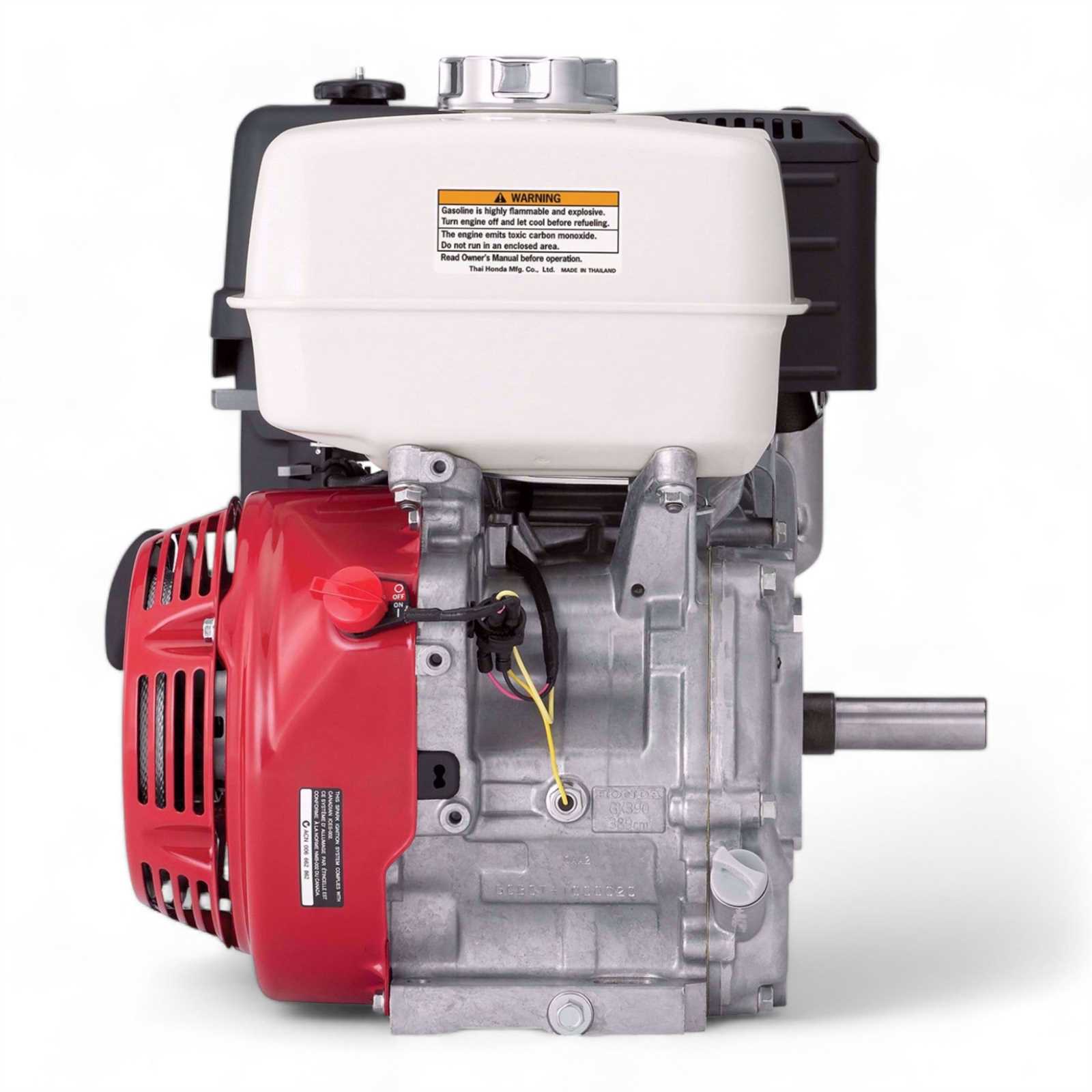

The intricate design of small engines involves a multitude of interconnected elements that work together to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the configuration and functionality of these components is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the essential features of a specific engine model, providing a comprehensive overview of its construction and parts arrangement.
By examining the various elements, one can gain insight into how each piece contributes to the overall efficiency of the engine. This knowledge not only aids in effective repairs but also enhances the user’s ability to optimize the engine’s operation. In this exploration, the focus will be on detailing the arrangement and purpose of individual components, highlighting their importance in the engine’s performance.
Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a novice enthusiast, familiarizing yourself with the layout of engine components is invaluable. This understanding fosters better repair practices, enabling users to confidently address any issues that may arise during operation. By exploring the specifics of each part, you will be better equipped to maintain and enhance engine functionality effectively.
Overview of the Honda GX390 Engine Components
The engine in question comprises various crucial elements that work in harmony to ensure efficient operation. Understanding these components is essential for anyone looking to maintain or repair the machinery, as each part plays a specific role in the overall functionality.
Powerhead: The powerhead serves as the heart of the system, housing the core mechanisms that generate energy. Its robust design is pivotal for delivering consistent performance under various loads.
Cylinder: The cylinder is where the combustion process occurs. It is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, facilitating efficient energy conversion from fuel into mechanical power.
Piston: The piston moves within the cylinder, compressing the fuel-air mixture before ignition. Its motion is integral to converting combustion energy into mechanical force, propelling the entire system.
Crankshaft: The crankshaft translates the linear motion of the piston into rotational energy, driving the output. Its precision engineering is vital for smooth operation and longevity.
Valves: Valves control the intake of air-fuel mixture and the exhaust of combustion gases. Their timely opening and closing are critical for optimal engine performance.
Ignition System: This system is responsible for igniting the fuel-air mixture, initiating the combustion process. A reliable ignition system ensures efficient operation and responsiveness.
Fuel System: The fuel system manages the delivery of fuel to the combustion chamber, ensuring that the engine receives the correct amount for efficient operation. Components like the fuel tank and carburetor play crucial roles in this process.
By familiarizing oneself with these components, users can better appreciate the engineering behind this machinery and enhance their ability to troubleshoot and maintain it effectively.
Exploring the Ignition System
The ignition mechanism plays a crucial role in the operation of internal combustion engines, providing the necessary spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture. Understanding its components and functionality can enhance maintenance practices and troubleshooting efforts, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Key Components of the Ignition Mechanism
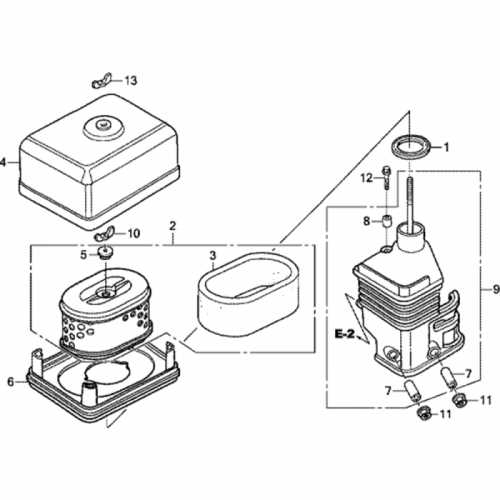
- Spark Plug: This device generates the spark required to ignite the mixture within the combustion chamber.
- Ignition Coil: It transforms the battery voltage into a higher voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plug.
- Flywheel Magnet: Responsible for producing the magnetic field that powers the ignition coil when the engine spins.
- Ignition Module: Controls the timing of the spark and ensures it occurs at the optimal moment for effective combustion.
Functionality Overview

The ignition system operates by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, initiating the combustion process. The ignition coil receives low voltage from the battery and transforms it into a high voltage. This high voltage travels through the wires to the spark plug, creating a spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinder. Proper maintenance of these components is vital for the efficient operation of the engine.
Regular checks and replacements of worn-out parts can significantly improve performance and extend the lifespan of the engine.
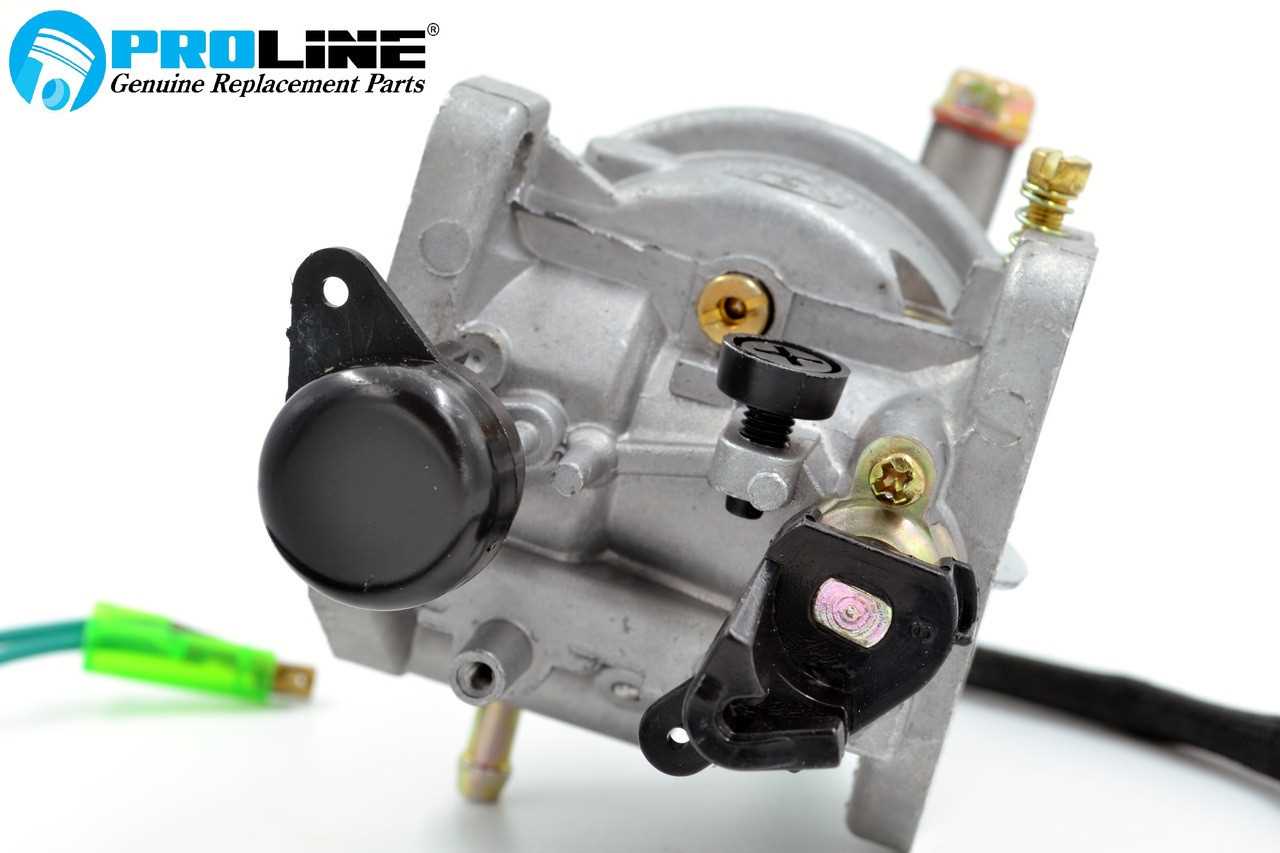
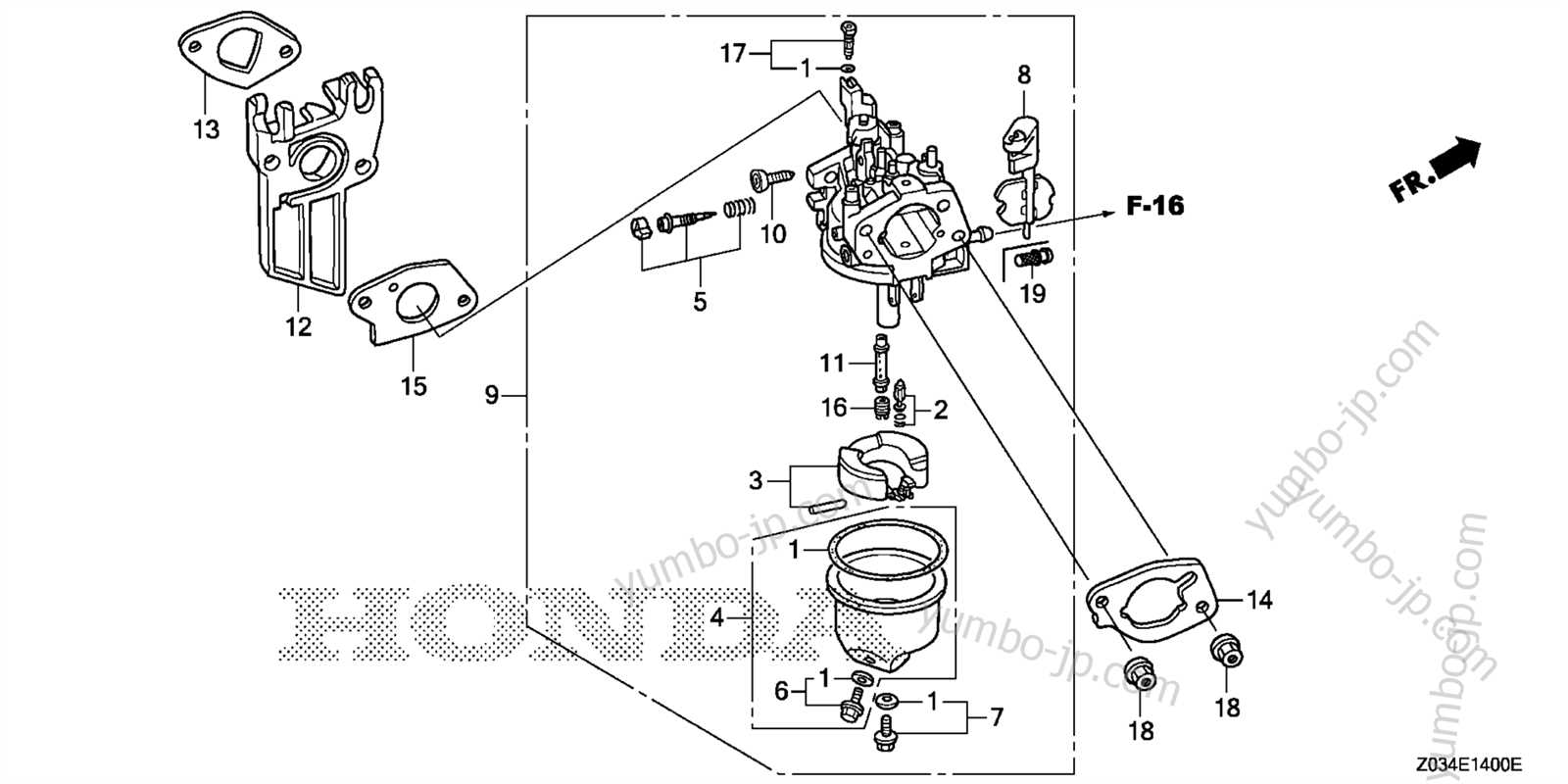
Understanding the Carburetor and Fuel Flow
The carburetor is a vital component of the engine’s fuel system, responsible for mixing air and fuel in the appropriate proportions to facilitate combustion. This essential process ensures that the engine operates efficiently, delivering the necessary power for various applications. A thorough understanding of how this device functions, along with the dynamics of fuel flow, is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Functionality of the Carburetor
The carburetor utilizes a system of jets, float chambers, and throttle valves to regulate the mixture of air and liquid fuel. As air enters the carburetor, it passes through a venturi, creating a vacuum that draws fuel from the float chamber. This fuel is then atomized and mixed with air, resulting in a fine mist that ignites in the combustion chamber. Adjusting the throttle position controls the amount of air and fuel mixture entering the engine, influencing its speed and power output.
Fuel Flow Mechanics
Fuel flow is primarily governed by the fuel pump and the carburetor’s design. The pump ensures a steady supply of fuel from the tank to the carburetor, where it is metered precisely according to the engine’s demand. Any blockages or irregularities in this flow can lead to performance issues, including stalling or inefficient operation. Regular checks and cleaning of the fuel system components help maintain optimal performance and prolong the engine’s lifespan.
Examining the Cooling Mechanism
The cooling system plays a critical role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures in internal combustion engines. Efficient heat dissipation prevents overheating and ensures longevity and performance. Understanding the components and functions of this system is essential for effective maintenance and operation.
Key Components of the Cooling System
- Radiator: Responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow based on temperature.
- Cooling Fins: Enhance heat transfer from the engine block to the surrounding air.
- Hoses: Transport coolant between various components.
Cooling Mechanism Operation
- As the engine operates, it generates heat.
- The water pump circulates coolant to absorb this heat.
- Hot coolant flows to the radiator, where it releases heat to the air.
- The cooled coolant returns to the engine, completing the cycle.
- The thermostat opens or closes to maintain the desired operating temperature.
Regular maintenance of the cooling system is essential to prevent overheating and ensure efficient engine performance. Checking coolant levels, inspecting hoses for leaks, and ensuring proper airflow around the radiator are all vital steps in maintaining this crucial system.
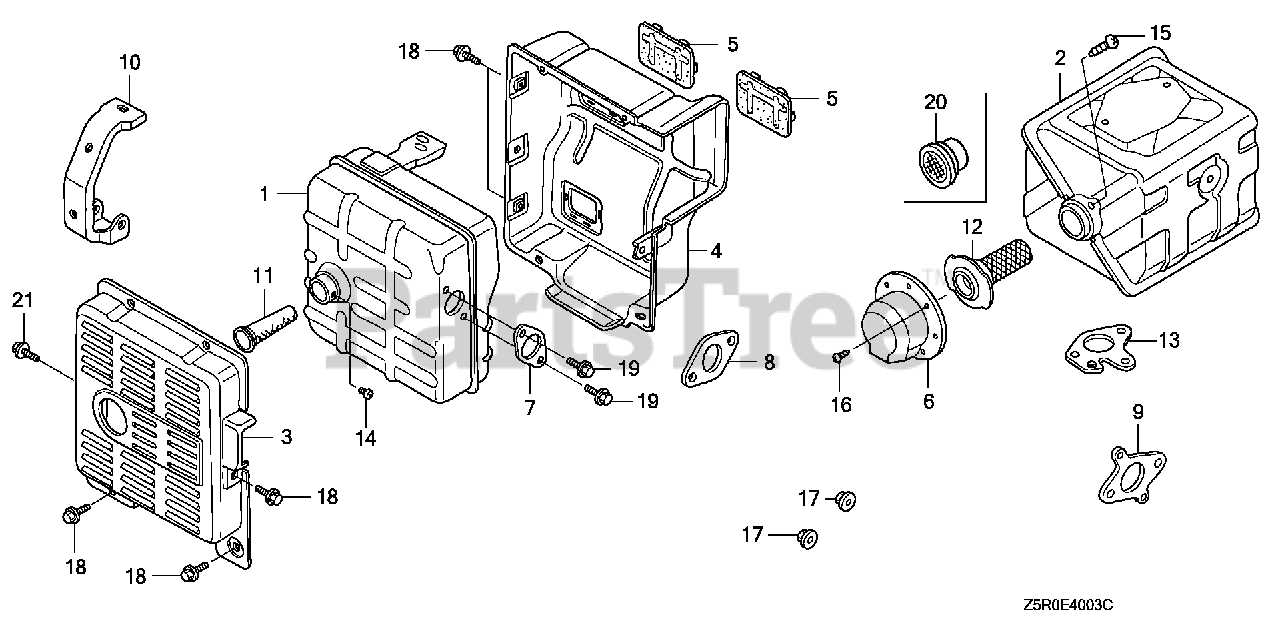
Role of the Air Filter in Performance

The air filter is a vital component that significantly influences the overall functionality and efficiency of an engine. Its primary purpose is to prevent contaminants from entering the combustion chamber, ensuring that the engine operates smoothly and efficiently. A clean and properly maintained air filter contributes to optimal air intake, which is crucial for achieving the desired power output and fuel efficiency.
Impact on Engine Efficiency
A well-functioning air filter enhances the performance of an engine in several ways:
- Improved Airflow: A clean filter allows for unobstructed airflow, promoting better combustion and maximizing energy production.
- Enhanced Fuel Economy: Efficient air intake leads to more complete fuel combustion, reducing fuel consumption and saving costs over time.
- Reduced Emissions: An effective filter helps in minimizing harmful emissions by ensuring that the combustion process is as efficient as possible.
Maintenance Considerations
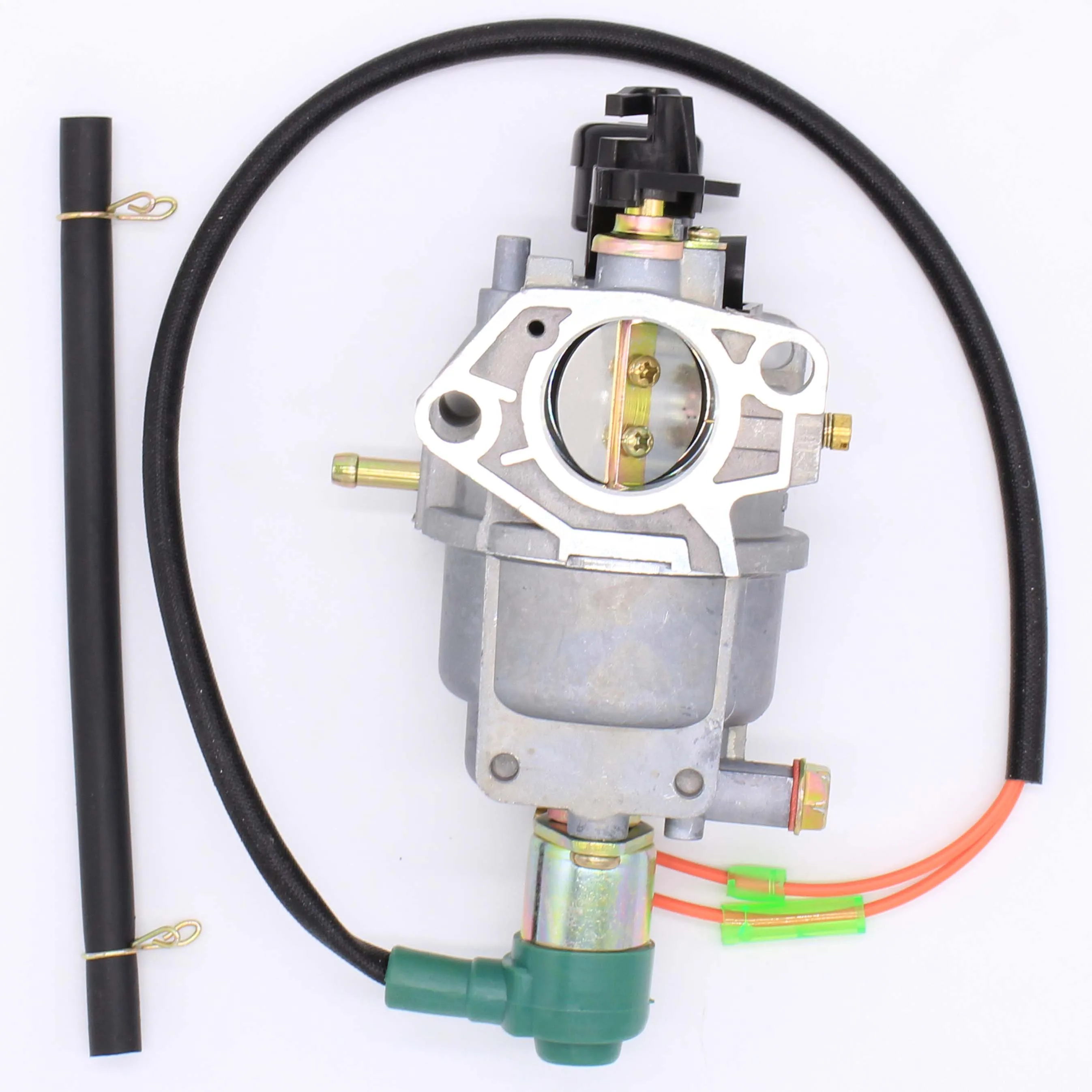

Regular maintenance of the air filter is essential for maintaining peak performance. Key considerations include:
- Regular Inspection: Check the air filter periodically for dirt and debris buildup.
- Replacement Schedule: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacement intervals to ensure optimal functionality.
- Cleaning: In some cases, filters can be cleaned and reused, but ensure they are properly dried before reinstallation.
By prioritizing the maintenance of the air filter, users can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of their engine, ensuring reliable performance in various conditions.
Detailed Look at the Exhaust System
The exhaust system is a critical component in any engine setup, designed to manage and expel combustion gases efficiently. Its primary function is to ensure optimal performance while minimizing emissions. Understanding the various elements that constitute this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
This system typically includes several key components, each playing a unique role in the overall functionality. The design of the exhaust layout significantly impacts both the engine’s efficiency and the noise levels produced during operation. Below is a table outlining the primary components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system. |
| Exhaust Pipe | Transports gases away from the manifold to the muffler. |
| Muffler | Reduces noise produced by the engine while allowing gases to escape freely. |
| Exhaust Tip | Finishes the exhaust system, directing gases away from the vehicle. |
Each of these elements must be maintained in good condition to ensure the system operates effectively. Regular inspections can prevent issues that may lead to reduced performance or increased emissions.
How the Crankshaft Powers the Generator
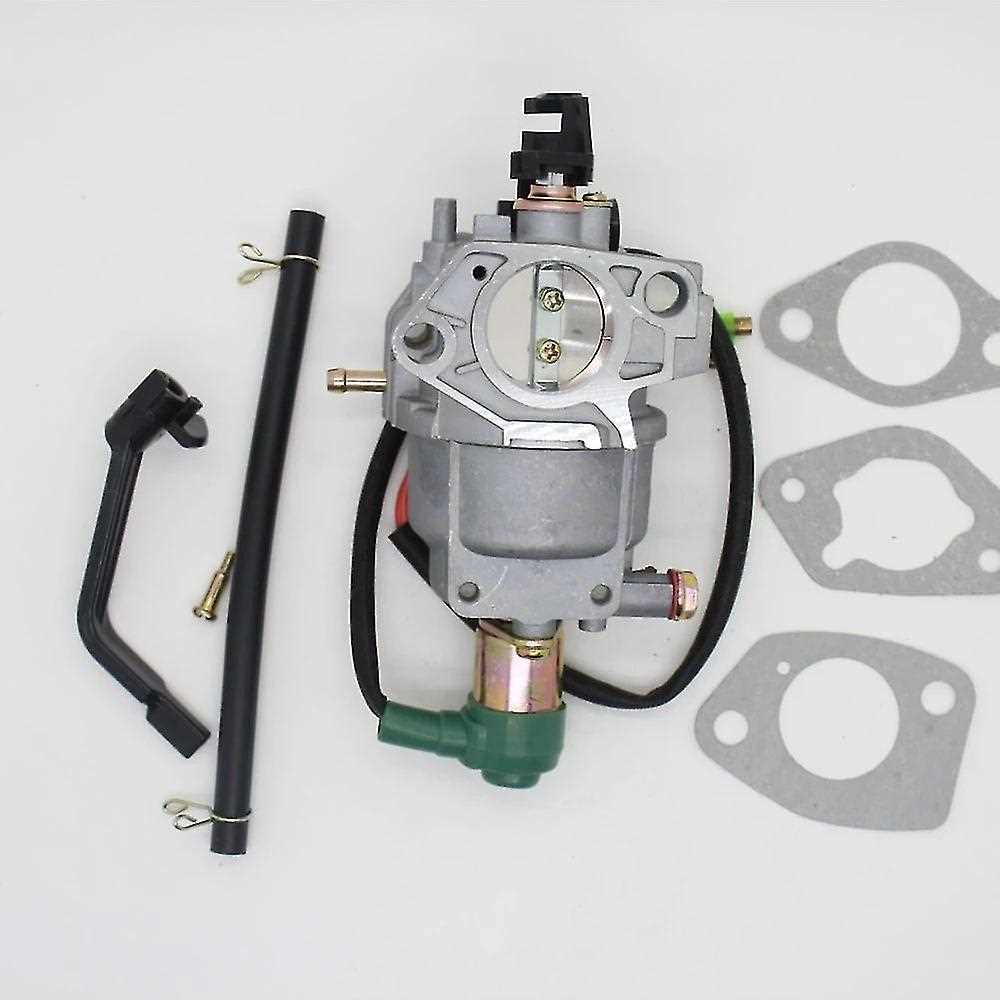

The crankshaft is a vital component that plays a significant role in the functioning of an engine. It converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which is essential for generating power. This section explores how this mechanical element effectively drives the overall energy production process.
At the core of this process are several key mechanisms:
- Combustion Process: The engine’s cylinders undergo combustion, where fuel and air mix and ignite. This explosion pushes the piston down.
- Piston Movement: As the piston descends, it is connected to the crankshaft. The linear motion of the piston rotates the crankshaft, converting the energy generated from combustion into mechanical energy.
- Power Transmission: The rotational force generated by the crankshaft is then transmitted to other components, including the flywheel and alternator, facilitating the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Synchronization: The crankshaft’s movement must be precisely timed with the other engine parts to ensure smooth operation and maximum efficiency.
This transformation of energy is crucial for the overall functionality of the system. Without a properly functioning crankshaft, the entire mechanism would fail to produce the necessary power, underscoring its importance in energy generation.
Maintaining the Oil Pump for Longevity
Proper maintenance of the lubrication system is crucial for ensuring the durability and efficiency of your engine. Regularly attending to this component can prevent wear and tear, ultimately extending its lifespan and maintaining optimal performance. A well-functioning pump ensures that the engine receives a consistent supply of oil, which is vital for reducing friction and dissipating heat.
Regular Inspection: Periodically examine the pump for any signs of wear or damage. Look for leaks, unusual noises, or fluctuations in pressure. Early detection of issues can save time and resources in the long run.
Oil Quality: Always use high-quality lubricants recommended for your engine. Contaminated or degraded oil can lead to inefficient operation and potential damage to the pump and engine components.
Filter Replacement: Changing the oil filter at regular intervals helps maintain clean oil circulation. A clogged filter can restrict oil flow, putting additional strain on the pump and potentially causing it to fail.
Consistent Oil Changes: Adhering to a routine oil change schedule is essential for optimal performance. Fresh oil ensures proper lubrication and cooling, reducing the burden on the pump.
Temperature Management: Monitor the operating temperature of your engine. Excessive heat can degrade oil and compromise the lubrication system. Ensure that the cooling system is functioning properly to maintain a safe temperature range.
Expert Assistance: If you encounter persistent issues with the lubrication system, consult a professional. Expert technicians can provide insights and repairs that can enhance the longevity of your pump and overall engine performance.
Electrical Connections and Wiring Overview
The efficient functioning of any power-producing unit heavily relies on its electrical connections and wiring systems. These elements play a crucial role in ensuring that energy flows seamlessly between the components, allowing for optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the layout and functionality of these connections is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Typically, the electrical wiring consists of various cables and terminals that facilitate the transmission of electricity. Each connection is designed to handle specific voltage and current levels, which must be considered when diagnosing issues or replacing components. Proper insulation is vital to prevent short circuits and ensure safety during operation.
In addition to cables and terminals, connectors are used to join different sections of the wiring harness. These connectors must be secure to maintain good conductivity and prevent corrosion. Regular inspections of these components can help identify wear and tear that may lead to performance issues.
Finally, it is essential to understand the overall wiring layout to effectively manage any electrical malfunctions. A well-organized wiring system not only enhances the durability of the unit but also simplifies the maintenance process, allowing for quick repairs and replacements when necessary.
Understanding the Fuel Tank Setup
The fuel tank is a critical component of any engine system, providing the necessary fuel for efficient operation. Its design and arrangement play a significant role in overall performance and reliability. Understanding how this system is set up can help in maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring long-lasting service.
Location and Positioning: The placement of the fuel reservoir is essential for proper fuel flow to the engine. It is typically situated at a height that allows gravity to assist in directing the fuel to the carburetor. This strategic positioning minimizes the risk of vapor lock and ensures a steady supply during operation.
Fuel Supply Lines: The setup includes various lines that transport fuel from the tank to the engine. These lines should be inspected regularly for any signs of wear or leaks, as a compromised line can lead to performance issues or safety hazards. Ensuring that all connections are secure is vital for optimal operation.
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining the right pressure within the fuel tank. This allows for the smooth flow of fuel and prevents any vacuum buildup that could hinder performance. Vent lines must be clear and functional to ensure uninterrupted fuel delivery.
Capacity and Material: The size and material of the fuel tank can impact overall efficiency. A tank made from durable materials can withstand various environmental conditions while preventing rust and corrosion. Additionally, understanding the tank’s capacity helps in managing fuel levels effectively, preventing both overfilling and running low.
In summary, the setup of the fuel reservoir encompasses various elements that work together to ensure smooth operation. Regular maintenance and understanding these components are key to achieving reliable performance.
Evaluating the Recoil Starter Operation
The recoil starter is a crucial component in various small engines, playing a significant role in initiating the combustion process. Its efficient functioning ensures that the engine starts smoothly and reliably, providing the necessary power for operation. Understanding the intricacies of this mechanism can lead to better maintenance practices and improved performance.
Here are the primary aspects to consider when assessing the operation of the recoil starter:
- Engagement Mechanism: The engagement of the starter should be smooth, with no unusual resistance. If the recoil cord feels stiff or does not retract properly, it may indicate wear or damage.
- Spring Condition: The internal spring must be in good condition to ensure proper recoil. A weakened or broken spring can lead to failure in returning the cord after pulling.
- Handle Integrity: The handle should be secure and free from cracks. A damaged handle can slip during operation, making it difficult to start the engine.
- Pull Cord Quality: The pull cord should be intact without frays or knots. A compromised cord can lead to difficulty in starting and may require replacement.
- Mounting and Alignment: Ensure that the recoil starter is properly mounted and aligned with the engine. Misalignment can cause unnecessary strain and potential failure of the mechanism.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the recoil starter can prevent common issues and enhance the overall reliability of the engine. Addressing minor problems promptly will contribute to a longer service life and optimal performance.