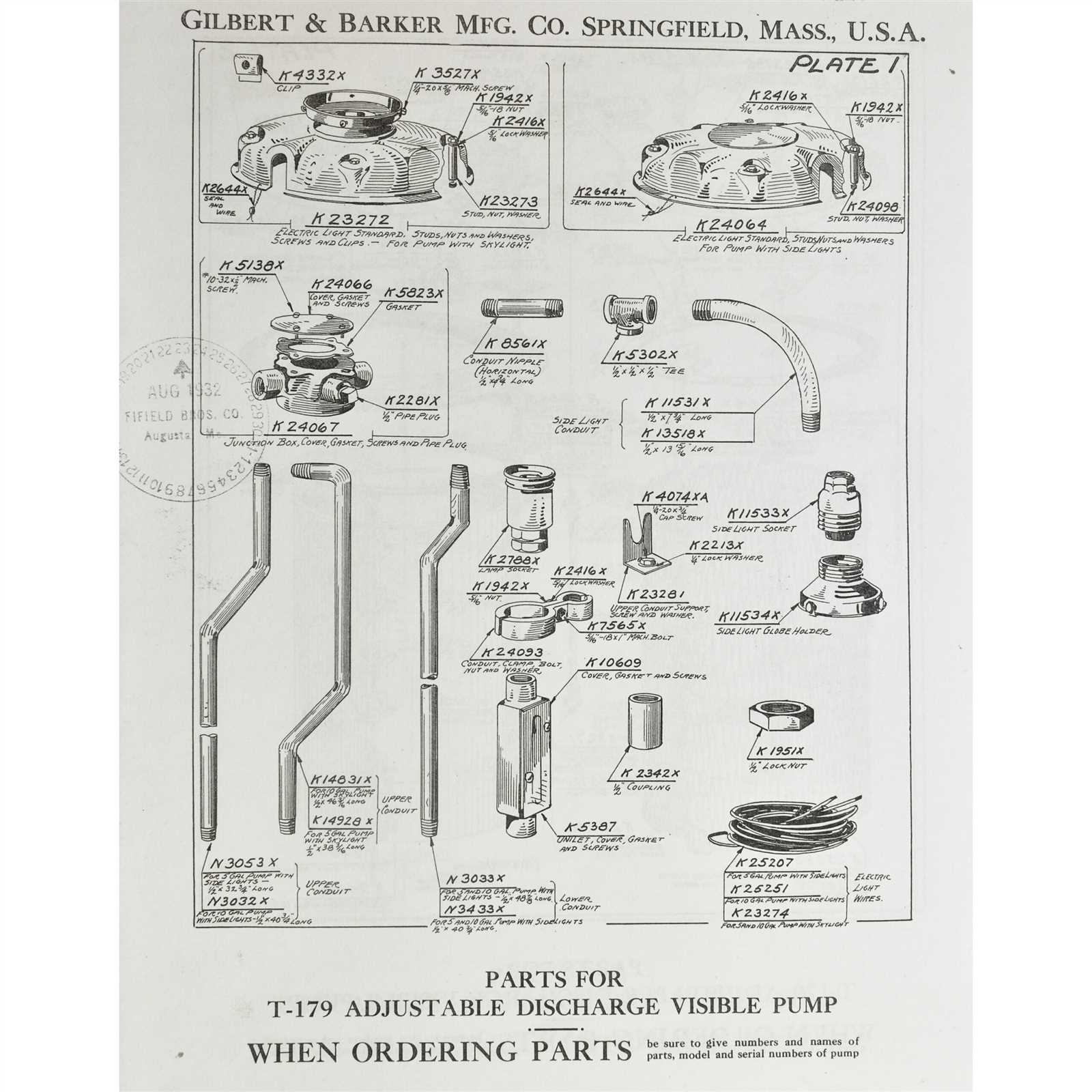
In the realm of liquid transfer mechanisms, an intricate assembly of elements plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation. Each component within this system is designed to work harmoniously, contributing to the overall functionality and reliability of the unit. A comprehensive overview of these components provides valuable insights into their arrangement and interaction.
Familiarity with the arrangement of these elements is essential for anyone involved in maintenance or troubleshooting. By grasping how each section integrates, one can enhance their understanding of the mechanisms at play, leading to more informed decisions during repairs or modifications. This knowledge serves as a foundation for both novice and seasoned professionals alike.
Moreover, an accurate representation of these systems can facilitate training and improve communication among technicians. With clear visual guidance, individuals can quickly identify issues and implement solutions, thereby minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal performance. Understanding these layouts is not merely beneficial; it is a necessity for effective management of liquid transfer operations.
This section delves into the fundamental components that constitute the sophisticated mechanisms of these advanced systems. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless operation and optimal performance, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the setup.
Core Components

The primary elements encompass various modules and subsystems that work in harmony to facilitate effective functionality. These components are designed with precision to meet the demands of modern applications, ensuring durability and longevity.
Operational Features

Additionally, specific operational features enhance user interaction and service delivery. By integrating innovative technology, these systems provide intuitive interfaces and robust security measures that streamline processes and safeguard transactions.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Control Unit | Central processor that manages all operations and user interfaces. |
| Pumping Mechanism | Device responsible for the movement of the liquid through the system. |
| Metering Device | Instrument that measures the volume of liquid dispensed accurately. |
| Display Interface | User interface that provides essential information and transaction details. |
| Safety Features | Systems designed to prevent leaks, spills, and unauthorized access. |
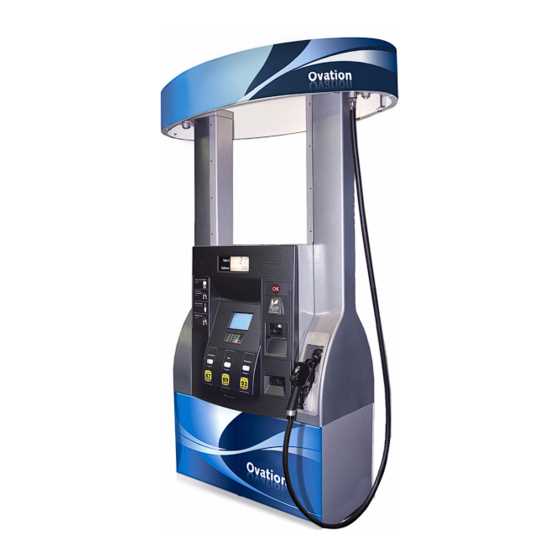
Identifying Control Unit Features
The control unit serves as the brain of a dispensing mechanism, overseeing operations and ensuring seamless functionality. Its design is crucial for efficient performance, influencing how various components communicate and respond during use. Understanding the key characteristics of this unit can greatly enhance maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Key Functionalities
At the core of the control unit’s design are several essential functionalities. This includes monitoring system diagnostics, regulating power supply, and facilitating user interactions. With integrated software, it provides real-time feedback on performance metrics, allowing for swift identification of any anomalies.
Connectivity Options
Modern control units often feature diverse connectivity options. These may include serial ports for data exchange, network interfaces for remote management, and input/output ports for peripheral devices. Such connectivity ensures that the system remains adaptable to evolving technologies and user requirements.
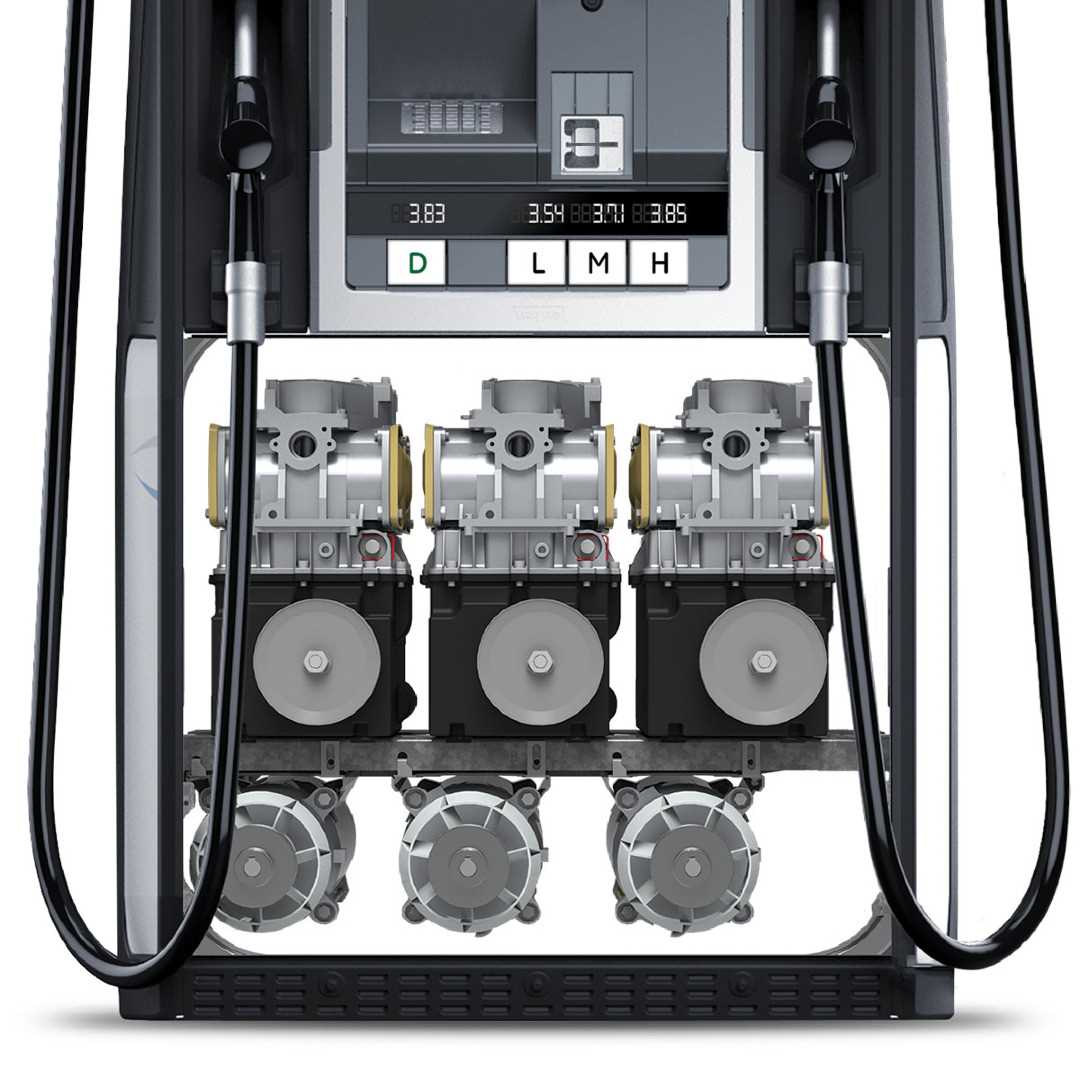
Electrical System Layout Explanation
This section delves into the organization and functionality of the electrical framework utilized in a dispensing unit. Understanding the configuration of the components is crucial for efficient operation and maintenance. A well-structured layout enhances performance and ensures safety throughout the system.
Components Overview

The electrical setup comprises various elements that work in concert to facilitate the seamless operation of the unit. Each component plays a specific role, contributing to the overall efficiency of the assembly.
Wiring and Connections
The connections among the different elements are vital for functionality. Proper wiring not only ensures the reliability of power supply but also minimizes the risk of electrical failures. Below is a summary of key connections:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides electrical energy to the entire system. |
| Control Unit | Regulates operations and processes user inputs. |
| Sensors | Monitor levels and ensure safe operation. |
| Relay | Controls the power flow to different components. |
| Display Panel | Shows operational status and user information. |
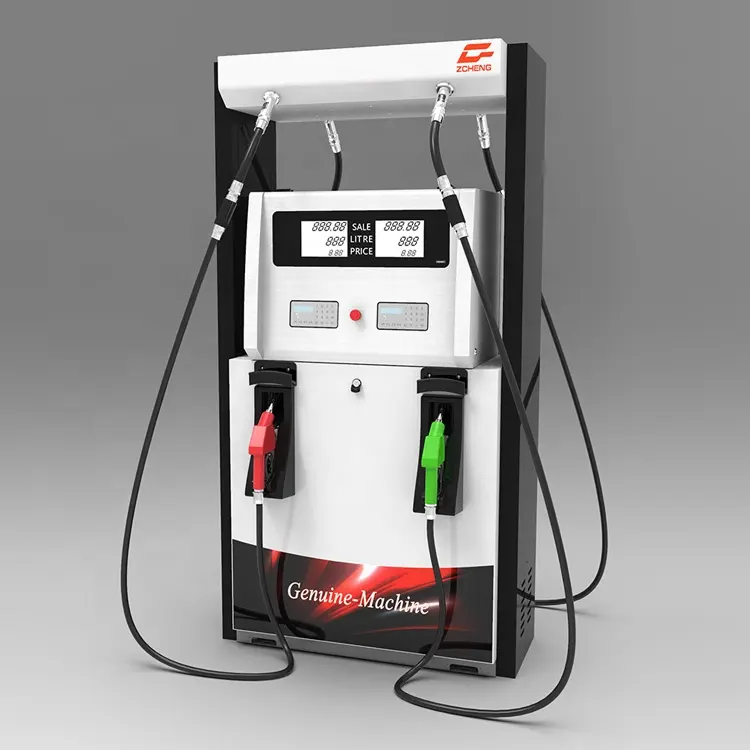
Fluid Management Parts Description
The efficient operation of liquid distribution systems relies on various components that ensure precise control and monitoring. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and performance in any liquid handling application. This section delves into the essential components involved in managing liquid flow and their significance in the overall system.
Key Components
Flow Meters: These instruments are vital for measuring the volume of liquid passing through the system. They provide accurate readings that facilitate inventory management and help in identifying discrepancies in flow rates. High-quality flow meters contribute to operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards.
Control Valves

Control Valves: Acting as the gatekeepers of liquid flow, these devices regulate the passage of liquid within the system. They can adjust the flow rate based on various parameters, ensuring that the right amount of liquid is dispensed at any given time. This precision not only enhances performance but also minimizes waste and reduces operational costs.
Maintenance Considerations for Components
Proper upkeep of essential elements is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to these components can prevent unexpected failures and costly repairs. This section outlines crucial maintenance practices that can enhance reliability and functionality.
Regular Inspection
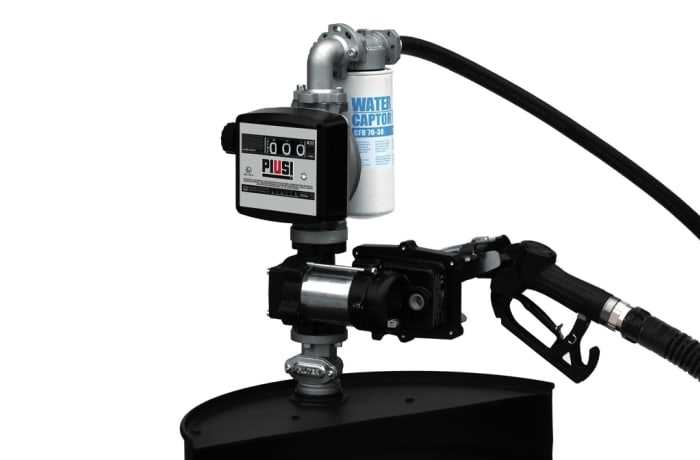

Frequent assessments of various components help identify potential issues before they escalate. Key areas to focus on include:
- Seals and gaskets: Check for wear or damage that could lead to leaks.
- Connections and fittings: Ensure tightness and integrity to avoid malfunctions.
- Electrical components: Inspect wiring and connectors for signs of corrosion or fraying.
Cleaning and Lubrication

Maintaining cleanliness and applying appropriate lubricants can significantly impact the functionality of critical parts. Consider the following practices:
- Remove dirt and debris from surfaces regularly to prevent buildup.
- Use recommended lubricants on moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Clean filters and screens to ensure unobstructed flow and efficiency.
Common Issues in Fuel Dispensing

The process of liquid transfer at service stations can encounter several challenges that may hinder efficient operations. Understanding these common complications is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring customer satisfaction.
One prevalent issue is the inconsistency in liquid flow, which can be attributed to various factors such as blockages, worn-out components, or malfunctioning sensors. These disruptions not only frustrate users but can also lead to operational delays.
Another significant concern involves inaccurate measurement readings. Discrepancies in the displayed amount can arise from calibration errors or mechanical failures, resulting in potential financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
Additionally, wear and tear on critical components can lead to leaks, posing environmental hazards and safety risks. Regular maintenance and timely replacements are crucial in mitigating these issues and ensuring safe operations.
Finally, electrical malfunctions may impede functionality, often linked to faulty wiring or connection problems. Addressing these electrical concerns promptly is vital to maintaining reliability and performance.
Parts Replacement Guidelines
When it comes to maintaining and enhancing the efficiency of your equipment, understanding the process of component substitution is crucial. Proper replacement not only ensures optimal functionality but also prolongs the lifespan of the system. This section provides essential insights and best practices for effective replacement procedures.
Identification of Components
Before initiating any replacement, accurately identifying the components that require substitution is vital. Take note of the model number and specifications to ensure compatibility. Here are some common elements that may need attention:
| Component | Common Issues | Replacement Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Seals | Wear and tear, leakage | Every 6 months |
| Pumps | Decreased performance, noise | As needed, typically every 2-3 years |
| Hoses | Cracks, blockages | Annually |
Replacement Process
Once the components are identified, follow a systematic approach for replacement. Ensure that the equipment is powered down and properly isolated to avoid accidents. Utilize the manufacturer’s guidelines for disassembly and installation, and always use quality replacements to maintain performance standards.
Importance of Accurate Diagrams

Clear and precise illustrations play a crucial role in various technical fields, ensuring that individuals can understand complex systems effectively. These visual aids facilitate the identification of components and their interconnections, thus enhancing comprehension and enabling efficient troubleshooting. Without well-defined schematics, the risk of misinterpretation increases, leading to potential operational failures or safety hazards.
Benefits of Clarity

Well-crafted visuals contribute to a streamlined approach in maintenance and repair tasks. Technicians can quickly locate the necessary elements, significantly reducing the time spent on diagnostics. Additionally, accurate representations support training efforts, allowing newcomers to familiarize themselves with the structure and functionality of systems more efficiently.
Impact on Safety and Efficiency
Inaccurate or ambiguous illustrations can lead to mistakes that compromise both safety and efficiency. By adhering to rigorous standards in creating visual representations, organizations can minimize errors and enhance operational performance. It is essential for diagrams to reflect the true nature of systems, as this fosters a safe working environment and ensures the longevity of equipment.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Reduces time spent on diagnostics |
| Detail | Facilitates effective training |
| Accuracy | Minimizes operational errors |
| Standardization | Enhances safety measures |