| Braking Mechanism |
Provides reliable stopping power, ensuring safety under
Identifying Key Engine Components
Understanding the core elements of an engine is essential for proper maintenance and repair. By recognizing the primary systems and their roles, you can better diagnose issues and ensure the machine operates efficiently. These mechanical parts work together to generate power and keep the system running smoothly, making it crucial to know how they interact.
Cylinder Block: Often referred to as the foundation, this section houses vital elements like pistons and crankshaft, playing a pivotal role in the motor’s overall function.
Piston Assembly: This part is responsible for converting fuel combustion into motion. It moves within the cylinder to compress air and fuel, driving the crankshaft.
Crankshaft: This rotating component transforms the linear movement of the pistons into rotational energy, which ultimately powers the drivetrain.
Additional elements, like the camshaft, valves, and connecting rods, also contribute significantly to the performance of the system, each playing a specialized role in ensuring smooth operation.
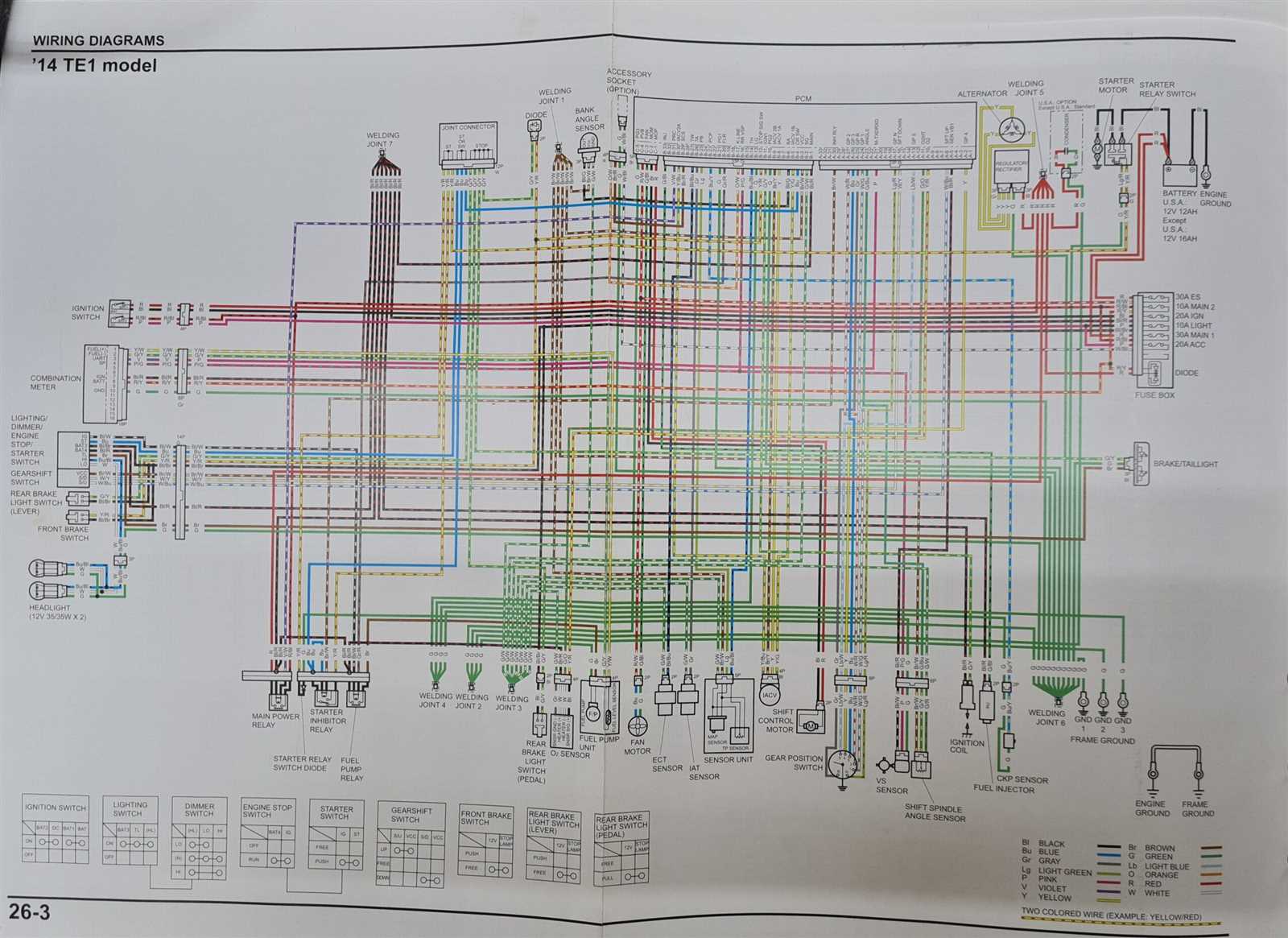
Electrical System Breakdown and Features
The electrical architecture of this utility vehicle plays a critical role in powering its various functions, ensuring reliable performance in different environments. Understanding how its core components interact helps in diagnosing potential issues and optimizing overall performance. This section delves into the intricate workings of the system, highlighting the key elements and their interconnections.
Main Power Distribution

At the heart of the system is the main power source, which delivers energy to multiple circuits, ensuring smooth operation of essential systems. From the ignition to the lighting, each function depends on precise current distribution. A central relay manages this flow, maintaining the correct voltage levels and preventing overloading.
Key Components and Connections
Several vital components work in unison to manage the electrical demands. These include the charging unit, responsible for maintaining energy levels, and the control module that regulates various functions. Wiring pathways are carefully routed to protect against wear and ensure efficient power delivery to lights, controls, and auxiliary systems.
Transmission Structure and Mechanisms
The transmission system is an intricate assembly designed to efficiently transfer power from the engine to the wheels. Its components work in unison to adjust speed and torque, ensuring smooth and responsive performance across a variety of terrains. Understanding how these elements interact helps in diagnosing issues and optimizing maintenance practices.
Key features of this system include gear sets, shifting mechanisms, and clutches, each serving a specific role in controlling power flow. Below is a breakdown of its primary components and their functions:
- Gear Sets: Multiple gear ratios allow the engine to operate efficiently at different speeds, offering versatility in driving conditions.
- Clutches: These devices engage and disengage the power transmission, enabling smooth gear changes and preventing overload on mechanical components.
- Shifting Mechanisms: These controls allow the rider to select different gears, adjusting speed and torque output to match the terrain or load requirements.
Maintaining these parts is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. Regular inspections and timely repairs can significantly extend the lifespan of the entire system.
Exploring the Fuel System Layout
The fuel delivery system is essential for ensuring optimal engine performance and reliable operation. Understanding the key elements of this system helps maintain efficiency and troubleshoot issues effectively. In this section, we will examine the major components that enable the smooth flow of fuel to the engine and their respective roles in ensuring stable operation.
Main Components of the Fuel System
- Fuel Reservoir: Acts as the storage unit for liquid energy, designed to safely hold it and supply it when needed.
- Pumping Mechanism: Responsible for transferring liquid from the reservoir to the power source at the correct pressure.
- Filter: Positioned along the path to remove contaminants and ensure clean flow.
- Delivery Lines: Tubing or channels that transport the liquid between various components.
Ensuring Efficiency and Maintenance
To ensure efficient operation, regular inspection and maintenance of these components are crucial. Over time, the pumping mechanism and filters may experience wear, and keeping them clean or replacing them can prevent potential performance issues.
- Regularly check for leaks along the
Suspension Parts and Their Functions
The suspension system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It absorbs shocks from uneven terrain, providing comfort to the rider while maintaining vehicle control. Various components work together to achieve this, each with its specific function and importance.
Key Components of the Suspension System
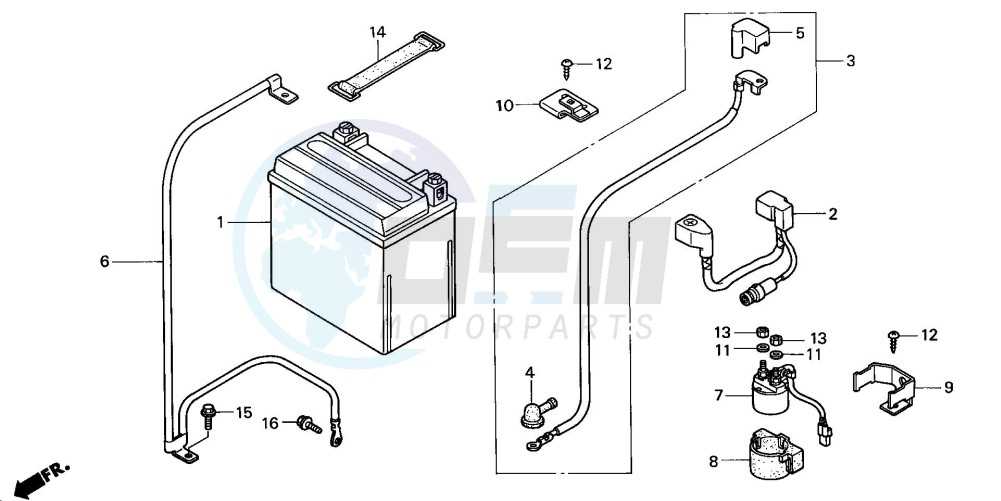
- Shock Absorbers: These elements control the oscillations of the springs, preventing excessive bouncing and improving ride quality.
- Springs: They support the vehicle’s weight and absorb impacts from the ground, allowing for smoother travel over rough surfaces.
- A-arms: These are pivotal in connecting the wheel assembly to the frame, allowing for upward and downward movement while maintaining stability.
- Stabilizer Bar: This component reduces body roll during cornering, enhancing handling and control.
Functionality of Suspension Elements
- Shock absorbers enhance vehicle handling by dampening vibrations and maintaining tire contact with the ground.
- Springs compress and expand as needed, adapting to different driving conditions and loads.
- A-arms facilitate wheel movement, allowing for proper alignment and improved performance over varied terrains.
- The stabilizer bar works to maintain balance during turns, preventing the vehicle from tipping or swaying excessively.
Understanding the components and their roles within the suspension framework is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety on various terrains. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prolong the lifespan of these vital elements, ensuring a comfortable and controlled ride.
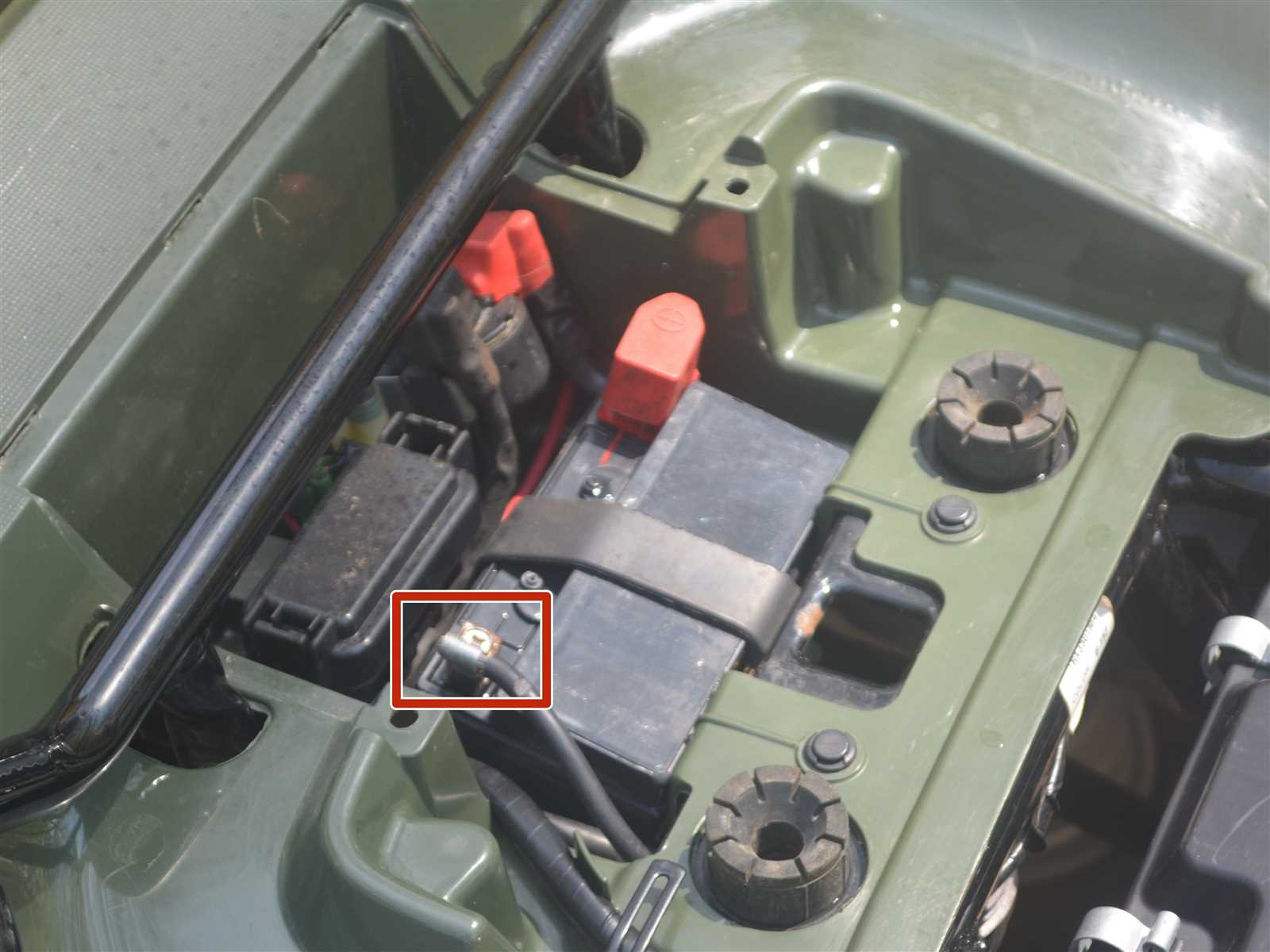
Analyzing the Honda Rancher Brake System

This section focuses on the examination of the braking mechanism found in a specific all-terrain vehicle model. The brake system is a crucial component, ensuring safety and performance during various terrains and driving conditions. Understanding its elements and functionality is essential for maintenance and effective operation.
Components of the Brake Mechanism

The braking system consists of several integral parts that work in harmony to provide reliable stopping power. Each component plays a significant role in the overall efficiency of the system.
| Component |
Description |
| Brake Pads |
Friction materials that press against the rotor to create stopping force. |
| Brake Rotor |
A circular metal disc that the brake pads clamp onto, slowing down the vehicle. |
| Brake Caliper |
The housing that contains the brake pads and pistons, applying pressure to the pads. |
| Brake Fluid |
A hydraulic fluid that transmits force from the brake lever to the calipers. |
| Master Cylinder |
The component that generates hydraulic pressure when the brake lever is engaged. |
Functionality and Maintenance

The brake system operates through hydraulic principles, where pressure from the master cylinder activates the calipers, resulting in the pads gripping the rotor. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for ensuring optimal performance and safety. Signs of wear, such as decreased responsiveness or unusual noises, should prompt immediate attention to prevent potential failures.
Understanding the Steering Assembly

The steering assembly is a critical component of any all-terrain vehicle, providing the necessary control and maneuverability to navigate various terrains. This system consists of several key elements that work together to ensure precise handling and responsiveness when steering. A solid understanding of this assembly helps users maintain their vehicles effectively and enhances their overall riding experience.
Key Components
At the core of the steering assembly lies the steering column, which connects the handlebars to the front wheels. This column is equipped with various linkages and joints that facilitate smooth movement. Additionally, the steering rack or gear is crucial for converting the rotational motion of the handlebars into lateral movement of the wheels, allowing for quick directional changes.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance of the steering assembly is essential for optimal performance. Checking for loose connections, worn-out bushings, and fluid levels ensures that the system operates smoothly. Proper lubrication of moving parts also prevents wear and prolongs the lifespan of the assembly. By staying attentive to these aspects, users can enjoy a safe and enjoyable riding experience.
Detailed View of the Exhaust System

The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of an all-terrain vehicle. It is designed to channel exhaust gases away from the engine, reducing noise and harmful emissions while enhancing engine efficiency. Understanding its components and their functions can help maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
This system consists of several key components, each contributing to the effective management of exhaust gases:
- Exhaust Header: This part collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe. Its design influences the flow rate and overall performance.
- Exhaust Pipe: This component carries the exhaust gases away from the header towards the muffler. The length and diameter of the pipe can affect backpressure and engine performance.
- Muffler: The primary purpose of the muffler is to reduce noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases. It also helps to control backpressure, which is essential for maintaining engine efficiency.
- Tailpipe: This is the final segment of the exhaust system, directing gases safely away from the vehicle. It often features a design that helps to minimize turbulence, ensuring smooth gas flow.
Proper maintenance of the exhaust system is vital. Regular inspections can help identify any signs of wear or damage, such as:
- Rust or corrosion
- Loose connections or hangers
- Unusual noises, such as rattling or hissing
- Visible exhaust leaks
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more severe problems and ensure the vehicle operates at its best.
Frame and Chassis: A Structural Guide
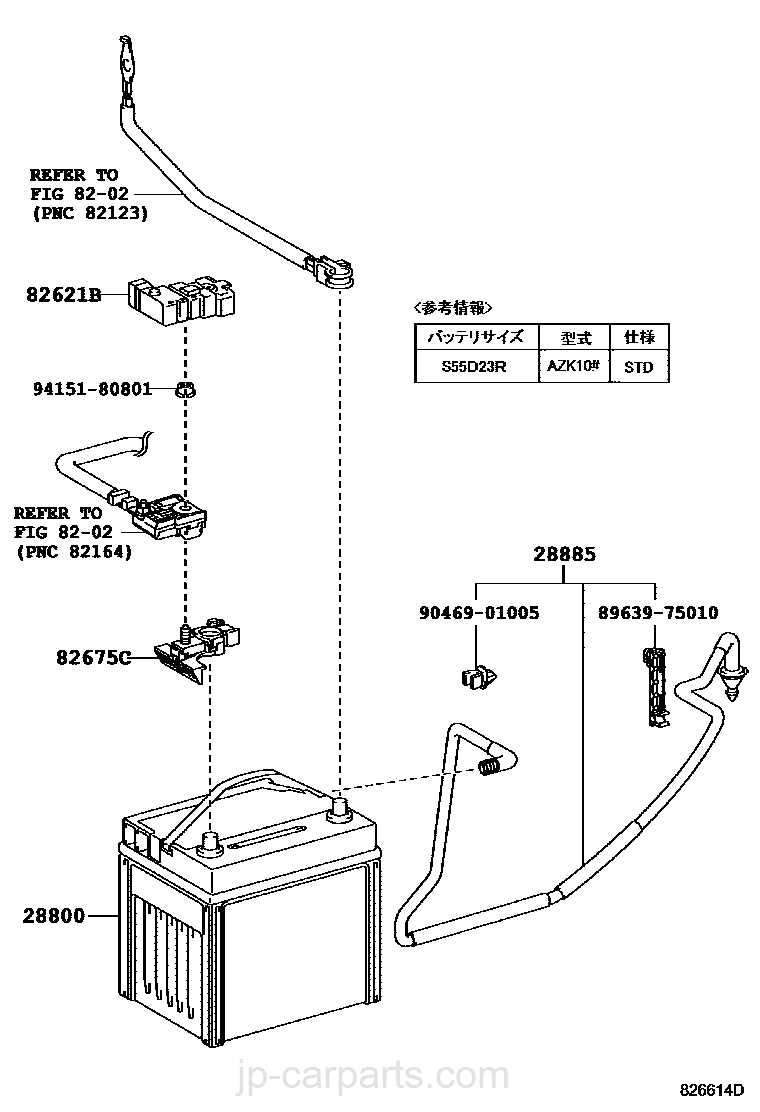
The frame and chassis form the backbone of any off-road vehicle, providing stability and support for various components. Understanding the structural elements of this assembly is essential for maintenance and enhancement, ensuring optimal performance and safety. This guide will explore the critical aspects and features that define the integrity of the vehicle’s construction.
Key components of the frame and chassis include:
- Main Frame: The primary structure that supports the vehicle’s weight and withstands external forces.
- Subframe: A secondary structure that provides additional support for specific components such as the engine and suspension system.
- Mounting Points: Designated areas where various parts are secured, ensuring proper alignment and stability.
- Suspension Attachment: Connections that allow for the integration of the suspension system, crucial for handling and ride quality.
- Reinforcements: Strategic additions that enhance structural integrity and durability, particularly in high-stress areas.
Proper inspection and maintenance of these elements are vital for ensuring long-term reliability. Regular checks can help identify wear, corrosion, or misalignment, preventing potential issues before they escalate. Furthermore, modifications to enhance performance can be made with a comprehensive understanding of how the frame interacts with other vehicle systems.
In conclusion, the framework and chassis serve as a fundamental aspect of off-road vehicles, impacting not only performance but also safety. A thorough grasp of these structural components will aid in effective maintenance and improvements, ensuring a well-functioning vehicle for various terrains.
Cooling System Components and Operation
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance by regulating temperature and preventing overheating. It comprises various elements that work in harmony to ensure effective heat dissipation during operation.
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant as it circulates through the system. It utilizes airflow, assisted by a fan, to enhance cooling efficiency.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring a continuous flow that helps maintain a stable temperature.
- Thermostat: This device regulates the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, opening and closing to maintain the desired operating range.
- Coolant Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components, allowing for efficient heat exchange.
- Coolant: A mixture of water and antifreeze that absorbs heat from the engine and transfers it to the radiator for cooling.
Understanding the function and interrelationship of these components is crucial for maintaining an efficient cooling system. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent overheating and extend the lifespan of the engine.
|