Understanding the intricacies of a classic two-wheeler involves delving into its individual elements and how they interconnect. This knowledge is essential for enthusiasts and restorers aiming to preserve the essence of vintage machines. A well-structured overview of these components not only aids in maintenance but also enhances the overall appreciation of the craftsmanship involved.
Components of any motorcycle play a crucial role in its performance and longevity. Each part, from the engine to the electrical systems, has a specific function that contributes to the bike’s overall operation. Grasping the relationship between these elements allows for a more profound understanding of how the motorcycle functions as a cohesive unit.
Additionally, visual representations of the layout can serve as valuable references during repairs or upgrades. By examining the arrangement of each component, one can gain insights into potential issues and solutions, ensuring that the machine remains in optimal condition. This exploration not only fosters a connection between the rider and their vehicle but also ignites a passion for the art of motorcycle restoration.
Overview of 1972 Honda CB350
This section provides a comprehensive look at a classic motorcycle from the early ’70s, known for its blend of style, performance, and practicality. The model has become iconic, appealing to enthusiasts and collectors alike. Its engineering reflects the innovative spirit of its time, combining functionality with a sleek design that captures the essence of the era.
Design and Features
The motorcycle boasts a distinctive aesthetic, characterized by clean lines and a well-proportioned frame. Key components include a powerful engine that delivers a satisfying ride, complemented by a robust chassis designed for stability and control. The attention to detail in the craftsmanship is evident, making it not just a mode of transportation but also a piece of art.
Performance and Handling
With its responsive handling and smooth power delivery, the vehicle is suitable for both urban commuting and weekend adventures. Riders appreciate its balance and maneuverability, which enhance the overall experience on the road. The combination of performance and comfort has made this model a favorite among enthusiasts, solidifying its legacy in motorcycle history.
Engine Specifications and Components
This section delves into the essential features and elements that constitute the power unit of a classic motorcycle. Understanding these specifications is crucial for enthusiasts and mechanics alike, as they ensure optimal performance and maintenance of the machine.
The heart of the motorcycle is its engine, which comprises various interconnected components, each playing a vital role in its functionality. Here are the primary specifications and parts:
- Engine Type: Air-cooled, four-stroke, twin-cylinder.
- Displacement: Approximately 325 cc.
- Bore and Stroke: 69 mm x 64 mm.
- Compression Ratio: 9.0:1.
- Maximum Power: Approximately 34 horsepower at 10,000 RPM.
- Fuel System: Dual carburetors.
In addition to the specifications, the following components are integral to the engine’s operation:
- Cylinder Head: Houses the valves and combustion chamber.
- Crankshaft: Converts linear motion into rotational power.
- Camshaft: Operates the intake and exhaust valves.
- Pistons: Move within the cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
- Ignition System: Responsible for initiating combustion.
Each component must be carefully considered during repairs or upgrades to maintain the overall performance of the engine. Proper understanding of these specifications and parts allows for informed decisions when restoring or enhancing the motorcycle.
Transmission and Gear Assembly Details
The transmission system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and functionality of a motorcycle. This assembly is designed to facilitate smooth gear shifting and effective power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the components involved in this mechanism can enhance maintenance and repair processes, ensuring optimal operation.
Key Components
The primary elements of the transmission assembly include the gearbox, shift forks, and various gears. Each component works in harmony to achieve the desired speed and torque. The gearbox houses the gears, which are precisely engineered to provide different ratios, allowing the rider to adjust to various riding conditions. Shift forks play a pivotal role in engaging and disengaging the gears during shifting, ensuring smooth transitions.
Assembly Insights
Proper assembly and alignment of the transmission components are vital for performance. Any misalignment can lead to shifting difficulties or even mechanical failure. Regular inspections and maintenance can prevent issues such as excessive wear and ensure that the system operates efficiently. Utilizing high-quality lubricants is also essential for reducing friction and prolonging the lifespan of the transmission assembly.
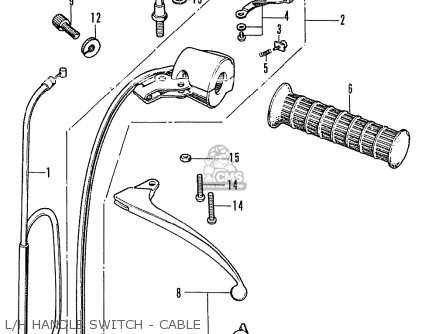
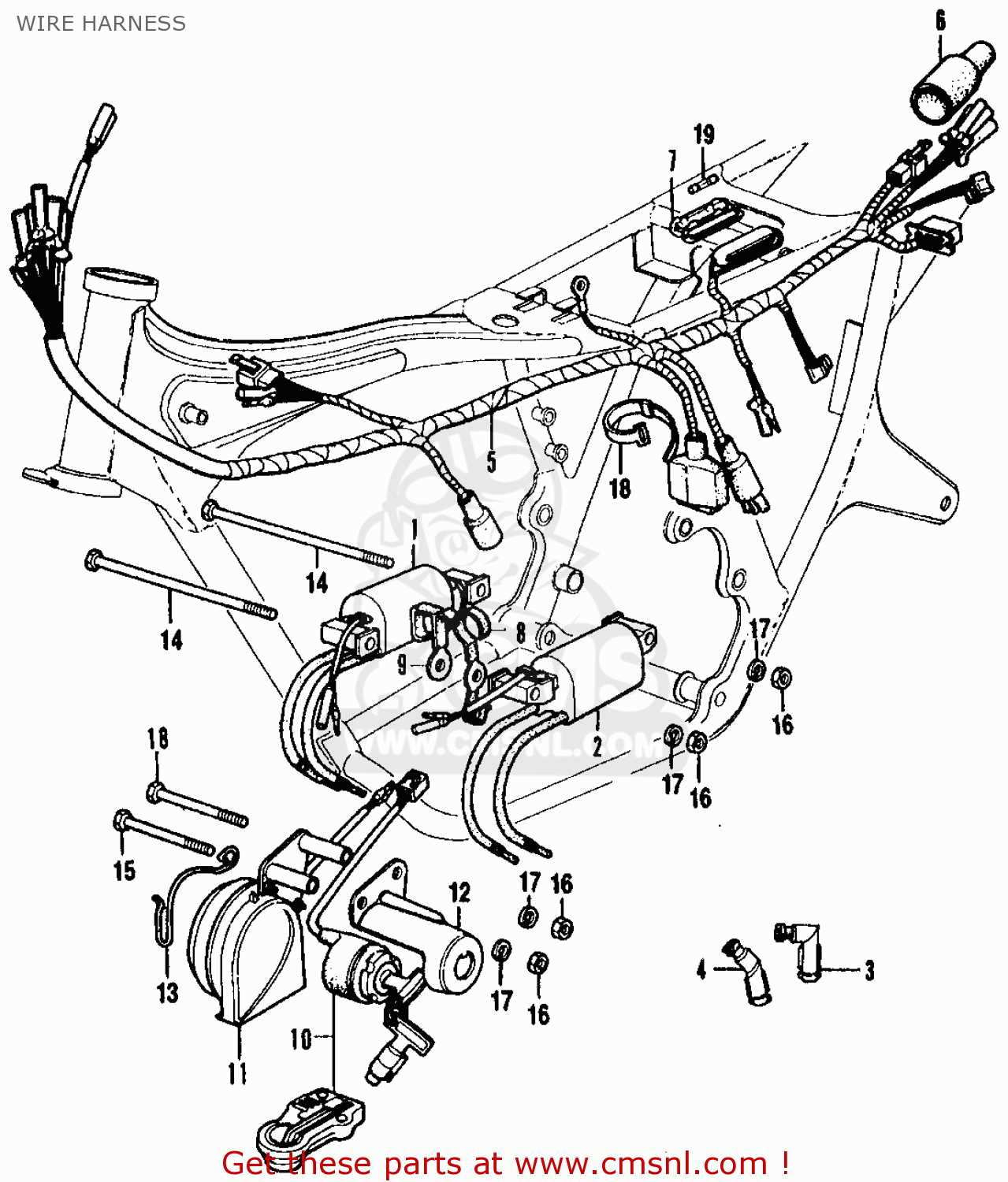
Electrical System Wiring Diagram
The wiring layout of a motorcycle’s electrical system is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and safety. This section explores the intricate connections that allow various components to operate harmoniously. Understanding this configuration is essential for both troubleshooting issues and performing maintenance tasks effectively.
Key Components
Several key elements comprise the electrical framework of a motorcycle. These include the battery, ignition system, lighting, and charging mechanisms. Each part plays a vital role in the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle.
Wiring Connections
Proper connections between the components ensure that electricity flows seamlessly, minimizing the risk of failures. Below is a representation of the essential connections found in the electrical layout:
| Component | Function | Wiring Color |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Power supply for the electrical system | Black (Negative), Red (Positive) |
| Ignition Coil | Produces high voltage for spark generation | Green, Yellow |
| Headlight | Provides illumination for night riding | White, Blue |
| Taillight | Indicates braking and rear presence | Brown, Red |
| Charging System | Maintains battery charge during operation | Orange, Gray |
Frame and Chassis Parts Breakdown
The structural components of a motorcycle are crucial for its overall integrity and performance. Understanding the various elements that make up the framework allows enthusiasts and technicians to identify, repair, or enhance the riding experience. This section delves into the essential components that constitute the chassis, highlighting their functions and interrelationships.
1. Main Frame: The primary structure of the bike, designed to provide support and stability. It serves as the foundation for all other components, ensuring that the vehicle can withstand various stresses while maintaining its shape.
2. Swingarm: This part connects the rear wheel to the main frame, allowing for suspension movement. It plays a vital role in maintaining traction while absorbing shocks during rides.
3. Front Forks: These components connect the front wheel to the main frame, providing steering control and absorbing impacts from the road. Their design influences the motorcycle’s handling and ride comfort.
4. Subframe: An extension of the main structure, the subframe supports additional components such as the seat and rear fender. It is typically lighter and designed for easier access during repairs.
5. Engine Mounts: These brackets secure the engine to the frame, ensuring proper alignment and minimizing vibration. Their integrity is essential for optimal performance and rider comfort.
Understanding the composition and function of these components is essential for anyone looking to maintain or modify their motorcycle effectively.
Suspension System Components Explained
The suspension system is a crucial aspect of any motorcycle, playing a vital role in ensuring a smooth ride and maintaining stability. This system comprises various components that work together to absorb shocks from uneven surfaces, enhancing comfort and control while riding. Understanding these elements can help enthusiasts appreciate their function and importance in vehicle performance.
Key Components of the Suspension System
The primary components of a motorcycle’s suspension system include the forks, rear shock absorbers, and swingarm. Each of these parts contributes to the overall effectiveness of the suspension, impacting handling, comfort, and safety. Below is a table outlining the main components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Front Forks | Provide support for the front wheel and absorb shocks from the road. |
| Rear Shock Absorbers | Stabilize the rear wheel and manage the bike’s rear end movement during rides. |
| Swingarm | Connects the rear wheel to the frame, allowing for controlled wheel movement. |
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular maintenance of suspension components is essential for optimal performance and safety. Worn-out parts can lead to decreased handling capabilities and an uncomfortable ride. Routine inspections and timely replacements can ensure a motorcycle remains responsive and stable, providing an enjoyable riding experience.
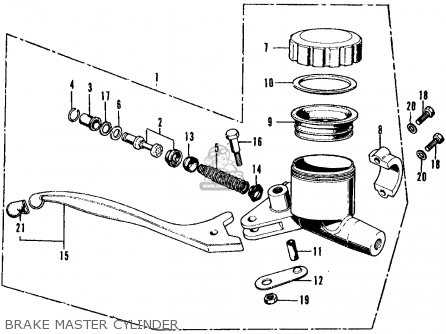
Brake System Parts Overview

The braking mechanism is crucial for ensuring safety and control during operation. This system comprises various components that work in harmony to provide effective stopping power. Understanding each element’s role can enhance maintenance and performance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Brake Lever | This component allows the rider to activate the braking system manually, initiating the braking process. |
| Cable | The cable transmits force from the lever to the brake mechanism, enabling seamless operation. |
| Brake Shoe | This element presses against the drum or disc, creating friction that slows down the vehicle. |
| Drum/Disc | The surface against which the brake shoe makes contact to reduce speed or stop movement. |
| Master Cylinder | This hydraulic component converts the mechanical force from the lever into hydraulic pressure. |
| Brake Fluid | This fluid transmits force within the hydraulic system, ensuring effective braking action. |
| Caliper | In disc brake systems, the caliper houses the brake pads and applies pressure against the disc. |
Fuel System and Tank Layout
The fuel delivery mechanism in motorcycles is crucial for optimal engine performance and efficiency. This section will delve into the components of the fuel system, outlining their arrangement and functionality to ensure a seamless flow of fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding this layout is essential for both maintenance and upgrades.
Components of the Fuel System
The fuel system comprises several key elements, each playing a vital role in the delivery process. The main components include the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel filter, and carburetors. Each part must work harmoniously to ensure that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for combustion.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel and is usually mounted on the frame of the bike. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel from the tank to the engine and must be free of leaks. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the carburetors. |
| Carburetors | Mixes the fuel with air for optimal combustion in the engine. |
Tank Layout Considerations
The arrangement of the fuel tank is also significant, as it affects the motorcycle’s center of gravity and overall balance. The tank is designed to fit snugly between the frame rails, ensuring stability while riding. Additionally, proper positioning of fuel outlets and vents is crucial to prevent fuel starvation and ensure that the tank can vent properly during operation.
Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a motorcycle. It is designed to channel the gases produced during combustion away from the engine, ensuring optimal operation and reducing harmful emissions. Proper configuration of this system is essential for maintaining engine health and enhancing the riding experience.
Key Components
Understanding the main elements of the exhaust system is vital for effective maintenance and upgrades. The configuration typically includes components such as headers, mufflers, and exhaust pipes, each serving a specific purpose in the expulsion of gases and noise reduction.
Table of Components

| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Headers | These pipes connect the engine to the exhaust system, directing gases away from the combustion chamber. |
| Mufflers | Designed to reduce noise levels, mufflers also contribute to exhaust gas flow efficiency. |
| Exhaust Pipes | These pipes carry exhaust gases from the headers to the rear of the motorcycle, allowing for efficient discharge. |
Clutch Mechanism and Parts List
The clutch assembly is a crucial component in the transmission system, allowing for smooth engagement and disengagement of the engine power. Understanding its construction and function is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This section provides an overview of the clutch mechanism, including its essential components and their respective functions.
- Clutch Lever: This lever is operated by the rider’s hand, controlling the engagement of the clutch.
- Cable: Connects the clutch lever to the clutch mechanism, facilitating the transfer of motion.
- Clutch Basket: A circular housing that holds the clutch plates and provides a mounting point for the assembly.
- Clutch Plates:
- Friction Plates: Made from materials that create friction, allowing for power transfer when engaged.
- Steel Plates: Provide structural support and are alternated with friction plates within the basket.
- Pressure Plate: Sits on top of the clutch plates and applies pressure to engage the clutch when the lever is released.
- Clutch Springs: These springs apply pressure to the pressure plate, ensuring the clutch engages effectively.
- Release Mechanism: Allows for disengagement of the clutch when the lever is pulled, usually comprising a push rod and bearing.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the functionality of the clutch system. Regular inspection and replacement of worn parts can significantly enhance performance and reliability.
Bodywork and Fairing Elements

The aesthetics and functionality of a motorcycle are heavily influenced by its outer components. These elements not only contribute to the visual appeal but also play a crucial role in aerodynamics and rider protection. Understanding the various aspects of bodywork can enhance both maintenance and customization efforts.
Key Components
- Fuel Tank: Essential for storing gasoline, it often serves as a focal point in the bike’s design.
- Side Panels: These cover and protect the internal mechanisms while contributing to the overall look.
- Front Fairing: This piece helps reduce wind resistance and protects the rider from debris.
- Seat: Providing comfort for the rider, the seat also contributes to the bike’s silhouette.
- Rear Fender: This part helps keep the bike clean by deflecting road debris and water.
Maintenance Tips

- Regularly clean the bodywork to prevent dirt accumulation and maintain appearance.
- Inspect for cracks or damages that may compromise the integrity of the components.
- Ensure all fasteners are secure to avoid vibrations that can lead to wear over time.
- Consider applying a protective coating to prevent rust and corrosion on metallic parts.
Accessories and Optional Equipment

Enhancing the riding experience often involves additional components that provide comfort, convenience, and improved functionality. These supplementary items can transform a standard motorcycle into a personalized machine tailored to the rider’s preferences.
Various accessories can be added to enrich the overall experience:
- Windshields: Protect against wind and debris while improving aerodynamics.
- Comfort Seats: Enhance riding comfort on longer journeys.
- Backrests: Offer support for both the rider and passenger, adding comfort on extended rides.
- Crash Bars: Provide protection for the bike’s frame and critical components during falls.
- Storage Solutions: Include saddlebags, tail bags, and tank bags for carrying essentials securely.
- Lighting Upgrades: Improve visibility with additional or upgraded lighting systems.
Optional equipment can also improve performance and handling:
- Performance Exhausts: Enhance engine efficiency and sound.
- Aftermarket Suspension Kits: Offer better handling and ride quality.
- Custom Footpegs: Improve comfort and control.
Investing in these optional components can greatly enhance the overall riding experience, ensuring that every journey is enjoyable and tailored to individual needs.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the durability and performance of your motorcycle. Proper care can significantly enhance the lifespan of your machine, making it both enjoyable and reliable for years to come. By following a systematic maintenance routine, you can prevent common issues and keep your ride in optimal condition.
Start with routine inspections of critical components such as the engine, brakes, and electrical systems. Regularly check fluid levels, including oil and coolant, and replace them as needed. Maintaining clean and properly adjusted brakes is vital for safety and performance.
Pay attention to the chain and sprockets; keep them well-lubricated and properly tensioned to avoid premature wear. Tires should be inspected for adequate tread depth and inflation, ensuring a safe and smooth ride. Regularly clean the air filter to promote optimal airflow and engine efficiency.
Lastly, store your motorcycle in a dry, sheltered area to protect it from the elements. Covering it with a breathable cover can help prevent moisture buildup. By implementing these practices, you can enjoy a reliable and long-lasting ride, enhancing your overall experience on the road.