe driving experience. Any damage to these elements can lead to structural weakness, potentially compromising safety. Regular inspections and prompt repairs can help in preserving the vehicle’s strength and longevity, ensuring that it performs at its best throughout its lifespan.
Exhaust System Layout and Parts

The exhaust system is a critical component of a vehicle, responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine and ensuring efficient performance. Understanding its configuration and individual elements can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components Overview
This system typically consists of several key elements, including the manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and tailpipe. Each part plays a vital role in controlling emissions and reducing noise.
Functionality and Importance
The proper arrangement of these components ensures optimal flow of exhaust gases, which enhances engine efficiency. Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system are essential to prevent leaks and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Fuel System Components and Layout
The fuel system is crucial for the efficient operation of any vehicle, ensuring the engine receives the right amount of fuel for optimal performance. This section explores the various elements that comprise this system and their arrangement, providing insights into how each component contributes to overall functionality.
Key Components
- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel needed for the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Moves fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel before it enters the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the combustion chamber at precise intervals.
- Fuel Lines: Transport fuel between various components of the system.
System Layout
The arrangement of the fuel system components is designed to maximize efficiency and reliability. Generally, the fuel flows from the tank through the fuel pump, passes through the filter, and is then injected into the engine. Each part plays a specific role, ensuring that the engine operates smoothly and effectively.
Lighting and Exterior Electrical Elements
The illumination and external electrical components play a crucial role in ensuring visibility and safety while enhancing the overall aesthetics of a vehicle. These features are designed to provide effective lighting solutions for various driving conditions and to facilitate the operation of essential systems.
Key components in this category include:
- Headlights: Essential for nighttime driving, they illuminate the road ahead.
- Taillights: Indicate the presence of the vehicle to others from behind.
- Turn Signal Lights: Communicate the driver’s intentions to change lanes or turn.
- Fog Lights: Improve visibility in adverse weather conditions, such as rain or fog.
- Interior Lighting: Enhances visibility inside the vehicle, making it easier for passengers to find items.
- Wiring Harnesses: Connect various electrical components, ensuring proper functionality.
Maintaining these elements in optimal condition is vital for safe driving experiences. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent potential issues and enhance overall performance.
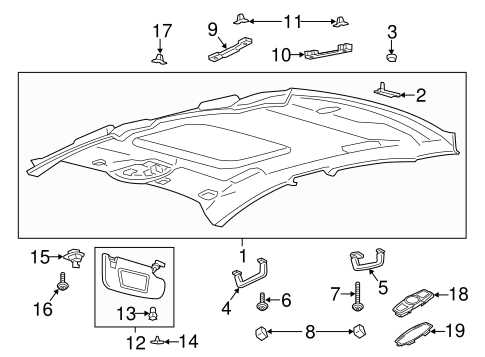
Safety Features and Airbag Diagram
The incorporation of safety mechanisms in modern vehicles is crucial for protecting occupants during unexpected events. Understanding how these systems work together can enhance the overall driving experience and ensure peace of mind on the road.
Airbags play a significant role in safeguarding passengers by deploying during collisions. They are strategically positioned throughout the vehicle to provide maximum protection. The placement and functionality of these cushions are designed to minimize injury risk in various types of impacts.
Active safety systems, such as electronic stability control and anti-lock braking systems, complement airbags by helping drivers maintain control in challenging situations. These technologies work in unison to prevent accidents before they occur, emphasizing the importance of both passive and active safety features in contemporary automobile design.