
Understanding the internal structure and key elements of machinery is crucial for ensuring smooth operation and timely repairs. Having a clear visual reference helps technicians and operators identify specific elements that may require attention. This kind of layout provides essential insights into how different elements work together within a larger system, allowing for quicker troubleshooting and enhanced performance.
In-depth knowledge of the equipment’s internal structure supports better decision-making during maintenance tasks. Whether you are looking to replace an element or simply understand its role, a detailed overview of the various connections and functions is invaluable. Such illustrations simplify complex tasks by offering a clear roadmap to follow.
Additionally, these visual guides serve as an educational tool, helping new users familiarize themselves with the equipment. By studying these layouts, individuals can enhance their technical skills and confidently approach both routine and advanced tasks, ensuring the longevity and reliability of their machinery.
Component Overview
This section provides a detailed examination of the machinery’s key structural elements, highlighting the most critical aspects of its construction and functionality. By understanding how the individual pieces interact, operators can ensure efficient performance and long-lasting durability. This breakdown will focus on mechanical, hydraulic, and electrical components, illustrating how each system supports the machine’s operation.
Mechanical Systems
The mechanical framework serves as the backbone of the equipment, supporting the entire structure. Its robust build ensures stability during operation, especially when navigating tough terrains. Moving parts, including joints, arms, and pivot points, allow the machine to handle a variety of tasks with precision. Regular maintenance of these elements is vital for smooth operation.
Hydraulic and Electrical Components

The hydraulic system provides the power needed for precise control over the movement of the working arms. These components are essential for lifting, digging, and maneuvering heavy loads with ease. Meanwhile, the electrical setup integrates control units and wiring that ensure seamless communication between
Understanding the Main Sections of the KX121-2
The equipment we are exploring is divided into several key areas, each responsible for specific tasks and operations. By understanding how these major components work together, one can ensure smoother performance, easier maintenance, and quicker troubleshooting.
Core Structural Components

- Chassis and Framework: This supports the machine’s overall structure, providing stability and protection for internal systems.
- Hydraulic System: This is responsible for controlling various movements, including the lifting and tilting mechanisms. It’s crucial for the equipment’s mobility and operational capacity.
- Powertrain: The section that delivers energy to the machine’s working parts, ensuring efficient power distribution and functionality.
Operational Mechanisms

- Control Panel: Where the operator interacts with the system,
Hydraulic System Layout for the KX121-2
The hydraulic system is designed to provide precise control and power for various operations. It integrates multiple components that work together to ensure efficient movement and functionality of the machine. The system’s layout is structured to maximize the flow of hydraulic fluid, ensuring that each function operates smoothly under varying conditions. Understanding this layout helps in identifying how different elements contribute to the overall performance of the machine.
Main Components Overview
At the core of the system, a series of pumps, valves, and hoses distribute hydraulic fluid to critical areas. The pumps generate the necessary pressure, while the valves control the direction and intensity of fluid flow. Hoses act as the channels that transport the fluid, ensuring each section receives the required amount. These components work in unison to deliver seamless operation.
Control and Efficiency
Control levers inside the operator’s cab direct the hydraulic system, enabling precise handling of the machine’s functions. The responsiveness of
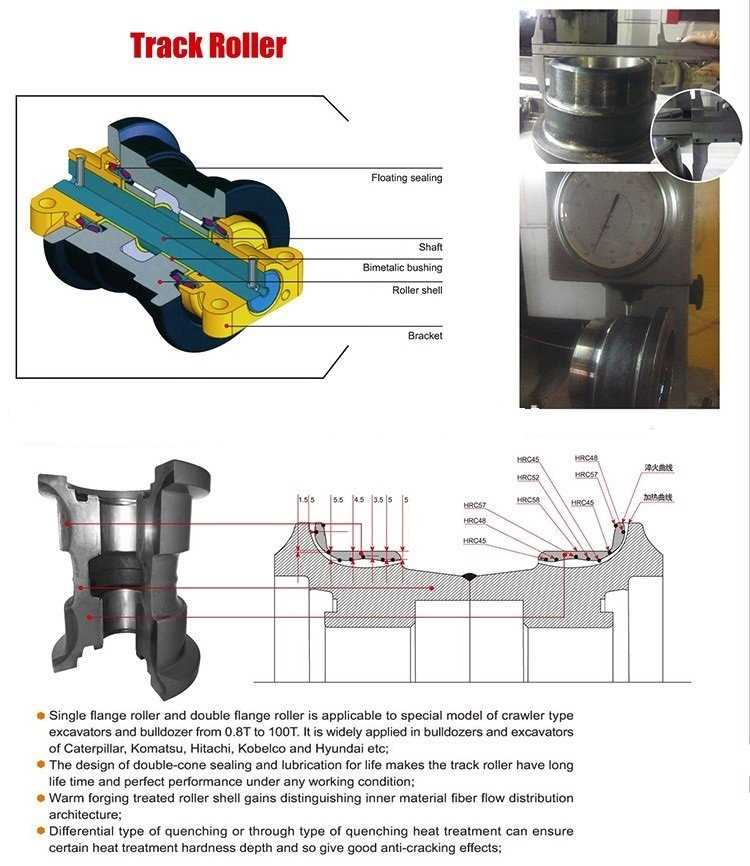
Track Assembly and Undercarriage Components
The track system and the components that support it play a crucial role in ensuring the stability and mobility of construction equipment. These elements are designed to distribute the machine’s weight evenly and provide reliable traction, especially on challenging surfaces. Proper maintenance of these components is essential for extending the service life of the machinery and ensuring smooth operation across various terrains.
Main Components of the Track Assembly
The track system typically consists of several key elements that work together to provide movement and stability. These include the track itself, rollers, idlers, and the drive sprockets. Each part must be in good condition for optimal performance. Regular inspection and adjustment are necessary to prevent excessive wear and ensure that the system functions correctly under different working conditions.
Undercarriage Support Elements
Engine Compartment Parts Overview
The layout of components inside the engine area is essential for ensuring smooth operation and easy maintenance. This section provides an overview of the key elements found within this space, focusing on their functions and how they work together to keep the machine running efficiently.
Below is a breakdown of the main elements within this area:
- Power Source: The central mechanism that provides the necessary force to drive the entire system.
- Cooling System: Responsible for maintaining optimal temperature during operation, preventing overheating and ensuring longevity.
- Filtration Unit: Keeps unwanted particles from entering the main components, contributing to cleaner and more efficient performance.
- Fuel Delivery System: Ensures a consistent flow of energy, allowing the machine to function without interruption.
- Exhaust Assembly: Directs gases away from the system, reducing the build
Bucket and Arm Mechanism Breakdown
The bucket and arm assembly is a critical component in any compact excavation machine, allowing for effective digging, lifting, and maneuvering of materials. This section delves into the intricacies of this mechanism, examining its essential elements and how they work in harmony to enhance operational efficiency.
The arm serves as the primary support structure, providing the necessary reach and stability for various tasks. Typically, it consists of multiple segments that can pivot, enabling the bucket to achieve different angles and positions. This articulating feature is crucial for optimizing performance in tight spaces or when tackling uneven terrain.
The bucket, attached to the end of the arm, comes in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different applications. Its design directly impacts the machine’s ability to excavate, carry, or grade materials. Understanding the geometry and functionality of the bucket is essential for selecting the right type for specific job requirements.
Hydraulic cylinders play a vital role in the operation of the arm and bucket assembly. These cylinders convert hydraulic fluid pressure into mechanical force, allowing for smooth and controlled movement. Proper maintenance of these hydraulic components is necessary to ensure reliability and efficiency during operation.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the bucket and arm mechanism is crucial for maximizing the performance of excavation equipment. By familiarizing oneself with the components and their interactions, operators can enhance their productivity and prolong the lifespan of their machinery.
Cooling System Parts Diagram for KX121-2
The cooling mechanism of this machinery is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. A well-functioning system ensures efficient performance and extends the life of various components. Understanding the elements involved in this setup can help users identify potential issues and carry out effective maintenance.
Key components of the cooling mechanism include the radiator, which dissipates heat from the engine, and the water pump, responsible for circulating coolant throughout the system. The thermostat plays a vital role by regulating the coolant temperature, ensuring it remains within an appropriate range.
Additionally, the coolant reservoir is essential for holding excess fluid and maintaining pressure, while the hoses connect various parts, allowing for fluid movement. Regular inspection of these elements is recommended to prevent overheating and maintain system efficiency.
Electrical Wiring and Circuitry Structure
The effective operation of machinery relies heavily on the proper arrangement of electrical components and connections. Understanding the intricate layout of wiring and circuitry is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This structure facilitates the flow of electricity, ensuring that all systems function seamlessly together.
At the core of this arrangement lies a network of wires and connectors, each serving a specific purpose. These elements are designed to transmit power and signals throughout the system, enabling various functionalities. Careful attention to detail in the wiring setup helps prevent issues such as short circuits or power failures, which can disrupt operations.
Additionally, the organization of electrical pathways plays a crucial role in safety and efficiency. Implementing protective measures, such as fuses and circuit breakers, ensures that the equipment operates within safe parameters. This thoughtful configuration enhances reliability and reduces the risk of electrical hazards, ultimately contributing to the longevity of the machinery.
Fuel System Components and Arrangement
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance by delivering the necessary energy source. Understanding the various elements involved and their configuration helps in maintaining efficiency and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
At the heart of this system is the fuel tank, which stores the liquid energy. Connected to it is the fuel pump, responsible for transferring the fuel to the engine. The pump’s operation is essential, as it maintains the correct pressure for effective fuel delivery.
Additionally, a fuel filter is integrated into the setup to eliminate contaminants, safeguarding the engine from damage. This component ensures that only clean fuel reaches the combustion chamber, promoting longevity and performance.
Furthermore, the injectors are key elements that atomize the fuel, allowing it to mix efficiently with air. The arrangement of these injectors is meticulously designed to optimize combustion, enhancing power output and fuel efficiency.
Overall, the configuration of these components is vital for the seamless operation of the engine, and understanding their arrangement aids in effective troubleshooting and maintenance practices.
Cabin and Operator Controls Overview

The operator’s cabin is designed to provide a comfortable and efficient working environment. This space is equipped with various controls and features that enhance usability and facilitate smooth operation of the machine. Understanding the layout and functionality of these controls is essential for maximizing productivity and ensuring safety while working.
Key Features of the Operator’s Cabin
- Ergonomic Design: The cabin is crafted with ergonomics in mind, allowing operators to maintain comfort during extended use.
- Visibility: Large windows provide excellent sightlines, enabling better awareness of the surroundings and enhancing operational safety.
- Noise Reduction: The cabin incorporates sound insulation to minimize noise, creating a more pleasant working environment.
Control Elements
- Steering Wheel: Facilitates precise maneuvering of the vehicle.
- Control Levers: These levers are used for various functions, including movement and attachment engagement.
- Pedals: Foot pedals control acceleration and braking, allowing for responsive operation.
- Instrument Panel: Displays vital information such as engine status, fuel level, and temperature, ensuring the operator remains informed.
Exhaust and Airflow System Layout
The arrangement of the exhaust and airflow mechanisms plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency of machinery. These systems are designed to manage the release of combustion gases while optimizing the intake of fresh air, ensuring the engine operates smoothly and effectively. A well-organized layout enhances performance, reduces emissions, and contributes to the longevity of the engine components.
Components of the Exhaust System
The exhaust system typically includes various elements such as pipes, mufflers, and catalytic converters. Each part serves a specific function, from directing exhaust gases away from the engine to minimizing noise and harmful emissions. The integration of these components is essential for achieving optimal exhaust flow and meeting regulatory standards.
Airflow Management
Effective airflow management is equally important. It involves the intake system, which allows clean air to enter the engine, mixing with fuel for combustion. This system includes air filters and ducts that maintain airflow efficiency while preventing contaminants from entering the engine. A well-designed airflow system not only boosts performance but also enhances fuel efficiency.
Steering and Control Linkages
The functionality of steering and control systems is essential for the effective operation of machinery. These linkages serve as the vital connection between the operator and the vehicle, allowing for precise maneuvering and responsiveness during operation. Understanding their layout and mechanics is crucial for anyone involved in maintenance or repair tasks.
Components and Functionality
The steering mechanism comprises various elements, including rods, levers, and joints, which work together to translate the operator’s movements into directional control. Each component plays a specific role, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Regular inspection of these parts is necessary to prevent wear and maintain optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips
Proper upkeep of steering and control linkages enhances safety and efficiency. It is advisable to periodically check for signs of damage or wear, such as loose connections or corrosion. Additionally, lubricating moving parts can significantly improve responsiveness and extend the lifespan of the system. Regular maintenance not only ensures reliability but also contributes to the overall longevity of the equipment.
Maintenance Points and Service Parts
Proper upkeep of heavy machinery is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the essential components and maintenance practices ensures that equipment operates smoothly and efficiently. Regular checks and timely replacements can prevent costly breakdowns and extend the life of the machine.
Key Areas for Regular Inspection
Routine inspections should focus on several critical areas that impact functionality. Operators should pay attention to hydraulic systems, engine components, and electrical connections. Identifying wear and tear early can lead to proactive maintenance, reducing the risk of major repairs.
Recommended Replacement Components
When servicing machinery, certain components should be prioritized for replacement. Below is a table highlighting common items to monitor and replace as needed:
Component Description Maintenance Frequency Filters Ensure clean operation of fluids Every 100 hours Fluids Engine oil and hydraulic fluid Every 250 hours Belts Check for signs of wear or damage Every 500 hours Battery Ensure proper charge and connections Annually Electrical Connections Inspect for corrosion or looseness Quarterly