Understanding the intricate structure of two-wheeled vehicles is essential for both riders and mechanics. Familiarity with the arrangement of various elements can significantly enhance maintenance and repair efficiency, ensuring the machine operates at peak performance. In this section, we will explore the general framework and organization of key elements that contribute to the overall functionality of the vehicle.
Each component plays a crucial role in the seamless operation of the machine, from mechanical to electrical systems. Knowing how these systems interconnect can provide valuable insights into troubleshooting and optimizing the vehicle’s performance. By gaining a clear understanding of how all these aspects come together, riders can ensure a safer and more reliable riding experience.
Exploring these assemblies in detail helps to grasp the interdependencies between different parts, which is important for anyone involved in routine maintenance or more complex mechanical work. Such knowledge aids in prolonging the lifespan of the machine while reducing the likelihood of malfunctions.
Overview of 2009 Kawasaki Ninja 250R Components
The key elements of this motorcycle are designed to provide a well-balanced experience for both beginners and seasoned riders. Each part contributes to its performance, enhancing the ride’s stability, speed, and handling. Understanding the various sections of the vehicle helps in maintenance and optimization.
Engine and Performance: The heart of the bike features a compact yet powerful unit that delivers consistent power across various riding conditions. Its design allows for smooth acceleration and responsiveness, making it suitable for both city commutes and longer trips.
Frame and Suspension: A lightweight structure forms the core, providing strength and durability without adding unnecessary bulk. Coupled with an adjustable suspension system, the ride offers comfort and control, adapting to different road surfaces with ease.
Braking and Safety Systems: High-performance braking mechanisms ensure reliable stopping power. These systems are designed with rider safety in mind, offering excellent feedback and precision control during sudden stops or when navigating tight corners.
Additional Features: Several auxiliary components, from the exhaust system to the fuel delivery setup, work together to enhance overall efficiency and comfort, making the riding experience more enjoyable and smooth.
Engine Assembly Layout and Components
The structure of the motor unit consists of various interconnected elements that work together to ensure smooth and efficient operation. Understanding the layout of these elements can help in maintaining and servicing the system effectively. This section provides an overview of the core components and their arrangement, ensuring proper functionality.
- Cylinder Block: The central part of the motor that houses the cylinders, where combustion occurs.
- Pistons: Moving components that convert fuel combustion into mechanical motion.
- Crankshaft: Translates the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational force.
- Camshaft: Manages the opening and closing of valves, synchronizing with piston movements.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and allow exhaust gases to escape.
- Timing Chain: Ensures the camshaft and crankshaft work in harmony, maintaining the correct timing of operations.
- Suspension System Structure and Elements
The suspension system plays a vital role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride by managing the vehicle’s interaction with the road surface. It helps absorb shocks and maintain stability during movement, allowing for better handling and comfort. This section explores the key components that make up the system and their respective functions in delivering an optimal driving experience.
- Shock Absorbers: These components help reduce the impact of bumps and uneven terrain, ensuring a smoother ride by dissipating the energy from road shocks.
- Springs: Springs provide support by bearing the weight of the vehicle, allowing it to move over obstacles and maintain proper height while driving.
- Control Arms: These parts connect the suspension to the frame and manage the range of motion for the wheels, ensuring they move in sync with the body of the vehicle.
- Stabilizer Bar: The stabilizer bar
Braking Mechanism Breakdown and Functions
The braking system is essential for safe and efficient operation, allowing the rider to control and manage the vehicle’s speed in various conditions. This section provides an overview of how the components work together to ensure reliable deceleration and stopping power without delving into technical jargon.
Main Components and Their Roles
The primary elements of the system include the caliper, pads, and rotor. Each part contributes to transforming kinetic energy into heat through friction, effectively reducing momentum. The caliper houses the brake pads and applies pressure to the rotor, while the rotor, mounted on the wheel, dissipates the heat generated during this process.
Types of Brake Operation
There are different types of braking mechanisms, including disc brakes and drum systems, each with its unique method of applying force to slow the vehicle. Disc brakes are widely regarded for their superior performance, especially in high-speed scenarios, providing consistent and smooth operation in various environments
Body Panels and Fairing Composition

The exterior structure of a motorcycle plays a critical role in both its aerodynamics and protection. The body panels and fairing are designed not only to enhance the vehicle’s appearance but also to provide functional benefits, such as reducing wind resistance and shielding vital components. Understanding the materials and layout of these panels can help with maintenance and customization.
Main Fairing Materials
The body panels are typically made from lightweight yet durable materials. These materials are chosen to withstand the stresses of high-speed riding while also contributing to the overall aesthetics of the motorcycle.
- Plastic Composites: Known for their flexibility and resistance to cracking.
- Fiberglass: Provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice for many bikes.
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores fuel until needed by the engine.
- Fuel Pump: A device that pumps fuel from the tank to the engine, often electronically controlled.
- Fuel Filter: A component that removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine, protecting it from damage.
- Fuel Injectors: Devices that atomize fuel, allowing it to mix effectively with air for combustion.
- Throttle Body: The part that regulates the amount of air-fuel mixture entering the engine based on the rider’s input.
- Battery: The power source that provides energy to start the engine and run various electrical components.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects different electrical parts, facilitating communication and power distribution.
- Ignition System: Responsible for igniting the fuel-air mixture in the engine, critical for starting and running the motorcycle.
- Fuse Box: Protects the electrical circuit by preventing overload, ensuring safety and functionality.
- Headlight and Taillight: Essential for visibility and safety during night riding, enhancing the overall riding experience.
- Indicators: Provide signals to other road users, improving safety and communication on the road.
- Transmission Housing: The main structure that contains all the internal parts and protects them from external elements.
- Gear Set: A series of gears that regulate speed and torque, enabling the rider to change the bike’s performance characteristics.
- Clutch Mechanism: Facilitates smooth engagement and disengagement of power between the engine and the transmission.
- Shift Forks: Devices that move the gears into place when changing speeds.
- Output Shaft: Transmits power from the transmission to the final drive system, connecting to the rear wheel.
Exhaust System Configuration and Components
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of a motorcycle. It is responsible for directing the exhaust gases away from the engine, minimizing back pressure, and enhancing the sound profile. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Key Elements of the Exhaust System
At the heart of the exhaust configuration are several vital components that work together to facilitate the efficient expulsion of gases. These include the header pipes, which collect exhaust from the engine cylinders, and the muffler, which reduces noise and controls the sound produced during operation. Additionally, the catalytic converter, when present, plays a significant role in minimizing harmful emissions by converting toxic substances into less harmful compounds.
Impact on Performance
A well-designed exhaust setup can significantly enhance a motorcycle’s performance by improving airflow and reducing restrictions. Upgrading or modifying the exhaust system may lead to noticeable gains in horsepower and torque, offering a more exhilarating riding experience. Careful consideration should be given to the compatibility of each component to ensure a harmonious balance between performance and sound output.
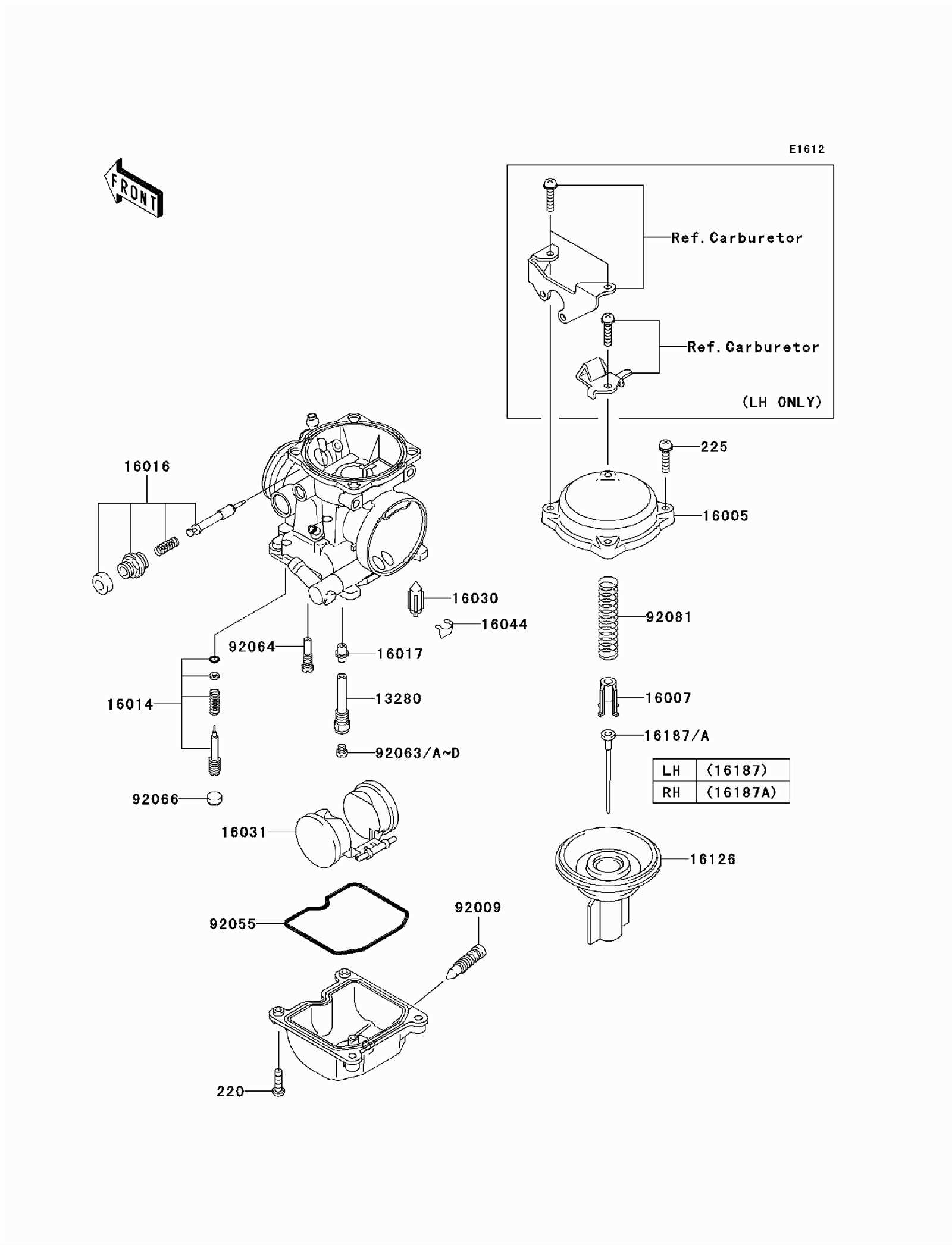
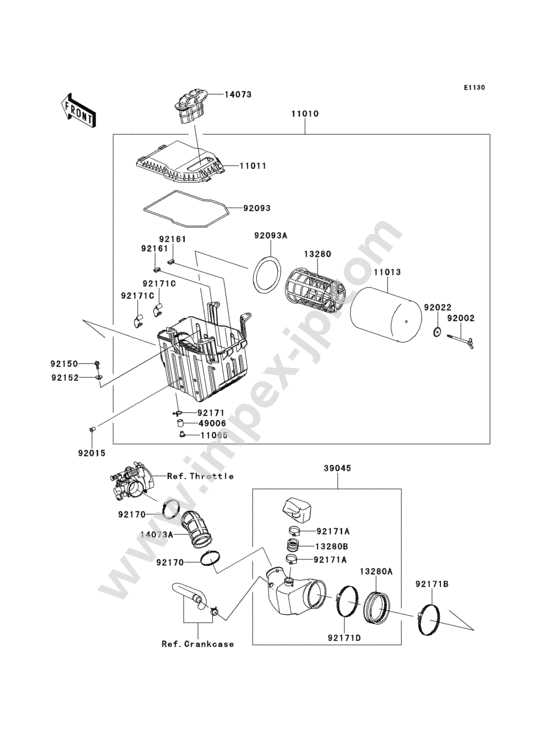
Fuel Delivery System Overview

The fuel delivery mechanism is essential for the efficient operation of a motorcycle’s engine, ensuring a smooth and consistent supply of fuel for optimal performance. This system encompasses various components that work together to transport fuel from the tank to the combustion chamber, facilitating combustion and, ultimately, engine power.
Key elements of the fuel delivery system include:
Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for maintaining the overall health and efficiency of a motorcycle’s engine. Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel delivery system can help prevent performance issues and ensure reliable operation.
Electrical System Wiring and Key Elements
The electrical framework of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding the wiring and essential components is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the primary elements that make up the electrical system, highlighting their functions and interconnections.
Each component is interconnected, forming a cohesive system that contributes to the motorcycle’s overall efficiency and performance. Proper knowledge of these elements is indispensable for any rider or technician looking to maintain or repair the electrical system effectively.
Transmission and Gearbox Layout
The transmission and gearbox system plays a crucial role in a motorcycle’s performance and efficiency. This assembly is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for smooth acceleration and effective handling. Understanding its layout can enhance the maintenance and operation of the vehicle.
Key components of this system include:
When examining the layout, it is essential to consider:
- Alignment of Components: Proper alignment ensures effective power transfer and minimizes wear on parts.
- Lubrication Points: Adequate lubrication is vital for reducing friction and extending the lifespan of components.
- Accessibility for Maintenance: A well-designed layout allows for easier access to key parts, facilitating routine checks and repairs.
Understanding these elements contributes to improved performance and longevity of the motorcycle’s drivetrain.
Cooling System Diagram and Key Parts
The cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the engine, ensuring efficiency and performance. This section provides an overview of the essential components that work together to regulate heat, preventing overheating and facilitating smooth operation.
Core Components of the Cooling System
The main elements of this system include a radiator, water pump, thermostat, and coolant hoses. The radiator dissipates heat from the coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant throughout the engine and back to the radiator. The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, ensuring that the engine reaches its ideal operating range efficiently.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are crucial for the longevity of the engine. Any malfunction in the cooling system can lead to serious engine damage. Keeping an eye on coolant levels, checking for leaks, and ensuring that the radiator is free of debris will contribute to the effective functioning of this essential system.
Steering and Handlebar Component Breakdown

This section provides a comprehensive overview of the steering and handlebar elements that contribute to the maneuverability and control of a motorcycle. Understanding these components is essential for maintenance and enhancement of riding experience.
Key components in the steering assembly include:
- Handlebars: The primary interface for the rider, allowing for directional control.
- Triple Trees: The parts that connect the front fork to the frame, providing stability and support.
- Forks: The elements that absorb shocks and maintain front wheel alignment.
- Headset: A bearing system that facilitates smooth rotation of the handlebars.
- Grip Covers: The outer layer of the handlebars, enhancing comfort and control.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring precise handling and overall riding safety. Regular inspection and proper maintenance can prolong their lifespan and improve performance.
Wheels and Tires Assembly Structure
The assembly of wheels and tires is a crucial component in ensuring the overall performance and safety of a motorcycle. This structure plays a significant role in providing stability, handling, and grip during various riding conditions. Understanding the individual elements involved in this assembly helps in maintaining and optimizing the vehicle’s functionality.
- Wheel Rim: The outer circular part that supports the tire and helps maintain its shape.
- Tire: The rubber outer covering that provides traction and absorbs shocks from the road surface.
- Hub: The central part of the wheel that connects to the axle, allowing for rotation.
- Spokes: The rods connecting the rim to the hub, providing strength and stability.
- Valve Stem: The component used to inflate and deflate the tire, crucial for maintaining proper pressure.
Proper assembly and maintenance of these components ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular checks for wear and tear, as well as correct air pressure, are essential for safe and enjoyable riding experiences.